Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Fuzeon 90 mg/ml powder and solvent for solution for injection
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each vial contains 108 mg enfuvirtide.
Each ml of reconstituted solution contains 90 mg enfuvirtide.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Powder and solvent for solution for injection.
White to off-white lyophilised powder.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Fuzeon is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of
HIV-1 infected patients who have received treatment with and failed on regimens containing at least
one medicinal product from each of the following antiretroviral classes
:
protease inhibitors, non-
nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors and nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, or who have
intolerance to previous antiretroviral regimens. (see section 5.1)
In deciding on a new regimen for patients who have failed an antiretroviral regimen, careful
consideration should be given to the treatment history of the individual patient and the patterns of
mutations associated with different medicinal products. Where available, resistance testing may be
appropriate.
(See sections 4.4 and 5.1)
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Fuzeon should be prescribed by physicians who are experienced in the treatment of HIV infection.
Fuzeon is only to be administered by subcutaneous injection.
Adults and adolescents ≥ 16 years
: The recommended dose of Fuzeon is 90 mg twice daily injected
subcutaneously into the upper arm, anterior thigh or abdomen.
Elderly
: There is no experience in patients > 65 years old.
Children ≥ 6 years and adolescents
: The experience in children is limited (See section 5.2). In clinical
trials the dosage regimen in table 1 below was used:
Table 1: Paediatric Dosing
Weight (kg)
Dose per bid injection
(mg/dose)
Injection volume
(90 mg enfuvirtide
per ml)
Fuzeon is not recommended for use in children below age 6 due to insufficient data on safety and
efficacy (see section 5.2).
Renal impairment:
No dose adjustment is required for patients with renal impairment including those
receiving dialysis. (See sections 4.4 and 5.2).
Hepatic impairment:
No data are available to establish a dose recommendation for patients with
hepatic impairment. (See sections 4.4 and 5.2).
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Fuzeon must be taken as part of a combination regimen. Please also refer to the respective summary of
product characteristics of the other antiretroviral medicinal products used in the combination. As with
other antiretrovirals, enfuvirtide should optimally be combined with other antiretrovirals to which the
patient’s virus is sensitive. (See section 5.1)
Patients must be advised that antiretroviral therapies including enfuvirtide have not been proved to
prevent the risk of transmission to HIV to others through sexual contact or blood contamination. They
must continue to use appropriate precautions. Patients should also be informed that Fuzeon is not a
cure for HIV-1 infection.
Animal studies have shown that enfuvirtide may impair some immune functions (see section 5.3). In
clinical trials, an increased rate of some bacterial infections, most notably a higher rate of pneumonia,
was seen in patients treated with Fuzeon; however, an increased risk of bacterial pneumonia related to
the use of Fuzeon has not been confirmed by subsequent epidemiological data.
Hypersensitivity reactions have occasionally been associated with therapy with enfuvirtide and in rare
cases hypersensitivity reactions have recurred on rechallenge. Events included rash, fever, nausea and
vomiting, chills, rigors, low blood pressure and elevated serum liver transaminases in various
combinations, and possibly primary immune complex reaction, respiratory distress and
glomerulonephritis. Patients developing signs/symptoms of a systemic hypersensitivity reaction should
discontinue enfuvirtide treatment and should seek medical evaluation immediately. Therapy with
enfuvirtide should not be restarted following systemic signs and symptoms consistent with a
hypersensitivity reaction considered related to enfuvirtide. Risk factors that may predict the
occurrence or severity of hypersensitivity to enfuvirtide have not been identified.
Liver disease:
The safety and efficacy of enfuvirtide has not been specifically studied in patients with
significant underlying liver disorders. Patients with chronic hepatitis B and C and treated with













antiretroviral therapy are at an increased risk for severe and potentially fatal hepatic adverse events.
Few patients included in the phase III trials were co-infected with hepatitis B/C. In these the addition
of Fuzeon did not increase the incidence of hepatic events. In case of concomitant antiviral therapy for
hepatitis B or C, please refer also to the relevant product information for these medicinal products.
Administration of Fuzeon to non-HIV-1 infected individuals may induce anti-enfuvirtide antibodies
that cross-react with HIV gp41. This may result in a false positive HIV test with the anti-HIV ELISA
test.
There is no experience in patients with reduced hepatic function. Data is limited in patients with
moderate to severe renal impairment, and in patients maintained on dialysis. Fuzeon should be used
with caution in these populations. (See sections 4.2 and 5.2)
Immune Reactivation Syndrome:
In HIV-infected patients with severe immune deficiency at the time
of institution of combination antiretroviral therapy (CART), an inflammatory reaction to
asymptomatic or residual opportunistic pathogens may arise and cause serious clinical conditions, or
aggravation of symptoms. Typically, such reactions have been observed within the first few weeks or
months of initiation of CART. Relevant examples are cytomegalovirus retinitis, generalised and/or
focal mycobacterial infections, and Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Any inflammatory symptoms
should be evaluated and treatment instituted when necessary.
