Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
BeneFIX 250 IU powder and solvent for solution for injection.
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each vial contains nominally 250 IU nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX). After
reconstitution with the accompanying 5 ml (0.234%) sodium chloride solution for injection, each ml
of the solution contains approximately 50 IU nonacog alfa.
The potency (IU) is determined using the European Pharmacopoeia one-stage clotting assay. The
specific activity of BeneFIX is not less than 200 IU/mg protein.
BeneFIX contains recombinant coagulation factor IX, (INN = nonacog alfa). Nonacog alfa is a
purified protein that has 415 amino acids in a single chain. It has a primary amino acid sequence that
is comparable to the Ala
148
allelic form of plasma-derived factor IX, and some post-translational
modifications of the recombinant molecule are different from those of the plasma-derived molecule.
Recombinant coagulation factor IX is a glycoprotein that is secreted by genetically engineered
mammalian cells derived from a Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line.
Each vial contains 40 mg sucrose.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
White/almost white powder and clear and colourless solvent for solution for injection.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Treatment and prophylaxis of bleeding in patients with haemophilia B (congenital factor IX
deficiency).
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Treatment should be initiated under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of
haemophilia.
The dosage and duration of the substitution therapy depends on the severity of the factor IX
deficiency, the location and extent of bleeding, and the patient's clinical condition. Dosing of
BeneFIX may differ from that of plasma-derived factor IX products.
To ensure that the desired factor IX activity level has been achieved, precise monitoring using the
factor IX activity assay is advised and doses should be calculated taking the factor IX activity,
pharmacokinetic parameters such as half-life and recovery, as well as the clinical situation into
consideration in order to adjust the dose as appropriate.
The amount to be administered and the frequency of administration should always be oriented to the
clinical effectiveness in the individual case. Factor IX products rarely require to be administered
more than once daily.
The number of units of factor IX administered is expressed in International Units (IU), which are
related to the current WHO standard for factor IX products. Factor IX activity in plasma is expressed
either as a percentage (relative to normal human plasma) or in International Units (relative to an
international standard for factor IX in plasma).
One International Unit (IU) of factor IX activity is equivalent to that quantity of factor IX in one ml of
normal human plasma. Estimation of the required dose of BeneFIX can be based on the finding that
one unit of factor IX activity per kg body weight is expected to increase the circulating level of
factor IX, an average of 0.8 IU/dl (range from 0.4 to 1.4 IU/dl) in adult patients ( 15 years).
Pharmacokinetics have to be assessed regularly in each patient and posology has to be adjusted
accordingly.
The required dosage is determined using the following formula:
Number of
factor IX IU
required
= body weight (in kg) X desired factor IX
increase (%) or (IU/dl)
X reciprocal of
observed recovery
For a recovery 0.8 IU/dl (average increase of factor IX), then:
Number of
factor IX IU
required
= body weight (in kg) X desired factor IX
increase (%) or (IU/dl)
In the case of the following haemorrhagic events, the factor IX activity should not fall below the
given plasma activity levels (in % of normal or in IU/dl) in the corresponding period. The following
table can be used to guide dosing in bleeding episodes and surgery:
Degree of
haemorrhage/Type of
surgical procedure
Factor IX level
required (%) or
(IU/dl)
Frequency of doses (hours)/Duration of
Therapy (days)
Early haemarthrosis, muscle
bleeding or oral bleeding
Repeat every 24 hours. At least 1 day, until
the bleeding episode as indicated by pain is
resolved or healing is achieved.
More extensive
haemarthrosis, muscle
bleeding or haematoma
Repeat infusion every 24 hours for 3-4 days or
more until pain and acute disability are
resolved.
Life-threatening
haemorrhages
Repeat infusion every 8 to 24 hours until threat
is resolved.
Degree of
haemorrhage/Type of
surgical procedure
Factor IX level
required (%) or
(IU/dl)
Frequency of doses (hours)/Duration of
Therapy (days)
Minor:
Including tooth extraction
Every 24 hours, at least
1 day, until healing is achieved.
80-100
(pre- and
postoperative)
Repeat infusion every 8-24 hours until
adequate wound healing, then therapy for at
least another 7 days to maintain a factor IX
activity of 30% to 60% (IU/dl)
During the course of treatment, appropriate determination of factor IX levels is advised to guide the
dose to be administered and the frequency of repeated infusions. In the case of major surgical
interventions in particular, precise monitoring of the substitution therapy by means of coagulation
analysis (plasma factor IX activity) is indispensable. Individual patients may vary in their response to
factor IX, achieving different levels of
in vivo
recovery and demonstrating different half-lives.
For long term prophylaxis against bleeding in patients with severe haemophilia B, BeneFIX may be
administered. In a clinical study for routine secondary prophylaxis the average dose for previously
treated patients (PTP) was 40
IU/kg (range 13 to 78 IU/kg) at intervals of 3 to 4 days. In younger
patients, shorter dosage intervals or higher doses may be necessary.
There are insufficient data to recommend the use of BeneFIX in children less than 6 years of age. In
clinical studies, 57% of the paediatric patients increased their doses due to lower than expected
recovery or to obtain sufficient therapeutic response or both, some to an average dose of >50 IU/kg.
Therefore, close monitoring of factor IX plasma activity should be performed, as well as calculation
of pharmacokinetic parameters such as recovery and half-life, as clinically indicated, in order to adjust
doses as appropriate. If doses >100 IU/kg have been repeatedly needed during routine prophylaxis or
treatment, a switch to another FIX product should be considered.
Patients should be monitored for the development of factor IX inhibitors. If the expected factor IX
activity plasma levels are not attained, or if bleeding is not controlled with an appropriate dose,
biological testing should be performed to determine if a factor IX inhibitor is present.
In patients with high levels of inhibitor factor IX therapy may not be effective and other therapeutic
options must be considered. Management of such patients should be directed by physicians with
experience in the care of patients with haemophilia. See also section 4.4.
BeneFIX is administered by intravenous infusion after reconstitution of the lyophilised powder for
solution for injection with sterile 0.234% sodium chloride solution (see section 6.6).
BeneFIX should be administered at a slow infusion rate. In most of the cases, an infusion rate of up to
4 ml per minute has been used. The rate of administration should be determined by the patient’s
comfort level.
Administration by continuous infusion has not been approved and is not recommended (see also
sections 4.4, 4.8 and 6.6).

Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
Known allergic reaction to hamster proteins.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Activity-neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) are an uncommon event in previously treated patients
(PTPs) receiving factor IX-containing products. Since during clinical studies one PTP treated with
BeneFIX developed a clinically relevant low responding inhibitor and experience on antigenicity with
recombinant factor IX is still limited, patients treated with BeneFIX should be carefully monitored for
the development of factor IX inhibitors that should be titrated in Bethesda Units using appropriate
biological testing.
Sufficient data have not been obtained from ongoing clinical studies on the treatment of previously
untreated patients (PUPs), with BeneFIX. Additional safety and efficacy studies in paediatric patients
are ongoing in previously treated, minimally treated, and previously untreated paediatric patients.
Clinical studies of BeneFIX did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to
determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. As with any patient receiving
BeneFIX, dose selection for an elderly patient should be individualised.
As with any intravenous protein product, allergic-type hypersensitivity reactions are possible. The
product contains traces of hamster proteins. Potentially life-threatening anaphylactic/anaphylactoid
reactions have occurred with factor IX products, including BeneFIX. Patients should be informed of
early signs of hypersensitivity reactions including difficult breathing, shortness of breath, swelling,
hives, itching, tightness of the chest, bronchospasm, laryngospasm, wheezing, hypotension, blurred
vision, and anaphylaxis.
If allergic or anaphylactic-type reactions occur, the administration of BeneFIX has to be discontinued
immediately and an appropriate treatment has to be initiated. In some cases, these reactions have
progressed to severe anaphylaxis. In the case of shock, the current medical standards for treatment of
shock should be observed. In case of severe allergic reactions, alternative haemostatic measures
should be considered.
There have been reports in the literature showing a correlation between the occurrence of a factor IX
inhibitor and allergic reactions. Therefore, patients experiencing allergic reactions should be
evaluated for the presence of an inhibitor. It should be noted that patients with factor IX inhibitors
may be at an increased risk of anaphylaxis with subsequent challenge with factor IX. Preliminary
information suggests a relationship may exist between the presence of major deletion mutations in a
patient's
factor IX gene and an increased risk of inhibitor formation and of acute hypersensitivity
reactions. Patients known to have major deletion mutations of the factor IX gene should be observed
closely for signs and symptoms of acute hypersensitivity reactions, particularly during the early
phases of initial exposure to product.
Because of the risk of allergic reactions with factor IX concentrates, the initial administrations of
factor IX should, according to the treating physician’s judgement, be performed under medical
observation where proper medical care for allergic reactions could be provided.
Posology has to be adjusted according to the pharmacokinetics of each patient.
Although BeneFIX contains only factor IX, the risk of thrombosis and disseminated intravascular
coagulation (DIC) should be recognised. Since the use of factor IX complex concentrates has
historically been associated with the development of thromboembolic complications, the use of factor
IX-containing products may be potentially hazardous in patients with signs of fibrinolysis and in
patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Because of the potential risk of
thrombotic complications, clinical surveillance for early signs of thrombotic and consumptive
coagulopathy should be initiated with appropriate biological testing when administering this product
to patients with liver disease, to patients post-operatively, to neonates, or to patients at risk of
thrombotic phenomena or DIC. In each of these situations, the benefit of treatment with BeneFIX
should be weighed against the risk of these complications.
The safety and efficacy of BeneFIX administration by continuous infusion have not been established
(see also sections 4.2 and 4.8). There have been post-marketing reports of thrombotic events,
including life-threatening superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome in critically ill neonates, while
receiving continuous-infusion BeneFIX through a central venous catheter (see also section 4.8).
There have been reports of agglutination of red blood cells in the tube/syringe with the administration
of BeneFIX. So far, no clinical sequelae have been reported in association with this observation. To
minimize the possibility of agglutination, it is important to limit the amount of blood entering the
tubing. Blood should not enter the syringe. If agglutination of red blood cells in the tubing/syringe is
observed, discard all this material (tubing, syringe and BeneFIX solution) and resume administration
with a new package.
Nephrotic syndrome has been reported following attempted immune tolerance induction in
haemophilia B patients with Factor IX inhibitors and a history of allergic reaction. The safety and
efficacy of using BeneFIX for immune tolerance induction has not been established.
In the interest of patients, it is recommended that, whenever possible, every time that BeneFIX is
administered to them, the name and batch number of the product is registered.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No interaction studies have been performed.
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with factor IX. Based on the rare occurrence of
haemophilia B in women, experience regarding the use of factor IX during pregnancy and
breastfeeding is not available. Therefore, factor IX should be used during pregnancy and breast-
feeding only if clearly indicated.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
N
o studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
To date, no adverse reactions reported in association with BeneFIX occurred with a frequency of
1/100 to <1/10 (common). The frequency of adverse reactions reported in association with BeneFIX
would be categorized as uncommon (1/1,000 to 1/100) or rare (1/10,000 to 1/1,000). Of these
the most significant include: anaphylaxis, cellulitis, phlebitis, and neutralising antibodies.
Adverse reactions based on experience from clinical trials and postmarketing experience are presented
below by system organ class and frequency of occurrence. Within each frequency grouping,
undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness. These frequencies have been
estimated on a per-infusion basis and are described using the following categories: uncommon
(1/1,000 to 1/100); rare (1/10,000 to 1/1,000).
Uncommon: Dizziness, headache, altered taste, lightheadedness
Gastrointestinal disorders
General disorders and administration site conditions
Uncommon: Cellulitis, phlebitis, injection site reaction (including burning infusion site and
injection site stinging), injection site discomfort
Uncommon: Neutralising antibodies (factor IX inhibition)*
Rare:
Hypersensitivity/allergic reactions; such reactions may include anaphylaxis*,
bronchospasm/respiratory distress (dyspnoea), hypotension, angioedema, tachycardia,
chest tightness, urticaria, hives, rash, burning sensation in jaw and skull, chills
(rigors), tingling, flushing, lethargy, restlessness, dry cough/sneezing, blurred vision
* See additional information below.
Hypersensitivity/allergic reactions
Hypersensitivity or allergic reactions have been infrequently observed in patients treated with factor
IX containing products, including BeneFIX. In some cases, these reactions have progressed to severe
anaphylaxis. Allergic reactions have occurred in close temporal association with development of
factor IX inhibitor (see also section 4.4).
The aetiology of the allergic reactions to BeneFIX has not yet been elucidated. These reactions are
potentially life-threatening. If allergic/anaphylactic reactions occur, the administration of BeneFIX
should be discontinued at once. In case of severe allergic reactions, alternative haemostatic measures
should be considered. The treatment required depends on the nature and severity of side-effects (see
also section 4.4).
Due to the production process BeneFIX contains trace amounts of hamster cell proteins.
Hypersensitivity responses can occur.
Patients with haemophilia B may develop neutralising antibodies (inhibitors) to factor IX. If such
inhibitors occur, the condition may manifest itself as an insufficient clinical response. In such cases,
it is recommended that a specialised haemophilia centre be contacted. A clinically relevant, low
responding inhibitor was detected in 1 out of 65 BeneFIX patients (including 9 patients participating
only in the surgery study) who had previously received plasma-derived products. This patient was
able to continue treatment with BeneFIX with no anamnestic rise in inhibitor or anaphylaxis. There
are insufficient data to provide information on inhibitor incidence in PUPs.
Nephrotic syndrome has been reported following high doses of plasma-derived Factor IX to induce
immune tolerance in haemophilia B patients with factor IX inhibitors and a history of allergic
reactions.
In a clinical trial, twelve days after a dose of BeneFIX for a bleeding episode, one hepatitis C
antibody positive patient developed a renal infarct. The relationship of the infarct to prior
administration of BeneFIX is uncertain. The patient continued to be treated with BeneFIX.
There have been post-marketing reports of thrombotic events, including life-threatening SVC
syndrome in critically ill neonates, while receiving continuous-infusion BeneFIX through a central
venous catheter. Cases of peripheral thrombophlebitis and deep venous thrombosis have also been
reported; in most of these cases, BeneFIX was administered via continuous infusion, which is not an
approved method of administration (see also sections 4.2 and 4.4).
Inadequate therapeutic response and inadequate factor IX recovery
Inadequate therapeutic response and inadequate factor IX recovery have been reported during the
post-marketing use of BeneFIX (see also section 4.2).
If any adverse reaction takes place that is thought to be related to the administration of BeneFIX, the
rate of infusion should be decreased or the infusion stopped.
No case of overdose has been reported.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: antihaemorrhagic Blood Coagulation Factor IX; ATC code: B02BD09
BeneFIX contains recombinant coagulation factor IX, (nonacog alfa). Recombinant coagulation
factor IX is a single chain glycoprotein with an approximate molecular mass of 55,000 Daltons that is
a member of the serine protease family of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors. Recombinant
coagulation factor IX is a recombinant DNA-based protein therapeutic which has structural and
functional characteristics comparable to endogenous factor IX. Factor IX is activated by
factor VII/tissue factor complex in the extrinsic pathway as well as factor XIa in the intrinsic
coagulation pathway. Activated factor IX, in combination with activated factor VIII, activates
factor X. This results ultimately in the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. Thrombin then
converts fibrinogen into fibrin and a clot can be formed. Factor IX activity is absent or greatly
reduced in patients with haemophilia B and substitution therapy may be required.
Haemophilia B is a sex-linked hereditary disorder of blood coagulation due to decreased levels of
factor IX and results in profuse bleeding into joints, muscles or internal organs, either spontaneously
or as a result of accidental or surgical trauma. By replacement therapy the plasma levels of factor IX
is increased, thereby enabling a temporary correction of the factor deficiency and correction of the
bleeding tendencies.
There are insufficient data to recommend the use of BeneFIX in children less than 6 years of age.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Infusion of BeneFIX into 56 PTP patients (baseline data) with haemophilia B has shown an
in vivo
recovery ranging from 15 to 62% (mean 33.7 ± 10.3%). One International Unit of BeneFIX showed a
mean 0.75 IU/dl (range 0.3 to 1.4 IU/dl) increase in the circulating level of factor IX. The biologic
half-life ranged from 11 to 36 hours (mean of 19.3 ± 5.0 hours).
For a subset of the 56 patients, data are available from baseline to 24 months. The pharmacokinetic
data for these patients at various time points are shown in the following table:
Table 1. Summary of BeneFIX Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Activity Data by Month in
Previously Treated Patients
10.31
9.04
8.75
9.24
8.80
15.3–62.2
15.3–56.7
16.2–53.1
12.6–62.1
16.2–59.4
30.9, 36.4
29.4, 34.3
28.8, 33.7
28.0, 33.5
28.4, 33.6
FIX increase
(IU/dl per IU/kg)
0.34–1.38
0.34–1.26
0.36–1.18
0.28–1.38
0.36–1.32
0.69, 0.81
0.65, 0.76
0.64, 0.75
0.62, 0.74
0.63, 0.75
Elimination
half-life (h)
11.1–36.4
9.6–38.2
10.6–33.7
10.7–38.3
10.9–42.2
18.0, 20.7
18.1, 21.6
16.8, 20.2
16.8, 21.0
16.8, 20.9
619.8
579.8
575.7
561.8
577.6
605.2
562.2
566.0
560.9
551.7
155.7
146.1
151.0
155.6
154.7
366.5–1072.6
330.9–900.1
290.3–1080.8
254.5–940.8
284.1–1045.4
578.1, 661.5
539.5, 620.1
532.4, 619.1
515.7, 608.0
531.1, 624.1
Half-life
Initial Phase (h)
0.07–5.73
0.12–9.98
0.13–14.34
0.13–6.21
0.11–7.43
1.6,2.5
1.5,3.0
1.5,3.0
1.4,2.6
1.1,2.4



