Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Cerezyme 200 U Powder for concentrate for solution for infusion
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each vial contains 200 units* of imiglucerase**.
After reconstitution, the solution contains 40 units (approximately 1.0 mg) of imiglucerase per ml
(200 U/5 ml).
* An enzyme unit (U) is defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of one
micromole of the synthetic substrate para-nitrophenyl -D-glucopyranoside (pNP-Glc) per minute at
37°C.
** Imiglucerase is a modified form of human acid -glucosidase and is produced by recombinant
DNA technology using a mammalian Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cell culture, with mannose
modification for targeting macrophages.
Excipients:
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
This medicinal product contains sodium and is administered in 0.9% sodium chloride intravenous
solution (see section 6.6). After reconstitution, the solution contains 0.62 mmol sodium
(200 U/5 mL). To be taken into consideration by patients on a controlled sodium diet.
Powder for concentrate for solution for infusion.
Cerezyme is a white to off-white powder.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Cerezyme (imiglucerase) is indicated for use as long-term enzyme replacement therapy in patients
with a confirmed diagnosis of non-neuronopathic (Type 1) or chronic neuronopathic (Type 3)
Gaucher disease who exhibit clinically significant non-neurological manifestations of the disease.
The non-neurological manifestations of Gaucher disease include one or more of the following
conditions:
anaemia after exclusion of other causes, such as iron deficiency
bone disease after exclusion of other causes such as Vitamin D deficiency
hepatomegaly or splenomegaly
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Disease management should be directed by physicians knowledgeable in the treatment of Gaucher
disease.
Posology
Due to the heterogeneity and the multi-systemic nature of Gaucher disease, dosage should be
individualised for each patient based on a comprehensive evaluation of all clinical manifestations of
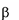





the disease. Once individual patient response for all relevant clinical manifestations is well-
established, dosages and frequency of administration may be adjusted with the goal to either maintain
already reached optimal parameters for all clinical manifestations or further improve those clinical
parameters which have not yet been normalised.
A range of dosage regimens has proven effective towards some or all of the non-neurological
manifestations of the disease. Initial doses of 60 U/kg of body weight once every 2 weeks have shown
improvement in haematological and visceral parameters within 6 months of therapy and continued use
has either stopped progression of or improved bone disease. Administration of doses as low as
15 U/kg of body weight once every 2 weeks has been shown to improve haematological parameters
and organomegaly, but not bone parameters. The usual frequency of infusion is once every 2 weeks;
this is the frequency of infusion for which the most data are available.
Paediatric population
No dose adjustment is necessary for the paediatric population
The efficacy of Cerezyme on neurological symptoms of chronic neuronopathic Gaucher patients has
not been established and no special dosage regimen can be recommended for these manifestations
(see section 5.1).
Method of Administration
After reconstitution and dilution, the preparation is administered by intravenous infusion. At initial
infusions, Cerezyme should be administered at a rate not exceeding 0.5 unit per kg body weight per
minute. At subsequent administrations, infusion rate may be increased but should not exceed 1 unit
per kg body weight per minute. Infusion rate increases should occur under supervision of a health care
professional.
Infusion of Cerezyme at home may be considered for patients who are tolerating their infusions well
for several months.. Decision to have patient move to home infusion should be made after evaluation
and recommendation by the treating physician. Infusion of Cerezyme by the patient or caregiver at
home requires training by a health care professional in a clinical setting. The patient or caregiver will
be instructed in infusion technique and the keeping of a treatment diary. Patients experiencing adverse
events during the infusion need to immediately
stop the infusion process and
seek the attention of a
healthcare professional. Subsequent infusions may need to occur in a clinical setting. Dose and
infusion rate should remain constant while at home, and not be changed without supervision of a
health care professional.
For instructions on reconstitution and dilution of the medicinal product before administration, see
section 6.6.
Medical or healthcare professionals are encouraged to register Gaucher patients, including those with
chronic neuronopathic manifestations of the disease, in the “ICGG Gaucher Registry” (see
section 5.1).
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients (see section 4.4).
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Hypersensitivity
Current data using a screening ELISA followed by a confirmatory radioimmunoprecipitation assay,
suggest that, during the first year of therapy, IgG antibodies to imiglucerase are formed in
approximately 15% of the treated patients. It appears that patients who will develop IgG antibody are
most likely to do so within 6 months of treatment and will rarely develop antibodies to Cerezyme after
12 months of therapy. It is suggested that patients suspected of a decreased response to the treatment
be monitored periodically for IgG antibody formation to imiglucerase
.
Patients with antibody to imiglucerase have a higher risk of hypersensitivity reactions (see section
4.8). If a patient experiences a reaction suggestive of hypersensitivity, subsequent testing for
imiglucerase antibodies is advised. As with any intravenous protein product, severe allergic-type
hypersensitivity reactions are possible, but occur uncommonly. If these reactions occur, immediate
discontinuation of the Cerezyme infusion is recommended and appropriate medical treatment should
be initiated. The current medical standards for emergency treatment are to be observed.
Patients who have developed antibodies or symptoms of hypersensitivity to Ceredase (alglucerase)
should be treated with caution when administering Cerezyme (imiglucerase).
Excipients
This medicinal product contains sodium and is administered in 0.9% sodium chloride intravenous
solution (see section 6.6). To be taken into consideration by patients on a controlled sodium diet.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No interaction studies have been performed.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Limited experience from 150 pregnancy outcomes (primarily based on spontaneous reporting and
literature review) is available suggesting that use of Cerezyme is beneficial to control the underlying
Gaucher disease in pregnancy. Furthermore, these data indicate no malformative toxicity for the
foetus by Cerezyme, although the statistical evidence is low. Foetal demise has been reported rarely,
although it is not clear whether this related to the use of Cerezyme or to the underlying Gaucher
disease.
No animal studies have been carried out with respect to assessing the effects of Cerezyme on
pregnancy, embryonal/foetal development, parturition and postnatal development. It is not known
whether Cerezyme passes via the placenta to the developing foetus.
In pregnant Gaucher patients and those intending to become pregnant, a risk-benefit treatment
assessment is required for each pregnancy. Patients who have Gaucher disease and become pregnant
may experience a period of increased disease activity during pregnancy and the puerperium. This
includes an increased risk of skeletal manifestations, exacerbation of cytopenia, haemorrhage, and an
increased need for transfusion. Both pregnancy and lactation are known to stress maternal calcium
homeostasis and to accelerate bone turnover. This may contribute to skeletal disease burden in
Gaucher disease.
Treatment naïve women should be advised to consider commencing therapy prior to conception in
order to attain optimal health. In women receiving Cerezyme treatment continuation throughout
pregnancy should be considered. Close monitoring of the pregnancy and clinical manifestations of
Gaucher disease is necessary for the individualization of dose according to the patient‟s needs and
therapeutic response.
It is not known whether this active substance is excreted in human milk, however, the enzyme is likely
to be digested in the child‟s gastrointestinal tract
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Cerezyme has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
Adverse drug reactions are listed by system organ class and frequency (common
1/10,000 to <1/1,000)) in the table below. Within each
frequency grouping, adverse drug reactions are presented in order of decreasing seriousness.
Adverse drug reactions are listed by system organ class and frequency (common
1/1,000 to <1/100) and rare (
Nervous system disorders
Uncommon: Dizziness, headache, paraesthesia*
Cardiac disorders
Uncommon: Tachycardia*, cyanosis*
Vascular disorders
Uncommon: Flushing*, hypotension*
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Common: Dyspnoea*, coughing*
Gastrointestinal disorders
Uncommon: Vomiting, nausea, abdominal cramping, diarrhoea
Hypersensitivity reactions
Skin and subcutaneous tissue
disorders
Common: Urticaria/angioedema*, pruritus*, rash*
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue
disorders
Uncommon: Arthralgia, backache*
General disorders and administration site
conditions
Uncommon: Infusion site discomfort, infusion site burning,
infusion site swelling, injection site sterile
abscess, chest discomfort*, fever, rigors, fatigue
Symptoms suggestive of hypersensitivity (* marked in the table above) have been noted, overall in
approximately 3% of the patients. Onset of such symptoms has occurred during or shortly after
infusions. These symptoms generally respond to treatment with antihistamines and/or corticosteroids.
Patients should be advised to discontinue infusion of the product and contact their physician if these
symptoms occur.
No case of overdose has been reported. In patients dosages up to 240 U/kg body weight once every
two weeks have been used.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Enzymes-Imiglucerase (recombinant macrophage targeted -
glucocerebrosidase), ATC code: A16AB02.
Gaucher disease is a rare recessively inherited metabolic disord
-glucosidase. This enzyme breaks down glucosylceramide, a key component
of the lipid structure of cell membranes, into glucose and ceramide. In individuals with Gaucher
disease, glucosylceramide degradation is insufficient, leading to accumulation of large quantities of
Adverse drug reactions are listed by system organ class and frequency (common ( 1/100 to <1/10),
uncommon (
Gaucher disease is a rare recessively inherited metabolic disorder that results from a deficiency of the
lysosomal enzyme acid



