Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
ALISADE 27.5 micrograms/spray
nasal spray suspension
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each spray actuation delivers 27.5 micrograms of fluticasone furoate.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Adults, adolescents (12 years and over) and children (6 – 11 years)
Alisade is indicated for the treatment of:
• the symptoms of allergic rhinitis
4.2
Posology and method of administration
Fluticasone furoate nasal spray is for administration by the intranasal route only.
For full therapeutic benefit regular, scheduled usage is recommended. Onset of action has been
observed as early as 8 hours after initial administration. However, it may take several days of
treatment to achieve maximum benefit, and the patient should be informed that their symptoms will
improve with continuous regular use (see section 5.1). The duration of treatment should be restricted
to the period that corresponds to allergenic exposure.
Adults and Adolescents (12 years and over)
The recommended starting dose is two spray actuations (27.5 micrograms of fluticasone furoate per
spray actuation) in each nostril once daily (total daily dose, 110 micrograms).
Once adequate control of symptoms is achieved, dose reduction to one spray actuation in each nostril
(total daily dose 55 micrograms) may be effective for maintenance.
The dose should be titrated to the lowest dose at which effective control of symptoms is maintained.
Children (6 to 11 years of age)
The recommended starting dose is one spray actuation (27.5 micrograms of fluticasone furoate per
spray actuation) in each nostril once daily (total daily dose, 55 micrograms).
Patients not adequately responding to one spray actuation in each nostril once daily (total daily dose,
55 micrograms) may use two spray actuations in each nostril once daily (total daily dose,
110 micrograms). Once adequate control of symptoms is achieved, dose reduction to one spray
actuation in each nostril once daily (total daily dose, 55 micrograms) is recommended.
Children under 6 years of age:
The experience in children under the age of 6 years is limited (see
section 5.1 and 5.2). Safety and efficacy in this group has not been well established.
Elderly Patients:
No dose adjustment is required in this population (see section 5.2).
Renal Impaired Patients:
No dose adjustment is required in this population (see section 5.2).
Hepatic Impaired Patients:
No dose adjustment is required in mild to moderate hepatic impairment.
There are no data in patients with severe hepatic impairment (see section 4.4 and 5.2).
The intranasal device should be shaken before use. The device is primed by pressing the mist release
button for at least six spray actuations (until a fine mist is seen), whilst holding the device upright. Re-
priming (approximately 6 sprays until a fine mist is seen) is only necessary if the cap is left off for 5
days or the intranasal device has not been used for 30 days or more.
The device should be cleaned after each use and the cap replaced.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients of Alisade.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Fluticasone furoate undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism, therefore the systemic exposure of
intranasal fluticasone furoate in patients with severe liver disease is likely to be increased. This may
result in a higher frequency of systemic adverse events (see section 4.2 and 5.2). Caution is advised
when treating these patients.
Ritonavir
Concomitant administration with ritonavir is not recommended because of the risk of increased
systemic exposure of fluticasone furoate (see section 4.5).
Systemic effects of nasal corticosteroid may occur, particularly at high doses prescribed for prolonged
periods. These effects vary between patients and different corticosteroids (see section 5.2).
Treatment with higher than recommended doses of nasal corticosteroids may result in clinically
significant adrenal suppression. If there is evidence for higher than recommended doses being used,
then additional systemic corticosteroid cover should be considered during periods of stress or elective
surgery. Fluticasone furoate 110 micrograms once daily was not associated with hypothalamic-
pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression in adult, adolescent or paediatric subjects. However the dose
of intranasal fluticasone furoate should be reduced to the lowest dose at which effective control of the
symptoms of rhinitis is maintained. As with all intranasal corticosteroids, the total systemic burden of
corticosteroids should be considered whenever other forms of corticosteroid treatment are prescribed
concurrently.
