Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Ceplene 0.5 mg/0.5 ml solution for injection
2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
One vial of 0.5 ml of solution contains 0.5 mg of histamine dihydrochloride.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Solution for injection.
Clear, colourless aqueous solution.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Ceplene maintenance therapy is indicated for adult patients with acute myeloid leukaemia in first
remission concomitantly treated with interleukin-2 (IL-2). The efficacy of Ceplene has not been fully
demonstrated in patients older than age 60.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Ceplene maintenance therapy should be administered following completion of consolidation therapy
in patients concomitantly treated with IL-2 under the supervision of a physician experienced in the
management of acute myeloid leukaemia.
For dosing instructions for Ceplene in combination with IL-2, see posology below.
Interleukin-2 (IL-2)
IL-2 is administered twice daily as a subcutaneous injection 1 to 3 minutes prior to the administration
of Ceplene; each dose of IL-2 is 16 400 IU/kg.
Ceplene
0.5 ml solution is sufficient for a single dose (see section 6.6).
Ceplene is administered 1 to 3 minutes after each injection of IL-2. Each 0.5 ml Ceplene dose is
injected slowly, over 5-15 minutes.
Treatment cycles
Ceplene and IL-2 are administered for 10 treatment cycles: each cycle consists of a treatment period
of 21 days (3 weeks) followed by a three-week or six-week treatment-free period.
For cycles 1-3, each cycle consists of 3 weeks of treatment, followed by a 3-week treatment free
period. For cycles 4-10, each cycle consists of 3 weeks of treatment, followed by a 6-week treatment-
free period.
The recommended dosing regimen is presented in Tables 1 and 2.
Table 1
: For treatment cycles 1-3 with Ceplene and IL-2
IL-2 16 400 IU/kg followed by 0.5 ml Ceplene.
Twice daily.
w.4 to w.6 w.10 to w.12 w.16 to w.18
Treatment-free (3 weeks)
*see dose modification for provisions for the modification to dose and dosage schedule
Table 2:
For treatment cycles 4-6 with Ceplene and IL-2, same as for Table 1 above, with the
exception of number of cycles and duration of rest periods
Cycles
4 5 6 7 8 9 10
w.1
9 to
w.2
1
IL-2 16 400 IU/kg followed by 0.5 ml
Ceplene. Twice daily
*see dose modification for provisions for the modification to dose and dosage schedule
Dose modification
Patients should be monitored for the expected symptomatic adverse reactions and laboratory changes
associated with this treatment. Doses of Ceplene and IL-2 should be modified as necessary based on
individual patient tolerance to treatment. It is recommended that dose modifications be addressed
early in treatment. The dose reductions can be temporary or permanent.
Should Ceplene related toxicities occur (such as hypotension, headache), the injection time can be
increased from 5 minutes to a maximum of duration of 15 minutes.
For patients experiencing grade 1 toxicity events:
No altered dose recommendations with the exception of grade 1 neurologic toxicity and grade 1
generalised toxic dermatitis. For the dose recommendations for these grade 1 toxicity events refer to
the relevant sections below:
For patients experiencing grade 1-4 neurologic toxicity
-for grade 1 to 3 toxicity, treatment should be discontinued until grade 0 toxicity event has
been achieved. Treatment should then be resumed at a 20% dose reduction for both Ceplene
and IL-2.
-for grade 4 toxicity, discontinuation of treatment should be considered.
For patients experiencing grade 1-4 generalised toxic dermatitis
-for grade 1 toxicity, the treatment should be delayed for 48 hours or until all symptoms have
been resolved. Treatment should then be resumed using the full dose of Ceplene, but
reducing the IL-2 dose by 20%.
-for grade 2 toxicity, the IL-2 dose should be reduced 50% and only increased to full dose if
the symptoms do not reappear. Ceplene and IL-2 doses should be separated by 60 minutes,
which should be maintained throughout treatment.
-for grade 3 and 4 toxicity, treatment should be discontinued and not resumed until events
have been resolved. Treatment should only be resumed after consideration of risk Î benefit
to the patient.
























For patients experiencing grade 2 (including cardiac function, renal, hepatic) toxicity:
- treatment should be discontinued until the event has returned to grade 1
- the time of injection of the dose of Ceplene should be extended to a maximum of 15
minutes.
- for cardiac, hepatic or renal toxicities the dose should be reduced by 20% for both Ceplene
and IL-2.
For patients experiencing grade 3 and 4 (including hypotension, arrhythmia) toxicities:
- treatment should be discontinued until the event is resolved. A maximum delay of one
treatment cycle can be considered for the resolution of grade 3 and 4 events.
For persistent hypotension, headache, arrhythmia, cardiac, hepatic and renal toxicities:
- the time of injection of the dose of Ceplene should be extended to a maximum of 15
minutes.
- the dose amount of both Ceplene and IL-2 should be reduced by 20%.
- IL-2 can be discontinued for 24 hours and then restarted at a 20% dose reduction level.
Abnormal WBC counts
- the dose of IL-2 can be reduced by 20% for the remaining duration of the treatment course
and if abnormal WBC counts re-occur during the following cycle a permanent IL-2 reduction
is recommended.
Localised toxic dermatitis
- treatment should be discontinued until symptoms resolved. Treatment can be resumed by
administering Ceplene at the full dose and IL-2 at 50%.
Renal impairment:
Patients with renal impairment may be more sensitive to the blood pressure lowering effects of
Ceplene. Although the degree of renal impairment has no demonstrable effect on the pharmacokinetic
disposition of Ceplene, caution is warranted when Ceplene is administered to patients with severe
renal impairment. However, no Ceplene dose reduction is normally required in renally impaired
patients.