Table 1. Summary of BeneFIX Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Activity Data by Month in
Previously Treated Patients
4.66–13.64
5.55–15.11
4.63–17.22
5.31–19.65
4.78–17.60
7.86,8.94
8.53,9.89
8.56,10.01
8.78,10.47
8.52,9.96
24.35,27.60
24.01,27.15
22.75,26.47
22.55,26.94
23.00,27.17
Data exclude those collected from one patient after evidence of inhibitor development was observed at
9 months.
AUC
0 -
= Area Under the Curve
MRT = Mean Residence Time
SD = Standard Deviation
CI = Confidence Interval
15.81–46.09
13.44–42.26
14.83–38.75
15.30–50.75
15.65–47.52
A 28% lower recovery of BeneFIX in comparison to plasma-derived Factor IX was shown.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of BeneFIX have also been determined after single and multiple
intravenous doses in different species. The pharmacokinetic parameters obtained in studies comparing
BeneFIX to plasma-derived Factor IX were similar to those obtained in human studies. Structural
differences of BeneFIX compared with plasma-derived Factor IX appear to contribute to the different
recovery compared to plasma-derived Factor IX.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-
clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of genotoxicity.
No investigations on carcinogenicity, fertility impairment and foetal development have been
conducted.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Powder
Sucrose
Glycine
L-Histidine
Polysorbate 80
Solvent
Sodium chloride solution





In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other
medicinal products. Only the provided infusion set should be used. Treatment failure can occur as a
consequence of human coagulation factor IX adsorption to the internal surfaces of some infusion
equipment.
The reconstituted product should be used immediately, but no longer than 3 hours after reconstitution.
Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 3 hours at temperatures up to 25
o
C.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store and transport refrigerated (2C - 8C). Do not freeze, in order to prevent damage to the prefilled
syringe.
For the purpose of ambulatory use the product may be removed from refrigerated storage for one
single period of maximum 6 months at room temperature (up to 30 ºC). At the end of this period, the
product should not be put back in the refrigerator, but should be used or discarded.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
250 IU of powder in a 10 ml vial (type 1 glass) with a stopper (chlorobutyl) and a flip-off seal
(aluminium) and 5 ml of solvent in a prefilled syringe (type 1 glass) with a plunger stopper
(bromobutyl), a tip-cap (bromobutyl) and a sterile vial adapter reconstitution device, a sterile infusion
set, two alcohol swabs, a plaster, and a gauze pad.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
BeneFIX is administered by intravenous (IV) injection after reconstitution of the lyophilised powder
for injection with the supplied solvent (0.234% w/v sodium chloride solution) in the pre-filled
syringe.
BeneFIX, when reconstituted, contains polysorbate-80, which is known to increase the rate of
di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) extraction from polyvinyl chloride (PVC). This should be
considered during the preparation and administration of BeneFIX. It is important that the
recommendations in section 4.2 be followed closely.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
The product does not contain a preservative, and the reconstituted solution should be used
immediately or within 3 hours after reconstitution.
Because the use of BeneFIX by continuous infusion has not been evaluated, BeneFIX should not be
mixed with infusion solutions or be given in a drip.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Wyeth Europa Ltd.
Huntercombe Lane South
Taplow, Maidenhead
Berkshire, SL6 0PH
United Kingdom
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 27 August 1997
Date of last renewal: 27 August 2007
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines
Agency (EMEA) http://www.emea.europa.eu
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
BeneFIX 500 IU powder and solvent for solution for injection.
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each vial contains nominally 500 IU nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX). After
reconstitution with the accompanying 5 ml (0.234%) sodium chloride solution for injection, each ml
of the solution contains approximately 100 IU nonacog alfa.
The potency (IU) is determined using the European Pharmacopoeia one-stage clotting assay. The
specific activity of BeneFIX is not less than 200 IU/mg protein.
BeneFIX contains recombinant coagulation factor IX, (INN = nonacog alfa). Nonacog alfa is a
purified protein that has 415 amino acids in a single chain. It has a primary amino acid sequence that
is comparable to the Ala
148
allelic form of plasma-derived factor IX, and some post-translational
modifications of the recombinant molecule are different from those of the plasma-derived molecule.
Recombinant coagulation factor IX is a glycoprotein that is secreted by genetically engineered
mammalian cells derived from a Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line.
Each vial contains 40 mg sucrose.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
White/almost white powder and clear and colourless solvent for solution for injection.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
T
reatment and prophylaxis of bleeding in patients with haemophilia B (congenital factor IX
deficiency).
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Treatment should be initiated under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of
haemophilia.
The dosage and duration of the substitution therapy depends on the severity of the factor IX
deficiency, the location and extent of bleeding, and the patient's clinical condition. Dosing of
BeneFIX may differ from that of plasma-derived factor IX products.
To ensure that the desired factor IX activity level has been achieved, precise monitoring using the
factor IX activity assay is advised and doses should be calculated taking the factor IX activity,
pharmacokinetic parameters such as half-life and recovery, as well as the clinical situation into
consideration in order to adjust the dose as appropriate.
The amount to be administered and the frequency of administration should always be oriented to the
clinical effectiveness in the individual case. Factor IX products rarely require to be administered
more than once daily.
The number of units of factor IX administered is expressed in International Units (IU), which are
related to the current WHO standard for factor IX products. Factor IX activity in plasma is expressed
either as a percentage (relative to normal human plasma) or in International Units (relative to an
international standard for factor IX in plasma).
One International Unit (IU) of factor IX activity is equivalent to that quantity of factor IX in one ml of
normal human plasma. Estimation of the required dose of BeneFIX can be based on the finding that
one unit of factor IX activity per kg body weight is expected to increase the circulating level of
factor IX, an average of 0.8 IU/dl (range from 0.4 to 1.4 IU/dl) in adult patients ( 15 years).
Pharmacokinetics have to be assessed regularly in each patient and posology has to be adjusted
accordingly.
The required dosage is determined using the following formula:
Number of
factor IX IU
required
= body weight (in kg) X desired factor IX
increase (%) or (IU/dl)
X reciprocal of
observed recovery
For a recovery 0.8 IU/dl (average increase of factor IX), then:
Number of
factor IX IU
required
= body weight (in kg) X desired factor IX
increase (%) or (IU/dl)
In the case of the following haemorrhagic events, the factor IX activity should not fall below the
given plasma activity levels (in % of normal or in IU/dl) in the corresponding period. The following
table can be used to guide dosing in bleeding episodes and surgery:
Degree of
haemorrhage/Type of
surgical procedure
Factor IX level
required (%) or
(IU/dl)
Frequency of doses (hours)/Duration of
Therapy (days)
Early haemarthrosis, muscle
bleeding or oral bleeding
Repeat every 24 hours. At least 1 day, until
the bleeding episode as indicated by pain is
resolved or healing is achieved.
More extensive
haemarthrosis, muscle
bleeding or haematoma
Repeat infusion every 24 hours for 3-4 days or
more until pain and acute disability are
resolved.
Life-threatening
haemorrhages
Repeat infusion every 8 to 24 hours until threat
is resolved.
Minor:
Including tooth extraction
Every 24 hours, at least
1 day, until healing is achieved.
80-100
(pre- and
postoperative)
Repeat infusion every 8-24 hours until
adequate wound healing, then therapy for at
least another 7 days to maintain a factor IX
activity of 30% to 60% (IU/dl)