Osteonecrosis:
Although the etiology is considered to be multifactorial (including corticosteroid use, alcohol
consumption, severe immunosuppression, higher body mass index), cases of osteonecrosis have been
reported particularly in patients with advanced HIV-disease and/or long-term exposure to CART.
Patients should be advised to seek medical advice if they experience joint aches and pain, joint
stiffness or difficulty in movement.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Interactions studies have only been performed in adults.
No clinically significant pharmacokinetic interactions are expected between enfuvirtide and
concomitantly given medicinal products metabolised by CYP450 enzymes.
Influence of enfuvirtide on metabolism of concomitant medicinal products:
In an in-vivo human
metabolism study enfuvirtide, at the recommended dose of 90 mg twice daily, did not inhibit the
metabolism of substrates by CYP3A4 (dapsone), CYP2D6 (debrisoquine), CYP1A2 (caffeine),
CYP2C19 (mephenytoin), and CYP2E1 (chlorzoxazone).
Influence of concomitant medicinal products on enfuvirtide metabolism:
In separate pharmacokinetic
interaction studies, co-administration of ritonavir (potent CYP3A4 inhibitor) or saquinavir in
combination with a booster dose of ritonavir or rifampicin (potent CYP34A inducer) did not result in
clinically significant changes of the pharmacokinetics of enfuvirtide.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Animal studies do not indicate
harmful effects with respect to foetal development. Enfuvirtide should be used during pregnancy only
if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the foetus.
It is not known whether enfuvirtide is secreted in human milk. Mothers should be instructed not to
breast-feed if they are receiving enfuvirtide because of the potential for HIV transmission and any
possible undesirable effects in breast-fed infants.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed. There is no
evidence that enfuvirtide may alter the patient’s ability to drive and use machines, however, the
adverse event profile of enfuvirtide should be taken into account. (See section 4.8)
Safety data mainly refer to 48-week data from studies TORO 1 and TORO 2 combined (see section
5.1). Safety results are expressed as the number of patients with an adverse reaction per 100 patient-
years of exposure (except for injection site reactions).
Injection site reactions (ISRs) were the most frequently reported adverse reaction and occurred in 98%
of the patients (Table 2). The vast majority of ISRs occurred within the first week of Fuzeon
administration and were associated with mild to moderate pain or discomfort at the injection site
without limitation of usual activities. The severity of the pain and discomfort did not increase with
treatment duration. The signs and symptoms generally lasted equal to or less than 7 days. Infections at
the injection site (including abscess and cellulitis) occurred in 1.5% of patients.
Table 2: Summary of individual signs/symptoms characterising local injection site reactions
in studies TORO 1 and TORO 2 combined (% of patients)
Withdrawal Rate due to ISRs
Fuzeon
+Optimised
background
a
% of Event
comprising
Grade 3 reactions
% of Event
comprising
Grade 4 reactions
a
Any severity grade.
b
Grade 3= severe pain requiring analgesics (or narcotic analgesics for ≤ 72 hours) and/or limiting usual activities; Grade 4= severe pain
requiring hospitalisation or prolongation of hospitalisation, resulting in death, or persistent or significant disability/incapacity, or life-
threatening, or medically significant.
c
Grade 3= ≥ 50 mm but < 85 mm average diameter; Grade 4= ≥ 85 mm average diameter.
d
Grade 3= ≥ 25 mm but < 50 mm average diameter; Grade 4= ≥ 50 mm average diameter.
e
Grade 3= ≥ 3 cm; Grade 4= If draining.
f
Grade 3= refractory to topical treatment or requiring oral or parenteral treatment; Grade 4= not defined.
g
Grade 3= > 3 cm but ≤ 5 cm; Grade 4= > 5 cm.
The addition of Fuzeon to background antiretroviral therapy generally did not increase the frequency
or severity of most adverse reactions. The most frequently reported events occurring in the TORO 1
and TORO 2 studies were diarrhoea (38 versus 73 patients with event per 100 patient years for
Fuzeon + OB versus OB) and nausea (27 versus 50 patients with event per 100 patient years for
Fuzeon + OB versus OB).
The following list presents events seen at a higher rate among patients receiving Fuzeon+OB regimen
than among patients on the OB alone regimen with an exposure adjusted increase of at least 2 patients
with event per 100 patient-years. These events are then designated frequency estimation (“very
common” (≥1/10), or “common” (≥1/100, <1/10)). A statistically significant increase was seen for
pneumonia and lymphadenopathy. Most adverse reactions were of mild or moderate intensity.
Infections and Infestations
Common:
- sinusitis, skin papilloma, influenza, pneumonia, ear infection.














Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders
Common:
-
lymphadenopathy.