Hepatic impairment:
Ceplene should be used with caution in patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment (see
section 5.2). Plasma Ceplene levels are higher in patients with moderate and severe liver impairment,
and these patient groups tend to experience more tachycardia and lower blood pressure after Ceplene
dosing than do patients with normal or mildly affected liver function. Plasma drug levels were not
predictive of adverse effects, however, and effects did not correlate closely with drug exposure. Dose
reduction of Ceplene is normally not required in hepatically impaired patients, but caution should be
used in these patients.
Paediatric Population:
Ceplene is not recommended for use in children below 18 years of age due to a lack of data on safety
and efficacy in this age group (see section 5.1 and 5.2).
Method of administration
For subcutaneous use only.


One to 3 minutes after the subcutaneous
administration of IL-2 has been completed, Ceplene should
be administered by slow subcutaneous injection at a rate not to exceed 0.1 ml (0.1 mg histamine
dihydrochloride) per minute. The usual time for administering a 0.5 ml Ceplene dose is 5 minutes.
To reduce potential adverse reactions, the administration time may be lengthened to a maximum of 15
minutes, see below. Ceplene can be administered via an
ambulatory infusion
syringe pump or by
controlled
manual subcutaneous injection
by syringe with a timer.
The first dose of Ceplene and IL-2 on day 1 of the initiation of the first cycle of treatment should be
administered in the clinic under direct supervision by a physician.
Patient monitoring on day 1 should
include vital signs, including pulse, blood pressure and respiratory rate. If the patient experiences a
significant change in vital signs, the physician should evaluate the status of the patient and continue to
monitor vital signs; these patients should be monitored during subsequent treatments.
Subsequent injections of Ceplene may be self-administered at home by a patient who demonstrates a
good understanding of necessary precautions and who has demonstrated adequate injection skills.
Injections should be preferably administered in a supervised setting in the presence of an adult family
member, friend, or other care provider who is capable of responding appropriately should signs or
symptoms of hypotension occur.
The preferred injection areas are the thighs and the abdomen. Ceplene should not be injected into the
same anatomic region as IL-2.
The twice daily dosing of IL-2 and Ceplene should be separated by a minimum of 6 hours. Patients
should remain at rest for 20 minutes after injection of Ceplene.
•
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
•
Patients with significantly compromised cardiac function, e.g., NYHA Class III/IV.
•
Patients receiving systemic steroid therapy, clonidine and H
2
blocking agents.
•
Patients who have received an allogenic stem cell transplant.
•
During pregnancy.
•
During breast feeding.
4.4 Special warnings and special precautions for use
Ceplene should be administered 1 to 3 minutes after IL-2 administration, and not concomitantly.
•
Rapid subcutaneous injection or injection into a vascular space may result in
severe
hypotension, tachycardia, or syncope.
Treatment with Ceplene in conjunction with IL-2 should be used with caution in patients with poorly
compensated cardiac function. Patients with cardiac disease should be evaluated for ventricular
ejection fraction and wall function by echocardiography or nuclear medicine stress test and then
treated with caution.
•
Patients should be monitored during treatment for possible clinical complications due to
hypotension or hypovolaemia. Ceplene should be administered in the clinic under supervision
of the physician on day 1 of the initial treatment cycle. Patient monitoring on day 1 should
include vital signs, including pulse, blood pressure and respiratory rate.
•
Patient monitoring during subsequent treatment days or cycles should be performed as long as
the patient continues to experience significant changes in vital signs during administration of
Ceplene. If significant hypotension or related symptoms are observed in subsequent treatment
cycles, dose reduction should be initiated and if required, administered in hospital until
responses to treatment allow for home administration.
•
Caution should be used for patients with any of the following: symptomatic peripheral arterial
disease, past or present peptic or oesophageal ulcer disease with a history of bleeding, clinically
significant renal disease and stroke within the last 12 months. Where appropriate,
consideration should be made to providing concomitant treatment with a proton pump inhibitor.
•
Patients with clinically significant infection requiring the use of antibiotics, antifungals, or
antivirals, or who have completed prior anti-infectious therapy within 14 days of starting
treatment should be treated with caution unless the use of antibiotics and antivirals were for
prophylaxis purposes.
•
Patients with a prior history of autoimmune disease (including systemic lupus, inflammatory
bowel disease, psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis) should be treated with caution.
•
Monitoring of laboratory test results is recommended including standard haematological and
blood chemistry tests.
•
Patients receiving the following medicinal products should be treated with caution (see section
4.5)
-Beta-blockers or other anti-hypertensive agents.
-H
1
blocking agents and neuroleptics (anti-psychotics) with H
1
receptor blocking properties.
-Tricyclic anti-depressants that may have H
1
and H
2
receptor blocking properties.
-Monoamine oxidase inhibitors and anti-malarial and anti-trypanosomal agents.
-Neuromuscular blocking agents, narcotic analgesics, and various contrast media.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
While posology differs, when Ceplene is used in conjunction with IL-2, physicians should also refer
to the SmPC for IL-2 and observe the respective medical product interactions.
H
2
receptor antagonists with imidazole structures similar to histamine, e.g., cimetidine, systemic
steroids and clonidine, must not be used during treatment with Ceplene (see section 4.3).
Beta-blockers and other anti-hypertensive agents should be used with caution during treatment with
Ceplene. Concurrent administration of medicinal products with cardiotoxicity or blood pressure
lowering effects may increase the toxicity of Ceplene.