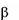
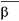











this substrate within the lysosomes of macrophages (termed „Gaucher cells‟), leading to widespread
secondary pathology.
Gaucher cells are typically found in liver, spleen and bone marrow and occasionally in lung, kidney
and intestine. Clinically, Gaucher disease is a heterogeneous phenotypic spectrum. The most frequent
disease manifestations are hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, anaemia, and skeletal pathology,
The skeletal abnormalities are frequently the most debilitating and disabling features of Gaucher
disease. These skeletal manifestations include bone marrow infiltration, osteonecrosis, bone pain and
bone crises, osteopenia and osteoporosis, pathological fractures, and growth impairment. Gaucher
disease is associated with increased glucose production and increased resting energy expenditure rate,
which may contribute to fatigue and cachexia. Patients with Gaucher disease may also have a low
grade inflammatory profile. In addition, Gaucher disease has been associated with an increased risk of
immunoglobulin abnormalities such as hyperimmunoglobulinemia, polyclonal gammopathy,
monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
(MGUS) and multiple myeloma. The natural
history of Gaucher disease usually shows progression, with the risk of irreversible complications
arising in various organs over time. The clinical manifestations of Gaucher disease can adversely
affect quality of life. Gaucher disease is associated with increased morbidity and early mortality.
Signs and symptoms presenting in childhood typically represent more severe Gaucher disease. In
children, Gaucher disease can lead to growth retardation and delayed puberty.
Pulmonary hypertension is a known complication of Gaucher disease. Patients who have undergone a
splenectomy have an increased risk of pulmonary hypertension. Cerezyme therapy reduces the
requirement for splenectomy in most cases and early treatment with Cerezyme has been associated
with a reduced risk of pulmonary hypertension. Routine evaluation to detect the presence of
pulmonary hypertension after diagnosis of Gaucher disease and over time is recommended. Patients
diagnosed with pulmonary hypertension, in particular, should receive adequate doses of Cerezyme to
ensure control of underlying Gaucher disease as well as be evaluated for the need of additional
pulmonary hypertension specific treatments.
Imiglucerase (recombinant macrophage targeted acid ß-glucosidase) replaces the deficient enzyme
activity, hydrolysing glucosylceramide, thus correcting initial pathophysiology and preventing
secondary pathology. Cerezyme reduces spleen and liver size, improves or normalises
thrombocytopenia and anaemia, improves or normalises bone mineral density and bone marrow
burden, and reduces or eliminates bone pain and bone crises. Cerezyme reduces resting energy
expenditure rate. Cerezyme has been shown to improve both mental and physical aspects in the
quality of life of Gaucher disease. Cerezyme decreases chitotriosidase, a biomarker for
glucosylceramide accumulation in macrophages and response to treatment. In children, Cerezyme has
been shown to enable normal pubertal development, and to induce catch-up growth, leading to normal
height and bone mineral density in adulthood.
The rate and extent of response to Cerezyme treatment is dose-dependent. Generally, improvements in
organ systems with a faster turnover rate, such as the haematological, can be noted far more rapidly
than in those with a slower turnover, such as the bone.
In an ICGG Gaucher Registry analysis of a large cohort of patients (n=528) with Gaucher disease
type 1, a time- and dose-dependent effect for Cerezyme was observed for haematological and visceral
parameters (platelet count, haemoglobin concentration, spleen and liver volume) within the dose
range of 15, 30 and 60 U/kg body weight once every 2 weeks. Patients treated with 60 U/kg body
weight every 2 weeks showed a faster improvement and a greater maximum treatment effect as
compared to patients receiving the lower doses.
Similarly, in an ICGG Gaucher Registry analysis of bone mineral density using dual-energy X-ray
absorptiometry (DXA) in 342 patients, after 8 years of treatment normal bone mineral density was
achieved with a Cerezyme dose of 60 U/kg body weight once every 2 weeks, but not with lower doses
of 15 and 30 U/kg body weight once every 2 weeks (Wenstrup et al, 2007).
nd a median dose of 30 U/kg body weight every 4 weeks, among the patients with bone
6, more patients in the higher dose cohort (33%; n=22) achieved a decrease in
the score of 2 points after 24 months of Cerezyme treatment compared with patients in the lower dose
cohort (10%; n=13) (de Fost et al, 2006).
Treatment with Cerezyme at a dose of 60 U/kg body weight once every 2 weeks, showed
improvement in bone pain as early as 3 months, decrease in bone crises within 12 months, and
improvement in bone mineral density after 24 months of treatment (Sims et al, 2008).
The usual frequency of infusion is once every 2 weeks (see section 4.2). Maintenance therapy every 4
weeks (Q4) at the same cumulative dose as the bi-weekly (Q2) dose has been studied in adult patients
with stable residual Gaucher disease type 1. Changes from baseline in hemoglobin, platelets, liver and
spleen volumes, bone crisis, and bone disease comprised a predefined composite endpoint;
achievement or maintenance of established Gaucher disease therapeutic goals for the hematologic and
visceral parameters comprised an additional endpoint. Sixty-three percent of Q4- and 81% of Q2-
treated patients met the composite endpoint at Month 24; the difference was not statistically
significant based on the 95% CI (-0.357, 0.058). Eighty-nine percent of Q4- and 100% of Q2-treated
patients met the therapeutic goals-based endpoint; the difference was not statistically significant based
on the 95% CI (-0.231, 0.060). A Q4 infusion regimen may be a therapeutic option for some adult
patients with stable residual Gaucher disease type 1, but clinical data are limited.
No controlled clinical studies have been conducted on the efficacy of Cerezyme on neurological
manifestations of the disease. Therefore no conclusions on the effect of enzyme replacement therapy
on the neurological manifestations of the disease can be drawn.
Medical or healthcare professionals are encouraged to register Gaucher patients, including those with
chronic neuronopathic manifestations of the disease, in the “ICGG Gaucher Registry”. Patient data
will be anonymously collected in this Registry. The objectives of the “ICGG Gaucher Registry” are to
enhance the understanding of Gaucher disease and to evaluate the effectiveness of enzyme
replacement therapy, ultimately leading to improvement in the safe and efficacious use of Cerezyme.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
During 1 hour intravenous infusions of 4 doses (7.5, 15, 30, 60 U/kg) of imiglucerase, steady-state
enzymatic activity was achieved by 30 minutes. Following infusion, plasma enzymatic activity
declined rapidly with a half-life ranging from 3.6 to 10.4 minutes. Plasma clearance ranged from 9.8
to 20.3 ml/min/kg, (mean ± S.D, 14.5 ± 4.0 ml/min/kg). The volume of distribution corrected for
weight ranged from 0.09 to 0.15 l/kg (mean ± S.D 0.12 ± 0.02 l/kg). These variables do not appear to
be influenced by dose or duration of infusion, however, only 1 or 2 patients were studied at each dose
level and infusion rate.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety
pharmacology, single and repeated dose toxicity, and genotoxicity.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Mannitol, Sodium citrate (to adjust pH), Citric acid monohydrate (to adjust pH), Polysorbate 80
In a study investigating 2 cohorts of patients treated with a median dose of 80 U/kg body weight every
4 weeks and a median dose of 30 U/kg body weight every 4 weeks, among the patients with bone
marrow burden score

