Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
FIRMAGON 80 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each vial contains 80 mg degarelix (as acetate). After reconstitution, each ml of solution contains
20 mg of degarelix.
For a full list of excipients, see section
6.1
.
Powder and solvent for solution for injection (Powder for injection and solvent)
Powder: White to off-white powder
Solvent: Clear, colourless solution
4.1 Therapeutic indications
FIRMAGON is a gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist indicated for treatment of
adult male patients with advanced hormone-dependent prostate cancer.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Maintenance dose – monthly
administration
240 mg administered as two
subcutaneous injections of 120 mg each
80 mg administered as one subcutaneous
injection
The first maintenance dose should be given one month after the starting dose.
The therapeutic effect of degarelix should be monitored by clinical parameters and prostate specific
antigen (PSA) serum levels. Clinical studies have shown that testosterone (T) suppression occurs
immediately after administration of the starting dose with 96% of the patients having plasma
testosterone levels corresponding to medical castration (T
≤
0.5 ng/ml) after three days and 100% after
one month. Long term treatment with the maintenance dose up to 1 year shows that 97% of the
patients have sustained suppressed testosterone levels (T
≤
0.5 ng/ml).
In case the patient's clinical response appears to be sub-optimal, it should be confirmed that serum
testosterone levels are remaining sufficiently suppressed.
Since degarelix does not induce a testosterone surge it is not necessary to add an anti-androgen as
surge protection at initiation of therapy
.
Method of administration
FIRMAGON must be reconstituted prior to administration. For instructions on reconstitution and
administration, please see section
6.6
.
Subcutaneous use ONLY
, not to be administered intravenously.






Intramuscular administration is not recommended as it has not been studied.
FIRMAGON is administered as a subcutaneous injection in the abdominal region. As with other
medicinal products administered by subcutaneous injection, the injection site should vary periodically.
Injections should be given in areas where the patient will not be exposed to pressure e.g. not close to
waistband or belt and not close to the ribs.
Special patient populations
Elderly, hepatically or renally impaired patients:
There is no need to adjust the dose for the elderly or in patients with mild or moderate liver or kidney
function impairment (see section
5.2
)
. Patients with severe liver or kidney impairment have not been
studied and caution is therefore warranted (see section
4.4
)
.
There is no relevant indication for use of FIRMAGON in women, children and adolescents.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
The data available on efficacy and safety experience with degarelix is limited to a one year treatment.
Effect on QT/QTc interval
Long-term androgen deprivation therapy may prolong the QT interval. In the confirmatory study
comparing FIRMAGON to leuprorelin periodic
(monthly) ECGs were performed;
both therapies
showed QT/QTc intervals exceeding 450 msec in approximately 20% of the patients, and 500 msec in
1% and 2% of the degarelix and leuprorelin patients, respectively (see section
5.1
)
.
FIRMAGON has not been studied in patients with a history of a corrected QT interval over 450 msec,
in
patients with a
history of or risk factors for torsades de pointes and in
patients receiving
concomitant medicinal products that might prolong the QT interval. Therefore in such patients, the
benefit/risk ratio of FIRMAGON must be thoroughly appraised (see sections
4.5
and
4.8
)
.
Hepatic impairment
Patients with known or suspected hepatic disorder have not been included in long-term clinical trials
with degarelix. Mild, transient increases in ALT and AST have been seen, these were not accompanied
by a rise in bilirubin or clinical symptoms. Monitoring of liver function in patients with known or
suspected hepatic disorder is advised during treatment. The pharmacokinetics of degarelix has been
investigated after single intravenous administration in subjects with mild to moderate hepatic
impairment (see section
5.2
)
.
Renal impairment
Degarelix has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment and caution is therefore
warranted.
Hypersensitivity
Degarelix has not been studied in patients with a history of severe untreated asthma, anaphylactic
reactions or severe urticaria or angioedema.
Changes in bone density
Decreased bone density has been reported in the medical literature in men who have had orchiectomy
or who have been treated with a GnRH agonist. It can be anticipated that long periods of testosterone
suppression in men will have effects on bone density. Bone density has not been measured during
treatment with degarelix.
A reduction in glucose tolerance has been observed in men who have had orchiectomy or who have
been treated with a GnRH agonist. Development or aggravation of diabetes may occur; therefore
diabetic patients may require more frequent monitoring of blood glucose when receiving androgen
deprivation therapy. The effect of degarelix on insulin and glucose levels has not been studied.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No formal drug-drug interaction studies have been performed.
Since androgen deprivation treatment may prolong the QTc interval, the concomitant use of degarelix
with medicinal products known to prolong the QTc interval or medicinal products able to induce
torsades de pointes such as class IA (e.g. quinidine, disopyramide) or class III (e.g. amiodarone,
sotalol, dofetilide, ibutilide) antiarrhythmic medicinal products, methadone, cisapride, moxifloxacine,
antipsychotics, etc. should be carefully evaluated (see section
4.4
)
.
Degarelix is not a substrate for the human CYP450 system and has not been shown to induce or inhibit
CYP1A2, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, or CYP3A4/5 to any great extent
in
vitro
. Therefore, clinically significant pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions in metabolism related to
these isoenzymes are unlikely.
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
There is no relevant indication for use of FIRMAGON in women.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects of degarelix on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
However, fatigue and dizziness are common adverse reactions that might influence the ability to drive
and use machines.
The most commonly observed adverse reactions during degarelix therapy in the confirmatory phase III
study (N=409) were due to the expected physiological effects of testosterone suppression, including
hot flushes and weight increase (reported in 25% and 7%, respectively, of patients receiving treatment
for one year), or injection site adverse events. Transient chills, fever or influenza like illness were
reported to occur hours after dosing (in 3%, 2% and 1% of patients, respectively).
The injection site adverse events reported were mainly pain and erythema, reported in 28% and 17%
of patients, respectively, less frequently reported were swelling (6%), induration (4%) and nodule
(3%). These events occurred primarily with the starting dose whereas during maintenance therapy with
the 80 mg dose, the incidence of these events pr 100 injections was: 3 for pain and <1 for erythema,
swelling, nodule and induration. The reported events were mostly transient, of mild to moderate
intensity and led to very few discontinuations (<1%).
The frequency of undesirable effects listed below is defined using the following convention:
Very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100). Within each
frequency grouping, undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness.
Table 1: Frequency of adverse drug reactions reported in 1259 patients treated for a total of
1781 patient years (phase II and III studies).
MedDRA System
Organ Class (SOC)
Blood and
lymphatic system
disorders







Metabolism and
nutrition disorders
Hyperglycemia/Diabetes
mellitus, cholesterol
increased, weight
decreased, appetite
decreased, changes in
blood calcium
Depression, libido
decreased*
Mental impairment,
hypoaesthesia
Cardiac arrhythmia (incl.
atrial fibrillation),
palpitations,
QT prolongation*(see
Vascular disorders Hot flush*
Hypertension, vasovagal
reaction (incl. hypotension)
Respiratory,
thoracic and
mediastinal
disorders
Gastrointestinal
disorders
Constipation, vomiting,
abdominal pain, abdominal
discomfort, dry mouth
Liver transaminases
increased
Bilirubin increased,
alkaline phosphatase
increased
Skin and
subcutaneous tissue
disorders
Hyperhidrosis (incl.
night sweats)*, rash
Urticaria, skin nodule,
alopecia, pruritus, erythema
Musculoskeletal,
connective tissue
and bone disorders
Musculoskeletal pain
and discomfort
Osteoporosis/osteopenia,
arthralgia muscular
weakness, muscle spasms,
joint swelling/stiffness
Renal and urinary
disorders
Pollakiuria, micturition
urgency, dysuria, nocturia,
renal impairment,
incontinence
Reproductive
system and breast
disorders
Gynaecomastia*,
testicular atrophy*,
erectile dysfunction*
Testicular pain, breast pain,
pelvic pain, genital
irritation, ejaculation
failure
General disorders
and administration
site conditions
Injection site
adverse events
Chills, pyrexia,
fatigue*, Influenza-
like illness
Malaise, peripheral oedema
*Known physiological consequence of testosterone suppression
The following events have been reported as being related to treatment in single patients: Febrile
neutropenia, myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure.
Changes in laboratory parameters
Changes in laboratory values seen during one year of treatment in the confirmatory phase III study
(N=409) were in the same range for degarelix and a GnRH-agonist (leuprorelin) used as comparator.
Markedly abnormal (>3*ULN) liver transaminase values (ALT, AST and GGT) were seen in 2-6% of




















