Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Cholestagel 625 mg film-coated tablets
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each tablet contains 625 mg colesevelam (as hydrochloride).
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Film-coated tablet (tablet).
Off-white, capsule-shaped film-coated tablets imprinted with “Cholestagel” on one side.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Cholestagel co-administered with a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase
inhibitor (statin) is indicated as adjunctive therapy to diet to provide an additive reduction in
low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels in adult patients with primary
hypercholesterolaemia who are not adequately controlled with a statin alone.
Cholestagel as monotherapy is indicated as adjunctive therapy to diet for reduction of elevated
total-cholesterol and LDL-C in adult patients with primary hypercholesterolaemia, in whom a statin is
considered inappropriate or is not well-tolerated.
Cholestagel can also be used in combination with ezetimibe, with or without a statin, in adult patients
with primary hypercholesterolaemia, including patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia (see
section 5.1).
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Posology
Combination therapy
The recommended dose of Cholestagel for combination with a statin with or without ezetimibe is 4 to
6 tablets per day. The maximum recommended dose is 6 tablets per day taken as 3 tablets twice per
day with meals or 6 tablets taken once per day with a meal. Clinical trials have shown that
Cholestagel and statins can be co-administered or dosed apart, and that Cholestagel and ezetimibe can
be co-administered or dosed apart.
Monotherapy
The recommended starting dose of Cholestagel is 6 tablets per day taken as 3 tablets twice per day
with meals or 6 tablets once per day with a meal. The maximum recommended dose is 7 tablets per
day.
During therapy, the cholesterol-lowering diet should be continued, and serum total-C, LDL-C and
triglyceride levels should be determined periodically during treatment to confirm favourable initial
and adequate long-term responses.
When a drug interaction cannot be excluded with a concomitant medicinal product for which minor
variations in the therapeutic level would be clinically important, or where no clinical data are
available on co-administration, Cholestagel should be administered at least four hours before or at
least four hours after the concomitant medication in order to minimize the risk of reduced absorption
of the concomitant medication (see section 4.5).
Elderly population
There is no need for dose adjustment when Cholestagel is administered to elderly patients.
Paediatric population
Currently available data are described in section 5.1 but no recommendation on a posology can be
made.
Method of administration
Cholestagel tablets should be taken orally with a meal and liquid.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients
Bowel or biliary obstruction
4.4 Special warnings and special precautions for use
Prior to initiating therapy with Cholestagel, if secondary causes of hypercholesterolaemia (i.e., poorly
controlled diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, nephrotic syndrome, dysproteinaemias, obstructive liver
disease) are considered, these should be diagnosed and properly treated.
For patients on ciclosporin starting or stopping Cholestagel or patients on Cholestagel with a need to
start ciclosporin
: Cholestagel reduces the bioavailability of ciclosporin (see also section 4.5).
Patients starting on ciclosporin already taking Cholestagel should have their ciclosporin blood
concentrations monitored as normal and their dose adjusted as normal. Patients starting on
Cholestagel already taking ciclosporin should have their blood concentrations monitored prior to
combination therapy and frequently monitored immediately starting co-therapy with the ciclosporin
dose adjusted accordingly. It should be noted that stopping Cholestagel therapy will result in
increased ciclosporin blood concentrations. Therefore, patients taking both ciclosporin and
Cholestagel should have their blood concentrations monitored prior to and frequently after when
Cholestagel therapy is stopped with their ciclosporin dose adjusted accordingly.
Caution should be exercised when treating patients with triglyceride levels greater than 3.4 mmol/L
due to the triglyceride increasing effect with Cholestagel. Safety and efficacy are not established for
patients with triglyceride levels greater than 3.4 mmol/L, since such patients were excluded from the
clinical studies.
The safety and efficacy of Cholestagel in patients with dysphagia, swallowing disorders, severe
gastrointestinal motility disorders, inflammatory bowel disease, liver failure or major gastrointestinal
tract surgery have not been established. Consequently, caution should be exercised when Cholestagel
is used in patients with these disorders.
Cholestagel can induce or worsen present constipation. The risk of constipation should especially be
considered in patients with coronary heart disease and angina pectoris.
Anticoagulant therapy should be monitored closely in patients receiving warfarin or similar agents, since
bile acid sequestrants, like Cholestagel, have been shown to reduce absorption of vitamin K and
therefore interfere with warfarin‟s anticoagulant effect (see also section 4.5).