H
1
receptor blocking antihistamines or neuroleptics (anti-psychotics) with H
1
receptor blocking
properties that might decrease efficacy of Ceplene should be avoided.
Tricyclic anti-depressants may have H
1
and H
2
receptor blocking properties and should be avoided.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, anti-malarial, and anti-trypanosomal active substances may alter the
metabolism of Ceplene and should be avoided (see section 4.4).
It has been noted that neuromuscular blocking agents, narcotic analgesics, and various contrast media
can induce the release of endogenous histamine; therefore in patients undergoing diagnostic or
surgical procedures, the additive effect of Ceplene treatment should be considered prior to the
procedure (see section 4.4).
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
For Ceplene, no clinical data on exposed pregnancies are available. Animal studies showed
reproductive toxicity but only at maternotoxic doses, and did not indicate direct harmful effects with
respect to pregnancy, embryonal/foetal development, parturition or postnatal development (see
Section 5.3). Ceplene in conjunction with IL-2 must not be used during pregnancy.
It is unknown whether histamine is excreted in human breast milk. The excretion of histamine in milk
has not been studied in animals, but
at maternotoxic doses in rats, offspring showed slight toxicity
during early lactation (see Section 5.3). Ceplene in conjunction with IL-2 must not be used during
breast-feeding.
No clinical data are available on the effects of Ceplene on fertility. Animal studies revealed no
adverse effects on fertility apart from a slight reduction in implantations and viable foetuses (see
section 5.3). Women of childbearing potential and sexually active men must use effective methods of
contraception during treatment with Ceplene and IL-2.
Refer to the IL-2 SmPC for information on pregnancy and lactation with IL-2.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Ceplene has minor or moderate influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Administration of
Ceplene can cause hypotension and may result in dizziness, light-headedness and blurred vision.
Patients should not drive or operate machines for at least 1 hour after receiving Ceplene.
Adverse reactions were reported to be at least possibly related to IL-2 and Ceplene treatment in
almost all patients in studies in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML).
The most common adverse reactions experienced by 30% or more of patients receiving IL-2 and
Ceplene (listed in descending order of frequency) were: flushing, headache, fatigue, injection site
granuloma, pyrexia and injection site erythema
.
The adverse reactions occurring in at least 5% of patients considered at least possibly related to the
treatment of low-dose IL-2 with Ceplene in AML studies (n=196 for the IL-2 and Ceplene treatment
arm) are listed below by body system organ, class and frequency. Within each frequency grouping,
undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness. Frequencies are defined as very
common (≥ 1/10) and common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10).
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Very common: eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Common: anorexia
Psychiatric disorders
Common: insomnia
Nervous system disorders
Very common: headache, dizziness, dysgeusia
Cardiac disorders
Very common: tachycardia
Common: palpitations
Vascular disorders
Very common: flushing, hypotension
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders
Very common: cough, dyspnoea
Common: nasal congestion
Gastrointestinal disorders
Very common: nausea, dyspepsia, diarrhoea.
Common: vomiting, upper abdominal pain, dry mouth


Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Very common: rash
Common: erythema, increased sweating, night sweats, pruritus
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Very common: arthralgia, myalgia
Common: limb pain, back pain
General disorders and administration site conditions
Very common: injection site granuloma, fatigue, pyrexia, injection site erythema,
feeling hot, injection site reaction, injection site pruritus, influenza like illness, rigors, injection site
inflammation, injection site pain
Common: injection site urticaria, injection site bruising, injection site rash, injection
site swelling, weakness, chest pain
Other oncology (advanced tumour) studies
Ceplene and low dose IL-2 have been investigated in other clinical studies at different doses (1.0 mg
histamine dihydrochloride twice a day) and with different dose regimens of low-dose IL-2 and
interferon-alfa. The following adverse events, not listed above, were reported in at least 5% of
patients and as at least possibly related to the study medicine:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Common: anaemia
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Very common: dry skin
Ear and labyrinth disorders
Common: vertigo
Endocrine disorders
Common: acquired hypothyroidism
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Very common: decreased appetite
Common: dehydration
Psychiatric disorders
Very common: anxiety
Common: depression
Nervous system disorders
Common: paraesthesia
Vascular disorders
Common: hot flushes
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders
Common: wheezing
Gastrointestinal disorders
Common: constipation, abdominal distention, stomatitis
General disorders and administration site conditions
Very common: malaise, oedema peripheral, weight decreased






Common: injection site fibrosis, pain
Administration of Ceplene or IL-2 by rapid infusion or into vascular spaces, at higher doses than the
approved ones, may exaggerate the adverse reactions associated with Ceplene.
5. PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Other cytokines and immunomodulators; ATC code: L03AX14.
Ceplene/IL-2 is an immunotherapy which aims to induce immune-mediated destruction of residual
myeloid leukaemic cells and thereby to prevent relapse of leukaemia. The role of Ceplene is to
protect lymphocytes, in particular NK cells and T cells, which are responsible for the immune-
mediated destruction of residual leukaemic cells. The role of IL-2 is to promote the functions of NK
cells and T cells by activating the anti-leukaemic properties of these cells and by expanding these cell
populations by inducing cell cycle proliferation. The mechanism by which Ceplene improves the anti-
leukaemic function of lymphocytes in AML is not completely established; it is considered to be by
inhibition of reactive oxygen species (ROS or Ðoxygen free radicalsÑ), which are synthesised by
monocytes/macrophages and granulocytes. ROS are known to limit the anti-leukaemic effects of
lymphocyte activators such as IL-2, by triggering dysfunction and death by apoptosis in NK cells and
T cells. Ceplene inhibits NAPDH oxidase which initiates the formation and release of ROS from
phagocytes. By inhibiting oxidase function and reducing ROS production, Ceplene protects IL-2-
activated NK cells and T cells from oxygen free radical-induced inhibition and apoptosis. The
concomitant administration of Ceplene and IL-2 therefore aims to optimise the anti-leukaemic
functions of NK cells and T cells.