patients with normal values prior to treatment, following treatment with both medicinal products.
Marked decrease in haematological values, hematocrit (≤0.37) and hemoglobin (≤115 g/l) were seen in
40% and 13-15%, respectively, of patients with normal values prior to treatment, following treatment
with both medicinal products. It is unknown to what extent this decrease in haematological values was
caused by the underlying prostate cancer and to what extent it was a consequence of androgen
deprivation therapy. Markedly abnormal values of potassium (≥5.8 mmol/l), creatinine (≥177 μmol/l)
and BUN (≥10.7 mmol/l) in patients with normal values prior to treatment, were seen in 6%, 2% and
15% of degarelix treated patients and 3%, 2% and 14% of leuprorelin treated patients, respectively.
Changes in ECG measurements
Changes in ECG measurements seen during one year of treatment in the confirmatory phase III study
(N=409) were in the same range for degarelix and a GnRH-agonist (leuprorelin) used as comparator.
Three (<1%) out of 409 patients in the degarelix group and four (2%) out of 201 patients in the
leuprorelin 7.5 mg group, had a QTcF ≥ 500 msec. From baseline to end of study the median change
in QTcF for degarelix was 12.0 msec and for leuprorelin was 16.7 msec.
There is no clinical experience with the effects of an acute overdose with degarelix. In the event of an
overdose the patient should be monitored and appropriate supportive treatment should be given, if
considered necessary.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Other hormone antagonists and related agents, ATC code: L02BX02
Degarelix is a selective gonadotrophin releasing-hormone (GnRH) antagonist that competitively and
reversibly binds to the pituitary GnRH receptors, thereby rapidly reducing the release of the
gonadotrophins, luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), and thereby
reducing the secretion of testosterone (T) by the testes. Prostatic carcinoma is known to be androgen
sensitive and responds to treatment that removes the source of androgen. Unlike GnRH agonists,
GnRH antagonists do not induce a LH surge with subsequent testosterone surge/tumour stimulation
and potential symptomatic flare after the initiation of treatment.
A single dose of 240 mg degarelix, followed by a monthly maintenance dose of 80 mg, rapidly causes
a decrease in the concentrations of LH, FSH and subsequently testosterone. The plasma concentration
of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) decreases in a similar manner to testosterone.
Degarelix is effective in achieving and maintaining testosterone suppression well below medical
castration level of 0.5 ng/ml. Maintenance monthly dosing of 80 mg resulted in sustained testosterone
suppression in 97% of patients for at least one year. Median testosterone levels after one year of
treatment were 0.087 ng/ml (interquartile range 0.06-0.15) N=167.
Results of the confirmatory Phase III study
The efficacy and safety of degarelix was evaluated in an open-label, multi-centre, randomised, active
comparator controlled, parallel-group study. The study investigated the efficacy and safety of two
different degarelix monthly dosing regimens with a starting dose of 240 mg (40 mg/ml) followed by
monthly doses subcutaneous administration of 160 mg (40 mg/ml) or 80 mg (20 mg/ml), in
comparison to monthly intramuscular administration of 7.5 mg leuprorelin in patients with prostate
cancer requiring androgen deprivation therapy. In total 620 patients were randomised to one of the
three treatment groups, of which 504 (81%) patients completed the study. In the degarelix 240/80 mg
treatment group 41 (20%) patients discontinued the study, as compared to 32 (16%) patients in the
leuprorelin group.
Of the 610 patients treated
•
31% had localised prostate cancer
29% had locally advanced prostate cancer
20% had metastatic prostate cancer
7% had an unknown metastatic status
13% had previous curative intent surgery or radiation and a rising PSA
Baseline demographics were similar between the arms. The median age was 74 years (range 47 to 98
years). The primary objective was to demonstrate that degarelix is effective with respect to achieving
and maintaining testosterone suppression to below 0.5 ng/ml, during 12 months of treatment.
The lowest effective maintenance dose of 80 mg degarelix was chosen.
Attainment of serum testosterone (T) ≤0.5 ng/ml
FIRMAGON is effective in achieving fast testosterone suppression, see Table 2.
Table 2: Percentage of patients attaining T≤0.5 ng/ml after start of treatment.
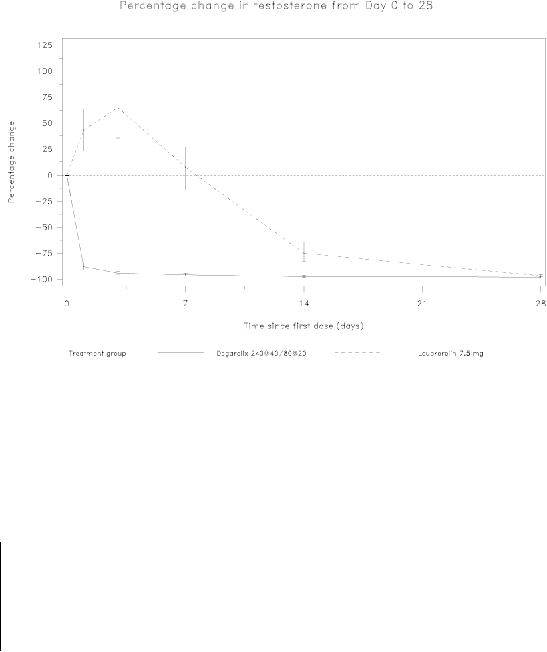
Avoidance of testosterone surge
Surge was defined as testosterone exceeding baseline by ≥15% within the first 2 weeks.
None of the degarelix-treated patients experienced a testosterone surge; there was an average decrease
of 94% in testosterone at day 3. Most of the leuprorelin-treated patients experienced testosterone
surge; there was an average increase of 65% in testosterone at day 3. This difference was statistically
significant (p<0.001).
Figure 1: Percentage change in testosterone from baseline by treatment group until day 28 (median
with interquartile ranges).










The primary end-point in the study was testosterone suppression rates after one year of treatment with
degarelix or leuprorelin. The clinical benefit for degarelix compared to leuprorelin plus anti-androgen
in the initial phase of treatment has not been demonstrated.
Long-term effect
Successful response in the study was defined as attainment of medical castration at day 28 and
maintenance through day 364 where no single testosterone concentration was greater than 0.5 ng/ml.
Table 3: Cumulative probability of testosterone ≤0.5 ng/ml from Day 28 to Day 364.
Degarelix 240/80 mg
N=207
Response Rate
(confidence intervals)*
* Kaplan Meier estimates within group
Attainment of prostate specific antigen (PSA) reduction
Tumour size was not measured directly during the clinical trial programme, but there was an indirect
beneficial tumour response as shown by a 95% reduction after 12 months in median PSA for
degarelix.
The median PSA in the study at baseline was:
•
for the degarelix 240/80 mg treatment group 19.8 ng/ml (interquartile range: P25 9.4 ng/ml, P75
46.4 ng/ml)
for the leuprorelin 7.5 mg treatment group 17.4 ng/ml (interquartile range: P25 8.4 ng/ml, P75
56.5 ng/ml)
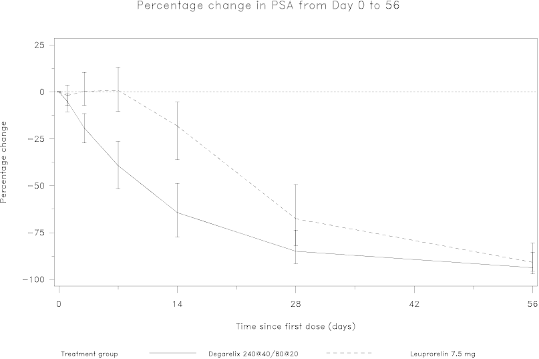
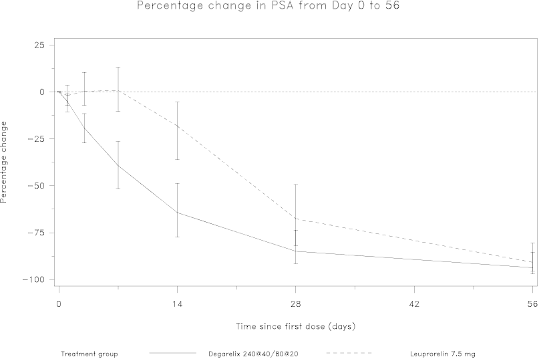
Figure 2: Percentage change in PSA from baseline by treatment group until day 56 (median with
interquartile ranges).