Cholestagel can affect the bioavailability of the oral contraceptive pill when administered
simultaneously. It is important to ensure that Cholestagel is administered at least 4 hours after the oral
contraceptive pill to minimise the risk of any interaction (see also section 4.5).
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
In general
Cholestagel may affect the bioavailability of other medicinal products. Therefore when a drug
interaction cannot be excluded with a concomitant medicinal product for which minor variations in
the therapeutic level would be clinically important, Cholestagel should be administered at least four
hours before or at least four hours after the concomitant medication to minimize the risk of reduced
absorption of the concomitant medication. For concomitant medications which require administration
via divided doses, it should be noted that the required dose of Cholestagel can be taken once a day.
When administering medicinal products for which alterations in blood levels could have a clinically
significant effect on safety or efficacy, physicians should consider monitoring serum levels or effects.
Interaction studies have only been performed in adults.
In interaction studies in healthy volunteers, Cholestagel had no effect on the bioavailability of digoxin,
metoprolol, quinidine, valproic acid, and warfarin. Cholestagel decreased the C
max
and AUC of
sustained-release verapamil by approximately 31% and 11%, respectively. Since there is a high degree
of variability in the bioavailability of verapamil, the clinical significance of this finding is unclear.
There have been very rare reports of reduced phenytoin levels in patients who have received Cholestagel
administered with phenytoin.
Anticoagulant therapy
Anticoagulant therapy should be monitored closely in patients receiving warfarin or similar agents,
since bile acid sequestrants, like Cholestagel, have been shown to reduce absorption of vitamin K and
therefore interfere with warfarin's anticoagulant effect. Specific clinical interaction studies with
colesevelam and vitamin K have not been performed.
Levothyroxine
In an interaction study in healthy volunteers, Cholestagel reduced the AUC and C
max
of levothyroxine
when administered either concomitantly or after 1 hour. No interaction was observed when
Cholestagel was administered at least four hours after levothyroxine.
Oral contraceptive pill
In an interaction study in healthy volunteers, Cholestagel reduced the C
max
of norethindrone as well as
the AUC and C
max
of ethinylestradiol when administered simultaneously with the oral contraceptive
pill. This interaction was also observed when Cholestagel was administered one hour after the oral
contraceptive pill. However no interaction was observed when Cholestagel was administered four
hours after the oral contraceptive pill.
Ciclosporin
In an interaction study in healthy volunteers, co-administration of Cholestagel and ciclosporin
significantly reduced the AUC
0-inf
and C
max
of ciclosporin by 34% by 44%, respectively. Therefore
advice is given to closely monitor ciclosporin blood concentrations (see also section 4.4). In addition,
based on theoretical grounds Cholestagel should be administered at least 4 hours after ciclosporin in
order to further minimise the risks related to the concomitant administration of ciclosporin and
Cholestagel. Furthermore, Cholestagel should always be administered at the same times consistently
since the timing of intake of Cholestagel and ciclosporin could theoretically influence the degree of
reduced bioavailability of ciclosporin.
Statins
When Cholestagel was co-administered with statins in clinical studies, an expected add-on LDL-C
lowering effect was observed, and no unexpected effects were observed. Cholestagel had no effect on
the bioavailability of lovastatin in an interaction study.
Antidiabetic agents
Co-administration of Cholestagel and glyburide (also known as glibenclamide) caused a decrease in
the AUC
0-inf
and C
max
of glyburide by 32% and 47%, respectively. No interaction was observed when
Cholestagel was administered four hours after glyburide.
Co-administration of Cholestagel and repaglinide had no effect on the AUC and caused a 19%
reduction in the C
max
of repaglinide, the clinical significance of which is unknown. No interaction was
observed when Cholestagel was administered one hour after repaglinide.
No interaction was observed when Cholestagel and pioglitazone were administered simultaneously in
healthy volunteers
Ursodeoxycholic acid
Cholestagel predominantly binds hydrophobic bile acids. In a clinical study Cholestagel did not affect
the faecal excretion of endogenous (hydrophilic) ursodeoxycholic acid. However, formal interaction
studies with ursodeoxycholic acid have not been performed. As noted in general, when a drug