Growth retardation has been reported in children receiving some nasal corticosteroids at licensed
doses. It is recommended that the height of children receiving prolonged treatment with nasal
corticosteroids is regularly monitored. If growth is slowed, therapy should be reviewed with the aim of
reducing the dose of nasal corticosteroid if possible, to the lowest dose at which effective control of
symptoms is maintained. In addition, consideration should be given to referring the patient to a
paediatric specialist (see section 5.1).
If there is any reason to believe that adrenal function is impaired, care must be taken when transferring
patients from systemic steroid treatment to fluticasone furoate.
Nasal and inhaled corticosteriods may result in the development of glaucoma and/or cataracts.
Therefore close monitoring is warranted in patients with a change in vision or with a history if
increased pressure, glaucoma and/or cataracts.
Alisade contains benzalkonium chloride. It may cause irritation of the nasal mucosa.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Fluticasone furoate is rapidly cleared by extensive first pass metabolism mediated by the cytochrome
P450 3A4.
Based on data with another glucocorticoid (fluticasone propionate), that is metabolised by CYP3A4,
co-administration with ritonavir is not recommended because of the risk of increased systemic
exposure of fluticasone furoate.
Caution is recommended when co-administering fluticasone furoate with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors as
an increase in systemic exposure cannot be ruled out. In a drug interaction study of intranasal
fluticasone furoate with the potent CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole there were more subjects with
measurable fluticasone furoate concentrations in the ketoconazole group (6 of the 20 subjects)
compared to placebo (1 out of 20 subjects). This small increase in exposure did not result in a
statistically significant difference in 24 hour serum cortisol levels between the two groups (see section
4.4).
The enzyme induction and inhibition data suggest that there is no theoretical basis for anticipating
metabolic interactions between fluticasone furoate and the cytochrome P450 mediated metabolism of
other compounds at clinically relevant intranasal doses. Therefore, no clinical studies have been
conducted to investigate interactions of fluticasone furoate on other drugs.
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
There are no adequate data from the use of fluticasone furoate in pregnant women. In animal studies
glucocorticoids have been shown to induce malformations including cleft palate and intra-uterine
growth retardation. This is not likely to be relevant for humans given recommended nasal doses which
results in minimal systemic exposure (see section 5.2). Fluticasone furoate should be used in
pregnancy only if the benefits to the mother outweigh the potential risks to the foetus or child.
It is unknown whether nasal administered fluticasone furoate is excreted in human breast milk.
Administration of fluticasone furoate to women who are breastfeeding should only be considered if the
expected benefit to the mother is greater than any possible risk to the child.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed as fluticasone
furoate is not expected to affect this ability.
Data from large clinical trials were used to determine the frequency of adverse reactions.
The following convention has been used for the classification of frequencies: Very common
>
1/10;
Common
>
1/100 to <1/10; Uncommon
>
1/1000 to <1/100; Rare
>
1/10,000 to <1/1000; Very rare
<1/10,000.
Immune system disorders
Rare Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, and
urticaria.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Very common








*Epistaxis was generally mild to moderate in intensity. In adults and adolescents, the incidence of
epistaxis was higher in longer-term use (more than 6 weeks) than in short-term use (up to 6 weeks). In
paediatric clinical studies of up to 12 weeks duration the incidence of epistaxis was similar between
patients receiving fluticasone furoate and patients receiving placebo.
Systemic effects of nasal corticosteroids may occur, particularly when prescribed at high doses for
prolonged periods.
In a bioavailability study, intranasal doses of up to 2640 micrograms per day were administered over
three days with no adverse systemic effects observed (see section 5.2).
Acute overdose is unlikely to require any therapy other than observation.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Corticosteroids. ATC code: R01AD12
Fluticasone furoate is a synthetic trifluorinated corticosteroid that possesses a very high affinity for the
glucocorticoid receptor and has a potent anti-inflammatory action.
Clinical experience:
Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis in adults and adolescents
Compared with placebo, fluticasone furoate nasal spray 110 micrograms once daily significantly
improved nasal symptoms (comprising rhinorrhoea, nasal congestion, sneezing and nasal itching) and
ocular symptoms (comprising itching/burning, tearing/watering and redness of the eyes) in all 4
studies. Efficacy was maintained over the full 24-hours dosing period with once daily administration.