This difference was statistically significant (p<0.001) for the pre-specified analysis at day 14 and day
28.
Prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels are lowered by 64% two weeks after administration of
degarelix, 85% after one month, 95% after three months, and remained suppressed (approximately
97%) throughout the one year of treatment.
From day 56 to day 364 there were no significant differences between degarelix and the comparator in
the percentage change from baseline.
In the confirmatory study comparing FIRMAGON to leuprorelin periodic electrocardiograms were
performed. Both therapies showed QT/QTc intervals exceeding 450 msec in approximately 20% of the
patients. From baseline to end of study the median change for FIRMAGON was 12.0 msec and for
leuprorelin it was 16.7 msec.
Anti-degarelix antibody development has been observed in 10% of patients after treatment with
FIRMAGON for one year. There is no indication that the efficacy or safety of FIRMAGON treatment
is affected by antibody formation after one year of treatment. Efficacy and safety data in relation to
antibody development beyond one year is not available.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Following subcutaneous administration of 240 mg degarelix at a concentration of 40 mg/ml to prostate
cancer patients in the pivotal study CS21, AUC
0-28 days
was 635 (602-668) day*ng/ml, C
max
was 66.0
(61.0-71.0) ng/ml and occurred at t
max
at 40 (37-42) hours. Mean trough values were approximately
11-12 ng/ml after the starting dose and 11-16 ng/ml after maintenance dosing of 80 mg at a
concentration of 20 mg/ml. Degarelix is eliminated in a biphasic fashion, with a median terminal half-
life (t
½
) of approximately 43 days for the starting dose or 28 days for the maintenance dose, as
estimated based on population pharmacokinetics modelling. The long half-life after subcutaneous
administration is a consequence of a very slow release of degarelix from the depot formed at the
injection site(s). The pharmacokinetic behavior of the medicinal product is influenced by its
concentration in the solution for injection. Thus, C
max
and bioavailability tend to decrease with
increasing dose concentration while the half-life is increased. Therefore, no other dose concentrations
than the recommended should be used.
Distribution
The distribution volume in healthy elderly men is approximately 1 l/kg. Plasma protein binding is
estimated to be approximately 90%.
Metabolism
Degarelix is subject to common peptidic degradation during the passage of the hepato-biliary system
and is mainly excreted as peptide fragments in the faeces. No significant metabolites were detected in
plasma samples after subcutaneous administration.
In vitro
studies have shown that degarelix is not a
substrate for the human CYP450 system.
Excretion
In healthy men, approximately 20-30% of a single intravenously administered dose is excreted in the
urine, suggesting that 70-80% is excreted via the hepato-biliary system. The clearance of degarelix
when administered as single intravenous doses (0.864-49.4 µg/kg) in healthy elderly men was found to
be 35-50 ml/h/kg.
Special populations:
Patients with renal impairment
No pharmacokinetic studies in renally impaired patients have been conducted. Only about 20-30% of a
given dose of degarelix is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. A population pharmacokinetics analysis
of the data from the confirmatory Phase III study has demonstrated that the clearance of degarelix in
patients with mild to moderate renal impairment is reduced by approximately 23%; therefore, dose
adjustment in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment is not recommended. Data on patients
with severe renal impairment is scarce and caution is therefore warranted in this patient population.
Patients with hepatic impairment
Degarelix has been investigated in a pharmacokinetic study in patients with mild to moderate hepatic
impairment. No signs of increased exposure in the hepatically impaired subjects were observed
compared to healthy subjects. Dose adjustment is not necessary in patients with mild or moderate
hepatic impairment. Patients with severe hepatic dysfunction have not been studied and caution is
therefore warranted in this group.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Animal reproduction studies showed that degarelix caused infertility in male animals. This is due to
the pharmacological effect; and the effect was reversible.
In female reproduction toxicity studies degarelix revealed findings expected from the pharmacological
properties. It caused a dosage dependent prolongation of the time to mating and to pregnancy, a
reduced number of
corpora lutea
, and an increase in the number of pre- and post-implantation losses,
abortions, early embryo/foetal deaths, premature deliveries and in the duration of parturition.
Preclinical studies on safety pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity, and carcinogenic
potential revealed no special hazard for humans. Both
in vitro
and
in vivo
studies showed no signs of
QT prolongation.
No target organ toxicity was observed from acute, subacute and chronic toxicity studies in rats
and monkeys following subcutaneous administration of degarelix. Drug-related local irritation was
noted in animals when degarelix was administered subcutaneously in high doses.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Solvent
Water for injections
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal
products.
After reconstitution
Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 2 hours at 25ºC. From a
microbiological point of view, unless the method of reconstitution precludes the risk of microbial
contamination, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use storage times
and conditions are the responsibility of the user.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
This medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions.
For storage conditions of the reconstituted medicinal product, see section
6.3
.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
Vials of glass Type I with bromobutyl rubber stopper and aluminium flip-off seal.
1 vial containing 80 mg powder for solution for injection
1 vial containing 6 ml solvent
1 syringe (5 ml with dual-line marking 4.0 and 4.2 ml)
2 vial adapters
1 injection needle (25G 0.5 x 25 mm)
1 pack containing 1 powder vial, 1 solvent vial, 1 syringe, 2 vial adapters and 1 needle.
3 pack containing 3x (1 powder vial, 1 solvent vial, 1 syringe, 2 vial adapters and 1 needle).
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
No special requirements for disposal.
Instructions for use:
The instructions for reconstitution must be followed carefully.
Administration of other concentrations is not recommended because the gel depot formation is
influenced by the concentration. The reconstituted solution should be a clear liquid, free of
undissolved matter.
NOTE:
• THE VIALS SHOULD NOT BE SHAKEN
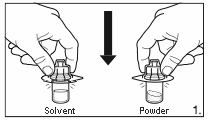
The pack contains 1 set of powder and solvent that must be prepared for subcutaneous injection.
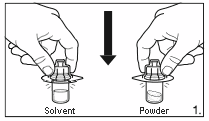
1.
Remove the cover from the vial adapter pack.
Attach the adapters to both the solvent and
powder vial by pressing the adapter down until
the spike pushes through the rubber stopper and
the adapter snap in place.
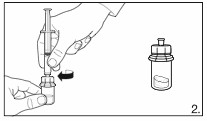
2.
Remove the cover from the syringe pack.
Attach the syringe to the solvent vial by
screwing it on to the adapter.
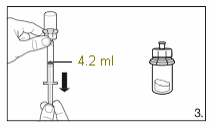
3.
Turn the vial upside down and draw
4.2 ml
of the
solvent into the syringe.
Always make sure to withdraw the precise
volume, as the amount of solvent affects the
reconstitution.
Detach the syringe from the adapter and discard
the vial with the remaining solvent.
4.
Attach the syringe to the powder vial by
screwing it on to the adapter. Transfer the
solvent to the powder vial. With the syringe
still attached to the adapter, swirl very gently
until the liquid looks clear and without undissolved
powder or particles. In case the powder adheres to
the vial over the liquid surface, the vial can be
tilted slightly.
AVOID SHAKING TO
PREVENT FOAM FORMATION.
A ring of small air bubbles on the surface of the
liquid is acceptable. The reconstitution procedure
may take, in some cases, up to 15 minutes, but
usually takes a few minutes.
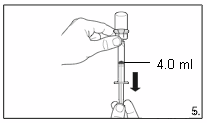
5.
Turn the vial upside down and,
holding it
vertically
, draw
4.0 ml
of the solution into the
syringe for injection.
Always make sure to withdraw the precise
volume. It can be necessary to tilt the vial
slightly.
6.
Detach the syringe from the vial adapter and attach the needle for deep subcutaneous
injection to the syringe. Carefully remove any air bubbles.
7.
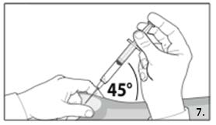
Grasp the skin of the abdomen, elevate the
subcutaneous tissue. Perform a profound
subcutaneous injection. To do so, insert the needle
deeply at an angle of not less than
45 degrees.











8.
Inject
4.0 ml of FIRMAGON 80 mg
immediately after reconstitution.*
9.
Do not inject directly into a vein. Gently pull back the plunger to check if blood is
aspirated. If blood appears in the syringe, the medicinal product can no longer be used.
Discontinue the procedure and discard the syringe and the needle (reconstitute a new dose
for the patient).
• No injections should be given in areas where the patient will be exposed to pressure, e.g. around
the belt or waistband or close to the ribs.
* Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 2 hours at 25ºC. From a
microbiological point of view, unless the method of reconstitution precludes the risk of microbial
contamination, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use storage
times and conditions are the responsibility of the user.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Ferring Pharmaceuticals A/S
Kay Fiskers Plads 11
DK-2300 Copenhagen S
Denmark
Tel: +45 88 33 88 34
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/08/504/001
EU/1/08/504/003
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines




NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
FIRMAGON 120 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each vial contains 120 mg degarelix (as acetate). After reconstitution, each ml solution contains 40 mg
of degarelix.
For a full list of excipients, see section
6.1
.
Powder and solvent for solution for injection (Powder for injection and solvent)
Powder: White to off-white powder
Solvent: Clear, colourless solution
4.1 Therapeutic indications
FIRMAGON is a gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist indicated for treatment of
adult male patients with advanced hormone-dependent prostate cancer.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Maintenance dose – monthly
administration
240 mg administered as two
subcutaneous injections of 120 mg each
80 mg administered as one subcutaneous
injection
The first maintenance dose should be given one month after the starting dose.
The therapeutic effect of degarelix should be monitored by clinical parameters and prostate specific
antigen (PSA) serum levels. Clinical studies have shown that testosterone (T) suppression occurs
immediately after administration of the starting dose with 96% of the patients having plasma
testosterone levels corresponding to medical castration (T
≤
0.5 ng/ml) after three days and 100% after
one month. Long term treatment with the maintenance dose up to 1 year shows that 97% of the
patients have sustained suppressed testosterone levels (T
≤
0.5 ng/ml).
In case the patient's clinical response appears to be sub-optimal, it should be confirmed that serum
testosterone levels are remaining sufficiently suppressed.
Since degarelix does not induce a testosterone surge it is not necessary to add an anti-androgen as
surge protection at initiation of therapy
.
Method of administration
FIRMAGON must be reconstituted prior to administration. For instructions on reconstitution and
administration, please see section
6.6
.
Subcutaneous use ONLY
, not to be administered intravenously.