During the course of treatment, appropriate determination of factor IX levels is advised to guide the
dose to be administered and the frequency of repeated infusions. In the case of major surgical
interventions in particular, precise monitoring of the substitution therapy by means of coagulation
analysis (plasma factor IX activity) is indispensable. Individual patients may vary in their response to
factor IX, achieving different levels of
in vivo
recovery and demonstrating different half-lives.
For long term prophylaxis against bleeding in patients with severe haemophilia B, BeneFIX may be
administered. In a clinical study for routine secondary prophylaxis the average dose for previously
treated patients (PTP) was 40 IU/kg (range 13 to 78 IU/kg) at intervals of 3 to 4 days. In younger
patients, shorter dosage intervals or higher doses may be necessary.
There are insufficient data to recommend the use of BeneFIX in children less than 6 years of age. In
clinical studies, 57% of the paediatric patients increased their doses due to lower than expected
recovery or to obtain sufficient therapeutic response or both, some to an average dose of >50 IU/kg.
Therefore, close monitoring of factor IX plasma activity should be performed, as well as calculation
of pharmacokinetic parameters such as recovery and half-life, as clinically indicated, in order to adjust
doses as appropriate. If doses >100 IU/kg have been repeatedly needed during routine prophylaxis or
treatment, a switch to another FIX product should be considered.
Patients should be monitored for the development of factor IX inhibitors. If the expected factor IX
activity plasma levels are not attained, or if bleeding is not controlled with an appropriate dose,
biological testing should be performed to determine if a factor IX inhibitor is present.
In patients with high levels of inhibitor factor IX therapy may not be effective and other therapeutic
options must be considered. Management of such patients should be directed by physicians with
experience in the care of patients with haemophilia. See also section 4.4.
BeneFIX is administered by intravenous infusion after reconstitution of the lyophilised powder for
solution for injection with sterile 0.234% sodium chloride solution (see section 6.6).
BeneFIX should be administered at a slow infusion rate. In most of the cases, an infusion rate of up to
4 ml per minute has been used. The rate of administration should be determined by the patient’s
comfort level.
Administration by continuous infusion has not been approved and is not recommended (see also
sections 4.4, 4.8 and 6.6).
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
Known allergic reaction to hamster proteins.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Activity-neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) are an uncommon event in previously treated patients
(PTPs) receiving factor IX-containing products. Since during clinical studies one PTP treated with
BeneFIX developed a clinically relevant low responding inhibitor and experience on antigenicity with
recombinant factor IX is still limited, patients treated with BeneFIX should be carefully monitored for
the development of factor IX inhibitors that should be titrated in Bethesda Units using appropriate
biological testing.
Sufficient data have not been obtained from ongoing clinical studies on the treatment of previously
untreated patients (PUPs), with BeneFIX. Additional safety and efficacy studies in paediatric patients
are ongoing in previously treated, minimally treated, and previously untreated paediatric patients.
Clinical studies of BeneFIX did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to
determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. As with any patient receiving
BeneFIX, dose selection for an elderly patient should be individualised.
As with any intravenous protein product, allergic-type hypersensitivity reactions are possible. The
product contains traces of hamster proteins. Potentially life-threatening anaphylactic/anaphylactoid
reactions have occurred with factor IX products, including BeneFIX. Patients should be informed of
early signs of hypersensitivity reactions including difficult breathing, shortness of breath, swelling,
hives, itching, tightness of the chest, bronchospasm, laryngospasm, wheezing, hypotension, blurred
vision, and anaphylaxis.
If allergic or anaphylactic-type reactions occur, the administration of BeneFIX has to be discontinued
immediately and an appropriate treatment has to be initiated. In some cases, these reactions have
progressed to severe anaphylaxis. In the case of shock, the current medical standards for treatment of
shock should be observed. In case of severe allergic reactions, alternative haemostatic measures
should be considered.
There have been reports in the literature showing a correlation between the occurrence of a factor IX
inhibitor and allergic reactions. Therefore, patients experiencing allergic reactions should be
evaluated for the presence of an inhibitor. It should be noted that patients with factor IX inhibitors
may be at an increased risk of anaphylaxis with subsequent challenge with factor IX. Preliminary
information suggests a relationship may exist between the presence of major deletion mutations in a
patient's
factor IX gene and an increased risk of inhibitor formation and of acute hypersensitivity
reactions. Patients known to have major deletion mutations of the factor IX gene should be observed
closely for signs and symptoms of acute hypersensitivity reactions, particularly during the early
phases of initial exposure to product.
Because of the risk of allergic reactions with factor IX concentrates, the initial administrations of
factor IX should, according to the treating physician’s judgement, be performed under medical
observation where proper medical care for allergic reactions could be provided.
Posology has to be adjusted according to the pharmacokinetics of each patient.
Although BeneFIX contains only factor IX, the risk of thrombosis and disseminated intravascular
coagulation (DIC) should be recognised. Since the use of factor IX complex concentrates has
historically been associated with the development of thromboembolic complications, the use of factor
IX-containing products may be potentially hazardous in patients with signs of fibrinolysis and in
patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Because of the potential risk of
thrombotic complications, clinical surveillance for early signs of thrombotic and consumptive
coagulopathy should be initiated with appropriate biological testing when administering this product
to patients with liver disease, to patients post-operatively, to neonates, or to patients at risk of
thrombotic phenomena or DIC. In each of these situations, the benefit of treatment with BeneFIX
should be weighed against the risk of these complications.
The safety and efficacy of BeneFIX administration by continuous infusion have not been established
(see also sections 4.2 and 4.8). There have been post-marketing reports of thrombotic events,
including life-threatening superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome in critically ill neonates, while
receiving continuous-infusion BeneFIX through a central venous catheter (see also section 4.8).
There have been reports of agglutination of red blood cells in the tube/syringe with the administration
of BeneFIX. So far, no clinical sequelae have been reported in association with this observation. To
minimize the possibility of agglutination, it is important to limit the amount of blood entering the
tubing. Blood should not enter the syringe. If agglutination of red blood cells in the tubing/syringe is
observed, discard all this material (tubing, syringe and BeneFIX solution) and resume administration
with a new package.
Nephrotic syndrome has been reported following attempted immune tolerance induction in
haemophilia B patients with Factor IX inhibitors and a history of allergic reaction. The safety and
efficacy of using BeneFIX for immune tolerance induction has not been established.
In the interest of patients, it is recommended that, whenever possible, every time that BeneFIX is
administered to them, the name and batch number of the product is registered.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No interaction studies have been performed.
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with factor IX. Based on the rare occurrence of
haemophilia B in women, experience regarding the use of factor IX during pregnancy and
breastfeeding is not available. Therefore, factor IX should be used during pregnancy and breast-
feeding only if clearly indicated.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
To date, no adverse reactions reported in association with BeneFIX occurred with a frequency of
1/100 to <1/10 (common). The frequency of adverse reactions reported in association with BeneFIX
would be categorized as uncommon (1/1,000 to 1/100) or rare (1/10,000 to 1/1,000). Of these
the most significant include: anaphylaxis, cellulitis, phlebitis, and neutralising antibodies.
Adverse reactions based on experience from clinical trials and postmarketing experience are presented
below by system organ class and frequency of occurrence. Within each frequency grouping,
undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness. These frequencies have been
estimated on a per-infusion basis and are described using the following categories: uncommon
(1/1,000 to 1/100); rare (1/10,000 to 1/1,000).
Uncommon: Dizziness, headache, altered taste, lightheadedness
Gastrointestinal disorders
General disorders and administration site conditions
Uncommon: Cellulitis, phlebitis, injection site reaction (including burning infusion site and
injection site stinging), injection site discomfort
Uncommon: Neutralising antibodies (factor IX inhibition)*
Rare:
Hypersensitivity/allergic reactions; such reactions may include anaphylaxis*,
bronchospasm/respiratory distress (dyspnoea), hypotension, angioedema, tachycardia,
chest tightness, urticaria, hives, rash, burning sensation in jaw and skull, chills
(rigors), tingling, flushing, lethargy, restlessness, dry cough/sneezing, blurred vision
* See additional information below.
Hypersensitivity/allergic reactions
Hypersensitivity or allergic reactions have been infrequently observed in patients treated with
factor IX containing products, including BeneFIX. In some cases, these reactions have progressed to
severe anaphylaxis. Allergic reactions have occurred in close temporal association with development
of factor IX inhibitor (see also section 4.4).
The aetiology of the allergic reactions to BeneFIX has not yet been elucidated. These reactions are
potentially life-threatening. If allergic/anaphylactic reactions occur, the administration of BeneFIX
should be discontinued at once. In case of severe allergic reactions, alternative haemostatic measures
should be considered. The treatment required depends on the nature and severity of side-effects (see
also section 4.4).
Due to the production process BeneFIX contains trace amounts of hamster cell proteins.
Hypersensitivity responses can occur.
Patients with haemophilia B may develop neutralising antibodies (inhibitors) to factor IX. If such
inhibitors occur, the condition may manifest itself as an insufficient clinical response. In such cases,
it is recommended that a specialised haemophilia centre be contacted. A clinically relevant, low
responding inhibitor was detected in 1 out of 65 BeneFIX patients (including 9 patients participating
only in the surgery study) who had previously received plasma-derived products. This patient was
able to continue treatment with BeneFIX with no anamnestic rise in inhibitor or anaphylaxis. There
are insufficient data to provide information on inhibitor incidence in PUPs.
Nephrotic syndrome has been reported following high doses of plasma-derived Factor IX to induce
immune tolerance in haemophilia B patients with factor IX inhibitors and a history of allergic
reactions.
In a clinical trial, twelve days after a dose of BeneFIX for a bleeding episode, one hepatitis C
antibody positive patient developed a renal infarct. The relationship of the infarct to prior
administration of BeneFIX is uncertain. The patient continued to be treated with BeneFIX.
There have been post-marketing reports of thrombotic events, including life-threatening SVC
syndrome in critically ill neonates, while receiving continuous-infusion BeneFIX through a central
venous catheter. Cases of peripheral thrombophlebitis and deep venous thrombosis have also been
reported; in most of these cases, BeneFIX was administered via continuous infusion, which is not an
approved method of administration (see also sections 4.2 and 4.4).
Inadequate therapeutic response and inadequate factor IX recovery
Inadequate therapeutic response and inadequate factor IX recovery have been reported during the
post-marketing use of BeneFIX (see also section 4.2).
If any adverse reaction takes place that is thought to be related to the administration of BeneFIX, the
rate of infusion should be decreased or the infusion stopped.
No case of overdose has been reported.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: antihaemorrhagic Blood Coagulation Factor IX; ATC code: B02BD09
BeneFIX contains recombinant coagulation factor IX, (nonacog alfa). Recombinant coagulation
factor IX is a single chain glycoprotein with an approximate molecular mass of 55,000 Daltons that is
a member of the serine protease family of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors. Recombinant
coagulation factor IX is a recombinant DNA-based protein therapeutic which has structural and
functional characteristics comparable to endogenous factor IX. Factor IX is activated by
factor VII/tissue factor complex in the extrinsic pathway as well as factor XIa in the intrinsic
coagulation pathway. Activated factor IX, in combination with activated factor VIII, activates
factor X. This results ultimately in the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. Thrombin then
converts fibrinogen into fibrin and a clot can be formed. Factor IX activity is absent or greatly
reduced in patients with haemophilia B and substitution therapy may be required.
Haemophilia B is a sex-linked hereditary disorder of blood coagulation due to decreased levels of
factor IX and results in profuse bleeding into joints, muscles or internal organs, either spontaneously
or as a result of accidental or surgical trauma. By replacement therapy the plasma levels of factor IX
is increased, thereby enabling a temporary correction of the factor deficiency and correction of the
bleeding tendencies.
There are insufficient data to recommend the use of BeneFIX in children less than 6 years of age.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Infusion of BeneFIX into 56 PTP patients (baseline data) with haemophilia B has shown an
in vivo
recovery ranging from 15 to 62% (mean 33.7 ± 10.3%). One International Unit of BeneFIX showed a
mean 0.75 IU/dl (range 0.3 to 1.4 IU/dl) increase in the circulating level of factor IX. The biologic
half-life ranged from 11 to 36 hours (mean of 19.3 ± 5.0 hours).
For a subset of the 56 patients, data are available from baseline to 24 months. The pharmacokinetic
data for these patients at various time points are shown in the following table:
Summary of BeneFIX Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Activity Data by Month
in Previously Treated Patients
15.3–62.2
15.3–56.7
16.2–53.1
30.9, 36.4
29.4, 34.3
28.8, 33.7





Summary of BeneFIX Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Activity Data by Month
in Previously Treated Patients
FIX increase
(IU/dl per IU/kg)
0.34–1.38
0.34–1.26
0.36–1.18
0.28–1.38
0.36–1.32
0.69, 0.81
0.65, 0.76
0.64, 0.75
0.62, 0.74
0.63, 0.75
Elimination
half-life (h)
11.1–36.4
9.6–38.2
10.6–33.7
10.7–38.3
10.9–42.2
18.0, 20.7
18.1, 21.6
16.8, 20.2
16.8, 21.0
16.8, 20.9
619.8
579.8
575.7
561.8
577.6
605.2
562.2
566.0
560.9
551.7
155.7
146.1
151.0
155.6
154.7
366.5–1072.6
330.9–900.1
290.3–1080.8
254.5–940.8
284.1–1045.4
578.1, 661.5
539.5, 620.1
532.4, 619.1
515.7, 608.0
531.1, 624.1
Half-life
Initial Phase (h)
0.07–5.73
0.12–9.98
0.13–14.34
0.13–6.21
0.11–7.43
1.6,2.5
1.5,3.0
1.5,3.0
1.4,2.6
1.1,2.4
4.66–13.64
5.55–15.11
4.63–17.22
5.31–19.65
4.78–17.60
7.86,8.94
8.53,9.89
8.56,10.01
8.78,10.47
8.52,9.96
24.35,27.60
24.01,27.15
22.75,26.47
22.55,26.94
23.00,27.17
Data exclude those collected from one patient after evidence of inhibitor development was observed at
9 months.
AUC
0 -
= Area Under the Curve
MRT = Mean Residence Time
SD = Standard Deviation
CI = Confidence Interval
15.81–46.09
13.44–42.26
14.83–38.75
15.30–50.75
15.65–47.52
A 28% lower recovery of BeneFIX in comparison to plasma-derived Factor IX was shown.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of BeneFIX have also been determined after single and multiple
intravenous doses in different species. The pharmacokinetic parameters obtained in studies comparing
BeneFIX to plasma-derived Factor IX were similar to those obtained in human studies. Structural
differences of BeneFIX compared with plasma-derived Factor IX appear to contribute to the different
recovery compared to plasmaderived Factor IX.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of genotoxicity.