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders
Common:
- appetite decreased, anorexia, hypertriglyceridaemia, diabetes mellitus.
Psychiatric Disorders
Common:
- anxiety, nightmare, irritability.
Nervous System Disorders
Very Common:
- peripheral neuropathy.
Common
: -hypoaesthesia, disturbance in attention, tremor.
Eye Disorders
Common:
- conjunctivitis.
Ear and Labyrinth disorders
Common:
- vertigo.
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders
Common:
- nasal congestion.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Common:
- pancreatitis, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Common:
- dry skin, eczema seborrhoeic, erythema, acne.
Musculoskeletal, Connective Tissue and Bone Disorders
Common:
- myalgia.
Renal and Urinary Disorders
Common:
- Calculus renal.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions
Common:
- influenza like illness, weakness.
Investigations
Very Common:
- weight decreased
Common:
- blood triglycerides increased, haematuria present.
In addition there have been a small number of hypersensitivity reactions attributed to enfuvirtide and
in some cases recurrence has occurred upon re-challenge. (See section 4.4)
In HIV-infected patients with severe immune deficiency at the time of initiation of combination
antiretroviral therapy (CART), an inflammatory reaction to asymptomatic or residual opportunistic
infections may arise (see section 4.4).
Cases of osteonecrosis have been reported, particularly in patients with generally acknowledged risk
factors, advanced HIV disease or long-term exposure to CART. The frequency of this is unknown (see
section 4.4).
The majority of patients had no change in the toxicity grade of any laboratory parameter during the
study except for those listed in Table 3. Through week 48, eosinophilia [greater than the Upper Limit
of Normal of > 0.7 x 10
9
/l] occurred at a higher rate amongst patients in the Fuzeon containing group
(12.4 patients with event per 100 patient-years) compared with OB alone regimen (5.6 patients with
event per 100 patient-years). When using a higher threshold for eosinophilia (>1.4 x 10
9
/l), the patient
exposure adjusted rate of eosinophilia is equal in both groups (1.8 patients with event per 100 patient-
years).
Table 3: Exposure adjusted Grade 3 & 4 laboratory abnormalities among patients on
Fuzeon+OB and OB alone regimens, reported at more than 2 patients with event per
100 patient years
Laboratory Parameters
Grading
Fuzeon+OB regimen
Per 100 patient years
OB alone regimen
Per 100 patient years
n
(Total Exposure patient years)
Haemoglobin
Gr. 3 (6.5-7.9 g/dL)
Creatinine phosphokinase
Gr. 3 (>5-10 x ULN)
No case of overdose has been reported. The highest dose administered to 12 patients in a clinical trial
was 180 mg as a single dose subcutaneously. These patients did not experience any adverse reactions
that were not seen with the recommended dose. In an Early Access Program study, one patient
administered 180 mg of Fuzeon as a single dose on one occasion. He did not experience an adverse
reaction as a result.
There is no specific antidote for overdose with enfuvirtide. Treatment of overdose should consist of
general supportive measures.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Other antivirals, ATC code: J05AX07
Mechanism of Action
: Enfuvirtide is a member of the therapeutic class called fusion inhibitors. It is an
inhibitor of the structural rearrangement of HIV-1 gp41 and functions by specifically binding to this
virus protein extracellularly thereby blocking fusion between the viral cell membrane and the target
cell membrane, preventing the viral RNA from entering into the target cell.
Antiviral activity
in vitro
: The susceptibility to enfuvirtide of 612 HIV recombinants containing the
env genes from HIV RNA samples taken at baseline from patients in Phase III studies gave a
geometric mean EC
50
of 0.259 μg/ml (geometric mean + 2SD = 1.96 μg/ml) in a recombinant
phenotype HIV entry assay. Enfuvirtide also inhibited HIV-1 envelope mediated cell-cell fusion.
Combination studies of enfuvirtide with representative members of the various antiretroviral classes
exhibited additive to synergistic antiviral activities and an absence of antagonism. The relationship
between the
in vitro
susceptibility of HIV-1 to enfuvirtide and inhibition of HIV-1 replication in
humans has not been established.
Antiretroviral drug resistance
: Incomplete viral suppression may lead to the development of drug
resistance to one or more components of the regimen.














In Vitro
resistance to enfuvirtide
: HIV-1 isolates with reduced susceptibility to enfuvirtide have been
selected
in vitro
which harbour substitutions in amino acids (aa) 36-38 of the gp41 ectodomain. These
substitutions were correlated with varying levels of reduced enfuvirtide susceptibility in HIV site-
directed mutants.