Intramuscular administration is not recommended as it has not been studied.
FIRMAGON is administered as a subcutaneous injection in the abdominal region. As with other
medicinal products administered by subcutaneous injection, the injection site should vary periodically.
Injections should be given in areas where the patient will not be exposed to pressure e.g. not close to
waistband or belt and not close to the ribs.
Special patient populations
Elderly, hepatically or renally impaired patients:
There is no need to adjust the dose for the elderly or in patients with mild or moderate liver or kidney
function impairment (see section
5.2
)
. Patients with severe liver or kidney impairment have not been
studied and caution is therefore warranted (see section
4.4
)
.
There is no relevant indication for use of FIRMAGON in women, children and adolescents.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
The data available on efficacy and safety experience with degarelix is limited to a one year treatment.
Effect on QT/QTc interval
Long-term androgen deprivation therapy may prolong the QT interval. In the confirmatory study
comparing FIRMAGON to leuprorelin periodic
(monthly) ECGs were performed;
both therapies
showed QT/QTc intervals exceeding 450 msec in approximately 20% of the patients, and 500 msec in
1% and 2% of the degarelix and leuprorelin patients, respectively (see section
5.1
)
.
FIRMAGON has not been studied in patients with a history of a corrected QT interval over 450 msec,
in
patients with a
history of or risk factors for torsades de pointes and in
patients receiving
concomitant medicinal products that might prolong the QT interval. Therefore in such patients, the
benefit/risk ratio of FIRMAGON must be thoroughly appraised (see sections
4.5
and
4.8
)
.
Hepatic impairment
Patients with known or suspected hepatic disorder have not been included in long-term clinical trials
with degarelix. Mild, transient increases in ALT and AST have been seen, these were not accompanied
by a rise in bilirubin or clinical symptoms. Monitoring of liver function in patients with known or
suspected hepatic disorder is advised during treatment. The pharmacokinetics of degarelix has been
investigated after single intravenous administration in subjects with mild to moderate hepatic
impairment (see section
5.2
)
.
Renal impairment
Degarelix has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment and caution is therefore
warranted.
Hypersensitivity
Degarelix has not been studied in patients with a history of severe untreated asthma, anaphylactic
reactions or severe urticaria or angioedema.
Changes in bone density
Decreased bone density has been reported in the medical literature in men who have had orchiectomy
or who have been treated with a GnRH agonist. It can be anticipated that long periods of testosterone
suppression in men will have effects on bone density. Bone density has not been measured during
treatment with degarelix.
A reduction in glucose tolerance has been observed in men who have had orchiectomy or who have
been treated with a GnRH agonist. Development or aggravation of diabetes may occur; therefore
diabetic patients may require more frequent monitoring of blood glucose when receiving androgen
deprivation therapy. The effect of degarelix on insulin and glucose levels has not been studied.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No formal drug-drug interaction studies have been performed.
Since androgen deprivation treatment may prolong the QTc interval, the concomitant use of degarelix
with medicinal products known to prolong the QTc interval or medicinal products able to induce
torsades de pointes such as class IA (e.g. quinidine, disopyramide) or class III (e.g. amiodarone,
sotalol, dofetilide, ibutilide) antiarrhythmic medicinal products, methadone, cisapride, moxifloxacine,
antipsychotics, etc. should be carefully evaluated (see section
4.4
)
.
Degarelix is not a substrate for the human CYP450 system and has not been shown to induce or inhibit
CYP1A2, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, or CYP3A4/5 to any great extent
in
vitro
. Therefore, clinically significant pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions in metabolism related to
these isoenzymes are unlikely.
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
There is no relevant indication for use of FIRMAGON in women.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects of degarelix on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
However, fatigue and dizziness are common adverse reactions that might influence the ability to drive
and use machines.
The most commonly observed adverse reactions during degarelix therapy in the confirmatory phase III
study (N=409) were due to the expected physiological effects of testosterone suppression, including
hot flushes and weight increase (reported in 25% and 7%, respectively, of patients receiving treatment
for one year), or injection site adverse events. Transient chills, fever or influenza like illness were
reported to occur hours after dosing (in 3%, 2% and 1% of patients, respectively).
The injection site adverse events reported were mainly pain and erythema, reported in 28% and 17%
of patients, respectively, less frequently reported were swelling (6%), induration (4%) and nodule
(3%). These events occurred primarily with the starting dose whereas during maintenance therapy with
the 80 mg dose, the incidence of these events pr 100 injections was: 3 for pain and <1 for erythema,
swelling, nodule and induration. The reported events were mostly transient, of mild to moderate
intensity and led to very few discontinuations (<1%).
The frequency of undesirable effects listed below is defined using the following convention:
Very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100). Within each
frequency grouping, undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness.
Table 1: Frequency of adverse drug reactions reported in 1259 patients treated for a total of
1781 patient years (phase II and III studies).
MedDRA System
Organ Class (SOC)
Blood and
lymphatic system
disorders







Metabolism and
nutrition disorders
Hyperglycemia/Diabetes
mellitus, cholesterol
increased, weight
decreased, appetite
decreased, changes in
blood calcium
Depression, libido
decreased*
Mental impairment,
hypoaesthesia
Cardiac arrhythmia (incl.
atrial fibrillation),
palpitations,
QT prolongation*(see
Vascular disorders Hot flush*
Hypertension, vasovagal
reaction (incl. hypotension)
Respiratory,
thoracic and
mediastinal
disorders
Gastrointestinal
disorders
Constipation, vomiting,
abdominal pain, abdominal
discomfort, dry mouth
Liver transaminases
increased
Bilirubin increased,
alkaline phosphatase
increased
Skin and
subcutaneous tissue
disorders
Hyperhidrosis (incl.
night sweats)* , rash
Urticaria, skin nodule,
alopecia, pruritus, erythema
Musculoskeletal,
connective tissue
and bone disorders
Musculoskeletal pain
and discomfort
Osteoporosis/osteopenia,
arthralgia, muscular
weakness, muscle spasms,
joint swelling/stiffness
Renal and urinary
disorders
Pollakiuria, micturition
urgency, dysuria, nocturia,
renal impairment,
incontinence
Reproductive
system and breast
disorders
Gynaecomastia*,
testicular atrophy*,
erectile dysfunction*
Testicular pain, breast pain,
pelvic pain, genital
irritation, ejaculation
failure
General disorders
and administration
site conditions
Injection site
adverse events
Chills, pyrexia,
fatigue*, Influenza-
like illness
Malaise, peripheral oedema
*Known physiological consequence of testosterone suppression
The following events have been reported as being related to treatment in single patients: Febrile
neutropenia, myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure.
Changes in laboratory parameters
Changes in laboratory values seen during one year of treatment in the confirmatory phase III study
(N=409) were in the same range for degarelix and a GnRH-agonist (leuprorelin) used as comparator.
Markedly abnormal (>3*ULN) liver transaminase values (ALT, AST and GGT) were seen in 2-6% of




















patients with normal values prior to treatment, following treatment with both medicinal products.
Marked decrease in haematological values, hematocrit (≤0.37) and hemoglobin (≤115 g/l) were seen in
40% and 13-15%, respectively, of patients with normal values prior to treatment, following treatment
with both medicinal products. It is unknown to what extent this decrease in haematological values was
caused by the underlying prostate cancer and to what extent it was a consequence of androgen
deprivation therapy. Markedly abnormal values of potassium (≥5.8 mmol/l), creatinine (≥177 μmol/l)
and BUN (≥10.7 mmol/l) in patients with normal values prior to treatment, were seen in 6%, 2% and
15% of degarelix treated patients and 3%, 2% and 14% of leuprorelin treated patients, respectively.
Changes in ECG measurements
Changes in ECG measurements seen during one year of treatment in the confirmatory phase III study
(N=409) were in the same range for degarelix and a GnRH-agonist (leuprorelin) used as comparator.
Three (<1%) out of 409 patients in the degarelix group and four (2%) out of 201 patients in the
leuprorelin 7.5 mg group, had a QTcF ≥ 500 msec. From baseline to end of study the median change
in QTcF for degarelix was 12.0 msec and for leuprorelin was 16.7 msec.
There is no clinical experience with the effects of an acute overdose with degarelix. In the event of an
overdose the patient should be monitored and appropriate supportive treatment should be given, if
considered necessary.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Other hormone antagonists and related agents, ATC code: L02BX02
Degarelix is a selective gonadotrophin releasing-hormone (GnRH) antagonist that competitively and
reversibly binds to the pituitary GnRH receptors, thereby rapidly reducing the release of the
gonadotrophins, luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), and thereby
reducing the secretion of testosterone (T) by the testes. Prostatic carcinoma is known to be androgen
sensitive and responds to treatment that removes the source of androgen. Unlike GnRH agonists,
GnRH antagonists do not induce a LH surge with subsequent testosterone surge/tumour stimulation
and potential symptomatic flare after the initiation of treatment.
A single dose of 240 mg degarelix, followed by a monthly maintenance dose of 80 mg, rapidly causes
a decrease in the concentrations of LH, FSH and subsequently testosterone. The plasma concentration
of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) decreases in a similar manner to testosterone.
Degarelix is effective in achieving and maintaining testosterone suppression well below medical
castration level of 0.5 ng/ml. Maintenance monthly dosing of 80 mg resulted in sustained testosterone
suppression in 97% of patients for at least one year. Median testosterone levels after one year of
treatment were 0.087 ng/ml (interquartile range 0.06-0.15) N=167.
Results of the confirmatory Phase III study
The efficacy and safety of degarelix was evaluated in an open-label, multi-centre, randomised, active
comparator controlled, parallel-group study. The study investigated the efficacy and safety of two
different degarelix monthly dosing regimens with a starting dose of 240 mg (40 mg/ml) followed by
monthly doses subcutaneous administration of 160 mg (40 mg/ml) or 80 mg (20 mg/ml), in
comparison to monthly intramuscular administration of 7.5 mg leuprorelin in patients with prostate
cancer requiring androgen deprivation therapy. In total 620 patients were randomised to one of the
three treatment groups, of which 504 (81%) patients completed the study. In the degarelix 240/80 mg
treatment group 41 (20%) patients discontinued the study, as compared to 32 (16%) patients in the
leuprorelin group.
Of the 610 patients treated
•
31% had localised prostate cancer
29% had locally advanced prostate cancer
20% had metastatic prostate cancer
7% had an unknown metastatic status
13% had previous curative intent surgery or radiation and a rising PSA
Baseline demographics were similar between the arms. The median age was 74 years (range 47 to 98
years). The primary objective was to demonstrate that degarelix is effective with respect to achieving
and maintaining testosterone suppression to below 0.5 ng/ml, during 12 months of treatment.
The lowest effective maintenance dose of 80 mg degarelix was chosen.
Attainment of serum testosterone (T) ≤0.5 ng/ml
FIRMAGON is effective in achieving fast testosterone suppression, see Table 2.
Table 2: Percentage of patients attaining T≤0.5 ng/ml after start of treatment.
Avoidance of testosterone surge
Surge was defined as testosterone exceeding baseline by ≥15% within the first 2 weeks.
None of the degarelix-treated patients experienced a testosterone surge; there was an average decrease
of 94% in testosterone at day 3. Most of the leuprorelin-treated patients experienced testosterone
surge; there was an average increase of 65% in testosterone at day 3. This difference was statistically
significant (p<0.001).
Figure 1: Percentage change in testosterone from baseline by treatment group until day 28 (median
with interquartile ranges).