No investigations on carcinogenicity, fertility impairment and foetal development have been
conducted.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Powder
Sucrose
Glycine
L-Histidine
Polysorbate 80
Solvent
Sodium chloride solution
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other
medicinal products. Only the provided infusion set should be used. Treatment failure can occur as a
consequence of human coagulation factor IX adsorption to the internal surfaces of some infusion
equipment.
The reconstituted product should be used immediately, but no longer than 3 hours after reconstitution.
Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 3 hours at temperatures up to 25
o
C.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store and transport refrigerated (2C - 8C). Do not freeze, in order to prevent damage to the prefilled
syringe.
For the purpose of ambulatory use the product may be removed from refrigerated storage for one
single period of maximum 6 months at room temperature (up to 30 ºC). At the end of this period, the
product should not be put back in the refrigerator, but should be used or discarded.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
500 IU of powder in a 10 ml vial (type 1 glass) with a stopper (chlorobutyl) and a flip-off seal
(aluminium) and 5 ml of solvent in a prefilled syringe (type 1 glass) with a plunger stopper
(bromobutyl), a tip-cap (bromobutyl) and a sterile vial adapter reconstitution device, a sterile infusion
set, two alcohol swabs, a plaster, and a gauze pad.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
BeneFIX is administered by intravenous (IV) injection after reconstitution of the lyophilised powder
for injection with the supplied solvent (0.234% w/v sodium chloride solution) in the pre-filled
syringe.
BeneFIX, when reconstituted, contains polysorbate-80, which is known to increase the rate of
di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) extraction from polyvinyl chloride (PVC). This should be
considered during the preparation and administration of BeneFIX. It is important that the
recommendations in section 4.2 be followed closely.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
The product does not contain a preservative, and the reconstituted solution should be used
immediately or within 3 hours after reconstitution.
Because the use of BeneFIX by continuous infusion has not been evaluated, BeneFIX should not be
mixed with infusion solutions or be given in a drip.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Wyeth Europa Ltd.
Huntercombe Lane South
Taplow, Maidenhead
Berkshire, SL6 0PH
United Kingdom
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 27 August 1997
Date of last renewal: 27 August 2007
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European
Medicines Agency (EMEA) http://www.emea.europa.eu
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
BeneFIX 1000 IU powder and solvent for solution for injection.
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each vial contains nominally 1000 IU nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX). After
reconstitution with the accompanying 5 ml (0.234%) sodium chloride solution for injection, each ml
of the solution contains approximately 200 IU nonacog alfa.
The potency (IU) is determined using the European Pharmacopoeia one-stage clotting assay. The
specific activity of BeneFIX is not less than 200 IU/mg protein.
BeneFIX contains recombinant coagulation factor IX, (INN = nonacog alfa). Nonacog alfa is a
purified protein that has 415 amino acids in a single chain. It has a primary amino acid sequence that
is comparable to the Ala
148
allelic form of plasma-derived factor IX, and some post-translational
modifications of the recombinant molecule are different from those of the plasma-derived molecule.
Recombinant coagulation factor IX is a glycoprotein that is secreted by genetically engineered
mammalian cells derived from a Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line.
Each vial contains 40 mg sucrose.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
White/almost white powder and clear and colourless solvent for solution for injection.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
T
reatment and prophylaxis of bleeding in patients with haemophilia B (congenital factor IX
deficiency).
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Treatment should be initiated under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of
haemophilia.
The dosage and duration of the substitution therapy depends on the severity of the factor IX
deficiency, the location and extent of bleeding, and the patient's clinical condition. Dosing of
BeneFIX may differ from that of plasma-derived factor IX products.
To ensure that the desired factor IX activity level has been achieved, precise monitoring using the
factor IX activity assay is advised and doses should be calculated taking the factor IX activity,
pharmacokinetic parameters such as half-life and recovery, as well as the clinical situation into
consideration in order to adjust the dose as appropriate.
The amount to be administered and the frequency of administration should always be oriented to the
clinical effectiveness in the individual case. Factor IX products rarely require to be administered
more than once daily.
The number of units of factor IX administered is expressed in International Units (IU), which are
related to the current WHO standard for factor IX products. Factor IX activity in plasma is expressed
either as a percentage (relative to normal human plasma) or in International Units (relative to an
international standard for factor IX in plasma).
One International Unit (IU) of factor IX activity is equivalent to that quantity of factor IX in one ml of
normal human plasma. Estimation of the required dose of BeneFIX can be based on the finding that
one unit of factor IX activity per kg body weight is expected to increase the circulating level of
factor IX, an average of 0.8 IU/dl (range from 0.4 to 1.4 IU/dl) in adult patients ( 15 years).
Pharmacokinetics have to be assessed regularly in each patient and posology has to be adjusted
accordingly.
The required dosage is determined using the following formula:
Number of
factor IX IU
required
X desired factor IX
increase (%) or (IU/dl)
X reciprocal of
observed recovery
For a recovery 0.8 IU/dl (average increase of factor IX), then:
Number of
factor IX IU
required
X desired factor IX
increase (%) or (IU/dl)
In the case of the following haemorrhagic events, the factor IX activity should not fall below the
given plasma activity levels (in % of normal or in IU/dl) in the corresponding period. The following
table can be used to guide dosing in bleeding episodes and surgery:
Degree of haemorrhage/Type
of surgical procedure
Factor IX level
required (%) or
(IU/dl)
Frequency of doses (hours)/Duration of
Therapy (days)
Early haemarthrosis, muscle
bleeding or oral bleeding
Repeat every 24 hours. At least 1 day,
until the bleeding episode as indicated by
pain is resolved or healing is achieved.
More extensive haemarthrosis,
muscle bleeding or haematoma
Repeat infusion every 24 hours for 3-4
days or more until pain and acute
disability are resolved.
Life-threatening haemorrhages
Repeat infusion every 8 to 24 hours until
threat is resolved.
Minor:
Including tooth extraction
Every 24 hours, at least
1 day, until healing is achieved.
80-100
(pre- and
postoperative)
Repeat infusion every 8-24 hours until
adequate wound healing, then therapy for
at least another 7 days to maintain a
factor IX activity of 30% to 60% (IU/dl)


During the course of treatment, appropriate determination of factor IX levels is advised to guide the
dose to be administered and the frequency of repeated infusions. In the case of major surgical
interventions in particular, precise monitoring of the substitution therapy by means of coagulation
analysis (plasma factor IX activity) is indispensable. Individual patients may vary in their response to
factor IX, achieving different levels of
in vivo
recovery and demonstrating different half-lives.
For long term prophylaxis against bleeding in patients with severe haemophilia B, BeneFIX may be
administered. In a clinical study for routine secondary prophylaxis the average dose for previously
treated patients (PTP) was 40 IU/kg (range 13 to 78 IU/kg) at intervals of 3 to 4 days. In younger
patients, shorter dosage intervals or higher doses may be necessary.
There are insufficient data to recommend the use of BeneFIX in children less than 6 years of age. In
clinical studies, 57% of the paediatric patients increased their doses due to lower than expected
recovery or to obtain sufficient therapeutic response or both, some to an average dose of >50 IU/kg.
Therefore, close monitoring of factor IX plasma activity should be performed, as well as calculation
of pharmacokinetic parameters such as recovery and half-life, as clinically indicated, in order to adjust
doses as appropriate. If doses >100 IU/kg have been repeatedly needed during routine prophylaxis or
treatment, a switch to another FIX product should be considered.
Patients should be monitored for the development of factor IX inhibitors. If the expected factor IX
activity plasma levels are not attained, or if bleeding is not controlled with an appropriate dose,
biological testing should be performed to determine if a factor IX inhibitor is present.
In patients with high levels of inhibitor factor IX therapy may not be effective and other therapeutic
options must be considered. Management of such patients should be directed by physicians with
experience in the care of patients with haemophilia. See also section 4.4.
BeneFIX is administered by intravenous infusion after reconstitution of the lyophilised powder for
solution for injection with sterile 0.234% sodium chloride solution (see section 6.6).
BeneFIX should be administered at a slow infusion rate. In most of the cases, an infusion rate of up to
4 ml per minute has been used. The rate of administration should be determined by the patient’s
comfort level.
Administration by continuous infusion has not been approved and is not recommended (see also
sections 4.4, 4.8 and 6.6).
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
Known allergic reaction to hamster proteins.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Activity-neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) are an uncommon event in previously treated patients
(PTPs) receiving factor IX-containing products. Since during clinical studies one PTP treated with
BeneFIX developed a clinically relevant low responding inhibitor and experience on antigenicity with
recombinant factor IX is still limited, patients treated with BeneFIX should be carefully monitored for
the development of factor IX inhibitors that should be titrated in Bethesda Units using appropriate
biological testing.
Sufficient data have not been obtained from ongoing clinical studies on the treatment of previously
untreated patients (PUPs), with BeneFIX. Additional safety and efficacy studies in paediatric patients
are ongoing in previously treated, minimally treated, and previously untreated paediatric patients.
Clinical studies of BeneFIX did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to
determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. As with any patient receiving
BeneFIX, dose selection for an elderly patient should be individualised.
As with any intravenous protein product, allergic-type hypersensitivity reactions are possible. The
product contains traces of hamster proteins. Potentially life-threatening anaphylactic/anaphylactoid
reactions have occurred with factor IX products, including BeneFIX. Patients should be informed of
early signs of hypersensitivity reactions including difficult breathing, shortness of breath, swelling,
hives, itching, tightness of the chest, bronchospasm, laryngospasm, wheezing, hypotension, blurred
vision, and anaphylaxis.
If allergic or anaphylactic-type reactions occur, the administration of BeneFIX has to be discontinued
immediately and an appropriate treatment has to be initiated. In some cases, these reactions have
progressed to severe anaphylaxis. In the case of shock, the current medical standards for treatment of
shock should be observed. In case of severe allergic reactions, alternative haemostatic measures
should be considered.
There have been reports in the literature showing a correlation between the occurrence of a factor IX
inhibitor and allergic reactions. Therefore, patients experiencing allergic reactions should be
evaluated for the presence of an inhibitor. It should be noted that patients with factor IX inhibitors
may be at an increased risk of anaphylaxis with subsequent challenge with factor IX. Preliminary
information suggests a relationship may exist between the presence of major deletion mutations in a
patient's
factor IX gene and an increased risk of inhibitor formation and of acute hypersensitivity
reactions. Patients known to have major deletion mutations of the factor IX gene should be observed
closely for signs and symptoms of acute hypersensitivity reactions, particularly during the early
phases of initial exposure to product.
Because of the risk of allergic reactions with factor IX concentrates, the initial administrations of
factor IX should, according to the treating physician’s judgement, be performed under medical
observation where proper medical care for allergic reactions could be provided.
Posology has to be adjusted according to the pharmacokinetics of each patient.
Although BeneFIX contains only factor IX, the risk of thrombosis and disseminated intravascular
coagulation (DIC) should be recognised. Since the use of factor IX complex concentrates has
historically been associated with the development of thromboembolic complications, the use of
factor IX-containing products may be potentially hazardous in patients with signs of fibrinolysis and
in patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Because of the potential risk of
thrombotic complications, clinical surveillance for early signs of thrombotic and consumptive
coagulopathy should be initiated with appropriate biological testing when administering this product
to patients with liver disease, to patients post-operatively, to neonates, or to patients at risk of
thrombotic phenomena or DIC. In each of these situations, the benefit of treatment with BeneFIX
should be weighed against the risk of these complications.
The safety and efficacy of BeneFIX administration by continuous infusion have not been established
(see also sections 4.2 and 4.8). There have been post-marketing reports of thrombotic events,
including life-threatening superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome in critically ill neonates, while
receiving continuous-infusion BeneFIX through a central venous catheter (see also section 4.8).
There have been reports of agglutination of red blood cells in the tube/syringe with the administration
of BeneFIX. So far, no clinical sequelae have been reported in association with this observation. To
minimize the possibility of agglutination, it is important to limit the amount of blood entering the
tubing. Blood should not enter the syringe. If agglutination of red blood cells in the tubing/syringe is
observed, discard all this material (tubing, syringe and BeneFIX solution) and resume administration
with a new package.
Nephrotic syndrome has been reported following attempted immune tolerance induction in
haemophilia B patients with Factor IX inhibitors and a history of allergic reaction. The safety and
efficacy of using BeneFIX for immune tolerance induction has not been established.
In the interest of patients, it is recommended that, whenever possible, every time that BeneFIX is
administered to them, the name and batch number of the product is registered.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No interaction studies have been performed.
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with factor IX. Based on the rare occurrence of
haemophilia B in women, experience regarding the use of factor IX during pregnancy and
breastfeeding is not available. Therefore, factor IX should be used during pregnancy and
breast-feeding only if clearly indicated.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
To date, no adverse reactions reported in association with BeneFIX occurred with a frequency of
1/100 to <1/10 (common). The frequency of adverse reactions reported in association with BeneFIX
would be categorized as uncommon (1/1,000 to 1/100) or rare (1/10,000 to 1/1,000). Of these
the most significant include: anaphylaxis, cellulitis, phlebitis, and neutralising antibodies.
Adverse reactions based on experience from clinical trials and postmarketing experience are presented
below by system organ class and frequency of occurrence. Within each frequency grouping,
undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness. These frequencies have been
estimated on a per-infusion basis and are described using the following categories: uncommon
(1/1,000 to 1/100); rare (1/10,000 to 1/1,000).
Uncommon: Dizziness, headache, altered taste, lightheadedness
Gastrointestinal disorders
General disorders and administration site conditions
Uncommon: Cellulitis, phlebitis, injection site reaction (including burning infusion site and
injection site stinging), injection site discomfort
Uncommon: Neutralising antibodies (factor IX inhibition)*
Rare:
Hypersensitivity/allergic reactions; such reactions may include anaphylaxis*,
bronchospasm/respiratory distress (dyspnoea), hypotension, angioedema, tachycardia,
chest tightness, urticaria, hives, rash, burning sensation in jaw and skull, chills
(rigors), tingling, flushing, lethargy, restlessness, dry cough/sneezing, blurred vision
* See additional information below.
Hypersensitivity/allergic reactions
Hypersensitivity or allergic reactions have been infrequently observed in patients treated with
factor IX containing products, including BeneFIX. In some cases, these reactions have progressed to
severe anaphylaxis. Allergic reactions have occurred in close temporal association with development
of factor IX inhibitor (see also section 4.4).
The aetiology of the allergic reactions to BeneFIX has not yet been elucidated. These reactions are
potentially life-threatening. If allergic/anaphylactic reactions occur, the administration of BeneFIX
should be discontinued at once. In case of severe allergic reactions, alternative haemostatic measures
should be considered. The treatment required depends on the nature and severity of side-effects (see
also section 4.4).
Due to the production process BeneFIX contains trace amounts of hamster cell proteins.
Hypersensitivity responses can occur.
Patients with haemophilia B may develop neutralising antibodies (inhibitors) to factor IX. If such
inhibitors occur, the condition may manifest itself as an insufficient clinical response. In such cases,
it is recommended that a specialised haemophilia centre be contacted. A clinically relevant, low
responding inhibitor was detected in 1 out of 65 BeneFIX patients (including 9 patients participating
only in the surgery study) who had previously received plasma-derived products. This patient was
able to continue treatment with BeneFIX with no anamnestic rise in inhibitor or anaphylaxis. There
are insufficient data to provide information on inhibitor incidence in PUPs.
Nephrotic syndrome has been reported following high doses of plasma-derived Factor IX to induce
immune tolerance in haemophilia B patients with factor IX inhibitors and a history of allergic
reactions.
In a clinical trial, twelve days after a dose of BeneFIX for a bleeding episode, one hepatitis C
antibody positive patient developed a renal infarct. The relationship of the infarct to prior
administration of BeneFIX is uncertain. The patient continued to be treated with BeneFIX.
There have been post-marketing reports of thrombotic events, including life-threatening SVC
syndrome in critically ill neonates, while receiving continuous-infusion BeneFIX through a central
venous catheter. Cases of peripheral thrombophlebitis and deep venous thrombosis have also been
reported; in most of these cases, BeneFIX was administered via continuous infusion, which is not an
approved method of administration (see also sections 4.2 and 4.4).
Inadequate therapeutic response and inadequate factor IX recovery
Inadequate therapeutic response and inadequate factor IX recovery have been reported during the
post-marketing use of BeneFIX (see also section 4.2).
If any adverse reaction takes place that is thought to be related to the administration of BeneFIX, the
rate of infusion should be decreased or the infusion stopped.
No case of overdose has been reported.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: antihaemorrhagic Blood Coagulation Factor IX; ATC code: B02BD09
BeneFIX contains recombinant coagulation factor IX, (nonacog alfa). Recombinant coagulation
factor IX is a single chain glycoprotein with an approximate molecular mass of 55,000 Daltons that is
a member of the serine protease family of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors. Recombinant
coagulation factor IX is a recombinant DNA-based protein therapeutic which has structural and
functional characteristics comparable to endogenous factor IX. Factor IX is activated by
factor VII/tissue factor complex in the extrinsic pathway as well as factor XIa in the intrinsic
coagulation pathway. Activated factor IX, in combination with activated factor VIII, activates
factor X. This results ultimately in the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. Thrombin then
converts fibrinogen into fibrin and a clot can be formed. Factor IX activity is absent or greatly
reduced in patients with haemophilia B and substitution therapy may be required.
Haemophilia B is a sex-linked hereditary disorder of blood coagulation due to decreased levels of
factor IX and results in profuse bleeding into joints, muscles or internal organs, either spontaneously
or as a result of accidental or surgical trauma. By replacement therapy the plasma levels of factor IX
is increased, thereby enabling a temporary correction of the factor deficiency and correction of the
bleeding tendencies.
There are insufficient data to recommend the use of BeneFIX in children less than 6 years of age.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Infusion of BeneFIX into 56 PTP patients (baseline data) with haemophilia B has shown an
in vivo
recovery ranging from 15 to 62% (mean 33.7 ± 10.3%). One International Unit of BeneFIX showed a
mean 0.75 IU/dl (range 0.3 to 1.4 IU/dl) increase in the circulating level of factor IX. The biologic
half-life ranged from 11 to 36 hours (mean of 19.3 ± 5.0 hours).
For a subset of the 56 patients, data are available from baseline to 24 months. The pharmacokinetic
data for these patients at various time points are shown in the following table:
Table 1. Summary of BeneFIX Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Activity Data by Month in
Previously Treated Patients
15.3–62.2
15.3–56.7
16.2–53.1
30.9, 36.4
29.4, 34.3
28.8, 33.7