Onset of therapeutic benefit was observed as early as 8 hours after initial administration, with further
improvement observed for several days afterwards.
Fluticasone furoate nasal spray significantly improved the patients’ perception of overall response to
therapy, and the patients’ disease-related quality of life (Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life
Questionnaire – RQLQ), in all 4 studies.
Perennial Allergic Rhinitis in adults and adolescents:
Fluticasone furoate nasal spray 110 micrograms once daily significantly improved nasal symptoms as
well as patients’ perception of overall response to therapy compared to placebo in three studies.
Fluticasone furoate nasal spray 110 micrograms once daily significantly improved ocular symptoms as
well as improving patients’ disease-related quality of life (RQLQ) compared to placebo in one study.
Efficacy was maintained over the full 24-hour dosing period with once daily administration.
Seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis in children:
The paediatric posology is based on assessment of the efficacy data across the allergic rhinitis
population in children.
In seasonal allergic rhinitis, fluticasone furoate nasal spray 110 micrograms once daily was effective
but no significant differences were observed between fluticasone furoate nasal spray 55 micrograms
once daily and placebo on any endpoint.
In perennial allergic rhinitis, fluticasone furoate nasal spray 55 micrograms once daily exhibited a
more consistent efficacy profile than fluticasone furoate nasal spray 110 micrograms once daily over 4
weeks’ treatment. Post-hoc analysis over 6 and 12 weeks in the same study, as well as 6-week HPA
axis safety study, supported the efficacy of fluticasone furoate nasal spray 110 micrograms once daily.
A 6-week study that assessed the effect of fluticasone furoate nasal spray 110 micrograms once daily
on adrenal function in children aged 2 to 11 years showed that there was no significant effect on 24-
hour serum cortisol profiles, compared with placebo.
Results from a placebo-controlled knemometry study of fluticasone furoate nasal spray
110 micrograms once daily revealed no clinically relevant effects on short-term lower leg growth rate
in children (6 to 11 years).
Seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis in children (under 6 years):
Safety and efficacy studies were performed in a total of 271 patients from 2 to 5 years of age in both
seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis, of whom 176 were exposed to fluticasone furoate.
Safety and efficacy in this group has not been well established.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption: Fluticasone furoate undergoes incomplete absorption and extensive first-pass metabolism
in the liver and gut resulting in negligible systemic exposure. The intranasal dosing of 110 micrograms
once daily does not typically result in measurable plasma concentrations (<10 pg/ml). The absolute
bioavailability for intranasal fluticasone furoate is 0.50 %, such that less than 1 microgram of
fluticasone furoate would be systemically available after administration of 110 micrograms (see
section 4.9).
Distribution: The plasma protein binding of fluticasone furoate is greater than 99 %. Fluticasone
furoate is widely distributed with volume of distribution at steady-state of, on average, 608 l.
Metabolism: Fluticasone furoate is rapidly cleared (total plasma clearance of 58.7 l/h) from systemic
circulation principally by hepatic metabolism to an inactive 17β-carboxylic metabolite (GW694301X),
by the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP3A4. The principal route of metabolism was hydrolysis of the S-
fluoromethyl carbothioate function to form the 17β-carboxylic acid metabolite. In vivo studies have
revealed no evidence of cleavage of the furoate moiety to form fluticasone.
Elimination: Elimination was primarily via the faecal route following oral and intravenous
administration indicative of excretion of fluticasone furoate and its metabolites via the bile. Following
intravenous administration, the elimination phase half-life averaged 15.1 hours. Urinary excretion
accounted for approximately 1 % and 2 % of the orally and intravenously administered dose,
respectively.