In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other
medicinal products.
Diluted solution:
From a microbiological safety point of view, the product should be used immediately. If not used
immediately, in-use storage and conditions prior to use are the responsibility of the user and should
not be longer than 24 hours at 2
use storage and conditions prior to use are the responsibility of the user and should
C - 8
use storage and conditions prior to use are the responsibility of the user and should
C under protection from light.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2 C – 8 C).
For storage conditions of the diluted medicinal product, see section 6.3
6.5 Nature and contents of container
Cerezyme is supplied in type I borosilicate (clear) glass 20 ml vials. The closure consists of a
siliconised butyl stopper with a tamper proof flip-off cap.
To provide sufficient volume to allow accurate dispensing, each vial is formulated to contain an
overfill of 0.3 ml.
Package sizes: 1 or 25 vials per carton.
Not all package sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Each vial of Cerezyme is for single use only.
The powder for concentrate for solution for infusion has to be reconstituted with water for injections,
diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride intravenous solution and then administered by intravenous
infusion.
Determine the number of vials to be reconstituted based on the individual patient's dosage regimen
and remove the vials from the refrigerator.
Occasionally, small dosage adjustments may be made to avoid discarding partially used vials.
Dosages may be rounded to the nearest full vial, as long as the monthly administered dosage remains
substantially unaltered.
Use Aseptic Technique
Reconstitution
Reconstitute each vial with 5.1 ml
water for injections
; avoid forceful impact of water for injections
on the powder and, by mixing gently, avoid foaming of the solution. The reconstituted volume is 5.3
ml. The pH of the reconstituted solution is approximately 6.1.
After reconstitution it is a clear, colourless liquid, free from foreign matter. The reconstituted solution
must be further diluted. Before further dilution, visually inspect the reconstituted solution in each vial
for foreign particles and discoloration. Do
not
use vials exhibiting foreign particles or discoloration.
After reconstitution,
promptly dilute
vials and do not store for subsequent use.
Dilution
The reconstituted solution contains 40 units imiglucerase per ml. The reconstituted volume allows
accurate withdrawal of 5.0 ml (equal to 200 units) from each vial. Withdraw 5.0 ml reconstituted
solution from each vial and combine the withdrawn volumes. Then dilute the combined volumes with
0.9% sodium chloride intravenous solution
to a total volume of 100 to 200 ml. Mix the infusion
solution gently.
It is recommended to administer the diluted solution through an in-line low protein-binding 0.2 µm
filter to remove any protein particles. This will not lead to any loss of imiglucerase activity. It is
recommended that the diluted solution be administered within 3 hours. The product diluted in 0.9%
sodium chloride intravenous solution will retain chemical stability if stored up to 24 hours at 2°C and
8°C under protection from light; but microbiological safety will depend on the reconstitution and
dilution having been performed aseptically.
Cerezyme contains no preservatives. Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in
accordance with local requirements.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Genzyme Europe B.V., Gooimeer 10, 1411 DD Naarden, The Netherlands
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBERS
EU/1/97/053/001
EU/1/97/053/002
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 17 November 1997
Date of latest renewal: 17 September 2007
10.
DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this product is available on the website of the European Medicines Agency
http://www.ema.europa.eu
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Cerezyme 400 U Powder for concentrate for solution for infusion
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each vial contains 400 units* of imiglucerase**.
After reconstitution, the solution contains 40 units (approximately 1.0 mg) of imiglucerase per ml
(400 U/10 ml).
* An enzyme unit (U) is defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of one
micromole of the synthetic substrate para-nitrophenyl -D-glucopyranoside (pNP-Glc) per minute at
37°C.
** Imiglucerase is a modified form of human acid -glucosidase and is produced by recombinant
DNA technology using a mammalian Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cell culture, with mannose
modification for targeting macrophages.
Excipients:
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
This medicinal product contains sodium and is administered in 0.9% sodium chloride intravenous
solution (see section 6.6). After reconstitution, the solution contains 1.24 mmol sodium
(400 U/10 mL). To be taken into consideration by patients on a controlled sodium diet.
Powder for concentrate for solution for infusion.
Cerezyme is a white to off-white powder.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Cerezyme (imiglucerase) is indicated for use as long-term enzyme replacement therapy in patients
with a confirmed diagnosis of non-neuronopathic (Type 1) or chronic neuronopathic (Type 3)
Gaucher disease who exhibit clinically significant non-neurological manifestations of the disease.
The non-neurological manifestations of Gaucher disease include one or more of the following
conditions:
anaemia after exclusion of other causes, such as iron deficiency
bone disease after exclusion of other causes such as Vitamin D deficiency
hepatomegaly or splenomegaly
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Disease management should be directed by physicians knowledgeable in the treatment of Gaucher
disease.
Posology
Due to the heterogeneity and the multi-systemic nature of Gaucher disease, dosage should be
individualised for each patient based on a comprehensive evaluation of all clinical manifestations of
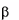