In Vivo
resistance to enfuvirtide
: In phase III clinical studies HIV recombinants containing the env
genes from HIV RNA samples taken up to week 24 from 187 patients showed > 4 fold reduced
susceptibility to enfuvirtide compared with the corresponding pre-treatment samples. Of these,
185 (98.9%) env genes carried specific substitutions in region of aa 36 - 45 of gp41. The substitutions
observed in decreasing frequency were at aa positions 38, 43, 36, 40, 42 and 45. Specific single
substitutions at these residues in gp41 each resulted in a range of decreases from baseline in
recombinant viral susceptibility to enfuvirtide. The geometric mean changes ranged from 15.2 fold for
V38M to 41.6 fold for V38A. There were insufficient examples of multiple substitutions to determine
any consistent patterns of substitutions or their effect on viral susceptibility to enfuvirtide. The
relationship of these substitutions to
in vivo
effectiveness of enfuvirtide has not been established.
Decrease in viral sensitivity was correlated to the degree of pre-treatment resistance to background
therapy. (See Table 5)
Cross-resistance
: Due to its novel viral target enfuvirtide is equally active
in vitro
against both wild-
type laboratory and clinical isolates and those with resistance to 1, 2 or 3 other classes of
antiretrovirals (nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase
inhibitors and protease inhibitors). Conversely, mutations in aa 36-45 of gp41 which give resistance to
enfuvirtide would not be expected to give cross resistance to other classes of antiretrovirals.
Clinical Pharmacodynamic data
Studies in Antiretroviral Experienced Patients:
The clinical activity of Fuzeon (in combination with
other antiretroviral agents) on plasma HIV RNA levels and CD4 counts have been investigated in two
randomised, multicentre, controlled studies (TORO 1 and TORO 2) of Fuzeon of 48 weeks duration.
995 patients comprised the intent-to-treat population. Patient demographics include a median baseline
HIV-1 RNA of 5.2 log
10
copies/ml and 5.1 log
10
copies/ml and median baseline CD4 cell count of
88 cells/mm
3
and 97 cells/mm
3
for Fuzeon + OB and OB, respectively. Patients had prior exposure to
a median of 12 antiretrovirals for a median of 7 years. All patients received an optimised background
(OB) regimen consisting of 3 to 5 antiretroviral agents selected on the basis of the patient's prior
treatment history, as well as baseline genotypic and phenotypic viral resistance measurements.
The proportion of patients achieving viral load of <400 copies/ml at week 48 was 30.4% among
patients on the Fuzeon+OB regimen compared to 12% among patients receiving OB regimen only.
The mean CD4 cell count increase was greater in patients on the Fuzeon + OB regimen than in
patients on OB regimen only. (see Table 4)
Outcomes of Randomised Treatment at Week 48 (Pooled Studies TORO 1 and
TORO 2, ITT)
Outcomes
Fuzeon +OB
90 mg bid
(N=661)
HIV-1 RNA
Log Change from baseline
(log
10
copies/ml)
*
CD4+ cell count
Change from baseline
(cells/mm
3
)
#
HIV RNA
>
1 log below
Baseline
**
247 (37.4%) 57 (17.1%) Odds Ratio
3.02
HIV RNA <400 copies/ml
**
201 (30.4%) 40 (12.0%) Odds Ratio
3.45
26 (7.8%) Odds Ratio
2.77
Discontinued due to adverse
reactions/intercurrent
illness/labs
†
Discontinued due to injection
site reactions
†
Discontinued due to other
reasons
†φ§
Based on results from pooled data of TORO 1 and TORO 2 on ITT population, week 48 viral load for subjects who
were lost to follow-up, discontinued therapy, or had virological failure replaced by their last observation (LOCF).
Last value carried forward.
M-H test: Discontinuations or virological failure considered as failures.
Percentages based on safety population Fuzeon+background (N=663) and background (N=334). Denominator for
non-switch patients: N=112.
As per the judgment of the investigator.
Includes discontinuations from loss to follow-up, treatment refusal, and other reasons.
Fuzeon+OB therapy was associated with a higher proportion of patients reaching <400 copies/ml (or
<50 copies/ml) across all subgroups based on baseline CD4, baseline HIV-1 RNA, number of prior
antiretrovirals (ARVs) or number of active ARVs in the OB regimen. However, subjects with baseline
CD4 >100 cells/mm
3
, baseline HIV-1 RNA <5.0 log
10
copies/ml, ≤ 10 prior ARVs, and/or other active
ARVs in their OB regimen were more likely to achieve a HIV-1 RNA of <400 copies/ml
(or <50 copies/ml) on either treatment. (see Table 5)























Proportion of Patients
achieving <400 copies/ml and <50 copies/ml at Week 48 by
subgroup (pooled TORO 1 and TORO 2, ITT)
HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/ml
Fuzeon + OB
90 mg bid
(N=661)
Fuzeon + OB
90 mg bid
(N=661)
BL HIV-1 RNA < 5.0
log
10
1
copies/ml
BL HIV-1 RNA ≥ 5.0
log
10
1
copies/ml
0 Active ARVs in
background
1,2
1 Active ARV in
background
1,2
≥ 2 Active ARVs in
background
1,2
1
Discontinuations or virological failures considered as failures.