Children:
In the majority of patients fluticasone furoate is not quantifiable (< 10 pg/ml) following intranasal
dosing of 110 micrograms once daily. Quantifiable levels were observed in 15.1 % of paediatric
patients following intranasal dosing of 110 micrograms once daily and only 6.8 % of paediatric
patients following 55 micrograms once daily. There was no evidence for higher quantifiable levels of
fluticasone furoate in younger children (less than 6 years of age). Median fluticasone furoate
concentrations in those subjects with quantifiable levels at 55 micrograms were 18.4 pg/ml and
18.9 pg/ml for 2-5 yrs and 6-11 yrs, respectively. At 110 micrograms, median concentrations in those
subjects with quantifiable levels were 14.3 pg/ml and 14.4 pg/ml for 2-5 yrs and 6-11 yrs, respectively.
The values are similar to those seen in adults (12+) where median concentrations in those subjects
with quantifiable levels were 15.4 pg/ml and 21.8 pg/ml at 55 micrograms and 110 micrograms,
respectively.
Elderly:
Only a small number of elderly patients (≥ 65 years, n=23/872; 2.6 %) provided pharmacokinetic data.
There was no evidence for a higher incidence of patients with quantifiable fluticasone furoate
concentrations in the elderly, when compared with the younger patients.
Fluticasone furoate is not detectable in urine from healthy volunteers after intranasal dosing. Less than
1 % of dose-related material is excreted in urine and therefore renal impairment would not be expected
to affect the pharmacokinetics of fluticasone furoate.
Hepatic Impairment:
There are no data with intranasal fluticasone furoate in patients with hepatic impairment. A study of a
single 400 microgram dose of orally inhaled fluticasone furoate in patients with moderate hepatic
impairment resulted in increased Cmax (42 %) and AUC(0-∞) (172 %) and a modest (on average
23 %) decrease in cortisol levels in patients compared to healthy subjects. From this study the average
predicted exposure of 110 micrograms of intranasal fluticasone furoate in patients with moderate
hepatic impairment would not be expected to result in suppression of cortisol. Therefore moderate
hepatic impairment is not predicted to result in a clinically relevant effect for the normal adult dose.
There are no data in patients with severe hepatic impairment. The exposure of fluticasone furoate is
likely to be further increased in such patients.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Findings in general toxicology studies were similar to those observed with other glucocorticoids and
are associated with exaggerated pharmacological activity. These findings are not likely to be relevant
for humans given recommended nasal doses which results in minimal systemic exposure. No
genotoxic effects of fluticasone furoate have been observed in conventional genotoxicity tests. Further,
there were no treatment-related increases in the incidence of tumours in two year inhalation studies in
rats and mice.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Glucose anhydrous
Dispersible cellulose
Polysorbate 80
Benzalkonium chloride
Disodium edetate
Purified water
3 years
In-use shelf life: 2 months
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Do not refrigerate or freeze.
6.5
Nature and contents of container
Alisade nasal spray is a predominantly off-white plastic device with a dose indicator window, light
blue side actuated lever and lid which contains a stopper. The plastic device contains the nasal spray
suspension within a Type I amber bottle (glass) fitted with a metering spray pump.
The medicinal product is available in three pack sizes: 30, 60 and 120 sprays.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Glaxo Group Ltd
Greenford, Middlesex, UB6 0NN
United Kingdom
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/08/474/001
EU/1/08/474/002
EU/1/08/474/003
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency (EMEA)
website:
http://www.emea.europa.eu/
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH RELEASE
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
A. MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
Glaxo Operations UK, Ltd,(trading as Glaxo Wellcome Operations)
Harmire Road
Barnard Castle
County Durham
DL12 8DT
Glaxo Wellcome S.A.
Avenida de Extremadura 3
09400 Aranda de Duero
Burgos
Spain
The printed package leaflet of the medicinal product must state the name and address of the
manufacturer responsible for the release of the concerned batch
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
The MAH must ensure that the system of pharmacovigilance, as described in version 7.2
YM2008/00227/00 presented in Module 1.8.1. of the Marketing Authorisation Application, is in place
and functioning before and whilst the product is on the market.