There have been 2 clinical studies to evaluate the use of Ceplene in the maintenance of remission in
adult AML patients. Study AML-1 was exploratory, enrolling 39 AML patients in remission to
determine the dose and feasibility of Ceplene administered together with IL-2. Results of this pilot
study were used to design and implement a multi-national phase 3 trial
.
The randomised phase 3 trial
(0201) compared Ceplene+IL-2 treatment to no treatment in 261 patients in first remission (CR1) and
in another 59 patients in subsequent remission after relapse (CR>1). For CR1 patients, the median
duration of leukaemia-free survival increased from 291 days (9.7 months) to 450 days (15 months)
after Ceplene/IL-2 versus no maintenance treatment (ITT, p=0.01. n=261). The number of CR1
patients remaining leukaemia-free for 3 years was 40% after Ceplene+IL-2 versus 26% in patients not
receiving this treatment (p=0.01).
This medicinal product has been authorised under ÐExceptional circumstancesÑ. This means that due
to the rarity of the disease it has not been possible to obtain complete information on this medicinal
product. The European Medicines Agency (EMEA) will review any new information which may
become available every year and this SPC will be updated as necessary.
Pharmacokinetic properties
Histamine is rapidly absorbed after subcutaneous injection. Maximum plasma concentration is
reached approximately 10 minutes after end of subcutaneous infusion. Histamine concentrations and
PK were highly variable across studies, as well as within the normal volunteer and patient groups.
Patients showed a higher degree of variability with respect to systemic exposure as compared to
healthy subjects.
Histamine is eliminated by metabolism in kidney, liver and other tissues. The main enzymes involved
in the metabolism of histamine are HNMT (histamine-N-methyltransferase) and DAO (diamine
oxidase). The metabolites are mainly excreted in urine. The mean half-life was 0.75 to 1.5 hours in
patients.
There are no significant effects of age or weight on the pharmacokinetic properties of histamine.
Clearance of Ceplene is almost twice as high in females resulting in considerably lower systemic
exposure than in males.
It is not known whether histamine crosses the placenta.
Renal impairment
The pharmacokinetics of histamine are similar in healthy volunteers with normal renal function
compared to volunteers with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment. In subjects with severe
renal impairment, there were decreases in systolic and diastolic blood pressure at plasma histamine
concentrations which caused no appreciable decrease in blood pressure in other subjects. Thus,
subjects with severe renal impairment may be more sensitive to the blood pressure lowering effects of
exogenously administered histamine than subjects with normal renal function or subjects with mild or
moderate renal impairment. Although the degree of renal impairment has little effect on the PK
disposition of histamine, caution should be used in the administration of histamine to patients with
severe renal impairment.
Hepatic impairment
A study was performed to measure the PK of histamine in normal volunteers compared to patients
with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment. There were no clinically significant differences
in safety parameters or in pharmacodynamics. Plasma histamine concentrations were highly variable
and were considerably higher in the groups of patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment
(medians 10 and 5 times the normal volunteers respectively). Patients with all degrees of hepatic
impairment may have tachycardia or hypotension for 30-60 minutes after Ceplene+IL-2
administration.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of repeated-dose
toxicity, local tolerance and genotoxicity. Effects in non-clinical studies were observed only at
exposures considered sufficiently in excess of the maximum human exposure, indicating little
relevance to clinical use. No carcinogenicity studies have been performed on Ceplene.
Histamine dihydrochloride was not teratogenic in rats or rabbits at doses resulting in several hundred-
fold greater systemic exposures than the clinical exposure. In female rats dosed before mating to
gestation day 7, slightly reduced numbers of implantations and viable foetuses were found, but
without any dose-response and within the range of historical control data. In the peri-post natal
development study, high doses of histamine dihydrochloride caused maternal toxicity, and the
offspring showed toxicity during lactation (fewer live pups at day 21 compared to lactation at day 4)
but not after weaning.
6. PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Sodium chloride
Sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment)
Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment)
Water for injections
In the absence of compatibility studies this medicinal product should not be mixed with other
medicinal products, diluents or infusion solutions.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
6.5 Nature and contents of container
2 ml type I glass vial, with bromobutyl rubber stopper and flip-off aluminium over seal, containing 0.5
ml of solution (0.70 ml including overfill).
Each carton contains 14 vials.
6.6 Special precaution for disposal and other handling
The vials contain 0.5 ml of solution (0.70 ml including overfill) to facilitate the dose extraction of a
single 0.5 ml dose.
Patients are provided with capped polypropylene syringes and instructed to extract 0.5 ml of solution
into the syringe.
The solution should be visually inspected for particulate matter and discolouration prior to
administration. The solution must be clear and colourless.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
7. MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
EpiCept GmbH
Goethestrasse 4
D-80336 Mnchen
Germany
8. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
9. DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE
AUTHORISATION
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
A. MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH RELEASE
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
C. SPECIFIC OBLIGATIONS TO BE FULFILLED BY THE
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
A. MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
Catalent UK Packaging Ltd
Lancaster Way, Wingates Industrial Park
Westhoughton, Bolton
Lancashire, BL5 3XX
United Kingdom
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
•
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to restricted medical prescription (See Annex I: Summary of Product
Characteristics, section 4.2).