2
Based on GSS score.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
The pharmacokinetic properties of enfuvirtide have been evaluated in HIV-1-infected adult and
paediatric patients.
Absorption:
The
absolute bioavailability after subcutaneous administration of enfuvirtide 90 mg in the
abdomen was 84.3 ± 15.5%. Mean (± SD) C
max
was 4.59 ± 1.5 μg/ml, AUC was 55.8 ± 12.1 μg*hr/ml
The subcutaneous absorption of enfuvirtide is proportional to the administered dose over the 45 to
180 mg dose range. Subcutaneous absorption at the 90 mg dose is comparable when injected into
abdomen, thigh or arm. In four separate studies (N = 9 to 12) the mean steady state trough plasma
concentration ranged from 2.6 to 3.4 μg/ml.
Distribution:
The steady state volume of distribution with intravenous administration of a 90 mg dose
of enfuvirtide was 5.5 ± 1.1 l. Enfuvirtide is 92% bound to plasma proteins in HIV
infected plasma
over a plasma concentration range of 2 to 10 μg/ml. It is bound predominantly to albumin and to a
lower extent to α-1 acid glycoprotein. In
in vitro
studies, enfuvirtide was not displaced from its
binding sites by other medicinal products, nor did enfuvirtide displace other medicinal products from
their binding sites. In HIV patients, enfuvirtide levels in the cerebrospinal fluid have been reported to
be negligible.
Metabolism:
As a peptide, enfuvirtide is expected to undergo catabolism to its constituent amino acids,
with subsequent recycling of the amino acids in the body pool.
In vitro
human microsomal studies and
in
in vivo
studies indicate that enfuvirtide is not an inhibitor of CYP450 enzymes. In
in vitro
human
microsomal and hepatocyte studies, hydrolysis of the amide group of the C-terminus amino acid,
phenylalanine results in a deamidated metabolite and the formation of this metabolite is not NADPH
dependent. This metabolite is detected in human plasma following administration of enfuvirtide, with
an AUC ranging from 2.4 to 15% of the enfuvirtide AUC.
Elimination:
Clearance of enfuvirtide after intravenous administration 90 mg was 1.4 ± 0.28 l/h and
the elimination half-life was 3.2 ± 0.42 h. Following a 90 mg subcutaneous dose of enfuvirtide the

















half-life of enfuvirtide is 3.8 ± 0.6 h. Mass balance studies to determine elimination pathway(s) of
enfuvirtide have not been performed in humans.
Hepatic Insufficiency:
The pharmacokinetics of enfuvirtide have not been studied in patients with
hepatic impairment.
Renal Insufficiency:
Analysis of plasma concentration data from patients in clinical trials indicated
that the clearance of enfuvirtide is not affected to any clinically relevant extent in patients with mild to
moderate renal impairment. In a renal impairment study AUC of enfuvirtide was increased on average
by 43-62% in patients with severe or end stage renal disease compared to patients with normal renal
function. Hemodialysis did not significantly alter enfuvirtide clearance. Less than 13% of the dose was
removed during hemodialysis. No dose adjustment is required for patients with impaired renal
function.
Elderly:
The pharmacokinetics of enfuvirtide have not been formally studied in elderly patients over
65 years of age.
Gender and Weight:
Analysis of plasma concentration data from patients in clinical trials indicated
that the clearance of enfuvirtide is 20% lower in females than males irrespective of weight and is
increased with increased body weight irrespective of gender (20% higher in a 100 kg and 20% lower
in a 40 kg body weight patient relative to a 70 kg reference patient). However, these changes are not
clinically significant and no dose adjustment is required.
Race:
Analysis of plasma concentration data from patients in clinical trials indicated that the clearance
of enfuvirtide was not different in Afro-Americans compared to Caucasians. Other PK studies suggest
no difference between Asians and Caucasians after adjusting exposure for body weight.
Paediatric Patients:
The pharmacokinetics of enfuvirtide have been studied in 37 paediatric patients. A
dose of 2 mg/kg bid (maximum 90 mg bid) provided enfuvirtide plasma concentrations similar to
those obtained in adult patients receiving 90 mg bid dosage. In 25 paediatric patients ranging in age
from 5 to 16 years and receiving the 2 mg/kg bid dose into the upper arm, anterior thigh or abdomen,
the mean steady-state AUC was 54.3 ± 23.5 μg*h/ml, C
max
was 6.14 ± 2.48 μg/ml, and C
trough
was
2.93 ± 1.55 μg/ml.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety
pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity and late embryonal development. Long-term
animal carcinogenicity studies have not been performed.