interaction cannot be excluded with a concomitant medicinal product, Cholestagel should be
administered at least fours hour before or at least four hours after the concomitant medication to
minimise the risk of reduced absorption of the concomitant medication. Monitoring of the clinical
effects of treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid should be considered.
Other forms of interaction
Cholestagel did not induce any clinically significant reduction in the absorption of vitamins A, D, E or
K during clinical studies of up to one year. However, caution should be exercised when treating
patients with a susceptibility to vitamin K or fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies, such as patients with
malabsorption. In these patients, monitoring vitamin A, D and E levels and assessing vitamin K status
through the measurement of coagulation parameters is recommended and the vitamins should be
supplemented if necessary.
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
No clinical data are available on the use of Cholestagel in pregnant women. Animal studies do not
indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to pregnancy, embryonic/foetal development,
parturition or postnatal development (see section 5.3). Caution should be exercised when prescribing
to pregnant women.
Lactation
The safety of Cholestagel has not been established in breast-feeding women. Caution should be
exercised when prescribing to breast-feeding women.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Cholestagel has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
In controlled clinical studies involving approximately 1400 patients, the following adverse reactions
were reported in patients given Cholestagel. The reporting rate is classified as very common (≥1/10),
common (≥1/100, <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1,000, <1/100), rare (≥1/10,000, <1/1,000), very rare
(<1/10,000), including isolated.
Investigations
Common:
Serum triglycerides increased
Uncommon
:Serum transaminase increased
Nervous system disorders
Common:
Headache
Gastrointestinal disorders
Very common
: Flatulence, constipation
Common
: Vomiting, diarrhoea, dyspepsia, , abdominal pain,
abnormal stools, nausea
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Uncommon
: Myalgia
The background incidence of flatulence and diarrhoea were higher in patients receiving placebo in the
same controlled clinical studies. Only constipation and dyspepsia were reported by a higher
percentage among those receiving Cholestagel, compared with placebo.
Adverse reactions were generally mild or moderate in intensity.
Cholestagel in combination with statins and in combination with ezetimibe was well tolerated and the
adverse reactions observed were consistent with the known safety profile of statins or ezetimibe
alone.
Since Cholestagel is not absorbed, the risk of systemic toxicity is low. Gastrointestinal symptoms could
occur. Doses in excess of the maximum recommended dose (4.5 g per day (7 tablets)) have not been
tested.
Should overdosage occur, however, the chief potential harm would be obstruction of the gastrointestinal
tract. The location of such potential obstruction, the degree of obstruction and the presence or absence of
normal gut motility would determine treatment.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1
Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: bile acid sequestrants, ATC code: C10A C 04
The mechanism of action for the activity of colesevelam, the active substance in Cholestagel, has been
evaluated in several
in vitro
and
in vivo
studies. These studies have demonstrated that colesevelam
binds bile acids, including glycocholic acid, the major bile acid in humans. Cholesterol is the sole
precursor of bile acids. During normal digestion, bile acids are secreted into the intestine. A major
portion of bile acids is then absorbed from the intestinal tract and returned to the liver via the
enterohepatic circulation.
Colesevelam is a non-absorbed, lipid-lowering polymer that binds bile acids in the intestine, impeding
their reabsorption. The LDL-C lowering mechanism of bile acid sequestrants has been previously
established as follows: As the bile acid pool becomes depleted, the hepatic enzyme, cholesterol
7- -hydroxylase, is upregulated, which increases the conversion of cholesterol to bile acids. This
causes an increased demand for cholesterol in the liver cells, resulting in the dual effects of increasing
transcription and activity of the cholesterol biosynthetic enzyme, hydroxymethyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A
(HMG-CoA) reductase, and increasing the number of hepatic low-density lipoprotein receptors. A
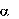