•
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
The MAH must ensure that the system of pharmacovigilance, as described in version 3.0 presented in
Module 1.8.1. of the Marketing Authorisation Application, is in place and functioning before and
whilst the product is on the market.
The MAH commits to performing the studies and additional pharmacovigilance activities detailed in
the Pharmacovigilance Plan, as agreed in version 3.0 of the Risk Management Plan (RMP) presented
in Module 1.8.2. of the Marketing Authorisation Application and any subsequent updates of the RMP
agreed by the CHMP.
As per the CHMP Guideline on Risk Management Systems for medicinal products for human use, the
updated RMP should be submitted at the same time as the next Periodic Safety Update Report
(PSUR).
In addition, an updated RMP should be submitted
•
When new information is received that may impact on the current Safety Specification,
Pharmacovigilance Plan or risk minimisation activities
•
Within 60 days of an important (pharmacovigilance or risk minimisation) milestone being
reached
•
At the request of the EMEA
C. SPECIFIC OBLIGATIONS TO BE FULFILLED BY THE MARKETING
AUTHORISATION HOLDER
The Marketing Authorisation Holder shall complete the following programme of studies within the
specified time frame, the results of which shall form the basis of the annual reassessment of the
benefit/risk profile.
Clinical Study to evaluate the Biomarkers and Pharmacologic Endpoints of Ceplene plus low dose
Interleukin-2 in approximately 100 Adult Patients stratified by age greater or less than 60 years with
Acute Myeloid Leukemia in First Complete Remission (CR), with well characterized Morphologic,
Cytogenetic and Molecular profiles (Final Study Results Q4, 2011)
Clinical study to evaluate Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) for the assessment of the anti-leukaemic
activity of Ceplene plus low dose Interleukin-2 in approximately 150 Adult Patients stratified by age
greater or less than 60 years with Acute Myeloid Leukemia in First Complete Remission. (Final Study
Results Q2, 2012)
Determine the feasibility of conducting, in conjunction with collaborative groups in Europe and/or the
United States, a Multicenter Randomized Open-Label Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of
Ceplene plus Interleukin-2 to be determined in approximately 350 adult Patients (stratified by age
greater or less than 60 years) with Acute Myeloid Leukemia in First Complete Remission by April
2010.
If this study design is feasible and agreed to by the CHMP, EpiCept commits to conduct the study and
to aim for a start of recruitment within 1 year of agreement on protocol synopsis and recruitment of 10
patients/month.
ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Ceplene 0.5 mg/0.5 ml solution for injection
Histamine dihydrochloride
2. STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
0.5 ml of solution contains 0.5 mg histamine dihydrochloride.
Sodium chloride, water for injections, and sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid to adjust the
pH.
4. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Solution for injection
14 x 2 ml glass vials
Each vial contains one 0.5 ml dose.
5. METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Read the package leaflet before use.
Subcutaneous use only.
Inject slowly over 5-15 minutes.
6. SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
7. OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
9. SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS



























10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
EpiCept GmbH
Goethestrasse 4
D-80336 Mnchen
Germany
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE

















MINIMUM PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON SMALL IMMEDIATE PACKAGING UNITS
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Ceplene 0.5 mg/0.5 ml solution for injection
Histamine dihydrochloride
Subcutaneous use only.
2. METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION
Read the package leaflet before use.
5. CONTENTS BY WEIGHT, BY VOLUME OR BY UNIT
Each vial contains one 0.5 ml dose
















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Ceplene 0.5 mg/0.5 ml solution for injection
Histamine dihydrochloride
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
•
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
•
If you have further questions, please ask your doctor or pharmacist.
•
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms are the same as yours.
•
If any of the side effects become serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this
leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
In this leaflet:
1.
What Ceplene is and what it is used for
2.
Before you use Ceplene
3.
How to use Ceplene
4.
Possible side effects
5.
How to store Ceplene
6.
Further information, instructions for self-injection of Ceplene
1.
WHAT CEPLENE IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
What Ceplene is
Ceplene belongs to a group of medicines called immunomodulatory medicines. These medicines help
the bodyÓs immune system fight diseases like cancer by improving the immune systemÓs natural role
in fighting disease. The active substance in Ceplene is histamine dihydrochloride; it is identical to a
naturally occurring substance in the body. It is used together with low doses of interleukin-2 (IL-2),
another medicine which helps the immune system to fight diseases like cancer.
What Ceplene is used for
Ceplene is used, together with IL-2, to treat a particular type of leukaemia called acute myeloid
leukaemia (AML). It is used to maintain the remission (the period during which the disease is less
severe or not detectable). As your doctor has discussed with you, acute myeloid leukaemia is a cancer
of blood forming cells in the bone marrow. Ceplene with IL-2 will help your immune system attack
any remaining cancer cells after a previous cancer treatment.
During your treatment, you will always use
IL-2 AND Ceplene
. Ask your doctor if you have any
questions about Ceplene or IL-2.
Do NOT use Ceplene
•
If you are
allergic
(hypersensitive) to histamine or any of the other ingredients of Ceplene.
•
If you have severe
heart problems
.
•
If you are receiving one of the following medicines:
-
Steroids
such as prednisone and dexamethasone. They are used to inhibit activity of
the immune system (immunosuppressant) and to reduce inflammation.
-
Clonidine
, a medicine used to reduce high blood pressure.