Studies in guinea pigs indicated a potential for enfuvirtide to produce delayed contact hypersensitivity.
In a rat model on the resistance to influenza infection, an impairment of IFN-γ production was
observed. The resistance to influenza and streptococcal infection in rats was only weakly
compromised.
The clinical relevance of these findings is unknown.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Powder
Sodium carbonate
Mannitol
Sodium hydroxide
Hydrochloric Acid
Solvent
Water for Injections
This medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products except those mentioned in
section 6.6.
Shelf life after reconstitution
After reconstitution: Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 48 hours at 5°C when protected from
light.
From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. If not used
immediately, in-use storage times and conditions prior to use are the responsibility of the user and
would normally not be longer than 24 hours at 2°C to 8°C, unless reconstitution has taken place in
controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Powder
Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light. For storage conditions of the
reconstituted medicinal product, see section 6.3.
Solvent
This medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
lyophilisate stopper, rubber (latex free)
aluminum seal with flip-off cap
2 ml vial, colourless glass type 1
aluminum seal with flip-off cap
Pack 1
60 vials powder for solution for injection
60 vials solvent
60 3 ml syringes
60 1 ml syringes
180 alcohol swabs
3 ml vial, colourless glass type 1
rubber stopper (latex free)
Pack 2
60 vials powder for solution for injection
60 vials solvent
6.6 Special precautions for disposal
Any unused product should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Patients should be instructed on the use and administration of Fuzeon by a healthcare professional
before using for the first time.
Fuzeon must only be reconstituted with 1.1 ml of Water for Injections. Patients must be instructed to
add the water for injections and then gently tap the vial with their fingertip until the powder begins to
dissolve.
They must
never shake the vial or turn it upside down to mix—this will cause excessive
foaming
. After the powder begins to dissolve they can set the vial aside to allow it to completely
dissolve. The powder may take up to 45 minutes to dissolve into solution. The patient can gently roll
the vial between their hands after adding the water for injections until it is fully dissolved and this may
reduce the time it takes for the powder to dissolve. Before the solution is withdrawn for
administration, the patient should inspect the vial visually to ensure that the contents are fully in
solution, and that the solution is clear and without bubbles or particulate matter. If there is evidence of
particulate matter, the vial must not be used and should be discarded or returned to the pharmacy.
The solvent vials contain 2 ml Water for Injections, of which 1.1 ml must be withdrawn for the
reconstitution of the powder. Patients should be instructed to discard the remaining volume in the
solvent vials.
Fuzeon contains no preservative. Once reconstituted, the solution should be injected immediately. If
the reconstituted solution cannot be injected immediately, it must be kept refrigerated until use and
used within 24 hours. Refrigerated reconstituted solution should be brought to room temperature
before injection.
1 ml of the reconstituted solution should be injected subcutaneously in the upper arm, abdomen or
anterior thigh. The injection should be given at a site different from the preceding injection site and
where there is no current injection site reaction. A vial is suitable for single use only; unused portions
must be discarded.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Roche Registration Limited
6 Falcon Way
Shire Park
Welwyn Garden City
AL7 1TW
United Kingdom
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation:
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the web site of the European Medicines
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Fuzeon 90 mg/ml powder for solution for injection
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each vial contains 108 mg enfuvirtide.
Each ml of reconstituted solution contains 90 mg enfuvirtide.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Powder for solution for injection.
White to off-white lyophilised powder.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Fuzeon is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of
HIV-1 infected patients who have received treatment with and failed on regimens containing at least
one medicinal product from each of the following antiretroviral classes
:
protease inhibitors, non-
nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors and nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, or who have
intolerance to previous antiretroviral regimens. (see section 5.1).
In deciding on a new regimen for patients who have failed an antiretroviral regimen, careful
consideration should be given treatment history of the individual patient and the patterns of mutations
associated with different drugs. Where available, resistance testing may be appropriate.
(See sections
4.4 and 5.1).
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Fuzeon should be prescribed by physicians who are experienced in the treatment of HIV infection.
Fuzeon is only to be administered by subcutaneous injection.
Adults and adolescents ≥ 16 years:
The recommended dose of Fuzeon is 90 mg twice daily injected
subcutaneously into the upper arm, anterior thigh or abdomen.
Elderly
: There is no experience in patients > 65 years old.
Children ≥ 6 years and adolescents:
The experience in children is limited (See section 5.2). In clinical
trials the dosage regimen in Table 1 below was used:
Table 1: Paediatric Dosing
Weight (kg)
Dose per bid injection
(mg/dose)
Injection volume
(90 mg enfuvirtide
per ml)
Fuzeon is not recommended for use in children below age 6 due to insufficient data on safety and
efficacy (see section 5.2).
Renal impairment:
No dose adjustment is required for patients with renal impairment including those
receiving dialysis. (See sections 4.4 and 5.2).