concomitant increase in very low density lipoprotein synthesis can occur. These compensatory effects
result in increased clearance of LDL-C from the blood, resulting in decreased serum LDL-C levels.
In a 6-month dose-response study in patients with primary hypercholesterolaemia receiving 3.8 or
4.5 g Cholestagel daily, a 15 to 18% decrease in LDL-C levels was observed, which was evident
within 2 weeks of administration. In addition, Total-C decreased 7 to 10%, HDL-C increased 3% and
triglycerides increased 9 to 10%. Apo B decreased by 12%. In comparison, in patients given placebo,
LDL-C, Total-C, HDL-C and Apo-B were unchanged, while triglycerides increased 5%. Studies
examining administration of Cholestagel as a single dose with breakfast, a single dose with dinner, or
as divided doses with breakfast and dinner did not show significant differences in LDL-C reduction
for different dosing schedules. However, in one study triglycerides tended to increased more when
Cholestagel was given as a single dose with breakfast.
In a 6 week study 129 patients with mixed hyperlipidaemia were randomised to fenofibrate 160 mg
plus 3.8 g Cholestagel or fenofibrate alone. The fenofibrate plus Cholestagel group (64 patients)
demonstrated a 10% reduction on LDL-C levels versus 2% increase for the fenofibrate group
(65 patients). Reductions were also seen for non-HDL-C, Total-C and Apo B. A small 5%,
non-significant increase in triglycerides was noted. The effects of combination of fenofibrate and
Cholestagel on the risks of myopathy or hepatotoxicity are not known.
Multi-centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in 487 patients demonstrated an
additive reduction of 8 to 16% in LDL-C when 2.3 to 3.8 g Cholestagel and a statin (atorvastatin,
lovastatin or simvastatin) were administered at the same time.
The effect of 3.8 g Cholestagel plus 10 mg ezetimibe versus 10 mg ezetimibe alone on LDL-C levels
was assessed in a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study in
86 patients with primary hypercholesterolaemia over a 6-week treatment period. The combination of
ezetimibe 10 mg and Cholestagel 3.8 g daily therapy in the absence of a statin resulted in a significant
combined effect for LDL-C lowering by 32% demonstrating an additional effect of 11% LDL-C
lowering with Cholestagel and ezetimibe compared to ezetimibe alone.
The addition of Cholestagel 3.8 g daily to maximally-tolerated statin and ezetimibe therapy was
assessed in a multi-centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 86 patients with
familial hypercholesterolaemia. A total of 85% of the patients were on either atorvastatin (50% of
whom received 80 mg dose) or rosuvastatin (72% of whom received 40 mg dose). Cholestagel
resulted in a statistically significant LDL-C reduction of 11% and 11% at 6 and 12 weeks vs an
increase of 7% and 1% in the placebo group; mean baseline levels were 3.75mmol/L and 3.86
mmol/L, respectively. Triglycerides in the Cholestagel group increased by 19% and 13% at 6 and 12
weeks vs an increase of 6% and 13% in the placebo group, but the increases were not significantly
different. HDL-C and hsCRP levels were also not significantly different compared to placebo at 12
weeks.
In the paediatric population, the safety and efficacy of 1.9 or 3.8 g/day Cholestagel was assessed in an
8 week multi-centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 194 boys and
postmenarchal girls, aged 10-17 years, with heterozygous FH on a stable dose of statins (47 patients,
24%) or treatment-naïve to lipid-lowering therapy (147 patients, 76%). For all patients, Cholestagel
resulted in a statistically significant LDL-C reduction of 11% at 3.8 g/day and 4% at 1.9 g/day, versus
a 3% increase in the placebo group. For statin-naïve patients on monotherapy, Cholestagel resulted in
a statistically significant LDL-C reduction of 12% at 3.8 g/day and 7% at 1.9 g/day, versus a 1%
reduction in the placebo group (see section 4.2). There were no significant effects on growth, sexual
maturation, fat-soluble vitamin levels or clotting factors, and the adverse reaction profile for
Cholestagel was comparable to that seen with placebo.
Cholestagel has not been compared directly to other bile acid sequestrants in clinical trials.
So far, no studies have been conducted that directly demonstrate whether treatment with Cholestagel
as monotherapy or combination therapy has any effect on cardiovascular morbidity or mortality.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Cholestagel is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Effects in non-clinical studies were observed only at exposures considered sufficiently in excess of
the maximum human exposure indicating little relevance to clinical use.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Tablet core:
Cellulose (E460), microcrystalline
Silica, colloidal anhydrous
Magnesium stearate
Water, purified
Film-coating:
Hypromellose (E464)
Diacetylated monoglycerides
Printing ink:
Iron oxide black (E172)
Hypromellose (E464)
Propylene glycol
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Keep the bottle tightly closed in order to protect from moisture.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
High density polyethylene bottles with a polypropylene cap.
Package sizes are: 24 tablets (1 X 24)
100 tablets (2 X 50)
180 tablets (1 X 180)
High density polyethylene bottles with a polypropylene cap without outer carton.
Package sizes are: 180 tablets (1 X 180)
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Instructions precautions for disposal and other handling
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Genzyme Europe B.V., Gooimeer 10, NL-1411 DD Naarden, The Netherlands.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
10 March 2004/12 March 2009
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this product is available on the website of the European Medicines
Agency (EMEA) http://www.emea.europa.eu/
MANUFACTURER(S) OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE
SUBSTANCE(S) AND MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION
HOLDER(S) RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH RELEASE
B.
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
MANUFACTURER(S) OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S) AND
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER(S) RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer(s) responsible for batch release
Genzyme Ireland Ltd., IDA Industrial Park, Old Kilmeaden Road, Waterford, Ireland
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Risk Management Plan
The MAH commits to performing the studies and additional pharmacovigilance activities detailed in
the Pharmacovigilance Plan, as agreed in version 1 of the Risk Management Plan (RMP) presented in
Module 1.8.2. of the Marketing Authorisation and any subsequent updates of the RMP agreed by the
CHMP.
The holder of this marketing authorisation must inform the European Commission about the
marketing plans for the medicinal product authorised by this decision.

ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING AND THE IMMEDIATE
PACKAGING
OUTER CARTON AND BOTTLE LABEL (24 TABLETS)
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Cholestagel 625 mg film-coated tablets
Colesevelam hydrochloride
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each tablet contains 625 mg of colesevelam (as hydrochloride).
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Oral use
Tablets should be taken with liquid and with a meal.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Keep the bottle tightly closed in order to protect from moisture.























10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Genzyme Europe B.V.
Gooimeer 10
1411 DD Naarden
The Netherlands
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE

















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING AND IMMEDIATE
PACKAGING
OUTER CARTON AND BOTTLE LABEL (100 TABLETS)
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Cholestagel 625 mg film-coated tablets
Colesevelam hydrochloride
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each tablet contains 625 mg of colesevelam (as hydrochloride).
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Oral use
Tablets should be taken with liquid and with a meal.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Keep the bottle tightly closed in order to protect from moisture.























10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Genzyme Europe B.V.
Gooimeer 10
1411 DD Naarden
The Netherlands
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE

















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING AND IMMEDIATE
PACKAGING
OUTER CARTON AND BOTTLE LABEL (180 TABLETS)
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Cholestagel 625 mg film-coated tablets
Colesevelam hydrochloride
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each tablet contains 625 mg of colesevelam (as hydrochloride).
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Oral use
Tablets should be taken with liquid and with a meal.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Keep the bottle tightly closed in order to protect from moisture.























10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Genzyme Europe B.V.
Gooimeer 10
1411 DD Naarden
The Netherlands
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE

















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
BOTTLE LABEL (180 TABLETS) WITHOUT CARTON
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Cholestagel 625 mg film-coated tablets
Colesevelam hydrochloride
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each tablet contains 625 mg of colesevelam (as hydrochloride).
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Oral use
Tablets should be taken with liquid and with a meal.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Keep the bottle tightly closed in order to protect from moisture.























10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Genzyme Europe B.V.
Gooimeer 10
1411 DD Naarden
The Netherlands
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE

