-
H
2
blockers
such as cimetidine, ranitidine, famotidine or nizatidine which are used to
treat stomach ulcers, indigestion (dyspepsia) or heartburn.
•
If you have received a stem cell transplant (a kind of
bone marrow transplant
) from a donor.
•
If you are
pregnant
.
•
If you are
breast-feeding
.
Take special care with Ceplene
•
Ceplene and IL-2 are not to be injected at the same time. IL-2 has to be injected first. Ceplene
must be injected
1 to 3 minutes later
.
•
Ceplene must be
injected slowly
in the layer of tissue just under the skin (
subcutaneously
),
over a period of approximately 5 to 15 minutes. Rapid injection can cause a drop in your blood
pressure and make you feel faint or even pass out.
•
You will start your treatment with Ceplene in the clinic under supervision of a doctor. You
must be monitored to check how you respond to treatment. Your doctor will check your blood
pressure, pulse rate and lung function. Your doctor will also carry out some blood tests during
treatment.
•
If you have had one of the following conditions you will be monitored in the hospital during the
next treatment days or the next cycles of treatment:
-
bleeding ulcers,
-
stroke,
-
narrowing of the arteries
(systemic peripheral arterial disease),
-
heart disease
(for severe heart problems see above ÐDo NOT use CepleneÑ),
-
a history of
auto-immune disease
(a disease where the immune system attacks the
bodyÓs own cells or tissues, such as systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis,
inflammatory bowel disease or psoriasis).
•
If you are taking any
other medicines
mentioned under
ÐTaking other medicinesÑ
or if you
are to have an
operation
or special
X-ray investigation requiring an injection,
talk to your
doctor.
•
If you
have an infection
your doctor will closely monitor you. If you
have had an infection
within 14 days of starting this treatment which required you to take medicines to treat
infections (antibiotics, antifungals or antivirals), your doctor will closely monitor you.
•
If you have
kidney problems
, talk to your doctor before using this medicine. A decrease of
blood pressure may occur.
•
If you have
liver problems
, talk to your doctor before using this medicine. Your doctor may
change your dose.
Children and adolescents
Ceplene use is not recommended in children and adolescents, as there is no information available
about using this medicine in this age group.
Taking other medicines
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines,
including medicines obtained without a prescription.

If you are taking any of the following medicines, please be sure to
discuss this with your doctor
or
pharmacist before using Ceplene. Some of them must not be taken during treatment with Ceplene or
may need special precautions:
•
Steroids
such as prednisone and dexamethasone. They are used to inhibit activity of the
immune system (immunosuppressant) and to reduce inflammation (see above ÐDo NOT use
CepleneÑ).
•
H
2
blockers
such as cimetidine, ranitidine, famotidine or nizatidine which are used to treat
stomach ulcers, indigestion (dyspepsia) or heartburn (see above ÐDo NOT use CepleneÑ).
•
Antihistamines
used to treat allergy.
•
Certain
anti-psychotics
such as chlorpromazine, flupenthixol, thoridazine, clozapine and
risperidone. They are used to treat mental conditions.
•
Tricyclic antidepressant medicines
such as amitryptiline, imipramine, or
monoamine
oxidase inhibitors
, such as phenelzine, isocarboxazide, tranylcypromine or moclobemide.
They are used to treat depression.
•
Malaria or medicines used to treat infections responsible for sleeping sickness
.
•
Beta-blockers
, such as propranolol, metoprolol, atenolol for angina and heart beat disorders or
any treatment of
high blood pressure
(for example thiazide diuretics (bendrofluazide), ACE
inhibitors (captopril), calcium antagonists (nifedipine) and alpha-blockers (prazosin).
Also, if you are to have an
operation
or special
X-ray investigation
requiring an injection, first make
sure that your doctor knows that you are receiving Ceplene. Certain medicines used for an operation
(for example neuromuscular blocking medicines and narcotic pain-killers) or dyes used for certain X-
rays may interfere with this medicine.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
There is no information about the use of Ceplene in pregnant women.
Therefore, the treatment with Ceplene and IL-2 must not be used during pregnancy.
It is not known whether Ceplene appears in breast milk. Therefore Ceplene and IL-2 must not be used
during breast-feeding.
For both men and women using this treatment, contraception must be used as it is important not to
conceive a child while being treated with Ceplene and IL-2.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
Do not drive or use machines within one hour after receiving a Ceplene injection as it may reduce
blood pressure causing dizziness, light-headedness and blurred vision which can affect your ability to
drive and operate machines.
Always use Ceplene exactly as your doctor has instructed. You should check with your doctor or
pharmacist if you are not sure about this.
This treatment must be prescribed and supervised by a physician with knowledge of acute myeloid
leukaemia.
Dosage
Since you will be using both IL-2 and Ceplene in a combined treatment, information about both
dosages is provided:
IL-2 is injected twice daily as a subcutaneous injection (in the layer of tissue just under the skin) 1 to
3 minutes before the injection of Ceplene. Each dose is calculated from your body weight.
You
should use 16400 IU* per kg bodyweight.
Your doctor will let you know how much it is and how to
inject it.
*IU=international units, a measurement specifying the amount of IL-2
Ceplene
The
usual dose
of Ceplene is
0.5 ml
of solution
twice a day
given as a slow subcutaneous injection
(in the layer of tissue just under the skin).
Ceplene must be injected
1 to 3 minutes after IL-2
.
The two medicines, IL-2 and Ceplene, are both injected twice a day, with a minimum of 6 hours
between injections.
Treatment periods and treatment breaks
The treatment with IL-2 and Ceplene lasts for 81 weeks and is cyclic.