Hepatic impairment:
No data are available to establish a dose recommendation for patients with
hepatic impairment (See sections 4.4 and 5.2).
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Fuzeon must be taken as part of a combination regimen. Please also refer to the respective summary of
product characteristics of the other antiretroviral medicinal products used in the combination. As with
other antiretrovirals, enfuvirtide should optimally be combined with other antiretrovirals to which the
patient’s virus is sensitive. (See section 5.1)
Patients must be advised that antiretroviral therapies including enfuvirtide have not been proved to
prevent the risk of transmission to HIV to others through sexual contact or blood contamination. They
must continue to use appropriate precautions. Patients should also be informed that Fuzeon is not a
cure for HIV-1 infection.
Animal studies have shown that enfuvirtide may impair some immune functions (see section 5.3). In
clinical trials, an increased rate of some bacterial infections, most notably a higher rate of pneumonia,
was seen in patients treated with Fuzeon; however, an increased risk of bacterial pneumonia related to
the use of Fuzeon has not been confirmed by subsequent epidemiological data.
Hypersensitivity reactions have occasionally been associated with therapy with enfuvirtide and in rare
cases hypersensitivity reactions have recurred on re-challenge. Events included rash, fever, nausea and
vomiting, chills, rigors, low blood pressure and elevated serum liver transaminases in various
combinations, and possibly primary immune complex reaction, respiratory distress and
glomerulonephritis. Patients developing signs/symptoms of a systemic hypersensitivity reaction should
discontinue enfuvirtide treatment and should seek medical evaluation immediately. Therapy with
enfuvirtide should not be restarted following systemic signs and symptoms consistent with a
hypersensitivity reaction considered related to enfuvirtide. Risk factors that may predict the
occurrence or severity of hypersensitivity to enfuvirtide have not been identified.
Liver disease:
The safety and efficacy of enfuvirtide has not been specifically studied in patients with
significant underlying liver disorders. Patients with chronic hepatitis B and C and treated with













antiretroviral therapy are at an increased risk for severe and potentially fatal hepatic adverse events.
Few patients included in the phase III trials were co-infected with hepatitis B/C. In these the addition
of Fuzeon did not increase the incidence of hepatic events. In case of concomitant antiviral therapy for
hepatitis B or C, please refer also to the relevant product information for these medicinal products.
Administration of Fuzeon to non-HIV-1 infected individuals may induce anti-enfuvirtide antibodies
that cross-react with HIV gp-41. This may result in a false positive HIV test with the anti-HIV ELISA
test.
There is no experience in patients with reduced hepatic function. Data is limited in patients with
moderate to severe renal impairment, and in patients maintained on dialysis. Fuzeon should be used
with caution in these populations. (See sections 4.2 and 5.2).
Immune Reactivation Syndrome:
In HIV-infected patients with severe immune deficiency at the time
of institution of combination antiretroviral therapy (CART), an inflammatory reaction to
asymptomatic or residual opportunistic pathogens may arise and cause serious clinical conditions, or
aggravation of symptoms. Typically, such reactions have been observed within the first few weeks or
months of initiation of CART. Relevant examples are cytomegalovirus retinitis, generalised and/or
focal mycobacterial infections, and Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Any inflammatory symptoms
should be evaluated and treatment instituted when necessary.
Osteonecrosis:
Although the etiology is considered to be multifactorial (including corticosteroid use, alcohol
consumption, severe immunosuppression, higher body mass index), cases of osteonecrosis have been
reported particularly in patients with advanced HIV-disease and/or long-term exposure to CART.
Patients should be advised to seek medical advice if they experience joint aches and pain, joint
stiffness or difficulty in movement.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Interaction studies have only been performed in adults.
No clinically significant pharmacokinetic interactions are expected between enfuvirtide and
concomitantly given medicinal products metabolised by CYP450 enzymes.
Influence of enfuvirtide on metabolism of concomitant medicinal products:
In an in-vivo human
metabolism study enfuviritide, at the recommended dose of 90 mg twice daily, did not inhibit the
metabolism of substrates by CYP3A4 (dapsone), CYP2D6 (debrisoquine), CYP1A2 (caffeine),
CYP2C19 (mephenytoin), and CYP2E1 (chlorzoxazone).
Influence of concomitant medicinal products on enfuvirtide metabolism:
In separate pharmacokinetic
interaction studies, co-administration of ritonavir (potent CYP3A4 inhibitor) or saquinavir in
combination with a booster dose of ritonavir or rifampicin (potent CYP34A inducer) did not result in
clinically significant changes of the pharmacokinetics of enfuvirtide.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Animal studies do not indicate
harmful effects with respect to foetal development. Enfuvirtide should be used during pregnancy only
if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the foetus.