The MAH commits to performing the studies and additional pharmacovigilance activities detailed in
the Pharmacovigilance Plan, as agreed in version GM2006/00247/05 of the Risk Management Plan
(RMP) presented in Module 1.8.2. of the Marketing Authorisation Application and any subsequent
updates of the RMP agreed by the CHMP.
As per the CHMP Guideline on Risk Management Systems for medicinal products for human use, the
updated RMP should be submitted at the same time as the next Periodic Safety Update Report
(PSUR).
In addition, an updated RMP should be submitted
•
When new information is received that may impact on the current Safety Specification,
Pharmacovigilance Plan or risk minimisation activities
•
Within 60 days of an important (pharmacovigilance or risk minimisation) milestone being
reached
•
At the request of the EMEA
PSURs
The PSUR cycle of Alisade will correspond to the one attributed to the cross-referred product,
Avamys, until otherwise specified.
ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING THE IMMEDIATE
PACKAGING>
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Alisade 27.5 micrograms/spray nasal spray suspension
Fluticasone furoate
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each spray delivers 27.5 micrograms of fluticasone furoate
Also contains: Glucose anhydrous, dispersible cellulose, polysorbate 80, benzalkonium chloride,
disodium edetate, purified water
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Nasal spray, suspension
1 bottle - 30 sprays
1 bottle - 60 sprays
1 bottle - 120 sprays
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Shake well before use
Read the package leaflet before use.
Nasal use
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
EXP {MM/YYYY]
In-use shelf life: 2 months























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Do not refrigerate or freeze
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Glaxo Group Ltd
Greenford, Middlesex, UB6 0NN
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/08/474/001
EU/1/08/474/002
EU/1/08/474/003
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE





















MINIMUM PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON SMALL IMMEDIATE PACKAGING UNITS
INTRANASAL SPRAY/DEVICE LABEL
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Alisade 27.5 micrograms/spray nasal spray suspension
Fluticasone furoate
Read the package leaflet before use
CONTENTS BY WEIGHT, BY VOLUME OR BY UNIT
30 sprays
60 sprays
120 sprays
















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Alisade 27.5 micrograms per spray nasal spray suspension
Fluticasone furoate
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine.
-
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Never pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if
their symptoms seem the same as yours.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
tell your doctor or pharmacist.
What Alisade is and what it is used for
Further information
Step-by-step guide to using the nasal spray
1.
WHAT ALISADE IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Alisade nasal spray is used to treat symptoms of allergic rhinitis including stuffy, runny or itchy nose,
sneezing and watery, itchy or red eyes, in adults and children aged 6 years and over.
Allergy symptoms can occur at specific times of the year and be caused by allergy to pollen from grass
or trees (hayfever), or they can occur all year round and be caused by allergy to animals, house-dust
mites or moulds.
Alisade belongs to a group of medicines called
glucocorticoids
.
Alisade works to decrease inflammation caused by allergy (
rhinitis
).
2.
BEFORE YOU USE ALISADE
Do not use Alisade:
If you are allergic
(
hypersensitive
) to fluticasone furoate or any of the other ingredients of Alisade.
Take special care with Alisade:
If you have any liver problems,
tell your doctor or pharmacist. Your doctor may adjust your dose of
Alisade.
Taking nasal glucocorticoids (such as Alisade):
•
may when taken for a long time cause children to grow more slowly. The doctor will check your
child’s height regularly, and make sure he or she is taking the lowest possible effective dose.
may cause eye conditions such as glaucoma (increase in pressure in the eye) or cataracts
(clouding of the lens of the eye). Tell your doctor if you had these conditions in the past, or if
you notice any change in your vision while you are taking Alisade
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor if you are taking, or have recently taken, any other medicines, including those bought
without a prescription.
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
It is especially important to tell your doctor if you are taking, or have recently taken any of the
following medicines:
•
steroid tablets or injected steroids
ritonavir, used to treat
HIV
ketoconazole, used to treat
fungal infections
Your doctor will assess whether you should take Alisade with these medicines.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Ask your doctor for advice before taking any medicine.