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Cholestagel 625 mg film-coated tablets
Colesevelam hydrochloride
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
-
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
What Cholestagel is and what it is used for
Before you take Cholestagel
WHAT CHOLESTAGEL IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Taking Cholestagel helps to lower the level of cholesterol in your blood. Your doctor should only give
you Cholestagel if a diet low in fat and cholesterol did not work well enough on its own.
Cholestagel works in your intestinal system by binding bile acids produced by your liver and carrying
the bile acids out of your body with your faeces. This prevents your body from recycling the bile acids
from your intestines in the usual way. Without the recycling process, your liver has to make additional
bile acids. Your liver uses cholesterol from your blood to do this, which lowers the level of
cholesterol in your blood.
Cholestagel is prescribed to treat a condition known as primary hypercholesterolaemia (when
cholesterol in the blood is elevated).
-
Cholestagel may be prescribed on its own in addition to a diet low in fat and cholesterol when
treatment with a statin (a class of cholesterol-lowering medicines that work in the liver) is
inappropriate or not well tolerated.
-
Cholestagel may be used together with a statin and the diet low in fat and cholesterol when
patients are not appropriately controlled by the statin on its own.
-
Cholestagel may also be used together with ezetimibe (a cholesterol-lowering medicine that works
by reducing cholesterol absorption from the gut), with or without a statin.
BEFORE YOU TAKE CHOLESTAGEL
Do not take Cholestagel
-
if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to colesevelam or to any of the other ingredients of
Cholestagel
-
if you have a blockage in your intestines or bile ducts (tubes that carry bile)
If you are prescribed Cholestagel and any other medication together you must also read the patient
information leaflet that comes with that particular medicine before you start to take your medicine.
Take special care with Cholestagel
-
if your triglyceride levels (a blood fat) are greater than 3.4 mmol/L
-
if you have difficulty in swallowing, or have a major stomach or intestinal disorder
-
if you are taking another medication called ciclosporin (a medicine used to suppress the immune
system)
-
if you are taking an oral contraceptive pill.
-
if you are taking anticoagulant therapy you should consult with your physician to closely monitor
anticoagulation levels, as Cholestagel may affect the absorption of vitamin K and therefore
interfere with the activity of warfarin, a medicine used to thin blood.
-
if you suffer from constipation, as Cholestagel may induce or worsen this condition. This is
especially important for patients with coronary heart disease and angina pectoris.
If you think any of these apply to you, you should inform your doctor or pharmacist before taking
Cholestagel.
Before starting therapy with Cholestagel, your physician should make sure that certain conditions do
not contribute to your elevated cholesterol levels. These could include poorly controlled diabetes,
untreated hypothyroidism (low levels of thyroid hormone for which no treatment is being given
currently), proteins in urine (nephrotic syndrome), altered protein levels in the blood
(dysproteinaemias), and blockage of the bile transport to your gall bladder (obstructive liver disease).
Taking other medicines
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines,
including medicines obtained without a prescription.
If your doctor suspects that Cholestagel may have an effect on the absorption of the other medication,
you may be advised to take Cholestagel at least 4 hours before or at least 4 hours after taking the other
medication. If you need to take other medicines more than once a day, remember that your
Cholestagel tablets can be taken once a day.
Cholestagel may affect the way in which the following medicines work:
Anticoagulant therapy
(medicines, such as warfarin, used to thin blood) (see section on
Taking special care with Cholestagel for further information)
Thyroid replacement therapy (medicines, such as thyroxine or levothyroxine, used to treat low
thyroid hormone levels)
Oral contraceptives (medicines to prevent pregnancy)
It is important you take Cholestagel at least 4 hours after you take the oral contraceptive to
ensure that the effectiveness of the contraceptive is not affected.
Verapamil (a medicine used to treat high blood pressure)
Antidiabetic medications (medicines, such as pioglitazone, repaglinide or glyburide used to
treat diabetes)
Anti-epileptic medicines (medicines, such as phenytoin, used to treat epilepsy).
Ciclosporin (a medicine used to suppress the immune system).
Ursodeoxycholic acid (a medicine used to dissolve gallstones or treat specific chronic liver
diseases).
If you are going to take Cholestagel and one of these medicines, your doctor may want to do tests to
make sure that Cholestagel does not interfere with these medicines.
Additionally, if you have any condition that could cause you to have a deficiency of vitamins A, D, E
or K, your doctor may want to check your vitamin levels periodically while you are taking
Cholestagel. If necessary, your doctor may advise you to take vitamin supplements.
Taking Cholestagel with food and drink
You should take your Cholestagel tablets with food and liquid.



Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or want to become pregnant. Your doctor may stop your
medicine.
If you are prescribed Cholestagel and a statin together it is important that you tell your doctor if you
are pregnant or if you are planning to become pregnant because statins must not be used during
pregnancy; the patient information leaflet that comes with that particular statin should be consulted.
Tell your doctor if you are breast-feeding. Your doctor may stop your medicine.
Driving and using machines
Your ability to drive or operate machines is not affected by taking Cholestagel tablets.
Before starting therapy with Cholestagel, you should be advised to follow a cholesterol-lowering diet
and you should continue this diet during treatment.
Always take Cholestagel exactly as your doctor has instructed you. You should check with your
doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure. As described in Section 2, if you will be taking Cholestagel
along with another medicine it is possible that your doctor will advise you to take Cholestagel at least
4 hours before or at least 4 hours after taking the other medicine.
If you take a drug called either Neoral
®
or ciclosporin, please ensure to take it with Cholestagel in a
consistent pattern over the day; either always together or always separate for a set number of hours.
Combination therapy:
The usual dose for Cholestagel, when used with a statin or ezetimibe or both together, is 4 to 6 tablets
a day by mouth. Your doctor may tell you to take the Cholestagel dose either once a day or twice a
day; in either case Cholestagel should be taken with a meal. The dosing of the statin and the ezetimibe
should follow the instructions for that particular medicine. The medicines may be taken at the same
time or at separate times according to what your doctor has prescribed.
Monotherapy:
The usual dose for Cholestagel is 3 tablets taken twice a day with meals or 6 tablets a day with a meal.
Your doctor may increase your dose to 7 tablets per day.
If you take more Cholestagel than you should
Please contact your doctor. Constipation or bloating could occur.
If you forget to take Cholestagel
You may take your dose with a later meal, but never take in one day more than the total number of
tablets that your doctor has prescribed to you in a single day.
If you stop taking Cholestagel
Your cholesterol may increase to the level it was before treatment was started.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Like all medicines, Cholestagel can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects have been reported in patients taking Cholestagel:
Very common
(affects more than 1 user in 10): flatulence (wind), constipation.
Common
(affects 1 to 10 users in 100): vomiting, diarrhoea, indigestion, abdominal pain, abnormal
stools, feeling sick, headache, raised levels of triglycerides (fats) in your blood.
Uncommon
(affects 1 to 10 users in 1,000): muscle pain, raised levels of liver enzymes in your blood.
Patients receiving Cholestagel in clinical studies were less likely to suffer flatulence (wind) and
diarrhoea as patients receiving placebo (inactive tablet). Only constipation and indigestion were
reported in higher numbers among those patients receiving Cholestagel.
All side effects were usually mild or moderate in intensity.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor
or pharmacist
.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Keep the bottle tightly closed in order to protect from moisture.
Do not use after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and bottle label after “EXP‟‟
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
What Cholestagel contains
The active substance is colesevelam hydrochloride. Each tablet contains 625 mg colesevelam
hydrochloride.
The other ingredients are:
Microcrystalline cellulose (E460)
Silica colloidal anhydrous
Diacetylated monoglycerides
What Cholestagel looks like and contents of the pack
Cholestagel tablets are off-white, capsule-shaped film-coated tablets and imprinted with „Cholestagel‟
on one side. The tablets are packed in plastic bottles with child resistant closures. Pack sizes are 24 (1
x 24), 100 (2 x 50) and 180 (1 x 180) tablets. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing authorisation holder
Genzyme Europe B.V., Gooimeer 10, 1411 DD Naarden, The Netherlands
Manufacturer
Genzyme Ireland Ltd., IDA Industrial Park, Old Kilmeaden Road, Waterford, Ireland
For any information about this medicinal product, please contact the local representative of the
Marketing Authorisation Holder.
België/Belgique/Belgien/
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
Genzyme Belgium N.V.
Tél/Tel: + 32 2 714 17 11
Italia/Malta
Genzyme Srl (Italia/Italja),
Tel: +39 059 349811
България
Търговско представителство на
Genzyme CEE GmbH
Тел. +359 2 971 1001
Magyarország
Genzyme Europe B.V. Képviselet
Tel: +36 1 310 7440
Česká Republika/Slovenská Republika/
Slovenija
Genzyme Czech, s.r.o.
Tel: +420 227 133 665
Nederland
Genzyme Europe B.V.,
Tel: +31 35 699 1200
Danmark/Norge/Sverige/Suomi/Finland/
Ísland
Genzyme A/S, (Danmark/Tanska/Danmörk),
Tlf/Puh./Sími: + 45 32712600
Österreich
Genzyme Austria GmbH,
Tel: + 43 1 774 65 38
Deutschland
Genzyme GmbH,
Tel: +49 610236740
Polska/Eesti/Latvija/Lietuva
Genzyme Polska Sp. z o.o.
(Poola/Polija/Lenkija),
Tel: + 48 22 24 60 900
Ελλά/Κύπρς
Genzyme Hellas Ltd. (Ελλά)
Τηλ: +30 210 99 49 270
Portugal
Genzyme Portugal S.A.,
Tel: +351 21 422 0100
España
Genzyme, S.A.,
Tel: +34 91 6591670
România
Genzyme CEE GmbH- Reprezentanţa pentru
România
Tel: +40 21 24 34 228
France
Genzyme S.A.S.,
Tél: + 33 (0) 825 825 863
United Kingdom/Ireland
Genzyme Therapeutics Ltd. (United
Kingdom),
Tel: +44 1865 405200
This leaflet was last approved in
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) web
Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/cholestagel.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|





















































































































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