•
For the first 18 weeks: you will use IL-2 and Ceplene
daily
for
3 weeks
, followed by a
3 week
break
(no treatment at all).
•
For the following 63 weeks: you will use IL-2 and Ceplene
daily
for
3 weeks
, followed by a
6 week break
(no treatment at all).
Injecting Ceplene yourself
Your doctor may decide that it would be more convenient for you to inject IL-2 and Ceplene yourself.
Your doctor or nurse will show you how to inject yourself.
Do not try to inject yourself unless a
qualified professional has trained you.
It is recommended that you
always have someone with you when injecting this medicine
, such as
an adult family member, friend or other care provider who could help you if you feel light-headed or
faint.
For further instructions on how to inject this medicine yourself, please read the section
ÐINSTRUCTIONS FOR SELF-INJECTION OF CEPLENEÑ at the end of this leaflet.
Your doctor may advise you that it is appropriate to use a syringe pump to regulate the injection of
Ceplene. If you are using a syringe pump you must refer to the instructions provided by the pump
manufacturer and the training provided by your doctor, nurse and/or pharmacist.
If you have used more Ceplene than you should
You must use this medicine exactly as it has been prescribed for you. If you accidentally inject more
than you were told to, contact your doctor or pharmacist immediately.
If you forget a dose of Ceplene
Do not take any additional dose to make up for the forgotten doses. Continue with the treatment as
prescribed. If you have missed one of your doses in a day, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Like all medicines, Ceplene can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If you experience any side effects during or soon after the injection, tell you doctor.
Side effects observed when
Ceplene is used as described in this package leaflet
Very common side effects
(occurs in more than 1 in 10 people who use the medicine)
•
Increase in the number of a certain type of white blood cells in the blood (eosinophilia) and
decrease in the number of blood platelets (thrombocytopenia)
•
Headache, dizziness and tiredness
•
Altered taste (dysgeusia)
•
Rapid heart beat (tachycardia)
•
Flushing and low blood pressure (hypotension) leading to light-headedness and fainting
•
Cough, difficulty in breathing (dyspnoea)
•
Nausea, indigestion (dyspepsia) and diarrhoea
•
Rash
•
Joint and muscle pain (arthralgia and myalgia)
•
Inflamed granulated skin at the injection site, fatigue, fever (pyrexia), injection site redness,
feeling hot, itching at the injection site, flu-like symptoms, shivering (rigors), injection site
inflammation and pain.
Common side effects
(occurs in less than 1 in 10 people but more than 1 in 100 people who use the
medicine)
•
Loss of appetite
•
Difficulty in sleeping (insomnia)
•
Feeling your own heart beat (palpitations)
•
Nasal congestion
•
Vomiting, upper abdominal pain and dry mouth
•
Abnormal redness of the skin (erythema), increased sweating, night sweats and itching
(pruritus)
•
Pain in limbs and back pain
•
Hives, bruising, rash and swelling at the injection site, weakness and chest pain
Side effects observed when
Ceplene was used in other types of treatment
Very common side effects
(occurs in more than 1 in 10 people who use the medicine)
•
Dry skin
•
Anxiety
•
Feeling of general discomfort or unease
•
Accumulation of fluid in the body especially in the legs and loss of weight
Common side effects
(occurs in less than 1 in 10 people but more than 1 in 100 people who use the
medicine)
•
Sensation of spinning (vertigo)
•
Your body does not make enough thyroxine, a body chemical called a hormone
(hypothyroidism)
•
Decrease in the number of red blood cells (anaemia)
•
Dehydration
•
Depression
•
Tingling, prickling or numbness of the skin (paraesthesis)
•
Hot flushes
•
Wheezing
•
Constipation, swollen stomach, inflamed mouth
•
Pain and formation of extra tissue in the skin around the injection site
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Ceplene after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and vial label . The expiry date
refers to the last day of that month.
Medicines must not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
What Ceplene contains
•
The active substance is histamine dihydrochloride. One vial contains 0.5 mg histamine
dihydrochloride in 0.5 ml solution.
•
The other ingredients are water for injections and sodium chloride, and it may also contain
sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid for pH adjustment.
What Ceplene looks like and contents of the pack
Ceplene is a clear, colourless liquid. It is provided in a glass vial with a grey rubber stopper and a
blue peel flip off aluminium tamper evident over seal.
Ceplene is available in pack sizes of 14 single-use vials.
Marketing Authorisation Holder
EpiCept GmbH, Goethestrasse 4, D-80336 Mnchen, Germany.
Manufacturer
Catalent UK Packaging Ltd, Lancaster Way, Wingates Industrial Park, Westhoughton, Bolton,
Lancashire, BL5 3XX, United Kingdom
This leaflet was last approved in
{MM/YYYY}
This medicine has been authorised ÐExceptional circumstancesÑ. This means that due to the rarity of
the disease it has not been possible to obtain complete information on this medicine. The European
Medicines Agency (EMEA) will review any new information on this medicine every year and this
package leaflet will be updated as necessary. Detailed information on this medicine is available on
the European Medicine Agency (EMEA) website: http//:www.emea.europa.eu They are also links to
other websites about rare diseases and treatments.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR SELF-INJECTION OF CEPLENE
This section contains information on how to give yourself an injection of Ceplene.
For general information about the dosage and how to use Ceplene and IL-2, please see Section
3, ÐHOW TO USE CEPLENEÑ
.
Read the following instructions carefully. It is important that you do not try to give yourself the
injection unless you have received special training from your doctor or nurse. If you are not sure
about how to give yourself the injection or you have any questions, please ask your doctor or nurse for
help.