Do not use Alisade if you are pregnant,
or planning to become pregnant, unless your doctor or
pharmacist tells you to.
Do not use Alisade if you are breast feeding
unless your doctor or pharmacist tells you to.
Driving and using machines
Alisade is unlikely to affect your ability to drive and use machines.
Important information about some of the ingredients of Alisade
Alisade contains benzalkonium chloride. In some patients this can cause irritation in the inside of the
nose. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you feel discomfort when using the spray.
Always use Alisade exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor if you are
not sure.
Alisade has virtually no taste or smell. It is sprayed into the nose as a fine mist. Be careful not to get
any spray into your eyes. If you do, rinse your eyes with water.
When to use Alisade
•
Use once a day
•
Use at the same time each day.
This will treat your symptoms throughout the day and night.
How long Alisade takes to work
Some people will not feel the full effects until several days after first using Alisade. However, it is
usually effective within 8 to 24 hours of use.
How much to use
Adults and children 12 years and over
•
The usual starting dose
is 2 sprays in each nostril once every day.
Once symptoms are controlled you may be able to decrease your dose to 1 spray in each nostril,
once every day.
The usual starting dose
is 1 spray in each nostril once a day.
If symptoms are very bad your doctor may increase the dose to 2 sprays in each nostril once
every day until the symptoms are under control. It may then be possible for the dose to be
reduced to 1 spray in each nostril once every day.
Do not use in children under 6 years old.
How to use the nasal spray
There is a step-by-step guide to using the nasal spray after Section 6 of this leaflet. Follow the guide
carefully to get full benefit from using Alisade
Ô
See
Step-by-step guide to using the nasal spray
, after Section 6.
If you use more Alisade than you should
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
If you forget to use Alisade
If you miss a dose, take it when you remember.
If it is nearly the time for your next dose, wait until then. Do not take a double dose to make up for a
forgotten dose.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, or if you have any discomfort using the
nasal spray ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Like all medicines, Alisade can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Allergic reactions: get a doctor’s help straight away
Allergic reactions to Alisade are rare and affect less than 1 person in 1,000. In a small number of
people, allergic reactions can develop into a more serious, even life-threatening problem if not treated.
Symptoms include:
- becoming very wheezy, coughing or having difficulty with breathing
- suddenly feeling weak or light-headed (which may lead to collapse or loss of consciousness)
- swelling around the face
- skin rashes or redness.
In many cases, these symptoms will be signs of less serious side effects.
But you must be aware that
they are potentially serious
— so, if you notice any of these symptoms:
See a doctor as soon as possible.
Very common side effects
(These can affect more than 1 person in 10)
•
Nosebleeds (generally minor), particularly if you use Alisade for more than 6 weeks continuously.
Common side effects
(These can affect less than 1 person in 10 and more than 1 person in 100)
•
Irritation or discomfort in the inside of the nose – you may also get streaks of blood when you blow
your nose. This may be due to nasal ulceration.
Nasal corticosteroids can affect the normal production of hormones in your body, particularly if you
use high doses for a long time. In children this side effect can cause them to grow more slowly than
others.

If you get side effects
If any of the side effects gets serious or troublesome,
or if you notice any side effects not
listed in this leaflet: Tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
It is best to store your Alisade nasal spray upright. Always keep the cap on.
Do not use Alisade after the expiry date which is stated on the label and carton. The expiry date refers
to the last day of the month. Alisade nasal spray should be used within 2 months after first opening.
Do not refrigerate or freeze.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
What Alisade contains
The active substance is fluticasone furoate. Each spray delivers 27.5 micrograms of fluticasone
furoate.
The other ingredients are glucose anhydrous, dispersible cellulose, polysorbate 80, benzalkonium
chloride, disodium edetate, purified water.
What Alisade looks like and contents of the pack
The medicine is a white nasal spray suspension contained in an amber glass bottle, fitted with a pump.