Table 1. Summary of BeneFIX Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Activity Data by Month in
Previously Treated Patients
FIX increase
(IU/dl per IU/kg)
0.34–1.38
0.34–1.26
0.36–1.18
0.28–1.38
0.36–1.32
0.69, 0.81
0.65, 0.76
0.64, 0.75
0.62, 0.74
0.63, 0.75
Elimination
half-life (h)
11.1–36.4
9.6–38.2
10.6–33.7
10.7–38.3
10.9–42.2
18.0, 20.7
18.1, 21.6
16.8, 20.2
16.8, 21.0
16.8, 20.9
619.8
579.8
575.7
561.8
577.6
605.2
562.2
566.0
560.9
551.7
155.7
146.1
151.0
155.6
154.7
366.5–1072.6
330.9–900.1
290.3–1080.8
254.5–940.8
284.1–1045.4
578.1, 661.5
539.5, 620.1
532.4, 619.1
515.7, 608.0
531.1, 624.1
Half-life
Initial Phase (h)
0.07–5.73
0.12–9.98
0.13–14.34
0.13–6.21
0.11–7.43
1.6,2.5
1.5,3.0
1.5,3.0
1.4,2.6
1.1,2.4
4.66–13.64
5.55–15.11
4.63–17.22
5.31–19.65
4.78–17.60
7.86,8.94
8.53,9.89
8.56,10.01
8.78,10.47
8.52,9.96
24.35,27.60
24.01,27.15
22.75,26.47
22.55,26.94
23.00,27.17
Data exclude those collected from one patient after evidence of inhibitor development was observed at
9 months.
AUC
0 -
= Area Under the Curve
MRT = Mean Residence Time
SD = Standard Deviation
CI = Confidence Interval
15.81–46.09
13.44–42.26
14.83–38.75
15.30–50.75
15.65–47.52
A 28% lower recovery of BeneFIX in comparison to plasma-derived Factor IX was shown.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of BeneFIX have also been determined after single and multiple
intravenous doses in different species. The pharmacokinetic parameters obtained in studies comparing
BeneFIX to plasma-derived Factor IX were similar to those obtained in human studies. Structural
differences of BeneFIX compared with plasma-derived Factor IX appear to contribute to the different
recovery compared to plasma-derived Factor IX.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of genotoxicity.





No investigations on carcinogenicity, fertility impairment and foetal development have been
conducted.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Powder
Sucrose
Glycine
L-Histidine
Polysorbate 80
Solvent
Sodium chloride solution
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other
medicinal products. Only the provided infusion set should be used. Treatment failure can occur as a
consequence of human coagulation factor IX adsorption to the internal surfaces of some infusion
equipment.
The reconstituted product should be used immediately, but no longer than 3 hours after reconstitution.
Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 3 hours at temperatures up to 25
o
C.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store and transport refrigerated (2C - 8C). Do not freeze, in order to prevent damage to the prefilled
syringe.
For the purpose of ambulatory use the product may be removed from refrigerated storage for one
single period of maximum 6 months at room temperature (up to 30 ºC). At the end of this period, the
product should not be put back in the refrigerator, but should be used or discarded.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
1000 IU of powder in a 10 ml vial (type 1 glass) with a stopper (chlorobutyl) and a flip-off seal
(aluminium) and 5 ml of solvent in a prefilled syringe (type 1 glass) with a plunger stopper
(bromobutyl), a tip-cap (bromobutyl) and a sterile vial adapter reconstitution device, a sterile infusion
set, two alcohol swabs, a plaster, and a gauze pad.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
BeneFIX is administered by intravenous (IV) injection after reconstitution of the lyophilised powder
for injection with the supplied solvent (0.234% w/v sodium chloride solution) in the pre-filled
syringe.
BeneFIX, when reconstituted, contains polysorbate-80, which is known to increase the rate of
di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) extraction from polyvinyl chloride (PVC). This should be
considered during the preparation and administration of BeneFIX. It is important that the
recommendations in section 4.2 be followed closely.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
The product does not contain a preservative, and the reconstituted solution should be used
immediately or within 3 hours after reconstitution.
Because the use of BeneFIX by continuous infusion has not been evaluated, BeneFIX should not be
mixed with infusion solutions or be given in a drip.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Wyeth Europa Ltd.
Huntercombe Lane South
Taplow, Maidenhead
Berkshire, SL6 0PH
United Kingdom
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 27 August 1997
Date of last renewal: 27 August 2007
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European
Medicines Agency (EMEA) http://www.emea.europa.eu
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
BeneFIX 2000 IU powder and solvent for solution for injection.
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each vial contains nominally 2000 IU nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX). After
reconstitution with the accompanying 5 ml (0.234%) sodium chloride solution for injection, each ml
of the solution contains approximately 400 IU nonacog alfa.
The potency (IU) is determined using the European Pharmacopoeia one-stage clotting assay. The
specific activity of BeneFIX is not less than 200 IU/mg protein.
BeneFIX contains recombinant coagulation factor IX, (INN = nonacog alfa). Nonacog alfa is a
purified protein that has 415 amino acids in a single chain. It has a primary amino acid sequence that
is comparable to the Ala
148
allelic form of plasma-derived factor IX, and some post-translational
modifications of the recombinant molecule are different from those of the plasma-derived molecule.
Recombinant coagulation factor IX is a glycoprotein that is secreted by genetically engineered
mammalian cells derived from a Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line.
Each vial contains 40 mg sucrose.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
White/almost white powder and clear and colourless solvent for solution for injection.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
T
reatment and prophylaxis of bleeding in patients with haemophilia B (congenital factor IX
deficiency).
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Treatment should be initiated under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of
haemophilia.
The dosage and duration of the substitution therapy depends on the severity of the factor IX
deficiency, the location and extent of bleeding, and the patient's clinical condition. Dosing of
BeneFIX may differ from that of plasma-derived factor IX products.
To ensure that the desired factor IX activity level has been achieved, precise monitoring using the
factor IX activity assay is advised and doses should be calculated taking the factor IX activity,
pharmacokinetic parameters such as half-life and recovery, as well as the clinical situation into
consideration in order to adjust the dose as appropriate.
The amount to be administered and the frequency of administration should always be oriented to the
clinical effectiveness in the individual case. Factor IX products rarely require to be administered
more than once daily.
The number of units of factor IX administered is expressed in International Units (IU), which are
related to the current WHO standard for factor IX products. Factor IX activity in plasma is expressed
either as a percentage (relative to normal human plasma) or in International Units (relative to an
international standard for factor IX in plasma).
One International Unit (IU) of factor IX activity is equivalent to that quantity of factor IX in one ml of
normal human plasma. Estimation of the required dose of BeneFIX can be based on the finding that
one unit of factor IX activity per kg body weight is expected to increase the circulating level of
factor IX, an average of 0.8 IU/dl (range from 0.4 to 1.4 IU/dl) in adult patients ( 15 years).
Pharmacokinetics have to be assessed regularly in each patient and posology has to be adjusted
accordingly.
The required dosage is determined using the following formula:
Number of
factor IX IU
required
X desired factor IX
increase (%) or (IU/dl)
X reciprocal of
observed recovery
For a recovery 0.8 IU/dl (average increase of factor IX), then:
Number of
factor IX IU
required
X desired factor IX
increase (%) or (IU/dl)
In the case of the following haemorrhagic events, the factor IX activity should not fall below the
given plasma activity levels (in % of normal or in IU/dl) in the corresponding period. The following
table can be used to guide dosing in bleeding episodes and surgery:
Degree of haemorrhage/Type
of surgical procedure
Factor IX level
required (%) or
(IU/dl)
Frequency of doses (hours)/Duration of
Therapy (days)
Early haemarthrosis, muscle
bleeding or oral bleeding
Repeat every 24 hours. At least 1 day,
until the bleeding episode as indicated by
pain is resolved or healing is achieved.
More extensive haemarthrosis,
muscle bleeding or haematoma
Repeat infusion every 24 hours for 3-4
days or more until pain and acute
disability are resolved.
Life-threatening haemorrhages
Repeat infusion every 8 to 24 hours until
threat is resolved.
Minor:
Including tooth extraction
Every 24 hours, at least
1 day, until healing is achieved.
80-100
(pre- and
postoperative)
Repeat infusion every 8-24 hours until
adequate wound healing, then therapy for
at least another 7 days to maintain a
factor IX activity of 30% to 60% (IU/dl)