If you feel faint or dizzy during or after the injections, tell your doctor before injecting your next
dose. Your doctor may want to increase the time you take to complete your injection, or change your
dose.
You will have to inject Ceplene and IL-2 twice a day by subcutaneous injection (in the layer of tissue
just under the skin), according to the directions provided by your doctor.
Always inject IL-2 first. Ceplene must be injected
1 to 3 minutes later
.
Ceplene must not be mixed with any other products and must not be diluted.
Your doctor will explain to you how to prepare and inject IL-2.
It is recommended that you always have
someone with you when injecting Ceplene
, such as an adult
family member, friend, or other care provider to help you if you feel light-headed or faint.
PREPARATION FOR INJECTION OF CEPLENE
To prepare a dose of Ceplene you will need the following:
•
1 vial of Ceplene solution (0.5 ml)
•
1 sterile syringe with needle
•
1 alcohol wipe
Method
1 Take 1 vial out of the carton. Check the expiry date (EXP) on the vial label.
2. Do not use if the date has passed the last day of the month shown.
3. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
4. Double check the vial label to make sure you are using the correct medicine. The solution must be
clear and colourless. If not, use another vial and inform your doctor or pharmacist.
5. Remove the plastic cap from the vial, exposing the stopper with the inner rubber circle.
6. Use an alcohol wipe to clean the rubber part of the stopper. Do not touch the stopper with your
hands.
7. Pick up the sterile syringe. Notice the numbered marks on it. Each mark (0.1, 0.2, 0.3, etc)
represents one-tenth of a millilitre (0.1 ml). With the needle cover on, pull back the plunger and
draw air into the syringe to the level (number of millilitres) instructed by your doctor.
See Figure
1.
8. Pull the needle cover straight off. With the vial standing on a flat surface, insert the needle straight
through the rubber stopper into the vial.
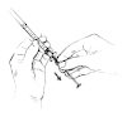

9. Push the plunger of the syringe down to inject air into the vial.
See Figure 2.
10 Holding both the vial and the syringe, turn the vial upside down. Adjust the syringe so that the tip of
the needle is slightly above the rubber stopper but still within the solution.
See Figure 3.
11. Slowly pull back the plunger to draw the solution into the syringe, filling it to the level (number
of millilitres) instructed by your doctor. If bubbles appear in the syringe, push the solution
slowly back into the vial and withdraw the solution again.
12 Take the needle out of the vial. Do not lay the syringe down or let the needle touch anything.
13. Replace the cover on the needle. Place the syringe on a clean flat surface.
14. There may be a small amount of solution left in the vial. This is to be returned to the
pharmacist for disposal.
15. Double check the syringe to make sure that you have withdrawn the correct amount.
16. Take the syringe and follow the ÐINSTRUCTIONS FOR INJECTIONÑ information below.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR INJECTION
You will usually inject two doses of 0.5 ml in a day, unless your doctor has prescribed a lower dose
for you.
For the injection you will need the following:
•
1 prepared syringe for your IL-2 injection (refer to the IL-2 package leaflet and your
doctorÓs dose instructions).
•
1 prepared syringe containing Ceplene.
•
Alcohol wipe(s).
•
A timer, clock or watch with a second hand.
•
A puncture-proof container so you can dispose of used syringes safely.
Method
1. Find a comfortable, well-lit place to sit and where you can lie back. Place the pre-prepared
syringes containing IL-2, Ceplene and an opened alcohol wipe where you can reach them. For


your safety it is very important that you are sitting where you can lean back or lie flat when you
perform the injections.
2. Inject IL-2 as you have been instructed.
3. Wait 1 to 3 minutes.
4. Decide where you will inject Ceplene. You may choose the inner or outer thighs, arms or stomach.
Ceplene and IL-2 must not be injected into the same region
. For example, if you inject IL-2 in
the left arm, you could inject Ceplene into the left or right thigh, the stomach, or the right arm.
Always vary the site that you inject. For possible injection sites,
see Figure 4.
5. Make sure that the area of the skin you selected is exposed. Use an alcohol wipe to clean it.
Allow the area to dry for 10 seconds.
6. Pinch up a section of the cleaned skin between your thumb and forefinger, without squeezing it.
See Figure 5.
7 Hold needle either vertically (90 ) or at a 45 angle to the skin and insert it under the skin as far as
it will go in one quick motion. The needle must be inserted under the skin, but not into any blood
vessels below the skin.
See Figure 6.
8. Slightly pull back the plunger.
If blood appears, do not inject Ceplene because the needle has
entered a blood vessel.
Withdraw and discard the syringe as instructed. Obtain new supplies and
start the procedure over again, even if 3 minutes have passed after injection of IL-2.
9. Notice the numbered marks on each syringe. Each mark (0.1, 0.2, 0.3, etc.) represents one-tenth
of a millilitre (0.1 ml).




10. Push down the syringe plunger and inject one-tenth of a millilitre (0.1 ml) every minute, or
more slowly if instructed to do so by your doctor.
See Figure 7.
11
Never inject Ceplene any faster or all at once.
12 When the syringe is empty, remove the needle from your skin.
13 Apply gentle pressure with the alcohol wipe over the injection site without rubbing it.
14
Remain seated or lying down for 20 minutes
after injecting Ceplene.
15 Dispose of the syringe in the puncture-proof container as instructed.


Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/ceplene.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|










































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