The bottle is in an off-white plastic casing with a light blue cap and side-actuated lever. The casing has
a window for viewing the bottle contents. Alisade is available in pack sizes 30, 60 and 120 sprays.
Marketing authorisation holder
Marketing authorisation:
Glaxo Group Ltd
Greenford, Middlesex, UB6 0NN
United Kingdom
Manufacturer:
Glaxo Operations UK Ltd (trading as Glaxo Wellcome Operations)
Harmire Road
Barnard Castle
County Durham
DL12 8DT
United Kingdom
Glaxo Wellcome S.A.
Avenida de Extremadura 3
09400 Aranda de Duero
Burgos
Spain
For any information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the Marketing
Authorisation Holder:

België/Belgique/Belgien
GlaxoSmithKline s.a./n.v.
Tél/Tel: + 32 (0)2 656 21 11
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
GlaxoSmithKline s.a./n.v.
Belgique/Belgien
Tél/Tel: + 32 (0)2 656 21 11
България
ГлаксоСмитКлайн ЕООД
Teл.: + 359 2 953 10 34
Magyarország
GlaxoSmithKline Kft.
Tel.: + 36 1 225 5300
Česká republika
GlaxoSmithKline s.r.o.
Tel: + 420 222 001 111
gsk.czmail@gsk.com
Malta
GlaxoSmithKline Malta
Tel: + 356 21 238131
Danmark
GlaxoSmithKline Pharma A/S
Tlf: + 45 36 35 91 00
dk-info@gsk.com
Nederland
GlaxoSmithKline BV
Tel: + 31 (0)30 6938100
nlinfo@gsk.com
Deutschland
GlaxoSmithKline GmbH & Co. KG
Tel.: + 49 (0)89 36044 8701
produkt.info@gsk.com
Norge
GlaxoSmithKline AS
Tlf: + 47 22 70 20 00
firmapost@gsk.no
Eesti
GlaxoSmithKline Eesti OÜ
Tel: + 372 6676 900
estonia@gsk.com
Österreich
GlaxoSmithKline Pharma GmbH
Tel: + 43 (0)1 97075 0
at.info@gsk.com
Ελλάδα
GlaxoSmithKline A.E.B.E.
Τηλ: + 30 210 68 82 100
Polska
GSK Commercial Sp. z o.o.
Tel.: + 48 (0)22 576 9000
España
GlaxoSmithKline, S.A.
Tel: + 34 902 202 700
es-ci@gsk.com
Portugal
GlaxoSmithKline – Produtos Farmacêuticos, Lda.
Tel: + 351 21 412 95 00
FI.PT@gsk.com
France
Laboratoire GlaxoSmithKline
Tél.: + 33 (0)1 39 17 84 44
diam@gsk.com
România
GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) S.R.L.
Tel: + 4021 3028 208
Ireland
GlaxoSmithKline (Ireland) Limited
Tel: + 353 (0)1 4955000
Slovenija
GlaxoSmithKline d.o.o.
Tel: + 386 (0)1 280 25 00
medical.x.si@gsk.com
Ísland
GlaxoSmithKline ehf.
Sími: + 354 530 3700
Slovenská republika
GlaxoSmithKline Slovakia s. r. o.
Tel: + 421 (0)2 48 26 11 11
recepcia.sk@gsk.com
Italia
GlaxoSmithKline S.p.A.
Tel: + 39 (0)45 9218 111
Suomi/Finland
GlaxoSmithKline Oy
Puh/Tel: + 358 (0)10 30 30 30
Finland.tuoteinfo@gsk.com
Κύπρος
GlaxoSmithKline Cyprus Ltd
Τηλ: + 357 22 39 70 00
Sverige
GlaxoSmithKline AB
Tel: + 46 (0)8 638 93 00
info.produkt@gsk.com
Latvija
GlaxoSmithKline Latvia SIA
Tel: + 371 67312687
lv-epasts@gsk.com
United Kingdom
GlaxoSmithKline UK
Tel: + 44 (0)800 221441
customercontactuk@gsk.com
Lietuva
GlaxoSmithKline Lietuva UAB
Tel: + 370 5 264 90 00
info.lt@gsk.com
This leaflet was last approved in
{MM/YYYY}.