the disease. Once individual patient response for all relevant clinical manifestations is well-
established, dosages and frequency of administration may be adjusted with the goal to either maintain
already reached optimal parameters for all clinical manifestations or further improve those clinical
parameters which have not yet been normalised.
A range of dosage regimens has proven effective towards some or all of the non-neurological
manifestations of the disease. Initial doses of 60 U/kg of body weight once every 2 weeks have shown
improvement in haematological and visceral parameters within 6 months of therapy and continued use
has either stopped progression of or improved bone disease. Administration of doses as low as
15 U/kg of body weight once every 2 weeks has been shown to improve haematological parameters
and organomegaly, but not bone parameters. The usual frequency of infusion is once every 2 weeks;
this is the frequency of infusion for which the most data are available.
Paediatric population
No dose adjustment is necessary for the paediatric population.
The efficacy of Cerezyme on neurological symptoms of chronic neuronopathic Gaucher patients has
not been established and no special dosage regimen can be recommended for these manifestations
(see section 5.1).
Method of Administration
After reconstitution and dilution, the preparation is administered by intravenous infusion. At initial
infusions, Cerezyme should be administered at a rate not exceeding 0.5 unit per kg body weight per
minute. At subsequent administrations, infusion rate may be increased but should not exceed 1 unit
per kg body weight per minute. Infusion rate increases should occur under supervision of a health care
professional.
Infusion of Cerezyme at home may be considered for patients who are tolerating their infusions well
for several months. Decision to have patient move to home infusion should be made after evaluation
and recommendation by the treating physician. Infusion of Cerezyme by the patient or caregiver at
home requires training by a health care professional in a clinical setting. The patient or caregiver will
be instructed in infusion technique and the keeping of a treatment diary. Patients experiencing adverse
events during the infusion need to immediately
stop the infusion process and
seek the attention of a
healthcare professional. Subsequent infusions may need to occur in a clinical setting. Dose and
infusion rate should remain constant while at home, and not be changed without supervision of a
health care professional.
For instructions on reconstitution and dilution of the medicinal product before administration, see
section 6.6.
Medical or healthcare professionals are encouraged to register Gaucher patients, including those with
chronic neuronopathic manifestations of the disease, in the “ICGG Gaucher Registry” (see
section 5.1).
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients (see section 4.4).
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Hypersensitivity
Current data using a screening ELISA followed by a confirmatory radioimmunoprecipitation assay,
suggest that, during the first year of therapy, IgG antibodies to imiglucerase are formed in
approximately 15% of the treated patients. It appears that patients who will develop IgG antibody are
most likely to do so within 6 months of treatment and will rarely develop antibodies to Cerezyme after
12 months of therapy. It is suggested that patients suspected of a decreased response to the treatment
be monitored periodically for IgG antibody formation to imiglucerase
.
Patients with antibody to imiglucerase have a higher risk of hypersensitivity reactions (see section
4.8). If a patient experiences a reaction suggestive of hypersensitivity, subsequent testing for
imiglucerase antibodies is advised. As with any intravenous protein product, severe allergic-type
hypersensitivity reactions are possible, but occur uncommonly. If these reactions occur, immediate
discontinuation of the Cerezyme infusion is recommended and appropriate medical treatment should
be initiated. The current medical standards for emergency treatment are to be observed.
Patients who have developed antibodies or symptoms of hypersensitivity to Ceredase (alglucerase)
should be treated with caution when administering Cerezyme (imiglucerase).
Excipients
This medicinal product contains sodium and is administered in 0.9% sodium chloride intravenous
solution (see section 6.6). To be taken into consideration by patients on a controlled sodium diet.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No interaction studies have been performed.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Limited experience from 150 pregnancy outcomes (primarily based on spontaneous reporting and
literature review) is available suggesting that use of Cerezyme is beneficial to control the underlying
Gaucher disease in pregnancy. Furthermore, these data indicate no malformative toxicity for the
foetus by Cerezyme, although the statistical evidence is low. Foetal demise has been reported rarely,
although it is not clear whether this related to the use of Cerezyme or to the underlying Gaucher
disease.
No animal studies have been carried out with respect to assessing the effects of Cerezyme on
pregnancy, embryonal/foetal development, parturition and postnatal development. It is not known
whether Cerezyme passes via the placenta to the developing foetus.
In pregnant Gaucher patients and those intending to become pregnant, a risk-benefit treatment
assessment is required for each pregnancy. Patients who have Gaucher disease and become pregnant
may experience a period of increased disease activity during pregnancy and the puerperium. This
includes an increased risk of skeletal manifestations, exacerbation of cytopenia, haemorrhage, and an
increased need for transfusion. Both pregnancy and lactation are known to stress maternal calcium
homeostasis and to accelerate bone turnover. This may contribute to skeletal disease burden in
Gaucher disease.
Treatment naïve women should be advised to consider commencing therapy prior to conception in
order to attain optimal health. In women receiving Cerezyme treatment continuation throughout
pregnancy should be considered. Close monitoring of the pregnancy and clinical manifestations of
Gaucher disease is necessary for the individualization of dose according to the patient‟s needs and
therapeutic response.
It is not known whether this active substance is excreted in human milk, however, the enzyme is likely
to be digested in the child‟s gastrointestinal tract
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Cerezyme has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
Adverse drug reactions are listed by system organ class and frequency (common
1/10,000 to <1/1,000)) in the table below. Within each
frequency grouping, adverse drug reactions are presented in order of decreasing seriousness.
Adverse drug reactions are listed by system organ class and frequency (common
1/1,000 to <1/100) and rare (
Nervous system disorders
Uncommon: Dizziness, headache, paraesthesia*
Cardiac disorders
Uncommon: Tachycardia*, cyanosis*
Vascular disorders
Uncommon: Flushing*, hypotension*
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Common: Dyspnoea*, coughing*
Gastrointestinal disorders
Uncommon: Vomiting, nausea, abdominal cramping, diarrhoea
Hypersensitivity reactions
Skin and subcutaneous tissue
disorders
Common: Urticaria/angioedema*, pruritus*, rash*
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue
disorders
Uncommon: Arthralgia, backache*
General disorders and administration site
conditions
Uncommon: Infusion site discomfort, infusion site burning,
infusion site swelling, injection site sterile
abscess, chest discomfort*, fever, rigors, fatigue
Symptoms suggestive of hypersensitivity (* marked in the table above) have been noted, overall in
approximately 3% of the patients. Onset of such symptoms has occurred during or shortly after
infusions. These symptoms generally respond to treatment with antihistamines and/or corticosteroids.
Patients should be advised to discontinue infusion of the product and contact their physician if these
symptoms occur.
No case of overdose has been reported. In patients dosages up to 240 U/kg body weight once every
two weeks have been used.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Enzymes-Imiglucerase (recombinant macrophage targeted -
glucocerebrosidase), ATC code: A16AB02.
Gaucher disease is a rare recessively inherited metabolic disorder that results from a deficiency of the
-glucosidase. This enzyme breaks down glucosylceramide, a key component
of the lipid structure of cell membranes, into glucose and ceramide. In individuals with Gaucher
disease, glucosylceramide degradation is insufficient, leading to accumulation of large quantities of
Adverse drug reactions are listed by system organ class and frequency (common ( 1/100 to <1/10),
uncommon (
Gaucher disease is a rare recessively inherited metabolic disorder that results from a deficiency of the
lysosomal enzyme acid