During the course of treatment, appropriate determination of factor IX levels is advised to guide the
dose to be administered and the frequency of repeated infusions. In the case of major surgical
interventions in particular, precise monitoring of the substitution therapy by means of coagulation
analysis (plasma factor IX activity) is indispensable. Individual patients may vary in their response to
factor IX, achieving different levels of
in vivo
recovery and demonstrating different half-lives.
For long term prophylaxis against bleeding in patients with severe haemophilia B, BeneFIX may be
administered. In a clinical study for routine secondary prophylaxis the average dose for previously
treated patients (PTP) was 40 IU/kg (range 13 to 78 IU/kg) at intervals of 3 to 4 days. In younger
patients, shorter dosage intervals or higher doses may be necessary.
There are insufficient data to recommend the use of BeneFIX in children less than 6 years of age. In
clinical studies, 57% of the paediatric patients increased their doses due to lower than expected
recovery or to obtain sufficient therapeutic response or both, some to an average dose of >50 IU/kg.
Therefore, close monitoring of factor IX plasma activity should be performed, as well as calculation
of pharmacokinetic parameters such as recovery and half-life, as clinically indicated, in order to adjust
doses as appropriate. If doses >100 IU/kg have been repeatedly needed during routine prophylaxis or
treatment, a switch to another FIX product should be considered.
Patients should be monitored for the development of factor IX inhibitors. If the expected factor IX
activity plasma levels are not attained, or if bleeding is not controlled with an appropriate dose,
biological testing should be performed to determine if a factor IX inhibitor is present.
In patients with high levels of inhibitor factor IX therapy may not be effective and other therapeutic
options must be considered. Management of such patients should be directed by physicians with
experience in the care of patients with haemophilia. See also section 4.4.
BeneFIX is administered by intravenous infusion after reconstitution of the lyophilised powder for
solution for injection with sterile 0.234% sodium chloride solution (see section 6.6).
BeneFIX should be administered at a slow infusion rate. In most of the cases, an infusion rate of up to
4 ml per minute has been used. The rate of administration should be determined by the patient’s
comfort level.
Administration by continuous infusion has not been approved and is not recommended (see also
sections 4.4, 4.8 and 6.6).
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
Known allergic reaction to hamster proteins.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Activity-neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) are an uncommon event in previously treated patients
(PTPs) receiving factor IX-containing products. Since during clinical studies one PTP treated with
BeneFIX developed a clinically relevant low responding inhibitor and experience on antigenicity with
recombinant factor IX is still limited, patients treated with BeneFIX should be carefully monitored for
the development of factor IX inhibitors that should be titrated in Bethesda Units using appropriate
biological testing.
Sufficient data have not been obtained from ongoing clinical studies on the treatment of previously
untreated patients (PUPs), with BeneFIX. Additional safety and efficacy studies in paediatric patients
are ongoing in previously treated, minimally treated, and previously untreated paediatric patients.
Clinical studies of BeneFIX did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to
determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. As with any patient receiving
BeneFIX, dose selection for an elderly patient should be individualised.
As with any intravenous protein product, allergic-type hypersensitivity reactions are possible. The
product contains traces of hamster proteins. Potentially life-threatening anaphylactic/anaphylactoid
reactions have occurred with factor IX products, including BeneFIX. Patients should be informed of
early signs of hypersensitivity reactions including difficult breathing, shortness of breath, swelling,
hives, itching, tightness of the chest, bronchospasm, laryngospasm, wheezing, hypotension, blurred
vision, and anaphylaxis.
If allergic or anaphylactic-type reactions occur, the administration of BeneFIX has to be discontinued
immediately and an appropriate treatment has to be initiated. In some cases, these reactions have
progressed to severe anaphylaxis. In the case of shock, the current medical standards for treatment of
shock should be observed. In case of severe allergic reactions, alternative haemostatic measures
should be considered.
There have been reports in the literature showing a correlation between the occurrence of a factor IX
inhibitor and allergic reactions. Therefore, patients experiencing allergic reactions should be
evaluated for the presence of an inhibitor. It should be noted that patients with factor IX inhibitors
may be at an increased risk of anaphylaxis with subsequent challenge with factor IX. Preliminary
information suggests a relationship may exist between the presence of major deletion mutations in a
patient's
factor IX gene and an increased risk of inhibitor formation and of acute hypersensitivity
reactions. Patients known to have major deletion mutations of the factor IX gene should be observed
closely for signs and symptoms of acute hypersensitivity reactions, particularly during the early
phases of initial exposure to product.
Because of the risk of allergic reactions with factor IX concentrates, the initial administrations of
factor IX should, according to the treating physician’s judgement, be performed under medical
observation where proper medical care for allergic reactions could be provided.
Posology has to be adjusted according to the pharmacokinetics of each patient.
Although BeneFIX contains only factor IX, the risk of thrombosis and disseminated intravascular
coagulation (DIC) should be recognised. Since the use of factor IX complex concentrates has
historically been associated with the development of thromboembolic complications, the use of
factor IX-containing products may be potentially hazardous in patients with signs of fibrinolysis and
in patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Because of the potential risk of
thrombotic complications, clinical surveillance for early signs of thrombotic and consumptive
coagulopathy should be initiated with appropriate biological testing when administering this product
to patients with liver disease, to patients post-operatively, to neonates, or to patients at risk of
thrombotic phenomena or DIC. In each of these situations, the benefit of treatment with BeneFIX
should be weighed against the risk of these complications.
The safety and efficacy of BeneFIX administration by continuous infusion have not been established
(see also sections 4.2 and 4.8). There have been post-marketing reports of thrombotic events,
including life-threatening superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome in critically ill neonates, while
receiving continuous-infusion BeneFIX through a central venous catheter (see also section 4.8).
There have been reports of agglutination of red blood cells in the tube/syringe with the administration
of BeneFIX. So far, no clinical sequelae have been reported in association with this observation. To
minimize the possibility of agglutination, it is important to limit the amount of blood entering the
tubing. Blood should not enter the syringe. If agglutination of red blood cells in the tubing/syringe is
observed, discard all this material (tubing, syringe and BeneFIX solution) and resume administration
with a new package.
Nephrotic syndrome has been reported following attempted immune tolerance induction in
haemophilia B patients with Factor IX inhibitors and a history of allergic reaction. The safety and
efficacy of using BeneFIX for immune tolerance induction has not been established.
In the interest of patients, it is recommended that, whenever possible, every time that BeneFIX is
administered to them, the name and batch number of the product is registered.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No interaction studies have been performed.
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with factor IX. Based on the rare occurrence of
haemophilia B in women, experience regarding the use of factor IX during pregnancy and
breastfeeding is not available. Therefore, factor IX should be used during pregnancy and
breast-feeding only if clearly indicated.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
To date, no adverse reactions reported in association with BeneFIX occurred with a frequency of
1/100 to <1/10 (common). The frequency of adverse reactions reported in association with BeneFIX
would be categorized as uncommon (1/1,000 to 1/100) or rare (1/10,000 to 1/1,000). Of these
the most significant include: anaphylaxis, cellulitis, phlebitis, and neutralising antibodies.
Adverse reactions based on experience from clinical trials and postmarketing experience are presented
below by system organ class and frequency of occurrence. Within each frequency grouping,
undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness. These frequencies have been
estimated on a per-infusion basis and are described using the following categories: uncommon
(1/1,000 to 1/100); rare (1/10,000 to 1/1,000).
Uncommon: Dizziness, headache, altered taste, lightheadedness
Gastrointestinal disorders
General disorders and administration site conditions
Uncommon: Cellulitis, phlebitis, injection site reaction (including burning infusion site and
injection site stinging), injection site discomfort
Uncommon: Neutralising antibodies (factor IX inhibition)*
Rare:
Hypersensitivity/allergic reactions; such reactions may include anaphylaxis*,
bronchospasm/respiratory distress (dyspnoea), hypotension, angioedema, tachycardia,
chest tightness, urticaria, hives, rash, burning sensation in jaw and skull, chills
(rigors), tingling, flushing, lethargy, restlessness, dry cough/sneezing, blurred vision
* See additional information below.
Hypersensitivity/allergic reactions
Hypersensitivity or allergic reactions have been infrequently observed in patients treated with
factor IX containing products, including BeneFIX. In some cases, these reactions have progressed to
severe anaphylaxis. Allergic reactions have occurred in close temporal association with development
of factor IX inhibitor (see also section 4.4).
The aetiology of the allergic reactions to BeneFIX has not yet been elucidated. These reactions are
potentially life-threatening. If allergic/anaphylactic reactions occur, the administration of BeneFIX
should be discontinued at once. In case of severe allergic reactions, alternative haemostatic measures
should be considered. The treatment required depends on the nature and severity of side-effects (see
also section 4.4).
Due to the production process BeneFIX contains trace amounts of hamster cell proteins.
Hypersensitivity responses can occur.
Patients with haemophilia B may develop neutralising antibodies (inhibitors) to factor IX. If such
inhibitors occur, the condition may manifest itself as an insufficient clinical response. In such cases,
it is recommended that a specialised haemophilia centre be contacted. A clinically relevant, low
responding inhibitor was detected in 1 out of 65 BeneFIX patients (including 9 patients participating
only in the surgery study) who had previously received plasma-derived products. This patient was
able to continue treatment with BeneFIX with no anamnestic rise in inhibitor or anaphylaxis. There
are insufficient data to provide information on inhibitor incidence in PUPs.
Nephrotic syndrome has been reported following high doses of plasma-derived Factor IX to induce
immune tolerance in haemophilia B patients with factor IX inhibitors and a history of allergic
reactions.
In a clinical trial, twelve days after a dose of BeneFIX for a bleeding episode, one hepatitis C
antibody positive patient developed a renal infarct. The relationship of the infarct to prior
administration of BeneFIX is uncertain. The patient continued to be treated with BeneFIX.
There have been post-marketing reports of thrombotic events, including life-threatening SVC
syndrome in critically ill neonates, while receiving continuous-infusion BeneFIX through a central
venous catheter. Cases of peripheral thrombophlebitis and deep venous thrombosis have also been
reported; in most of these cases, BeneFIX was administered via continuous infusion, which is not an
approved method of administration (see also sections 4.2 and 4.4).
Inadequate therapeutic response and inadequate factor IX recovery
Inadequate therapeutic response and inadequate factor IX recovery have been reported during the
post-marketing use of BeneFIX (see also section 4.2).
If any adverse reaction takes place that is thought to be related to the administration of BeneFIX, the
rate of infusion should be decreased or the infusion stopped.
No case of overdose has been reported.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: antihaemorrhagic Blood Coagulation Factor IX; ATC code: B02BD09
BeneFIX contains recombinant coagulation factor IX, (nonacog alfa). Recombinant coagulation
factor IX is a single chain glycoprotein with an approximate molecular mass of 55,000 Daltons that is
a member of the serine protease family of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors. Recombinant
coagulation factor IX is a recombinant DNA-based protein therapeutic which has structural and
functional characteristics comparable to endogenous factor IX. Factor IX is activated by
factor VII/tissue factor complex in the extrinsic pathway as well as factor XIa in the intrinsic
coagulation pathway. Activated factor IX, in combination with activated factor VIII, activates
factor X. This results ultimately in the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. Thrombin then
converts fibrinogen into fibrin and a clot can be formed. Factor IX activity is absent or greatly
reduced in patients with haemophilia B and substitution therapy may be required.
Haemophilia B is a sex-linked hereditary disorder of blood coagulation due to decreased levels of
factor IX and results in profuse bleeding into joints, muscles or internal organs, either spontaneously
or as a result of accidental or surgical trauma. By replacement therapy the plasma levels of factor IX
is increased, thereby enabling a temporary correction of the factor deficiency and correction of the
bleeding tendencies.
There are insufficient data to recommend the use of BeneFIX in children less than 6 years of age.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Infusion of BeneFIX into 56 PTP patients (baseline data) with haemophilia B has shown an
in vivo
recovery ranging from 15 to 62% (mean 33.7 ± 10.3%). One International Unit of BeneFIX showed a
mean 0.75 IU/dl (range 0.3 to 1.4 IU/dl) increase in the circulating level of factor IX. The biologic
half-life ranged from 11 to 36 hours (mean of 19.3 ± 5.0 hours).
For a subset of the 56 patients, data are available from baseline to 24 months. The pharmacokinetic
data for these patients at various time points are shown in the following table:
Table 1. Summary of BeneFIX Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Activity Data by Month in
Previously Treated Patients
15.3–62.2
15.3–56.7
16.2–53.1
30.9, 36.4
29.4, 34.3
28.8, 33.7



Table 1. Summary of BeneFIX Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Activity Data by Month in
Previously Treated Patients
FIX increase
(IU/dl per IU/kg)
0.34–1.38
0.34–1.26
0.36–1.18
0.28–1.38
0.36–1.32
0.69, 0.81
0.65, 0.76
0.64, 0.75
0.62, 0.74
0.63, 0.75
Elimination
half-life (h)
11.1–36.4
9.6–38.2
10.6–33.7
10.7–38.3
10.9–42.2
18.0, 20.7
18.1, 21.6
16.8, 20.2
16.8, 21.0
16.8, 20.9
619.8
579.8
575.7
561.8
577.6
605.2
562.2
566.0
560.9
551.7
155.7
146.1
151.0
155.6
154.7
366.5–1072.6
330.9–900.1
290.3–1080.8
254.5–940.8
284.1–1045.4
578.1, 661.5
539.5, 620.1
532.4, 619.1
515.7, 608.0
531.1, 624.1
Half-life
Initial Phase (h)
0.07–5.73
0.12–9.98
0.13–14.34
0.13–6.21
0.11–7.43
1.6,2.5
1.5,3.0
1.5,3.0
1.4,2.6
1.1,2.4
4.66–13.64
5.55–15.11
4.63–17.22
5.31–19.65
4.78–17.60
7.86,8.94
8.53,9.89
8.56,10.01
8.78,10.47
8.52,9.96
24.35,27.60
24.01,27.15
22.75,26.47
22.55,26.94
23.00,27.17
Data exclude those collected from one patient after evidence of inhibitor development was observed at
9 months.
AUC
0 -
=
Area Under the Curve
MRT = Mean Residence Time
SD = Standard Deviation
CI = Confidence Interval
15.81–46.09
13.44–42.26
14.83–38.75
15.30–50.75
15.65–47.52
A 28% lower recovery of BeneFIX in comparison to plasma-derived Factor IX was shown.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of BeneFIX have also been determined after single and multiple
intravenous doses in different species. The pharmacokinetic parameters obtained in studies comparing
BeneFIX to plasma-derived Factor IX were similar to those obtained in human studies. Structural
differences of BeneFIX compared with plasma-derived Factor IX appear to contribute to the different
recovery compared to plasma-derived Factor IX.