The primary end-point in the study was testosterone suppression rates after one year of treatment with
degarelix or leuprorelin. The clinical benefit for degarelix compared to leuprorelin plus anti-androgen
in the initial phase of treatment has not been demonstrated.
Long-term effect
Successful response in the study was defined as attainment of medical castration at day 28 and
maintenance through day 364 where no single testosterone concentration was greater than 0.5 ng/ml.
Table 3: Cumulative probability of testosterone ≤0.5 ng/ml from Day 28 to Day 364.
Degarelix 240/80 mg
N=207
Response Rate
(confidence intervals)*
* Kaplan Meier estimates within group
Attainment of prostate specific antigen (PSA) reduction
Tumour size was not measured directly during the clinical trial programme, but there was an indirect
beneficial tumour response as shown by a 95% reduction after 12 months in median PSA for
degarelix.
The median PSA in the study at baseline was:
•
for the degarelix 240/80 mg treatment group 19.8 ng/ml (interquartile range: P25 9.4 ng/ml, P75
46.4 ng/ml)
for the leuprorelin 7.5 mg treatment group 17.4 ng/ml (interquartile range: P25 8.4 ng/ml, P75
56.5 ng/ml)
Figure 2: Percentage change in PSA from baseline by treatment group until day 56 (median with
interquartile ranges).






This difference was statistically significant (p<0.001) for the pre-specified analysis at day 14 and day
28.
Prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels are lowered by 64% two weeks after administration of
degarelix, 85% after one month, 95% after three months, and remained suppressed (approximately
97%) throughout the one year of treatment.
From day 56 to day 364 there were no significant differences between degarelix and the comparator in
the percentage change from baseline.
In the confirmatory study comparing FIRMAGON to leuprorelin periodic electrocardiograms were
performed. Both therapies showed QT/QTc intervals exceeding 450 msec in approximately 20% of the
patients. From baseline to end of study the median change for FIRMAGON was 12.0 msec and for
leuprorelin it was 16.7 msec.
Anti-degarelix antibody development has been observed in 10% of patients after treatment with
FIRMAGON for one year. There is no indication that the efficacy or safety of FIRMAGON treatment
is affected by antibody formation after one year of treatment. Efficacy and safety data in relation to
antibody development beyond one year is not available.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Following subcutaneous administration of 240 mg degarelix at a concentration of 40 mg/ml to prostate
cancer patients in the pivotal study CS21, AUC
0-28 days
was 635 (602-668) day*ng/ml, C
max
was 66.0
(61.0-71.0) ng/ml and occurred at t
max
at 40 (37-42) hours. Mean trough values were approximately
11-12 ng/ml after the starting dose and 11-16 ng/ml after maintenance dosing of 80 mg at a
concentration of 20 mg/ml. Degarelix is eliminated in a biphasic fashion, with a median terminal half-
life (t
½
) of approximately 43 days for the starting dose or 28 days for the maintenance dose, as
estimated based on population pharmacokinetics modelling. The long half-life after subcutaneous
administration is a consequence of a very slow release of degarelix from the depot formed at the
injection site(s). The pharmacokinetic behavior of the medicinal product is influenced by its
concentration in the solution for injection. Thus, C
max
and bioavailability tend to decrease with
increasing dose concentration while the half-life is increased. Therefore, no other dose concentrations
than the recommended should be used.
Distribution
The distribution volume in healthy elderly men is approximately 1 l/kg. Plasma protein binding is
estimated to be approximately 90%.
Metabolism
Degarelix is subject to common peptidic degradation during the passage of the hepato-biliary system
and is mainly excreted as peptide fragments in the faeces. No significant metabolites were detected in
plasma samples after subcutaneous administration.
In vitro
studies have shown that degarelix is not a
substrate for the human CYP450 system.
Excretion
In healthy men, approximately 20-30% of a single intravenously administered dose is excreted in the
urine, suggesting that 70-80% is excreted via the hepato-biliary system. The clearance of degarelix
when administered as single intravenous doses (0.864-49.4 µg/kg) in healthy elderly men was found to
be 35-50 ml/h/kg.
Special populations:
Patients with renal impairment
No pharmacokinetic studies in renally impaired patients have been conducted. Only about 20-30% of a
given dose of degarelix is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. A population pharmacokinetics analysis
of the data from the confirmatory Phase III study has demonstrated that the clearance of degarelix in
patients with mild to moderate renal impairment is reduced by approximately 23%; therefore, dose
adjustment in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment is not recommended. Data on patients
with severe renal impairment is scarce and caution is therefore warranted in this patient population.
Patients with hepatic impairment
Degarelix has been investigated in a pharmacokinetic study in patients with mild to moderate hepatic
impairment. No signs of increased exposure in the hepatically impaired subjects were observed
compared to healthy subjects. Dose adjustment is not necessary in patients with mild or moderate
hepatic impairment. Patients with severe hepatic dysfunction have not been studied and caution is
therefore warranted in this group.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Animal reproduction studies showed that degarelix caused infertility in male animals. This is due to
the pharmacological effect; and the effect was reversible.
In female reproduction toxicity studies degarelix revealed findings expected from the pharmacological
properties. It caused a dosage dependent prolongation of the time to mating and to pregnancy, a
reduced number of
corpora lutea
, and an increase in the number of pre- and post-implantation losses,
abortions, early embryo/foetal deaths, premature deliveries and in the duration of parturition.
Preclinical studies on safety pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity, and carcinogenic
potential revealed no special hazard for humans. Both
in vitro
and
in vivo
studies showed no signs of
QT prolongation.
No target organ toxicity was observed from acute, subacute and chronic toxicity studies in rats
and monkeys following subcutaneous administration of degarelix. Drug-related local irritation was
noted in animals when degarelix was administered subcutaneously in high doses.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Solvent
Water for injections
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal
products.
After reconstitution
Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 2 hours at 25ºC. From a
microbiological point of view, unless the method of reconstitution precludes the risk of microbial
contamination, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use storage times
and conditions are the responsibility of the user.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
This medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions.
For storage conditions of the reconstituted medicinal product, see section
6.3
.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
Vials of glass Type I with bromobutyl rubber stopper and aluminium flip-off seal.
2 vials containing 120 mg powder for solution for injection
2 vials containing 6 ml solvent
2 syringes (5 ml with one-line marking 3.0 ml)
4 vial adapters
2 injection needles (25G 0.5 x 25 mm)
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
No special requirements for disposal.
Instructions for use:
The instructions for reconstitution must be followed carefully.
Administration of other concentrations is not recommended because the gel depot formation is
influenced by the concentration. The reconstituted solution should be a clear liquid, free of
undissolved matter.
NOTE:
• THE VIALS SHOULD NOT BE SHAKEN
The pack contains 2 sets of powder and solvent that must be prepared for subcutaneous injection.
Hence, the instructions here below need to be repeated a second time.
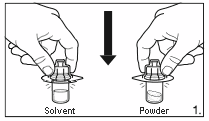
1.
Remove the cover from the vial adapter pack.
Attach the adapters to both the solvent and
powder vial by pressing the adapter down until
the spike pushes through the rubber stopper and
the adapter snap in place.
2.
Remove the cover from the syringe pack. Attach
the syringe to the solvent vial by screwing it on
to the adapter.
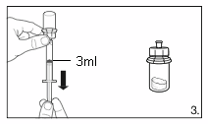
3.
Turn the vial upside down and draw
3.0 ml
of
the solvent into the syringe.
Always make sure to withdraw the precise
volume, as the amount of solvent affects the
reconstitution.
Detach the syringe from the adapter and discard
the vial with the remaining solvent.
4.
Attach the syringe to the powder vial by
screwing it on to the adapter. Transfer the
solvent to the powder vial. With the syringe
still attached to the adapter, swirl very gently
until the liquid looks clear and without undissolved
powder or particles. In case the powder adheres to
the vial over the liquid surface, the vial can be
tilted slightly.
AVOID SHAKING TO
PREVENT FOAM FORMATION.
A ring of small air bubbles on the surface of the
liquid is acceptable. The reconstitution procedure
may take, in some cases, up to 15 minutes, but
usually takes a few minutes.
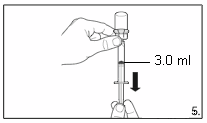
5.
Turn the vial upside down and,
holding it
vertically
, draw
3.0 ml
of the solution into the
syringe for injection.
Always make sure to withdraw the precise
volume. It can be necessary to tilt the vial
slightly.
7.
Grasp the skin of the abdomen, elevate the
subcutaneous tissue. Perform a profound
subcutaneous injection. To do so, insert the
needle deeply at an angle of not less than
45
degrees.
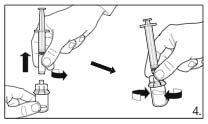
6.
Detach the syringe from the vial adapter and attach the needle for deep subcutaneous
injection to the syringe. Carefully remove any air bubbles.