this substrate within the lysosomes of macrophages (termed „Gaucher cells‟), leading to widespread
secondary pathology.
Gaucher cells are typically found in liver, spleen and bone marrow and occasionally in lung, kidney
and intestine. Clinically, Gaucher disease is a heterogeneous phenotypic spectrum. The most frequent
disease manifestations are hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, anaemia, and skeletal pathology,
The skeletal abnormalities are frequently the most debilitating and disabling features of Gaucher
disease. These skeletal manifestations include bone marrow infiltration, osteonecrosis, bone pain and
bone crises, osteopenia and osteoporosis, pathological fractures, and growth impairment. Gaucher
disease is associated with increased glucose production and increased resting energy expenditure rate,
which may contribute to fatigue and cachexia. Patients with Gaucher disease may also have a low
grade inflammatory profile. In addition, Gaucher disease has been associated with an increased risk of
immunoglobulin abnormalities such as hyperimmunoglobulinemia, polyclonal gammopathy,
monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
(MGUS) and multiple myeloma. The natural
history of Gaucher disease usually shows progression, with the risk of irreversible complications
arising in various organs over time. The clinical manifestations of Gaucher disease can adversely
affect quality of life. Gaucher disease is associated with increased morbidity and early mortality.
Signs and symptoms presenting in childhood typically represent more severe Gaucher disease. In
children, Gaucher disease can lead to growth retardation and delayed puberty.
Pulmonary hypertension is a known complication of Gaucher disease. Patients who have undergone a
splenectomy have an increased risk of pulmonary hypertension. Cerezyme therapy reduces the
requirement for splenectomy in most cases and early treatment with Cerezyme has been associated
with a reduced risk of pulmonary hypertension. Routine evaluation to detect the presence of
pulmonary hypertension after diagnosis of Gaucher disease and over time is recommended. Patients
diagnosed with pulmonary hypertension, in particular, should receive adequate doses of Cerezyme to
ensure control of underlying Gaucher disease as well as be evaluated for the need of additional
pulmonary hypertension specific treatments.
Imiglucerase (recombinant macrophage targeted acid ß-glucosidase) replaces the deficient enzyme
activity, hydrolysing glucosylceramide, thus correcting initial pathophysiology and preventing
secondary pathology. Cerezyme reduces spleen and liver size, improves or normalises
thrombocytopenia and anaemia, improves or normalises bone mineral density and bone marrow
burden, and reduces or eliminates bone pain and bone crises. Cerezyme reduces resting energy
expenditure rate. Cerezyme has been shown to improve both mental and physical aspects in the
quality of life of Gaucher disease. Cerezyme decreases chitotriosidase, a biomarker for
glucosylceramide accumulation in macrophages and response to treatment. In children, Cerezyme has
been shown to enable normal pubertal development, and to induce catch-up growth, leading to normal
height and bone mineral density in adulthood.
The rate and extent of response to Cerezyme treatment is dose-dependent. Generally, improvements in
organ systems with a faster turnover rate, such as the haematological, can be noted far more rapidly
than in those with a slower turnover, such as the bone.
In an ICGG Gaucher Registry analysis of a large cohort of patients (n=528) with Gaucher disease
type 1, a time- and dose-dependent effect for Cerezyme was observed for haematological and visceral
parameters (platelet count, haemoglobin concentration, spleen and liver volume) within the dose
range of 15, 30 and 60 U/kg body weight once every 2 weeks. Patients treated with 60 U/kg body
weight every 2 weeks showed a faster improvement and a greater maximum treatment effect as
compared to patients receiving the lower doses.
Similarly, in an ICGG Gaucher Registry analysis of bone mineral density using dual-energy X-ray
absorptiometry (DXA) in 342 patients, after 8 years of treatment normal bone mineral density was
achieved with a Cerezyme dose of 60 U/kg body weight once every 2 weeks, but not with lower doses
of 15 and 30 U/kg body weight once every 2 weeks (Wenstrup et al, 2007).
4 weeks and a median dose of 30 U/kg body weight every 4 weeks, among the patients with bone
6, more patients in the higher dose cohort (33%; n=22) achieved a decrease in
the score of 2 points after 24 months of Cerezyme treatment compared with patients in the lower dose
cohort (10%; n=13) (de Fost, 2006).
Treatment with Cerezyme at a dose of 60 U/kg body weight once every 2 weeks, showed
improvement in bone pain as early as 3 months, decrease in bone crises within 12 months, and
improvement in bone mineral density after 24 months of treatment (Sims et al, 2008).
The usual frequency of infusion is once every 2 weeks (see section 4.2). Maintenance therapy every 4
weeks (Q4) at the same cumulative dose as the bi-weekly (Q2) dose has been studied in adult patients
with stable residual Gaucher disease type 1. Changes from baseline in hemoglobin, platelets, liver and
spleen volumes, bone crisis, and bone disease comprised a predefined composite endpoint;
achievement or maintenance of established Gaucher disease therapeutic goals for the hematologic and
visceral parameters comprised an additional endpoint. Sixty-three percent of Q4- and 81% of Q2-
treated patients met the composite endpoint at Month 24; the difference was not statistically
significant based on the 95% CI (-0.357, 0.058). Eighty-nine percent of Q4- and 100% of Q2-treated
patients met the therapeutic goals-based endpoint; the difference was not statistically significant based
on the 95% CI (-0.231, 0.060). A Q4 infusion regimen may be a therapeutic option for some adult
patients with stable residual Gaucher disease type 1, but clinical data are limited.
No controlled clinical studies have been conducted on the efficacy of Cerezyme on neurological
manifestations of the disease. Therefore no conclusions on the effect of enzyme replacement therapy
on the neurological manifestations of the disease can be drawn.
Medical or healthcare professionals are encouraged to register Gaucher patients, including those with
chronic neuronopathic manifestations of the disease, in the “ICGG Gaucher Registry”. Patient data
will be anonymously collected in this Registry. The objectives of the “ICGG Gaucher Registry” are to
enhance the understanding of Gaucher disease and to evaluate the effectiveness of enzyme
replacement therapy, ultimately leading to improvement in the safe and efficacious use of Cerezyme.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
During 1 hour intravenous infusions of 4 doses (7.5, 15, 30, 60 U/kg) of imiglucerase, steady-state
enzymatic activity was achieved by 30 minutes. Following infusion, plasma enzymatic activity
declined rapidly with a half-life ranging from 3.6 to 10.4 minutes. Plasma clearance ranged from 9.8
to 20.3 ml/min/kg, (mean ± S.D, 14.5 ± 4.0 ml/min/kg). The volume of distribution corrected for
weight ranged from 0.09 to 0.15 l/kg (mean ± S.D 0.12 ± 0.02 l/kg). These variables do not appear to
be influenced by dose or duration of infusion, however, only 1 or 2 patients were studied at each dose
level and infusion rate.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety
pharmacology, single and repeated dose toxicity, and genotoxicicty.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Mannitol, Sodium citrate (to adjust pH), Citric acid monohydrate (to adjust pH), Polysorbate 80
In a study investigating 2 cohorts of patients treated with a median dose of 80 U/kg body weight every
4 weeks and a median dose of 30 U/kg body weight every 4 weeks, among the patients with bone
marrow burden score

In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other
medicinal products.
Diluted solution:
From a microbiological safety point of view, the product should be used immediately. If not used
immediately, in-use storage and conditions prior to use are the responsibility of the user and should
not be longer than 24 hours at 2 C - 8 C under protection from light.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2 C – 8 C).
For storage conditions of the diluted medicinal product, see section 6.3
6.5 Nature and contents of container
Cerezyme is supplied in type I borosilicate (clear) glass 20 ml vials. The closure consists of a
siliconised butyl stopper with a tamper proof flip-off cap.
To provide sufficient volume to allow accurate dispensing, each vial is formulated to contain an
overfill of 0.6 ml.
Package sizes: 1, 5 or 25 vials per carton.
Not all package sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Each vial of Cerezyme is for single use only.
The powder for concentrate for solution for infusion has to be reconstituted with water for injections,
diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride intravenous solution and then administered by intravenous
infusion.
Determine the number of vials to be reconstituted based on the individual patient's dosage regimen
and remove the vials from the refrigerator.
Occasionally, small dosage adjustments may be made to avoid discarding partially used vials.
Dosages may be rounded to the nearest full vial, as long as the monthly administered dosage remains
substantially unaltered.
Use Aseptic Technique
Reconstitution
Reconstitute each vial with 10.2 ml
water for injections
; avoid forceful impact of water for injections
on the powder and, by mixing gently, avoid foaming of the solution. The reconstituted volume is
10.6 ml. The pH of the reconstituted solution is approximately 6.1.
After reconstitution it is a clear, colourless liquid, free from foreign matter. The reconstituted solution
must be further diluted. Before further dilution, visually inspect the reconstituted solution in each vial
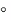



for foreign particles and discoloration. Do
not
use vials exhibiting foreign particles or discoloration.
After reconstitution,
promptly dilute
vials and do not store for subsequent use.
Dilution
The reconstituted solution contains 40 units imiglucerase per ml. The reconstituted volume allows
accurate withdrawal of 10.0 ml (equal to 400 units) from each vial. Withdraw 10.0 ml reconstituted
solution from each vial and combine the withdrawn volumes. Then dilute the combined volumes with
0.9% sodium chloride intravenous solution
to a total volume of 100 to 200 ml. Mix the infusion
solution gently.
It is recommended to administer the diluted solution through an in-line low protein-binding 0.2 µm
filter to remove any protein particles. This will not lead to any loss of imiglucerase activity. It is
recommended that the diluted solution be administered within 3 hours. The product diluted in 0.9%
sodium chloride intravenous solution will retain chemical stability if stored up to 24 hours at 2°C and
8°C under protection from light; but microbiological safety will depend on the reconstitution and
dilution having been performed aseptically.
Cerezyme contains no preservatives. Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in
accordance with local requirements.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Genzyme Europe B.V., Gooimeer 10, 1411 DD Naarden, The Netherlands
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBERS
EU/1/97/053/003
EU/1/97/053/004
EU/1/97/053/005
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 17 November 1997
Date of latest renewal: 17 September 2007
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this product is available on the website of the European Medicines Agency
http://www.ema.europa.eu
A. MANUFACTURER OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE
SUBSTANCE AND MANUFACTURING
AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
A. MANUFACTURER OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE SUBSTANCE AND
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
Name and address of the manufacturer of the biological active substance
Genzyme Corporation
500 Soldiers Field Road – Allston, MA 02134 – USA
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
Genzyme Ltd.
37 Hollands Road – Haverhill, Suffolk CB9 8PU - UK
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to restricted medical prescription (See Annex I: Summary of Product
Characteristics, section 4.2)
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Risk Management Plan
The MAH commits to performing the studies and additional pharmacovigilance activities detailed in
the Pharmacovigilance Plan, as agreed in version 3 of the Risk Management Plan (RMP) presented in
Module 1.8.2. of the Marketing Authorisation and any subsequent updates of the RMP agreed by the
CHMP.
As per the CHMP Guideline on Risk Management Systems for medicinal products for human use, any
updated RMP should be submitted at the same time as the following Periodic Safety Update Report
(PSUR).
In addition, an updated RMP should be submitted:
When new information is received that may impact on the current Safety Specification,
Pharmacovigilance Plan or risk minimisation activities
Within 60 days of an important (pharmacovigilance or risk minimisation) milestone being
reached
At the request of the EMEA






ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING AND THE IMMEDIATE
PACKAGING
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Cerezyme 200 U
Powder for concentrate for solution for infusion
imiglucerase
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE
Each vial contains 200 units of imiglucerase.
Excipients: Mannitol, Sodium Citrate, Citric acid monohydrate and Polysorbate 80.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
1 vial of powder for concentrate for solution for infusion.
25 vials of powder for concentrate for solution for infusion.
METHOD AND ROUTE OF ADMINISTRATION
For intravenous infusion.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY




















SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
Any unused solution should be discarded.
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Marketing Authorisation Holder:
Genzyme Europe B.V.
Gooimeer 10
1411 DD Naarden-NL
12. MARKETING AUTHORIZATION NUMBERS
EU/1/97/053/001
EU/1/97/053/002
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE



















MINIMUM PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON SMALL IMMEDIATE PACKAGING UNITS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT AND ROUTE OF ADMINISTRATION
Cerezyme 200 U
Powder for concentrate for solution for infusion
imiglucerase
For intravenous infusion.
CONTENTS BY WEIGHT, BY VOLUME OR BY UNIT
Each vial contains 200 units of imiglucerase.















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING AND THE IMMEDIATE
PACKAGING
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Cerezyme
400 U
Powder for concentrate for solution for infusion
imiglucerase
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE
Each vial contains 400 units of imiglucerase.
Excipients: Mannitol, Sodium Citrate, Citric acid monohydrate and Polysorbate 80.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
1 vial of powder for concentrate for solution for infusion.
5 vials of powder for concentrate for solution for infusion.
25 vials of powder for concentrate for solution for infusion.
METHOD AND ROUTE OF ADMINISTRATION
For intravenous infusion.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY






















SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
Any unused solution should be discarded.
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Marketing Authorisation Holder:
Genzyme Europe B.V.
Gooimeer 10
1411 DD Naarden-NL
12. MARKETING AUTHORIZATION NUMBERS
EU/1/97/053/003
EU/1/97/053/004
EU/1/97/053/005
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE





















MINIMUM PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON SMALL IMMEDIATE PACKAGING UNITS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT AND ROUTE OF ADMINISTRATION
Cerezyme 400 U
Powder for concentrate for solution for infusion
imiglucerase
For intravenous infusion.
CONTENTS BY WEIGHT, BY VOLUME OR BY UNIT
Each vial contains 400 units of imiglucerase















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Cerezyme 200 U powder for concentrate for solution for infusion
Imiglucerase
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
-
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
In this leaflet
:
1. What Cerezyme is and what it is used for.
2. Before you use Cerezyme.
3. How to use Cerezyme.
4. Possible side effects.
5.
How to store Cerezyme.
6.
Further Information
WHAT CEREZYME IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Cerezyme is used to treat patients who have a confirmed diagnosis of Type I or Type 3 Gaucher
disease, who show signs of the disease such as: anaemia (low number of red blood cells), a tendency
to bleed easily (due to low numbers of platelets - a type of blood cell), spleen or liver enlargement or
bone disease.
People with Gaucher disease have low levels of an enzyme called acid -glucosidase. This enzyme
helps the body control levels of glucosylceramide. Glucosylceramide is a natural substance in the
body, made of sugar and fat
.
In Gaucher disease glucosylceramide levels can get too high.
Cerezyme is an artificial enzyme called imiglucerase - this can replace the natural enzyme acid -
glucosidase which is lacking or not active enough in patients with Gaucher disease.
The information in this leaflet applies to all patient groups including children, adolescents, adults and
the elderly.
2.
BEFORE YOU USE CEREZYME
If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to imiglucerase, or
if you are allergic to any of the other ingredients of Cerezyme.
Take special care with Cerezyme
-
If you are treated with Cerezyme, you may experience an allergic reaction while you are being
given the medicine or shortly after. If you experience a reaction like this, you should
tell your
doctor immediately
. Your doctor may test if you have an allergic reaction to imiglucerase.
Some patients with Gaucher disease have high blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary
hypertension). The cause can be unknown, or it can be due to heart, lung or liver problems. It
can occur whether the patient is treated with Cerezyme or not. But, if you suffer with any
shortness of breath
you should tell your doctor.
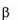

Using other medicines
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines,
including medicines obtained without a prescription.
Cerezyme should not be given as a mixture with other medicinal products in the same infusion (drip).
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine if you are pregnant or think you
may be pregnant. Cautious use of Cerezyme during pregnancy and breastfeeding is recommended.
Important information about some of the ingredients of Cerezyme
This medicinal product contains sodium and is administered in 0.9% sodium chloride intravenous
solution. To be taken into consideration by patients on a controlled sodium diet.
Instructions for proper use
Cerezyme is given through a drip into a vein (by intravenous infusion).
It is supplied as a powder which will be mixed with sterile water before it is given.
Cerezyme is only used under the supervision of a doctor who is knowledgeable in the treatment of
Gaucher disease. Your Doctor may advise that you can be treated at home provided you meet certain
criteria. Please contact your Doctor if you would like to be treated at home.
Your dose will be specific to you. Your doctor will work out your dose based on how severe your
symptoms are, and other factors. The recommended dose of Cerezyme is 60 units/kg body weight
given once every 2 weeks.
Your doctor will keep a close check on your response to your treatment, and may change your dose
(up or down) until he/she finds the best dose to control your symptoms.
Once this dose is found your doctor will still keep a check on your responses to make sure you are
using the right dose. This might be every 6 to 12 months.
There is no information on the effect of Cerezyme on brain-based symptoms of patients with chronic
neuronopathic Gaucher disease. Therefore no special dosage regimen can be recommended.
The ICGG Gaucher Registry
You can ask your doctor to register your patient information into the “ICGG Gaucher Registry”. The
aims of this Registry are to increase the understanding of Gaucher disease and to check how well
enzyme replacement therapy, like Cerezyme, works. This should lead to an improvement in the safe
and effective use of Cerezyme. Your patient data will be registered anonymously– nobody will know
it is information about you.
If you use more Cerezyme than you should
There are no cases of overdose of Cerezyme reported.
If you forget to use Cerezyme
If you have missed an infusion, please contact your doctor.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Like all medicines, Cerezyme can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If you experience any serious side effects or side effects not listed below, please
tell your doctor
immediately
.
Common side effects
(occurring in more than 1 in 100 patients) are:
-
hives/ localised swelling of the skin or lining of the mouth or throat
Uncommon side effects
(occurring in more than 1 in 1000 patients) are:
-
a sensation of tingling, pricking, burning or numbness of the skin
injection site sterile abcess
Some side effects were seen primarily while patients were being given the medicine or shortly after.
These have included itching, flushing, hives/localised swelling of the skin or lining of the mouth or
throat, chest discomfort, increased heart rate, bluish skin, breathlessness, a sensation of tingling,
pricking, burning or numbness of the skin, fall in blood pressure and backache. If you experience any
of these symptoms, please
tell your doctor immediately
. You may need to be given additional
medicines to prevent an allergic reaction (e.g. antihistamines and/or corticosteroids).
If any of these side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Cerezyme after the expiry date printed on the labelling after the letters “EXP”. The expiry
date refers to the last date of that month.
Unopened vials:
Store in a refrigerator (2 C – 8 C)
Diluted solution:
It is recommended that Cerezyme is used immediately after it has been mixed with sterile water. The
mixed solution in the vial cannot be stored and should be promptly diluted in an infusion bag; only the
diluted solution can be held for up to 24 hours if it is kept cool (2°C – 8°C) and in the dark.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
The active substance is imiglucerase. Imiglucerase is a modified form of the human enzyme
acid -glucosidase produced by recombinant DNA technology.
One vial contains 200 units of
imiglucerase. After reconstitution, the solution contains 40 units of imiglucerase per ml.
Mannitol, Sodium citrate, Citric acid monohydrate, Polysorbate 80
What Cerezyme looks like and contents of the pack
Cerezyme, 200 U, is presented as a powder for concentrate for solution for infusion (in a vial- pack
size of 1 or 25). Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Cerezyme is supplied as a white to off-white powder. After reconstitution it is a clear, colourless
liquid, free from foreign matter. The reconstituted solution must be further diluted.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Genzyme Europe B.V., Gooimeer 10, 1411 DD, Naarden, The Netherlands
Manufacturer
Genzyme Ltd., 37 Hollands Road, Haverhill, Suffolk CB9 8PU, United Kingdom