5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of genotoxicity.
No investigations on carcinogenicity, fertility impairment and foetal development have been
conducted.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Powder
Sucrose
Glycine
L-Histidine
Polysorbate 80
Solvent
Sodium chloride solution
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other
medicinal products. Only the provided infusion set should be used. Treatment failure can occur as a
consequence of human coagulation factor IX adsorption to the internal surfaces of some infusion
equipment.
The reconstituted product should be used immediately, but no longer than 3 hours after reconstitution.
Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 3 hours at temperatures up to 25
o
C.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store and transport refrigerated (2C - 8C). Do not freeze, in order to prevent damage to the prefilled
syringe.
For the purpose of ambulatory use the product may be removed from refrigerated storage for one
single period of maximum 6 months at room temperature (up to 30 ºC). At the end of this period, the
product should not be put back in the refrigerator, but should be used or discarded.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
2000 IU of powder in a 10 ml vial (type 1 glass) with a stopper (chlorobutyl) and a flip-off seal
(aluminium) and 5 ml of solvent in a prefilled syringe (type 1 glass) with a plunger stopper
(bromobutyl), a tip-cap (bromobutyl) and a sterile vial adapter reconstitution device, a sterile infusion
set, two alcohol swabs, a plaster, and a gauze pad.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
BeneFIX is administered by intravenous (IV) injection after reconstitution of the lyophilised powder
for injection with the supplied solvent (0.234% w/v sodium chloride solution) in the pre-filled
syringe.
BeneFIX, when reconstituted, contains polysorbate-80, which is known to increase the rate of
di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) extraction from polyvinyl chloride (PVC). This should be
considered during the preparation and administration of BeneFIX. It is important that the
recommendations in section 4.2 be followed closely.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
The product does not contain a preservative, and the reconstituted solution should be used
immediately or within 3 hours after reconstitution.
Because the use of BeneFIX by continuous infusion has not been evaluated, BeneFIX should not be
mixed with infusion solutions or be given in a drip.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Wyeth Europa Ltd.
Huntercombe Lane South
Taplow, Maidenhead
Berkshire, SL6 0PH
United Kingdom
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 27 August 1997
Date of last renewal: 27 August 2007
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines
Agency (EMEA) http://www.emea.europa.eu
ANNEX II
A.
MANUFACTURER OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE
SUBSTANCE AND MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION
HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH RELEASE
B.
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
A. MANUFACTURER OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE SUBSTANCE AND
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer of the biological active substance
Wyeth BioPharma
One Burtt Road
Andover MA 01810
USA
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
Wyeth Farma S.A.
Autovia del Norte. A-1, Km. 23. Desvio Algete, Km. 1, 28700 S. Sebastian de los Reyes, Madrid
Spain
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to restricted medical prescription (See Annex I: Summary of Product
Characteristics, section 4.2).
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
The
Marketing Authorisation Holder (
MAH) shall ensure that, at launch, all physicians who are
expected to prescribe/use BeneFIX are provided with an Educational pack containing the following:
Physician information pack
Patient information pack
Both information packs are to be used as part of an educational plan provided to minimise risk of
medication errors that may be associated with transition to reformulated BeneFIX and a new strength
of BeneFIX.
The physician information pack should contain the following key elements:
Summary of product characteristics, including highlighted changes that have been made for
reformulated BeneFIX
Clear demarcation of reformulated BeneFIX from original BeneFIX, with clear descriptions of
new EU-specific packaging for reformulated BeneFIX.
Training kit and instructions on step-by-step use of the R2 reconstitution kit.
Transition management information regarding administration of new reformulated BeneFIX,
prohibition of mixing up with current BeneFIX, and information about use of the new 2000 IU
dosage vial.
Information regarding the changed solvent type from sterile water to 0.234% normal saline, and
regarding reduced solvent volume for some dosage vials. Together with highlighting of the
correct technique of application this should aim at risk minimisation of red blood cell
agglutination.
The patient information pack to be used by health care professionals in education of the patients:
Patient information leaflet
Visualisation material for correct reconstitution and administration of the product
Instructions to patients to deplete their supply of current BeneFIX through their usual usage
schedule before starting reformulated BeneFIX. This will involve using vials of original
BeneFIX product along with the appropriate use of accompanying original BeneFIX sterile
water solvent.
Instructions that patients should not mix vials of current and reformulated product for a given
dose prior to transition to the new reformulated BeneFIX, and necessity not to mix up these two
products.
Pharmacovigilance system
The MAH must ensure that the system of pharmacovigilance, presented in Module 1.8.1. of the
Marketing Authorisation, is in place and functioning before and whilst the product is on the market.
Risk Management Plan
The MAH commits to performing the studies and additional pharmacovigilance activities detailed in
the Pharmacovigilance Plan, as agreed in version 3 of the Risk Management Plan (RMP) presented in
Module 1.8.2. of the Marketing Authorisation Application and any subsequent updates of the RMP
agreed by the CHMP.
As per the CHMP Guideline on Risk Management Systems for medicinal products for human use, the
updated RMP should be submitted at the same time as the next Periodic Safety Update Report
(PSUR).
In addition, an updated RMP should be submitted
•
When new information is received that may impact on the current Safety Specification,
Pharmacovigilance Plan or risk minimisation activities
Within 60 days of an important (pharmacovigilance or risk minimisation) milestone being
reached
At the request of the EMEA
The MAH will submit yearly PSURs unless otherwise specified by the CHMP.
ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
OUTER CARTON
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
BeneFIX 250 IU powder and solvent for solution for injection
Nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX)
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains nominally 250 IU nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX). After
reconstitution with the accompanying 5 ml (0.234%) sodium chloride solution for injection, each ml
of the solution contains approximately 50 IU nonacog alfa.
Sucrose, Glycine, L-histidine, sodium chloride and Polysorbate 80.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
One vial with powder for solution for injection contains nonacog alfa 250 IU and excipients.
One pre-filled syringe of solvent, 5 ml sterile 0.234% sodium chloride solution for injection for
reconstitution, with one plunger rod
One sterile vial adapter reconstitution device
One sterile infusion set
Two alcohol swabs
One plaster
One gauze pad
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
For intravenous use, single use administration only.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
Use only the pre-filled syringe of solvent provided in the box for reconstitution.























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store and transport refrigerated (2°C - 8°C). In order to prevent damage to the prefilled syringe, do
not freeze it.
BeneFIX powder for solution for injection can be stored below 30ºC for up to 6 months, without
being refrigerated again during this period and must be discarded if not used after this.
Date of setting at temperature not exceeding 30°C:
Date to which the vial must be withdrawn:
Use immediately or within 3 hours of reconstitution.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Wyeth Europa Ltd.
Huntercombe Lane South
Taplow, Maidenhead
Berkshire, SL6 0PH
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.





















MINIMUM PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON SMALL IMMEDIATE PACKAGING UNITS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
BeneFIX 250 IU powder for solution for injection
Nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX)
Intravenous use
See front label (Lot, Exp., Pot.)
CONTENTS BY WEIGHT, BY VOLUME OR BY UNIT
Store in a refrigerator (2-8 ºC).
Use only the pre-filled syringe provided in the box for reconstitution.



















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
BeneFIX 500 IU powder and solvent for solution for injection
Nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX)
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains nominally 500 IU nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX). After
reconstitution with the accompanying 5 ml (0.234%) sodium chloride solution for injection, each ml
of the solution contains approximately 100 IU nonacog alfa
Sucrose, Glycine, L-histidine, sodium chloride and Polysorbate 80.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
One vial with powder for solution for injection contains nonacog alfa 500 IU and excipients.
One pre-filled syringe of solvent, 5 ml sterile 0.234% sodium chloride solution for injection for
reconstitution, with one plunger rod
One sterile vial adapter reconstitution device
One sterile infusion set
Two alcohol swabs
One plaster
One gauze pad
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
For intravenous use, single use administration only.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
Use only the pre-filled syringe of solvent provided in the box for reconstitution.

























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store and transport refrigerated (2°C - 8°C). In order to prevent damage to the prefilled syringe, do
not freeze it.
BeneFIX powder for solution for injection can be stored below 30ºC for up to 6 months, without
being refrigerated again during this period and must be discarded if not used after this.
Date of setting at temperature not exceeding 30°C:
Date to which the vial must be withdrawn:
Use immediately or within 3 hours of reconstitution.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Wyeth Europa Ltd.
Huntercombe Lane South
Taplow, Maidenhead
Berkshire, SL6 0PH
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
























MINIMUM PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON SMALL IMMEDIATE PACKAGING UNITS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
BeneFIX 500 IU powder for solution for injection
Nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX)
Intravenous use
See front label (Lot, Exp., Pot.)
CONTENTS BY WEIGHT, BY VOLUME OR BY UNIT
Store in a refrigerator (2-8 ºC).
Use only the pre-filled syringe provided in the box for reconstitution.



















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
BeneFIX 1000 IU powder and solvent for solution for injection
Nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX)
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains nominally 1000 IU nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX). After
reconstitution with the accompanying 5 ml (0.234%) sodium chloride solution for injection, each ml
of the solution contains approximately 200 IU nonacog alfa
Sucrose, Glycine, L-histidine, sodium chloride and Polysorbate 80.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
One vial with powder for solution for injection contains nonacog alfa 1000 IU and excipients..
One pre-filled syringe of solvent, 5 ml sterile 0.234% sodium chloride solution for injection for
reconstitution, with one plunger rod
One sterile vial adapter reconstitution device
One sterile infusion set
Two alcohol swabs
One plaster
One gauze pad
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
For intravenous use, single use administration only.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
Use only the pre-filled syringe of solvent provided in the box for reconstitution.























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store and transport refrigerated (2°C - 8°C). In order to prevent damage to the prefilled syringe, do
not freeze it.
BeneFIX powder for solution for injection can be stored below 30ºC for up to 6 months, without
being refrigerated again during this period and must be discarded if not used after this.
Date of setting at temperature not exceeding 30°C:
Date to which the vial must be withdrawn:
Use immediately or within 3 hours of reconstitution.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Wyeth Europa Ltd.
Huntercombe Lane South
Taplow, Maidenhead
Berkshire, SL6 0PH
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.























16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE



MINIMUM PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON SMALL IMMEDIATE PACKAGING UNITS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
BeneFIX 1000 IU powder for solution for injection
Nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX)
Intravenous use
See front label (Lot, Exp., Pot.)
CONTENTS BY WEIGHT, BY VOLUME OR BY UNIT
Store in a refrigerator (2-8 ºC).
Use only the pre-filled syringe provided in the box for reconstitution.



















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
OUTER CARTON
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
BeneFIX 2000 IU powder and solvent for solution for injection
Nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX)
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains nominally 2000 IU nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX). After
reconstitution with the accompanying 5 ml (0.234%) sodium chloride solution for injection, each ml
of the solution contains approximately 400 IU nonacog alfa.
Sucrose, Glycine, L-histidine, sodium chloride and Polysorbate 80.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
One vial with powder for solution for injection contains nonacog alfa 2000 IU and excipients.
One pre-filled syringe of solvent, 5 ml sterile 0.234% sodium chloride solution for injection for
reconstitution, with one plunger rod
One sterile vial adapter reconstitution device
One sterile infusion set
Two alcohol swabs
One plaster
One gauze pad
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
For intravenous use, single use administration only.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
Use only the pre-filled syringe of solvent provided in the box for reconstitution.























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store and transport refrigerated (2°C - 8°C). In order to prevent damage to the prefilled syringe, do
not freeze it.
BeneFIX powder for solution for injection can be stored below 30ºC for up to 6 months, without
being refrigerated again during this period and must be discarded if not used after this.
Date of setting at temperature not exceeding 30°C:
Date to which the vial must be withdrawn:
Use immediately or within 3 hours of reconstitution.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Wyeth Europa Ltd.
Huntercombe Lane South
Taplow, Maidenhead
Berkshire, SL6 0PH
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.























16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE



MINIMUM PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON SMALL IMMEDIATE PACKAGING UNITS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
BeneFIX 2000 IU powder for solution for injection
Nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX)
Intravenous use
See front label (Lot, Exp., Pot.)
CONTENTS BY WEIGHT, BY VOLUME OR BY UNIT
Store in a refrigerator (2-8 ºC).
Use only the pre-filled syringe provided in the box for reconstitution.



