8.
Inject
3.0 ml of FIRMAGON 120 mg
immediately after reconstitution.*
9.
Do not inject directly into a vein. Gently pull back the plunger to check if blood is
aspirated. If blood appears in the syringe, the medicinal product can no longer be used.
Discontinue the procedure and discard the syringe and the needle (reconstitute a new dose
for the patient).
10.
Repeat the reconstitution procedure for the second dose. Choose a different injection site
and inject 3.0 ml.
• No injections should be given in areas where the patient will be exposed to pressure, e.g. around
the belt or waistband or close to the ribs.
* Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 2 hours at 25ºC. From a
microbiological point of view, unless the method of reconstitution precludes the risk of microbial
contamination, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use storage
times and conditions are the responsibility of the user.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Ferring Pharmaceuticals A/S
Kay Fiskers Plads 11
DK-2300 Copenhagen S
Denmark
Tel: +45 88 33 88 34
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines





MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH RELEASE
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
A. MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
Ferring GmbH
Wittland 11
D-24109 Kiel
Germany
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
•
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
•
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
The MAH shall agree the details of an educational programme with the National Competent
Authorities and must implement such programme nationally to ensure that, prior to prescribing, all
physicians are provided with a healthcare professional information pack containing the following:
•
Educational material
•
Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) and Package Leaflet and Labelling
Key elements to be included in the educational material
Instructions for administration
Information on gel depot formation and possible injections site reactions
Information on the identified and potential risks
Pharmacovigilance system
The MAH must ensure that the system of pharmacovigilance, as described in version 2.0 presented in
Module 1.8.1. of the Marketing Authorisation Application, is in place and functioning before and
whilst the product is on the market.
Risk Management Plan
The MAH commits to performing the studies and additional pharmacovigilance activities detailed in
the Pharmacovigilance Plan, as agreed in version 4.2 of the Risk Management Plan (RMP) presented
in Module 1.8.2. of the Marketing Authorisation Application and any subsequent updates of the RMP
agreed by the CHMP.
As per the CHMP Guideline on Risk Management Systems for medicinal products for human use, the
updated RMP should be submitted at the same time as the next Periodic Safety Update Report
(PSUR).
In addition, an updated RMP should be submitted
•
When new information is received that may impact on the current Safety Specification,
Pharmacovigilance Plan or risk minimisation activities
•
Within 60 days of an important (pharmacovigilance or risk minimisation) milestone being
reached
•
At the request of the EMEA
ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
CARTON FOR FIRMAGON 80 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
FIRMAGON 80 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
degarelix
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains 80 mg degarelix (as acetate). After reconstitution each ml of the solution contains
20 mg degarelix.
Mannitol (E421), water for injections
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder and solvent for solution for injection
1 vial with 80 mg degarelix (powder)
1 vial with 6 ml solvent
1 syringe
2 vial adapters
1 injection needle
Powder and solvent for solution for injection
3 x 1 vial with 80 mg degarelix (powder)
3 x 1 vial with 6 ml solvent
3 x 1 syringe
3 x 2 vial adapters
3 x 1 injection needle
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Read the package leaflet before use.
Subcutaneous use only.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY





















SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Ferring Pharmaceuticals A/S
Kay Fiskers Plads 11
2300 Copenhagen S
Denmark
+45 88 33 88 34
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/08/504/001 1 pack
EU/1/08/504/003 3 pack
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
Justification for not including Braille accepted.





















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
CARTON FOR FIRMAGON 120 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
FIRMAGON 120 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
degarelix
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains 120 mg degarelix (as acetate). After reconstitution each ml of the solution contains
40 mg degarelix.
Mannitol (E421), water for injections
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder and solvent for solution for injection
2 vials with 120 mg degarelix (powder)
2 vials with 6 ml solvent
2 syringes
4 vial adapters
2 injection needles
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Read the package leaflet before use.
Subcutaneous use only.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS























10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Ferring Pharmaceuticals A/S
Kay Fiskers Plads 11
2300 Copenhagen S
Denmark
+45 88 33 88 34
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
Justification for not including Braille accepted.


















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
FIRMAGON 80 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
Degarelix
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
−
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
−
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor.
−
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if
their symptoms are the same as yours.
−
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor.
What FIRMAGON is and what it is used for
WHAT FIRMAGON IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
FIRMAGON contains degarelix.
Degarelix is a synthetic hormone blocker used in the treatment of prostate cancer. Degarelix mimics a
natural hormone (gonadotrophin-relasing hormone, GnRH) and directly blocks its effects. By doing
so, degarelix immediately reduces the level of the male hormone testosterone that stimulates the
prostate cancer.
−
If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to degarelix or any of the other ingredients of FIRMAGON.
Take special care with FIRMAGON
Please tell your doctor if you have any of the following:
−
Heart rhythm problems (arrythmia), or are being treated with medicines for this condition. The
risk of heart rhythm problems may be increased when using FIRMAGON.
−
Diabetes mellitus. Worsening or onset of diabetes may occur. If you have diabetes, you may have
to measure blood glucose more frequently.
FIRMAGON might interfere with some medicines used to treat heart rhythm problems (e.g. quinidine,
procainamide, amiodarone and sotalol) or other medicines which can have an effect on heart rhythm
(e.g. methadone, cisapride, moxifloxacine, antipsychotics).
Please tell your doctor if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines, including
medicines obtained without a prescription.
Driving and using machines
Tiredness and dizziness are common side effects that may impaire your ability to drive and use
machines. These side effects may be due to the treatment or effects resulting from the
underlying disease.
This medicine is usually injected by a nurse or a doctor.
The usual starting dose is two injections of 120 mg. After that, you will receive a monthly 80 mg
injection. The injected liquid forms a gel from which a continuous release of degarelix takes place
over a period of one month.
FIRMAGON must be injected under the skin (subcutaneously) ONLY. FIRMAGON must NOT be
given into a blood vessel (intravenously). Precautions must be taken to avoid accidental injection into
a vein. The site of injection is likely to vary within the abdominal region.
If you forget to use FIRMAGON
If you believe your monthly dose of FIRMAGON has been forgotten, please talk to your doctor.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor.
Like all medicines, FIRMAGON can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The frequency of possible side effects listed below is defined using the following convention:
−
very common (affects more than 1 user in 10)
−
common (affects 1 to 10 users in 100)
−
uncommon (affects 1 to 10 users in 1,000)
−
rare (affects 1 to 10 users in 10,000)
−
very rare (affects less than 1 user in 10,000)
−
not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
Very common
Hot flushes, injection site pain and redness.
Common
−
injection site swelling, node and hardness
−
chills, fever or influenza-like illness after the injection
−
trouble sleeping, tiredness, dizziness, headache
−
increased weight, nausea, diarrhoea, elevated levels of some liver enzymes
−
excessive sweating (including night sweats), rash
−
anaemia
−
musculoskeletal pain and discomfort
−
reduced size of testicles, breast swelling, impotence
Uncommon
−
loss of sexual desire, testicular pain, pelvic pain, ejaculation failure, genital irritation, breast pain
−
depression, mental impairment
−
skin redness, loss of hair, skin nodule, numbness
−
allergic reactions, hives, itching
−
decreased appetite, constipation, vomiting, dry mouth, abdominal pain and discomfort, increased
blood sugar/diabetes mellitus, increased cholesterol, changes in blood calcium, decreased weight
−
high blood pressure, changes in heart rhythm, changes in ECG (QT-prolongation), feeling of
abnormal heart beat, dyspnoea, peripheral oedema
−
muscular weakness, muscle spasms, joint swelling/stiffness, osteoporosis/osteopenia, pain in the
joint
−
frequent urination, urinary urgency (must hurry to pass urine), difficult or painful urination,
urination at night, impaired renal function, incontinence
−
blurred vision
−
discomfort at injection including decreased blood pressure and heart rate (vasovagal reaction)
−
malaise
Side effects at the injection site are most common with the starting dose and less common with the
maintenance dose.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
This medicine does not require any special storage conditions.
Do not use FIRMAGON after the expiry date which is stated on the vials and outer packaging. The
expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
After reconstitution:
Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 2 hours at 25ºC.
From a microbiological point of view, unless the method of reconstitution precludes the risk of
microbial contamination, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use
storage times and conditions are the responsibility of the user.
−
The active substance is degarelix, each vial contains 80 mg degarelix. After reconstitution 1 ml of
the reconstituted solution contains 20 mg degarelix.
−
The other ingredient of the powder is mannitol (E 421).
−
The solvent is water for injections.
What FIRMAGON looks like and contents of the pack
FIRMAGON is a powder for solution for injection. The powder is white to off-white. The solvent is a
clear, colourless solution.
1 pack contains:
1 vial with powder containing 80 mg of degarelix and 1 vial with 6 ml of solvent.
1 syringe, 2 vial adapters and 1 injection needle.
3 pack contains:
3 x 1 vial with powder containing 80 mg of degarelix and 3 x 1 vial with 6 ml of solvent.
3 x 1 syringe, 3 x 2 vial adapters and 3 x 1 injection needle.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorisation Holder:
Ferring Pharmaceuticals A/S
Kay Fiskers Plads 11
DK-2300 Copenhagen S
Denmark
Tel. +45 8833 8834
Manufacturer:
Ferring GmbH
Wittland 11
D-24109 Kiel
Germany
For any information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the Marketing
Authorisation Holder:
België/Belgique/Belgien
NV Ferring SA
Hopmarkt 9 b.3
B-9300 Aalst/Alost
Tel/Tél: + 32-53 72 92 00
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
NV Ferring SA
Hopmarkt 9 b.3
B-9300 Alost/Aalst
Tél/Tel: + 32-53 72 92 00
ferringnvsa@ferring.be
България
Фармасуис
България
София 1612
ж.к. Лагера
ул.Троянски проход 16
тел.: + 359 2 895 21 10
BulgariaInfo@pharmaswiss.com
Magyarország
Ferring Magyarország Gyógyszerkereskedelmi
Kft.
Váci út 140.
H-1138 Budapest
Tel.: + 36 1 236 3800
Česká republika
Ferring Pharmaceuticals CZ s.r.o.
K Rybníku 475
PSČ 252 42 Jesenice u Prahy
Tel: + 420 241 041 111
Malta
E.J. BUSUTTIL LTD
NICHE Apts., No. 1, TRIQ IX-XORROX
B’KARA BKR 1633 MALTA
Tel: + 356 21447184
Danmark
Ferring Lægemidler A/S
Kay Fiskers Plads 11
DK-2300 København S
Tlf: + 45 88 16 88 17
Nederland
Ferring BV
Postbus 184
NL-2130 AD HOOFDDORP
Tel: + 31-235680300
Deutschland
Ferring Arzneimittel GmbH
Fabrikstraße 7
D-24103 Kiel
Tel: + 49-(0)431-5852 0
Norge
Ferring Legemidler AS
(Nydalsveien 36B)
Postboks 4445 Nydalen
N-0403 Oslo
Tlf: + 47 22 02 08 80
MediNet International Ltd
Narva mnt. 11D
EE 10151 Tallinn
Tel: + 372 62 61 025
Ferring Arzneimittel GesmbH
Wienerbergstraße 11
A-1100 Wien
Tel: + 43 1 60 808 0
Ελλάδα
Ferring Ελλάς ΑΕ
Γκύζη 3
GR 151 25 Μαρούσι
Τηλ: + 30 210 68 43 449
Polska
Ferring Pharmaceuticals B.V., Sp. z o.o.
Przedstawicielstwo w Polsce
Ul. Królowej Marysieńki 11 m. 4
PL – 02-954 Warszawa
Tel.: + 48 22 842 71 00
España
Ferring, S.A.U.
C/ Gobelas, nº 11
E-28023 Madrid
Tel: + 34 91 799 47 80
Portugal
Ferring Portuguesa – Produtos Farmacêuticos,
Sociedade Unipessoal, Lda.
Rua Alexandre Herculano, Edifício 1, Piso 6
P-2795-240 Linda-a-Velha
Tel: + 351 21 940 51 90
France
Ferring S.A.S.
7, rue Jean-Baptiste Clément
F-94250 Gentilly
Tél : + 33 1 49 08 91 23
România
Ferring Pharmaceuticals SA
Reprezentanţa în România
Str. C.A. Rosetti nr. 17, biroul 501
Bucureşti 020011 – RO
Tel: + 40 21 527 03 02
Ireland
Ferring Ireland Ltd.
United Drug House
Magna Drive
Magna Business Park
Citywest Road
IRL - Dublin 24
+ 353 (0)1 4637355
Slovenija
PharmaSwiss d.o.o.
Wolfowa 1
SI-1000 Ljubljana
Tel: + 386 1 23 64 700
Ísland
Vistor hf.
Hörgatúni 2
IS-210 Garðabæ
Sími: + 354 535 70 00
Slovenská republika
Ferring Pharmaceuticals SA
BC Aruba, Galvaniho 7/D
SK-821 04 Bratislava
Tel: + 421 2 54 416 010
Italia
Ferring S.p.A.
Via Senigallia 18/2
I-20161 Milano
Tel: + 39 02 640 00 11
Suomi/Finland
Ferring Lääkkeet Oy
PL 23
FIN-02241 Espoo
Puh/Tel: + 358-207 401440
Κύπρος
Χρ. Γ. Παπαλοΐζου Λτδ
T.Θ. 21148
CY 1502 Λευκωσία
Τηλ: + 357 22490305
Sverige
Ferring Läkemedel AB
Box 4041
SE-203 11 Malmö
Tel: + 46 40 691 69 00
Latvija
MediNet International Ltd
Ojāra Vācieša iela 13
Rīga LV-1004
Tel: + 371 67 805 140
United Kingdom
Ferring Pharmaceuticals Ltd
The Courtyard, Waterside Drive
Langley, Berkshire, SL3 6EZ – UK
Tel: + 01753 214800
Lietuva
MediNet International Ltd
Laisvės pr. 75
LT-06144 Vilnius
Tel: + 370 52 688 490
This leaflet was last approved in
{MM/YYYY}.
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency web site:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following information is intended for medical or healthcare professionals only:
Instructions for proper use
NOTE:
• DO NOT SHAKE THE VIALS
The pack contains 1 set of powder and solvent that must be prepared for subcutaneous injection.
1.
Remove the cover from the vial adapter pack.
Attach the adapters to both the solvent and
powder vial by pressing the adapter down until
the spike pushes through the rubber stopper and
the adapter snap in place.
2.
Remove the cover from the syringe pack.
Attach the syringe to the solvent vial by
screwing it on to the adapter.
3.
Turn the vial upside down and draw
4.2 ml
of the
solvent into the syringe.
Always make sure to withdraw the precise
volume, as the amount of solvent affects the
reconstitution.
Detach the syringe from the adapter and discard
the vial with the remaining solvent.