For any information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the Marketing
Authorisation Holder.
België/Belgique/Belgien/
Luxemburg/Luxembourg
Genzyme Belgium N.V.,
Tél/Tel: +32 2 714 17 11
Magyarország
Genzyme Europe B.V. Képviselet
Tel: +36 1 310 7440
България
Търговско представителство на Genzyme
CEE GmbH
Тел. +359 2 971 1001
Nederland
Genzyme Europe B.V.,
Tel: +31 35 6991200
Česká Republika/Slovenská Republika/
Slovenija
Genzyme Czech s.r.o.,
Tel: +420 +420 221 722 511
Österreich
Genzyme Austria GmbH,
Tel: +43 1 774 65 38
Danmark/Norge/Sverige/Suomi/Finland/
Ísland
Genzyme A/S, (Danmark/Tanska/Danmörk),
Tlf/Puh./Sími: +45 32712600
Polska/Eesti/Latvija/Lietuva
Genzyme Polska Sp. z o. o.
(Poola/Polija/Lenkija),
Tel: + 48 22 24 60 900
Deutschland
Genzyme GmbH,
Tel: +49 610236740
Portugal
Genzyme Portugal, S.A.,
Tel: +351 21 422 0100
Ελλά/Κύπρς
Genzyme Hellas Ltd. (Ελλά)
Τηλ: +30 210 99 49 270
România
Genzyme CEE GmbH- Reprezentanţa pentru
România
Tel: +40212434228
España
Genzyme, S.L.U.,
Tel: +34 91 6591670
United Kingdom/Ireland
Genzyme Therapeutics Ltd. (United
Kingdom), Tel: +44 1865 405200
France
Genzyme S.A.S,
Tél: + 33 (0) 825 825 863
Italia/Malta
Genzyme Srl (Italia/Italja),
Tel: +39 059 349811
This leaflet was last approved in:
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency web site:
<------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following information is intended for medical or healthcare professionals only:
Instructions for use – reconstitution, dilution and administration
Each vial of Cerezyme is for single use only. After reconstitution, each vial of Cerezyme contains 200
units of imiglucerase in 5.0 ml (40 units per ml).
Determine the number of vials to be reconstituted based on the individual patient's dosage regimen
and remove the vials from the refrigerator.