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
BeneFIX 250 IU powder and solvent for solution for injection
BeneFIX 500 IU powder and solvent for solution for injection
BeneFIX 1000 IU powder and solvent for solution for injection
BeneFIX 2000 IU powder and solvent for solution for injection
Nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX)
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine.
-
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
-
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or your pharmacist.
-
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if
their symptoms are the same as yours.
-
If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
What BeneFIX is and what it is used for
WHAT IS BENEFIX AND WHAT IS IT USED FOR
BeneFIX is a coagulation factor IX product that is produced by recombinant technology. Patients with
haemophilia B (Christmas disease) are deficient in coagulation factor IX. BeneFIX works by
replacing factor IX in haemophilia B patients to enable their blood to clot.
BeneFIX is used for the treatment and prevention of bleeding (prophylaxis) in patients with
haemophilia B (congenital factor IX deficiency).
- If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to nonacog alfa or any of the other ingredients of BeneFIX.
-
If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to hamster proteins.
Take special care with BeneFIX
See your doctor immediately if your bleeding does not stop as expected.
Activity-neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) are an uncommon event in previously treated
patients (PTPs) receiving factor IX-containing products. Since during clinical studies one PTP
treated with BeneFIX developed a clinically relevant low responding inhibitor, and experience
on antigenicity with recombinant factor IX is still limited, while being treated with BeneFIX
you should be
carefully monitored for the development of factor IX inhibitors. Sufficient data have not been
obtained from ongoing clinical studies on the treatment of previously untreated patients
(PUPs), with BeneFIX.
Clinical studies on BeneFIX did not determine whether patients aged 65 and over respond
differently from younger subjects. As for any patient receiving BeneFIX, if you are elderly
your doctor will choose a specific dose appropriate for you.
As with any intravenous protein product, allergic type hypersensitivity reactions are possible.
The product may contain traces of hamster proteins. Potentially life-threatening anaphylactic
reactions have occurred with factor IX products, including BeneFIX. You will be informed of
early signs of hypersensitivity reactions including difficulty breathing, shortness of breath,
swelling, hives, itching, tightness of the chest, wheezing, low blood pressure, blurred vision and
anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction that can cause difficulty in swallowing and/or breathing,
red or swollen face and/or hands).
If allergic or anaphylactic-type reactions occur, stop the infusion immediately and contact a
doctor or seek emergency medical care immediately. In case of severe allergic reactions,
alternative therapy should be considered.
There have been reports in the literature showing a correlation between the occurrence of a
factor IX inhibitor and allergic reactions. Therefore, if you experience allergic reactions such
as difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, swelling, hives, itching, tightness of the chest,
wheezing, hypotension, or blurred vision, you should be evaluated for the presence of an
inhibitor. It should be noted that patients with factor IX inhibitor may be at an increased risk of
anaphylaxis with subsequent challenge with factor IX.
The production of factor IX in the body is controlled by the factor IX gene. Patients who have
major deletion mutations of their factor IX gene may be more likely to have factor IX inhibitor
and an allergic reaction. Therefore if you are known to have a major deletion mutation of the
factor IX gene, your doctor will monitor you more closely for signs of an allergic reaction
particularly when you first start to take BeneFIX.
Because of the risk of allergic reactions with factor IX concentrates, your initial administrations
of factor IX should, according to the treating physician’s judgement, be performed under
medical observation where proper medical care for allergic reactions can be provided.
Even in the absence of factor IX inhibitor, higher doses of BeneFIX may be needed than
required for plasma-derived factor IX. Therefore, close monitoring of factor IX plasma activity
and pharmacokinetic assessment have to be performed in order to adjust doses as appropriate.
If bleeding is not controlled with the recommended dose, contact your doctor.
If you suffer from a liver or cardiac disease or if you have recently had surgery, there is an
increased risk for coagulation complications.
There have been reports of agglutination of red blood cells in the tube/syringe with the
administration of BeneFIX. So far, no clinical sequelae have been reported in association with
this observation. To minimize the possibility of agglutination, it is important to limit the
amount of blood entering the tubing. Blood should not enter the syringe. If agglutination of red
blood cells in the tubing/syringe is observed, discard all this material (tubing, syringe and
BeneFIX solution) and resume administration with a new package.
A kidney disorder (nephrotic syndrome) has been reported following high doses of plasma-
derived Factor IX to induce immune tolerance in haemophilia B patients with factor IX
inhibitors and a history of allergic reactions.
It is recommended that, whenever possible, every time you use BeneFIX, the name and batch
number of the product is registered.
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines,
including medicines obtained without a prescription.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding you should only take BeneFIX upon specific instructions from
your physician. It is not known whether BeneFIX can affect reproductive capacity or cause foetal
harm when given to pregnant women. Your doctor may advise you to stop treatment with BeneFIX if
you are breast-feeding or become pregnant.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
Always take BeneFIX exactly as your doctor has instructed you. You should check with your doctor
or pharmacist if you are not sure.
Your doctor will decide the dose of BeneFIX you will receive. This dose and duration will depend
upon your individual needs for replacement factor IX therapy and upon pharmacokinetics (recovery
and half-life) that have to be checked regularly. You may notice a difference in the dose you receive
if you are changing from a plasma-derived factor IX product to BeneFIX.
Your doctor may decide to change the dose of BeneFIX you receive during your treatment.
Reconstitution and administration
The procedures below are provided as guidelines for the reconstitution and administration of
BeneFIX. Patients should follow the specific venipuncture procedures provided by their physicians.
BeneFIX is administered by intravenous (IV) injection after reconstitution of the powder for injection
with the supplied solvent (0.234% w/v sodium chloride solution) in the pre-filled syringe.
Always wash your hands prior to performing the following procedures. Aseptic technique (meaning
clean and germ free) should be used during the reconstitution procedure.
BeneFIX will be administered by intravenous infusion (IV) after reconstitution with sterile solvent for
injection.
1.
Allow the vial of lyophilised BeneFIX and the pre-filled syringe to reach room temperature.
2.
Remove the plastic flip-top cap from the BeneFIX vial to expose the central portion of the
rubber stopper.
3.
Wipe the top of the vial with an alcohol swab provided, or use another antiseptic solution and
allow to dry. After cleaning do not touch the rubber stopper with your hand or allow it to touch
any surface.
4.
Peel back the lid from the clear plastic vial adapter package. Do not remove the adapter from
the package.
5.
Place the vial on a flat surface. While holding the adapter in the package, place the vial adapter
over the vial. Press down firmly on the package until the adapter snaps into place on top of the
vial, with the adapter spike penetrating the vial stopper.
6.
Lift the package away from the adapter and discard the package.
7.
Attach the plunger rod to the solvent syringe by pushing and turning firmly.
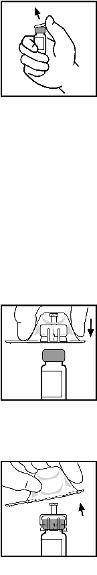
8.
Break off the tamper-resistant plastic tip cap from the solvent syringe by snapping the
perforation of the cap. This is done by bending the cap up and down until the perforation is
broken. Do not touch the inside of the cap or the syringe tip. The cap may need to be replaced
(if not administering reconstituted BeneFIX immediately), so set it aside by placing it on its
top.
9.
Place the vial on a flat surface. Connect the solvent syringe to the vial adapter by inserting the
tip of the syringe into the adapter opening while firmly pushing and turning the syringe
clockwise until the connection is secured.
10. Slowly depress the plunger rod to inject all the solvent into the BeneFIX vial
11. With the syringe still connected to the adapter, gently rotate the vial until the powder is
dissolved.
12. The final solution should be inspected visually for particulate matter before administration. The
solution should appear clear and colourless.
Note: If you use more than one vial of BeneFIX per infusion, each vial should be reconstituted
as per the previous instructions. The solvent syringe should be removed, leaving the vial
adapter in place, and a separate large luer lock syringe may be used to draw back the
reconstituted contents of each individual vial.
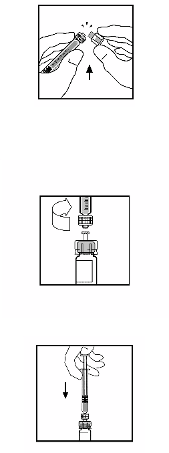

13. Ensuring that the syringe plunger rod is still fully depressed, invert the vial. Slowly draw back
all the solution into the syringe.
14. Detach the syringe from the vial adapter by gently pulling and turning the syringe counter-
clockwise. Discard the vial with the adapter attached.
Note: If the solution is not to be used immediately, the syringe cap should be carefully replaced.
Do not touch the syringe tip or the inside of the cap.
BeneFIX should be administered immediately or within 3 hours after reconstitution. The
reconstituted solution may be stored at room temperature prior to administration.
Administration (Intravenous Injection):
BeneFIX should be administered using the pre-filled solvent syringe provided or a single sterile
disposable plastic luer lock syringe. In addition, the solution should be withdrawn from the vial using
the vial adapter.
BeneFIX should be injected intravenously over several minutes. Your doctor may change your
recommended infusion rate to make the infusion more comfortable.
Because the use of BeneFIX by continuous infusion (drip) has not been evaluated, BeneFIX should
not be mixed with infusion solutions or be given in a drip.
Please dispose of all unused solution, empty vials and used needles and syringes in an appropriate
container for throwing away waste as it may hurt others if not handled properly.
If you take more BeneFIX than you should
Please contact your doctor immediately if you inject more BeneFIX than your doctor recommends.
If you stop taking BeneFIX
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your physician or pharmacist.
Like all medicines, BeneFIX can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Should you experience a significant increase in your usage of BeneFIX in order to control a bleed,
please contact your doctor immediately; your blood should be checked for inhibitors to factor IX
activity.
Possible side effects are listed according to the following categories:
Uncommon: between 1 in 100 and 1 in 1,000 patients
Rare: between 1 in 1,000 and 1 in 10,000 patients

Development of neutralising antibodies (inhibitors)*
Hypersensitivity/allergic reactions; such reactions may include burning sensation
in jaw and skull, chills (rigors), dry cough/sneeze, flushing, lethargy, restlessness,
tingling, hives, itching and rash, low blood pressure, fast heart rate, tightness of the
chest, wheezing, swelling of the throat, anaphylaxis*, rash, blurred vision
Dizziness, headache, altered taste, lightheadedness
Gastrointestinal disorders
General disorders and administration site conditions
Uncommon: Injection site reactions (including burning and stinging at the infusion site),
discomfort
at the IV site, cellulites, phlebitis
* See additional information below.
Hypersensitivity/allergic reactions
Hypersensitivity or allergic reactions have been infrequently observed in patients treated with factor
IX containing products, including BeneFIX. In some cases, these reactions have progressed to severe
anaphylaxis. Allergic reactions have occurred in close temporal association with development of
factor IX inhibitor (see also “Take special care with BeneFIX”).
The aetiology of the allergic reactions to BeneFIX has not yet been elucidated. These reactions are
potentially life-threatening. If allergic/anaphylactic reactions occur, stop the infusion immediately and
contact your doctor or seek emergency medical care immediately. In case of severe allergic reactions,
alternative therapy should be considered. The treatment required depends on the nature and severity
of side-effects (see also “Take special care with BeneFIX”).
Patients with haemophilia B may develop neutralising antibodies (inhibitors) to factor IX. If such
inhibitors occur, the condition may manifest itself as an insufficient clinical response. In such cases,
it is recommended that a specialised haemophilia centre be contacted.
A clinically relevant, low responding inhibitor was detected in 1 out of 65 BeneFIX patients who had
previously received plasma-derived products. This patient was able to continue treatment with
BeneFIX with no rise in inhibitor or anaphylaxis. Patients treated with BeneFIX should be monitored
for inhibitor development.
There are insufficient data to provide information on inhibitor incidence in previously untreated
patients (PUPs).
Due to the production process BeneFIX may contain trace amounts of hamster cell proteins.
Hypersensitivity responses can occur.
A kidney disorder has been reported following high doses of plasma-derived Factor IX to induce
immune tolerance in haemophilia B patients with factor IX inhibitors and a history of allergic
reactions (see also “Take special care with BeneFIX”).
One patient developed severe abdominal pain which was caused by an area of the kidney that lacked
the necessary blood supply (referred to as a renal infarct). The relationship of the infarct to prior
administration of BeneFIX is uncertain.
BeneFIX may increase the risk of thrombosis (abnormal blood clots) in your body if you have risk
factors for developing blood clots, including an indwelling venous catheter, through which BeneFIX
is given by continuous infusion. There have been reports of severe blood clotting events, including
life-threatening blood clots in critically ill neonates, while receiving continuous-infusion BeneFIX
through a central venous catheter. Cases of peripheral thrombophlebitis and deep venous thrombosis
have also been reported; in most of these cases, BeneFIX was administered via continuous infusion,
which is not an approved method of administration.
Inadequate therapeutic response and inadequate factor IX recovery
Inadequate therapeutic response and inadequate factor IX recovery have been reported during the
post-marketing use of BeneFIX.
If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effect not listed in this leaflet, please tell
your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use after the expiry date stated on the outer box and vial label. The expiry date refers to the
last day of that month.
Do not use BeneFIX if the solution is not clear or colourless.
BeneFIX must be stored continuously in a refrigerator at a temperature of 2°C to 8°C and must be
used by the expiry date on the label. For the purpose of ambulatory use the product may be removed
from such storage for one single period of maximum 6 months at room temperature (up to 30°C).
At
the end of this period the product should not be put back in the refrigerator, but should be used or
discarded. The date the product is removed from the refrigerator and set at room temperature (not
exceeding 30
o
C) and the date the vial should be withdrawn should be noted on the outer carton.
Do not freeze in order to prevent damage to the pre-filled syringe.
Use the reconstituted solution immediately or within 3 hours.
Use only the pre-filled syringe provided in the box for reconstitution. Other sterile disposable
syringes may be used for administration.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
The active substance is nonacog alfa (recombinant coagulation factor IX). Each vial of
BeneFIX contains nominally 250, 500, 1000 or 2000 IU of nonacog alfa.
The other ingredients are sucrose, glycine, L-histidine, polysorbate 80. A solvent (0.234%
sodium chloride solution) is also supplied for reconstitution.
After reconstitution with the supplied solvent (0.234% sodium chloride solution), each vial
contains 50, 100, 200 or 400 IU/ml (see Table 1).
Table 1. Strength of BeneFIX per ml prepared solution
Amount of BeneFIX per Vial
Amount of BeneFIX per 1 ml
of prepared solution for
injection
What BeneFIX looks like and contents of the pack
BeneFIX is provided as a powder for injection in a glass vial and a solvent provided in pre-filled
syringe.
The contents of the pack are:
one vial of BeneFIX 250, 500 1000 or 2000 IU powder
one pre-filled syringe of solvent, 5 ml sterile 0.234% sodium chloride solution for injection for
reconstitution, with one plunger rod
one sterile vial adapter reconstitution device
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Wyeth Europa Ltd.
Huntercombe Lane South
Taplow, Maidenhead
Berkshire, SL6 0PH
United Kingdom
Wyeth Farma S.A.
Autovia del Norte. A-1, Km. 23. Desvio Algete, Km. 1, 28700 S. Sebastian de los Reyes, Madrid
Spain








For any information about this medicinal product, please contact the local representative of the
Marketing Authorisation Holder.
België/Belgique/Belgien
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
Pfizer S.A. / N.V.
Tél/Tel: +32 (0)2 554 62 11
Magyarország
Pfizer Kft.
Tel:+36 1 488 3700
България/Eesti/Latvija/Lietuva/
Slovenija
Wyeth Whitehall Export GmbH
Teл./Tel/Tãlr: +43 1 89 1140
Malta
Vivian Corporation Ltd.
Tel:+356 21 344616
Česká republika
Pfizer s.r.o.
Tel: +420-283-004-111
Nederland
Wyeth Pharmaceuticals B.V.
Tel:+31 23 567 2567
Danmark
Pfizer ApS
Tlf: +45 44 201 100
Norge
Pfizer AS
Tlf: +47 67 526 100
Deutschland
Pfizer Pharma GmbH
Tel: +49 (0)30 550055-51000
Österreich
Pfizer Corporation Austria Ges.m.b.H.
Tel: +43 (0)1 521 15-0
Ελλάδα
Pfizer Hellas A.E.
Τηλ.: +30 210 6785 800
Polska
Pfizer Polska Sp. z o.o.
Tel: +48 22 335 61 00
España
Pfizer, S.A.
Télf: +34914909900
Portugal
Laboratórios Pfizer, Lda.
Tel: (+351) 21 423 55 00
France
Pfizer
Tél: +33 1 58 07 30 00
România
Pfizer Romania S.R.L
Tel: +40 (0) 21 207 28 00
Ireland
Wyeth Pharmaceuticals
Tel: +353 1 449 3500
Slovenská republika
Pfizer Luxembourg SARL,
organiza
č
ná zložka
Tel: + 421 2 3355 5500
Ísland
Icepharma hf.
Tel:+354 540 8000
Suomi/Finland
Pfizer Oy
Puh/Tel: +358 (0)9 430 040
Italia
Wyeth Lederle S.p.A.
Tel:+39 06 927151
Sverige
Pfizer AB
Tel: +46 (0)8 550 520 00
Kύπρος
Wyeth Hellas (Cyprus Branch) AEBE
T:+357 22 817690
United Kingdom
Wyeth Pharmaceuticals
Tel:+44 845 367 0098
This leaflet was last approved in
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) web
site: http://www.emea.europa.eu. There are also links to other websites about rare diseases and
treatments.
Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/benefix.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|





















































































































































































































































































































































































































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