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency (EMEA)
website:
http://www.emea.europa.eu/
STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO USING THE NASAL SPRAY
What the nasal spray looks like
The nasal spray comes in a brown glass bottle inside a plastic casing - see picture
a
. It will contain
either 30, 60 or 120 sprays, depending on the pack size that has been prescribed for you.
The window in the plastic casing lets you see how much Alisade is left in the bottle. You will be able
to see the liquid level for a new 30 or 60 spray bottle, but not in a new 120 spray bottle because the
liquid level is above the window.
Six important things you need to know about using the nasal spray
•
Alisade comes in a brown bottle. If you need to check how much is left
hold the nasal spray
upright against a bright light
. You will then be able to see the level through the window.
When you
first use the nasal spray
you will need to
shake it vigorously
with the cap on for
about 10 seconds. This is important as Alisade is a thick suspension that becomes liquid when
you shake it well - see picture
b
. It will only spray when it becomes liquid.


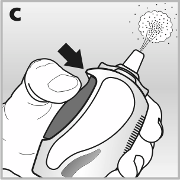
The mist-release button must be
pressed firmly all the way in,
to release the mist through the
nozzle - see picture
c
.
If you have difficulty pressing the button with your thumb, you can use two hands – see picture
d
Always
keep the cap on the nasal spray
when you are not using it. The cap keeps the dust out,
seals in the pressure and stops the nozzle from blocking up. When the cap is in place the mist-
release button cannot be pressed accidentally.
Never use a pin
or anything sharp to clear the nozzle. It will damage the nasal spray.
Preparing the nasal spray for use
You must prepare
the nasal spray:
before you use it for the first time
if you have left the cap off

Preparing the nasal spray helps to make sure you always get the full dose of medicine. Follow these
steps:
1 Shake the nasal spray vigorously
with the cap on for about 10 seconds.
2
Remove the cap by squeezing firmly on the sides of the cap with your thumb and forefinger–
see picture
e
.
3
Hold the nasal spray upright, then tilt and
point the nozzle away from you.
4 Press the button firmly
all the way in.
Do this at least 6 times
until it releases a fine mist of
spray into the air – see picture
f
.
The nasal spray is now ready for use.
Using the nasal spray
1 Shake the nasal spray
vigorously.
2
Remove the cap
.
3 Blow your nose
to clear your nostrils, then tilt your head forward a little bit.
4
Place the nozzle in one of your nostrils – see picture
g
. Point the end of the nozzle slightly
outwards, away from the centre ridge of your nose. This helps to get the medicine to the correct part of
your nose.
5
Press the
button firmly
all the way in,
while you breathe in through your nose
– see picture


Take the nozzle out and
breathe out through your mouth.
If your dose is two sprays in each nostril repeat steps 4 to 6.
Repeat steps 4 to 7 to treat the other nostril.
Replace the cap
on the nasal spray.
Cleaning the nasal spray
After each use:
1
Wipe the nozzle and inside of the cap with a clean, dry tissue – see pictures
i
and
j
.
Do not use water to clean it.
Never use a pin
or anything sharp on the nozzle.
Always replace the cap
once you have finished.
If the nasal spray does not seem to be working
:
•
Check you still have medicine left. Look at the level through the window. If the level is very
low there may not be enough left to work the nasal spray.
Check the nasal spray for damage
If you think the nozzle may be blocked,
do not use a pin
or anything sharp to clear it.
Try to reset it by following the instructions under ‘Preparing the nasal spray for use’.
If it is still not working, or if it produces a jet of liquid, take the nasal spray back to the
pharmacy to get advice.

Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/alisade.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|













































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