Use Aseptic Technique
Reconstitution
Reconstitute each vial with 5.1 ml
water for injections
; avoid forceful impact of water for injections
on the powder and, by mixing gently, avoid foaming of the solution. The reconstituted volume is
5.3 ml. The pH of the reconstituted solution is approximately 6.1.
After reconstitution it is a clear, colourless liquid, free from foreign matter. The reconstituted solution
must be further diluted. Before further dilution, visually inspect the reconstituted solution in each vial
for foreign particles and discoloration. Do
not
use vials exhibiting foreign particles or discoloration.
After reconstitution,
promptly dilute
vials and do not store for subsequent use.
Dilution
The reconstituted solution contains 40 units imiglucerase per ml. The reconstituted volume allows
accurate withdrawal of 5.0 ml (equal to 200 units) from each vial. Withdraw 5.0 ml reconstituted
solution from each vial and combine the withdrawn volumes. Then dilute the combined volumes with
0.9% sodium chloride intravenous solution
to a total volume of 100 to 200 ml. Mix the infusion
solution gently.
Administration
It is recommended to administer the diluted solution through an in-line low protein-binding 0.2 µm
filter to remove any protein particles. This will not lead to any loss of imiglucerase activity. It is
recommended that the diluted solution be administered within 3 hours. The product diluted in 0.9%
sodium chloride intravenous solution will retain chemical stability if stored up to 24 hours at 2°C and
8°C under protection from light; but microbiological safety will depend on the reconstitution and
dilution having been performed aseptically.
Cerezyme contains no preservatives. Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in
accordance with local requirements.
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Cerezyme 400 U powder for concentrate for solution for infusion
Imiglucerase
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
-
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet.
please tell your doctor or pharmacist
In this leaflet
:
1. What Cerezyme is and what it is used for.
2. Before you use Cerezyme.
3. How to use Cerezyme.
4. Possible side effects.
5.
How to store Cerezyme.
6.
Further Information
WHAT CEREZYME IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Cerezyme is used to treat patients who have a confirmed diagnosis of Type I or Type 3 Gaucher
disease, who show signs of the disease such as: anaemia (low number of red blood cells), a tendency
to bleeding easily (due to low numbers of platelets – a type of blood cell), spleen or liver enlargement
or bone disease.
People with Gaucher disease have low levels of an enzyme called acid -glucosidase. This enzyme
helps the body control levels of glucosylceramide. Glucosylceramide is a natural substance in the
body, made of sugar and fat
.
In Gaucher disease glucosylceramide levels can get too high.
Cerezyme is an artificial enzyme called imiglucerase -this can replace the natural enzyme acid -
glucosidase which is lacking or not active enough in patients with Gaucher disease.
The information in this leaflet applies to all patient groups including children, adolescents, adults and
the elderly.
2.
BEFORE YOU USE CEREZYME
If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to imiglucerase, or
if you are allergic to any of the other ingredients of Cerezyme.
Take special care with Cerezyme
-
If you are treated with Cerezyme, you may experience an allergic reaction while you are being
given the medicine or shortly after. If you experience a reaction like this, you should
tell your
doctor immediately
. Your doctor may test if you have an allergic reaction to imiglucerase.
Some patients with Gaucher disease have high blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary
hypertension). The cause can be unknown, or it can be due to heart, lung or liver problems. It
can occur whether the patient is treated with Cerezyme or not. But, if you suffer with any
shortness of breath
you should tell your doctor.
Using other medicines
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines,
including medicines obtained without a prescription.
Cerezyme should not be given as a mixture with other medicinal products in the same infusion (drip).
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine if you are pregnant or think you
may be pregnant. Cautious use of Cerezyme during pregnancy and breastfeeding is recommended.
Important information about some of the ingredients of Cerezyme
This medicinal product contains sodium and is administered in 0.9% sodium chloride intravenous
solution. To be taken into consideration by patients on a controlled sodium diet.
Instructions for proper use
Cerezyme is given through a drip into a vein (by intravenous infusion).
It is supplied as a powder which will be mixed with sterile water before it is given.
Cerezyme is only used under the supervision of a doctor who is knowledgeable in the treatment of
Gaucher disease. Your Doctor may advise that you can be treated at home provided you meet certain
criteria. Please contact your Doctor if you would like to be treated at home.
Your dose will be specific to you. Your doctor will work out your dose based on how severe your
symptoms are, and other factors. The recommended dose of Cerezyme is 60 units/kg body weight
given once every 2 weeks.
Your doctor will keep a close check on your response to your treatment, and may change your dose
(up or down) until he/she finds the best dose to control your symptoms.
Once this dose is found your doctor will still keep a check on your responses to make sure you are
using the right dose. This might be every 6 to 12 months.
There is no information on the effect of Cerezyme on brain-based symptoms of patients with chronic
neuronopathic Gaucher disease. Therefore no special dosage regimen can be recommended.
The ICGG Gaucher Registry
You can ask your doctor to register your patient information into the “ICGG Gaucher Registry”. The
aims of this Registry are to increase the understanding of Gaucher disease and to check how well
enzyme replacement therapy, like Cerezyme, works. This should lead to improvement in the safe and
effective use of Cerezyme. Your patient data will be registered anonymously– nobody will know it is
information about you.
If you use more Cerezyme than you should
There are no cases of overdose of Cerezyme reported.
If you forget to use Cerezyme
If you have missed an infusion, please contact your doctor.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Like all medicines, Cerezyme can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If you experience any serious side effects or side effects not listed below, please
tell your doctor
immediately
.
Common side effects
(occurring in more than 1 in 100 patients) are:
-
hives/ localised swelling of the skin or lining of the mouth or throat
Uncommon side effects
(occurring in more than 1 in 1000 patients) are:
-
a sensation of tingling, pricking, burning or numbness of the skin
injection site sterile abcess
Some side effects were seen primarily while patients were being given the medicine or shortly after.
These have included itching, flushing, hives/localised swelling of the skin or lining of the mouth or
throat, chest discomfort, increased heart rate, bluish skin, breathlessness, a sensation of tingling,
pricking, burning or numbness of the skin, fall in blood pressure and backache. If you experience any
of these symptoms, please
tell your doctor immediately
. You may need to be given additional
medicines to prevent an allergic reaction (e.g. antihistamines and/or corticosteroids).
If any of these side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Cerezyme after the expiry date printed on the labelling after the letters “EXP”. The expiry
date refers to the last date of that month.
Unopened vials:
Store in a refrigerator (2 C – 8 C)
Diluted solution:
It is recommended that Cerezyme is used immediately after it has been mixed with sterile water. The
mixed solution in the vial cannot be stored and should be promptly diluted in an infusion bag; only the
diluted solution can be held for up to 24 hours if it is kept cool (2°C – 8°C) and in the dark.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
The active substance is imiglucerase. Imiglucerase is a modified form of the human enzyme
acid -glucosidase produced by recombinant DNA technology.
One vial contains 400 units of
imiglucerase. After reconstitution, the solution contains 40 units of imiglucerase per ml.
Mannitol, Sodium citrate, Citric acid monohydrate, Polysorbate 80
What Cerezyme looks like and contents of the pack
Cerezyme, 400 U, is presented as a powder for concentrate for solution for infusion (in a vial- pack
size of 1, 5 or 25). Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Cerezyme is supplied as a white to off-white powder. After reconstitution it is a clear, colourless
liquid, free from foreign matter. The reconstituted solution must be further diluted.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Genzyme Europe B.V., Gooimeer 10, 1411 DD, Naarden, The Netherlands
Manufacturer
Genzyme Ltd., 37 Hollands Road, Haverhill, Suffolk CB9 8PU, United Kingdom

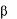
For any information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the Marketing
Authorisation Holder.
België/Belgique/Belgien/
Luxemburg/Luxembourg
Genzyme Belgium N.V.,
Tél/Tel: +32 2 714 17 11
Magyarország
Genzyme Europe B.V. Képviselet
Tel: +36 1 310 7440
България
Търговско представителство на Genzyme
CEE GmbH
Тел. +359 2 971 1001
Nederland
Genzyme Europe B.V.,
Tel: +31 35 6991200
Česká Republika/Slovenská Republika/
Slovenija
Genzyme Czech s.r.o.,
Tel: +420 221 722 511
Österreich
Genzyme Austria GmbH,
Tel: +43 1 774 65 38
Danmark/Norge/Sverige/Suomi/Finland/
Ísland
Genzyme A/S, (Danmark/Tanska/Danmörk),
Tlf/Puh./Sími: +45 32712600
Polska/Eesti/Latvija/Lietuva
Genzyme Polska Sp. z o. o.
(Poola/Polija/Lenkija),
Tel: + 48 22 24 60 900
Deutschland
Genzyme GmbH,
Tel: +49 610236740
Portugal
Genzyme Portugal, S.A.,
Tel: +351 21 422 0100
Ελλά/Κύπρς
Genzyme Hellas Ltd. (Ελλά)
Τηλ: +30 210 99 49 270
România
Genzyme CEE GmbH- Reprezentanţa pentru
România
Tel: +40212434228
España
Genzyme, S.L.U.,
Tel: +34 91 6591670
United Kingdom/Ireland
Genzyme Therapeutics Ltd. (United
Kingdom), Tel: +44 1865 405200
France
Genzyme S.A.S,
Tél: + 33 (0) 825 825 863
Italia/Malta
Genzyme Srl (Italia/Italja),
Tel: +39 059 349811
This leaflet was last approved in:
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency web site:
<------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following information is intended for medical or healthcare professionals only:
Instructions for use – reconstitution, dilution and administration
Each vial of Cerezyme is for single use only. After reconstitution, each vial of Cerezyme contains 400
units of imiglucerase in 10.0 ml (40 units per ml).
Determine the number of vials to be reconstituted based on the individual patient's dosage regimen
and remove the vials from the refrigerator.












Use Aseptic Technique
Reconstitution
Reconstitute each vial with 10.2 ml
water for injections
; avoid forceful impact of water for injections
on the powder and, by mixing gently, avoid foaming of the solution. The reconstituted volume is
10.6 ml. The pH of the reconstituted solution is approximately 6.1.
After reconstitution it is a clear, colourless liquid, free from foreign matter. The reconstituted solution
must be further diluted. Before further dilution, visually inspect the reconstituted solution in each vial
for foreign particles and discoloration. Do
not
use vials exhibiting foreign particles or discoloration.
After reconstitution,
promptly dilute
vials and do not store for subsequent use.
Dilution
The reconstituted solution contains 40 units imiglucerase per ml. The reconstituted volume allows
accurate withdrawal of 10.0 ml (equal to 400 units) from each vial. Withdraw 10.0 ml reconstituted
solution from each vial and combine the withdrawn volumes. Then dilute the combined volumes with
0.9% sodium chloride intravenous solution
to a total volume of 100 to 200 ml. Mix the infusion
solution gently.
Administration
It is recommended to administer the diluted solution through an in-line low protein-binding 0.2 µm
filter to remove any protein particles. This will not lead to any loss of imiglucerase activity. It is
recommended that the diluted solution be administered within 3 hours. The product diluted in 0.9%
sodium chloride intravenous solution will retain chemical stability if stored up to 24 hours at 2°C and
8°C under protection from light; but microbiological safety will depend on the reconstitution and
dilution having been performed aseptically.
Cerezyme contains no preservatives. Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in
accordance with local requirements.
Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/cerezyme.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|
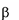








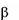
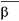












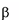
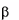








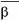





































































































































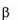















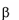
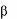

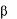












 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