4.
Attach the syringe to the powder vial by
screwing it on to the adapter. Transfer the
solvent to the powder vial. With the syringe
still attached to the adapter, swirl very gently
until the liquid looks clear and without undissolved
powder or particles. In case the powder adheres to
the vial over the liquid surface, the vial can be
tilted slightly.
AVOID SHAKING TO
PREVENT FOAM FORMATION.
A ring of small air bubbles on the surface of the
liquid is acceptable. The reconstitution procedure
may take, in some cases, up to 15 minutes, but
usually takes a few minutes.
5.
Turn the vial upside down and,
holding it
vertically
, draw
4.0 ml
of the solution into the
syringe for injection.
Always make sure to withdraw the precise
volume. It can be necessary to tilt the vial
slightly.
6.
Detach the syringe from the vial adapter and attach theneedle for deep subcutaneous
injection to the syringe. Carefully remove any air bubbles.
7.
Grasp the skin of the abdomen, elevate the
subcutaneous tissue. Perform a profound
subcutaneous injection. To do so, insert the needle
deeply at an angle of not less than
45 degrees.
8.
Inject
4.0 ml of FIRMAGON 80 mg
immediately after reconstitution.*
9.
Do not inject directly into a vein. Gently pull back the plunger to check if blood is
aspirated. If blood appears in the syringe, the medicinal product can no longer be used.
Discontinue the procedure and discard the syringe and the needle (reconstitute a new dose
for the patient).
− No injections should be given in areas where the patient will be exposed to pressure, e.g. around
the belt or waistband or close to the ribs.
* Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 2 hours at 25ºC. From a
microbiological point of view, unless the method of reconstitution precludes the risk of microbial
contamination, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use storage
times and conditions are the responsibility of the user.
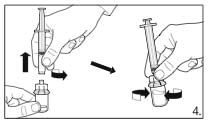
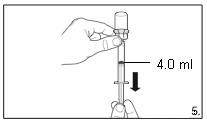
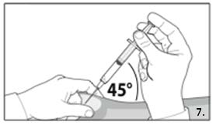









PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
FIRMAGON 120 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
Degarelix
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
−
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
−
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor.
−
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms are the same as yours.
−
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor.
What FIRMAGON is and what it is used for
WHAT FIRMAGON IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
FIRMAGON contains degarelix.
Degarelix is a synthetic hormone blocker used in the treatment of prostate cancer. Degarelix mimics a
natural hormone (gonadotrophin-relasing hormone, GnRH) and directly blocks its effects. By doing
so, degarelix immediately reduces the level of the male hormone testosterone that stimulates the
prostate cancer.
−
If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to degarelix or any of the other ingredients of FIRMAGON.
Take special care with FIRMAGON
Please tell your doctor if you have any of the following:
−
Heart rhythm problems (arrythmia), or are being treated with medicines for this condition. The
risk of heart rhythm problems may be increased when using FIRMAGON.
−
Diabetes mellitus. Worsening or onset of diabetes may occur. If you have diabetes, you may have
to measure blood glucose more frequently.
FIRMAGON might interfere with some medicines used to treat heart rhythm problems (e.g. quinidine,
procainamide, amiodarone and sotalol) or other medicines which can have an effect on heart rhythm
(e.g. methadone, cisapride, moxifloxacine, antipsychotics).
Please tell your doctor if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines, including
medicines obtained without a prescription.
Driving and using machines
Tiredness and dizziness are common side effects that may impaire your ability to drive and use
machines. These side effects may be due to the treatment or effects resulting from the
underlying disease.
This medicine is usually injected by a nurse or a doctor.
The usual starting dose is two injections of 120 mg. After that, you will receive a monthly 80 mg
injection. The injected liquid forms a gel from which a continuous release of degarelix takes place
over a period of one month.
FIRMAGON must be injected under the skin (subcutaneously) ONLY. FIRMAGON must NOT be
given into a blood vessel (intravenously). Precautions must be taken to avoid accidental injection into
a vein. The site of injection is likely to vary within the abdominal region.
If you forget to use FIRMAGON
If you believe your monthly dose of FIRMAGON has been forgotten, please talk to your doctor.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor.
Like all medicines, FIRMAGON can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The frequency of possible side effects listed below is defined using the following convention:
−
very common (affects more than 1 user in 10)
−
common (affects 1 to 10 users in 100)
−
uncommon (affects 1 to 10 users in 1,000)
−
rare (affects 1 to 10 users in 10,000)
−
very rare (affects less than 1 user in 10,000)
−
not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
Very common
Hot flushes, injection site pain and redness.
Common
−
injection site swelling, node and hardness
−
chills, fever or influenza-like illness after the injection
−
trouble sleeping, tiredness, dizziness, headache
−
increased weight, nausea, diarrhoea, elevated levels of some liver enzymes
−
excessive sweating (including night sweats), rash
−
anaemia
−
musculoskeletal pain and discomfort
−
reduced size of testicles, breast swelling, impotence
Uncommon
−
loss of sexual desire, testicular pain, pelvic pain, ejaculation failure, genital irritation, breast pain
−
depression, mental impairment
−
skin redness, loss of hair, skin nodule, numbness
−
allergic reactions, hives, itching
−
decreased appetite, constipation, vomiting, dry mouth, abdominal pain and discomfort, increased
blood sugar/diabetes mellitus, increased cholesterol, changes in blood calcium, decreased weight
−
high blood pressure, changes in heart rhythm, changes in ECG (QT-prolongation), feeling of
abnormal heart beat, dyspnoea, peripheral oedema
−
muscular weakness, muscle spasms, joint swelling/stiffness, osteoporosis/osteopenia, pain in the
joint
−
frequent urination, urinary urgency (must hurry to pass urine), difficult or painful urination,
urination at night, impaired renal function, incontinence
−
blurred vision
−
discomfort at injection including decreased blood pressure and heart rate (vasovagal reaction)
−
malaise
Side effects at the injection site are most common with the starting dose and less common with the
maintenance dose.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
This medicine does not require any special storage conditions.
Do not use FIRMAGON after the expiry date which is stated on the vials and outer packaging. The
expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
After reconstitution
Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 2 hours at 25ºC.
From a microbiological point of view, unless the method of reconstitution precludes the risk of
microbial contamination, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use
storage times and conditions are the responsibility of the user.
−
The active substance is degarelix. Each vial contains 120 mg degarelix. After reconstitution 1 ml
of the reconstituted solution contains 40 mg degarelix.
−
The other ingredient of the powder is mannitol (E 421).
−
The solvent is water for injections.
What FIRMAGON looks like and contents of the pack
FIRMAGON is a powder for solution for injection. The powder is white to off-white. The solvent is a
clear, colourless solution.
1 pack contains:
2 vials with powder containing 120 mg of degarelix and 2 vials with 6 ml of solvent.
2 syringes, 4 vial adapters and 2 injection needles.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorisation Holder:
Ferring Pharmaceuticals A/S
Kay Fiskers Plads 11
DK-2300 Copenhagen S
Denmark
Tel. +45 8833 8834
Manufacturer:
Ferring GmbH
Wittland 11
D-24109 Kiel
Germany
For any information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the Marketing
Authorisation Holder:
België/Belgique/Belgien
NV Ferring SA
Hopmarkt 9 b.3
B-9300 Aalst/Alost
Tel/Tél: + 32-53 72 92 00
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
NV Ferring SA
Hopmarkt 9 b.3
B-9300 Alost/Aalst
Tél/Tel: + 32-53 72 92 00
ferringnvsa@ferring.be
България
Фармасуис
България
София 1612
ж.к. Лагера
ул.Троянски проход 16
тел.: + 359 2 895 21 10
BulgariaInfo@pharmaswiss.com
Magyarország
Ferring Magyarország Gyógyszerkereskedelmi
Kft.
Váci út 140.
H-1138 Budapest
Tel.: + 36 1 236 3800
Česká republika
Ferring Pharmaceuticals CZ s.r.o.
K Rybníku 475
PSČ 252 42 Jesenice u Prahy
Tel: + 420 241 041 111
Malta
E.J. BUSUTTIL LTD
NICHE Apts., No. 1, TRIQ IX-XORROX
B’KARA BKR 1633 MALTA
Tel: + 356 21447184
Danmark
Ferring Lægemidler A/S
Kay Fiskers Plads 11
DK-2300 København S
Tlf: + 45 88 16 88 17
Nederland
Ferring BV
Postbus 184
NL-2130 AD HOOFDDORP
Tel: + 31-235680300
Deutschland
Ferring Arzneimittel GmbH
Fabrikstraße 7
D-24103 Kiel
Tel: + 49-(0)431-5852 0
Norge
Ferring Legemidler AS
(Nydalsveien 36B)
Postboks 4445 Nydalen
N-0403 Oslo
Tlf: + 47 22 02 08 80
Eesti
MediNet International Ltd
Narva mnt. 11D
EE 10151 Tallinn
Tel: + 372 62 61 025
Österreich
Ferring Arzneimittel GesmbH
Wienerbergstraße 11
A-1100 Wien
Tel: + 43 1 60 808 0
Ελλάδα
Ferring Ελλάς ΑΕ
Γκύζη 3
GR 151 25 Μαρούσι
Τηλ: + 30 210 68 43 449
Polska
Ferring Pharmaceuticals B.V., Sp. z o.o.
Przedstawicielstwo w Polsce
Ul. Królowej Marysieńki 11 m. 4
PL – 02-954 Warszawa
Tel.: + 48 22 842 71 00
España
Ferring, S.A.U.
C/ Gobelas, nº 11
E-28023 Madrid
Tel: + 34 91 799 47 80
Portugal
Ferring Portuguesa – Produtos Farmacêuticos,
Sociedade Unipessoal, Lda.
Rua Alexandre Herculano, Edifício 1, Piso 6
P-2795-240 Linda-a-Velha
Tel: + 351 21 940 51 90
France
Ferring S.A.S.
7, rue Jean-Baptiste Clément
F-94250 Gentilly
Tél : + 33 1 49 08 91 23
România
Ferring Pharmaceuticals SA
Reprezentanţa în România
Str. C.A. Rosetti nr. 17, biroul 501
Bucureşti 020011 – RO
Tel: + 40 21 527 03 02
Ireland
Ferring Ireland Ltd.
United Drug House
Magna Drive
Magna Business Park
Citywest Road
IRL - Dublin 24
+ 353 (0)1 4637355
Slovenija
PharmaSwiss d.o.o.
Wolfowa 1
SI-1000 Ljubljana
Tel: + 386 1 23 64 700
Ísland
Vistor hf.
Hörgatúni 2
IS-210 Garðabæ
Sími: + 354 535 70 00
Slovenská republika
Ferring Pharmaceuticals SA
BC Aruba, Galvaniho 7/D
SK-821 04 Bratislava
Tel: + 421 2 54 416 010
Italia
Ferring S.p.A.
Via Senigallia 18/2
I-20161 Milano
Tel: + 39 02 640 00 11
Suomi/Finland
Ferring Lääkkeet Oy
PL 23
FIN-02241 Espoo
Puh/Tel: + 358-207 401440
Κύπρος
Χρ. Γ. Παπαλοΐζου Λτδ
T.Θ. 21148
CY 1502 Λευκωσία
Τηλ: + 357 22490305
Sverige
Ferring Läkemedel AB
Box 4041
SE-203 11 Malmö
Tel: + 46 40 691 69 00
Latvija
MediNet International Ltd
Ojāra Vācieša iela 13
Rīga LV-1004
Tel: + 371 67 805 140
United Kingdom
Ferring Pharmaceuticals Ltd
The Courtyard, Waterside Drive
Langley, Berkshire, SL3 6EZ – UK
Tel: + 01753 214800
Lietuva
Laisvės pr. 75
LT-06144 Vilnius
Tel: + 370 52 688 490
This leaflet was last approved in
{MM/YYYY}.
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency web site:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following information is intended for medical or healthcare professionals only:
Instructions for proper use
NOTE:
• DO NOT SHAKE THE VIALS
The pack contains 2 sets of powder and solvent that must be prepared for subcutaneous injection.
Hence, the instructions here below need to be repeated a second time.
1.
Remove the cover from the vial adapter pack.
Attach the adapters to both the solvent and
powder vial by pressing the adapter down until
the spike pushes through the rubber stopper and
the adapter snap in place.
2.
Remove the cover from the syringe pack.
Attach the syringe to the solvent vial by
screwing it on to the adapter.
3.
Turn the vial upside down and draw
3.0 ml
of
the solvent into the syringe.
Always make sure to withdraw the precise
volume, as the amount of solvent affects the
reconstitution.
Detach the syringe from the adapter and discard
the vial with the remaining solvent.
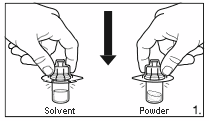
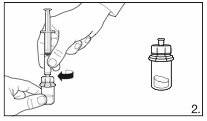
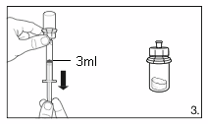






4.
Attach the syringe to the powder vial by
screwing it on to the adapter. Transfer the
solvent to the powder vial. With the syringe
still attached to the adapter, swirl very gently
until the liquid looks clear and without undissolved
powder or particles. In case the powder adheres to
the vial over the liquid surface, the vial can be
tilted slightly.
AVOID SHAKING TO
PREVENT FOAM FORMATION.
A ring of small air bubbles on the surface of the
liquid is acceptable. The reconstitution procedure
may take, in some cases, up to 15 minutes, but
usually takes a few minutes.
6
. Detach the syringe from the vial adapter and attach the needle for deep subcutaneous
injection to the syringe. Carefully remove any air bubbles.
5
. Turn the vial upside down and,
holding it
vertically
, draw
3.0 ml
of the solution
into the
syringe for injection.
Always make sure to withdraw the precise
volume. It can be necessary to tilt the vial
slightly.
7.
Grasp the skin of the abdomen, elevate the
subcutaneous tissue. Perform a profound
subcutaneous injection. To do so, insert the needle
deeply at an angle of not less than
45 degrees.
8.
Inject
3.0 ml of FIRMAGON 120 mg
immediately after reconstitution.*
9.
Do not inject directly into a vein. Gently pull back the plunger to check if blood is
aspirated. If blood appears in the syringe, the medicinal product can no longer be used.
Discontinue the procedure and discard the syringe and the needle (reconstitute a new dose
for the patient).
10.
Repeat the reconstitution procedure for the second dose. Choose a different injection site
and inject 3.0 ml.
− No injections should be given in areas where the patient will be exposed to pressure, e.g. around
the belt or waistband or close to the ribs.
* Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 2 hours at 25ºC. From a
microbiological point of view, unless the method of reconstitution precludes the risk of microbial
contamination, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use storage
times and conditions are the responsibility of the user.
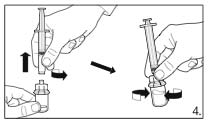
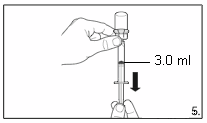
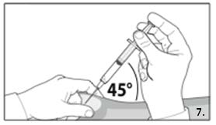










Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/firmagon.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|
































































































































































































































































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