It is not known whether enfuvirtide is secreted in human milk. Mothers should be instructed not to
breast-feed if they are receiving enfuvirtide because of the potential for HIV transmission and any
possible undesirable effects in breast-fed infants.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed. There is no
evidence that enfuviritide may alter the patient’s ability to drive and use machines, however, the
adverse event profile of enfuvirtide should be taken into account. (See section 4.8)
Safety data mainly refer to 48-week data from studies TORO 1 and TORO 2 combined (see section
5.1). Safety results are expressed as the number of patients with an adverse reaction per
100 patient-years of exposure (except for injection site reactions).
Injection site reactions (ISRs) were the most frequently reported adverse reaction and occurred in 98%
of the patients (Table 2). The vast majority of ISRs occurred within the first week of Fuzeon
administration and were associated with mild to moderate pain or discomfort at the injection site
without limitation of usual activities. The severity of the pain and discomfort did not increase with
treatment duration. The signs and symptoms generally lasted equal to or less than 7 days. Infections at
the injection site (including abscess and cellulitis) occurred in 1.5% of patients.
Table 2: Summary of individual signs/symptoms characterising local injection site reactions
in studies TORO 1 and TORO 2 combined (% of patients)
Withdrawal Rate due to ISRs
Fuzeon
+Optimised
Background
a
% of Event
comprising
Grade 3 reactions
% of Event
comprising
Grade 4 reactions
a
Any severity grade.
b
Grade 3= severe pain requiring analgesics (or narcotic analgesics for ≤ 72 hours) and/or limiting usual activities; Grade 4= severe pain
requiring hospitalisation or prolongation of hospitalisation, resulting in death, or persistent or significant disability/incapacity, or life-
threatening, or medically significant.
c
Grade 3= ≥ 50 mm but < 85 mm average diameter; Grade 4= ≥ 85 mm average diameter .
d
Grade 3= ≥ 25 mm but < 50 mm average diameter; Grade 4= ≥ 50 mm average diameter.
e
Grade 3= ≥ 3 cm; Grade 4= If draining.
f
Grade 3= refractory to topical treatment or requiring oral or parenteral treatment; Grade 4= not defined.
g
Grade 3= > 3 cm but ≤ 5 cm; Grade 4= > 5 cm.
The addition of Fuzeon to background antiretroviral therapy generally did not increase the frequency
or severity of most adverse reactions. The most frequently reported events occurring in the TORO 1
and TORO 2 studies were diarrhoea (38 versus 73 patients with event per 100 patient years for
Fuzeon + OB versus OB) and nausea (27 versus 50 patients with event per 100 patient years for
Fuzeon + OB versus OB).
The following list presents events seen at a higher rate among patients receiving Fuzeon+OB regimen
than among patients on the OB alone regimen with an exposure adjusted increase of at least 2 patients
with event per 100 patient-years. These events are then designated frequency estimation
(“very common” (≥1/10), or “common” (≥1/100, <1/10)). A statistically significant increase was seen
for pneumonia and lymphadenopathy. Most adverse reactions were of mild or moderate intensity.
Infections and Infestations
Common:
- sinusitis, skin papilloma, influenza, pneumonia, ear infection.














Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders
Common:
-
lymphadenopathy.
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders
Common:
-
appetite decreased, anorexia, hypertriglyceridaemia, diabetes mellitus.
Psychiatric Disorders
Common:
- anxiety, nightmare, irritability.
Nervous System Disorders
Very Common:
- peripheral neuropathy.
Common:
-
hypoaesthesia, disturbance in attention, tremor.
Eye Disorders
Common:
- conjunctivitis.
Ear and Labyrinth disorders
Common:
- vertigo.
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders
Common:
- nasal congestion.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Common:
- pancreatitis, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Common:
- dry skin, eczema seborrhoeic, erythema, acne.
Musculoskeletal, Connective Tissue and Bone Disorders
Common:
- myalgia.
Renal and Urinary Disorders
Common:
- Calculus renal.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions
Common:
-
influenza like illness, weakness.
Investigations
Very Common:
- weight decreased
Common:
- blood triglycerides increased, haematuria present.
In addition there have been a small number of hypersensitivity reactions attributed to enfuvirtide and
in some cases recurrence has occurred upon re-challenge. (See section 4.4)
In HIV-infected patients with severe immune deficiency at the time of initiation of combination
antiretroviral therapy (CART), an inflammatory reaction to asymptomatic or residual opportunistic
infections may arise (see section 4.4).
Cases of osteonecrosis have been reported, particularly in patients with generally acknowledged risk
factors, advanced HIV disease or long-term exposure to CART. The frequency of this is unknown (see
section 4.4).
The majority of patients had no change in the toxicity grade of any laboratory parameter during the
study except for those listed in Table 3. Through week 48, eosinophilia [greater than the Upper Limit
of Normal of > 0.7 x 10
9
/l] occurred at a higher rate amongst patients in the Fuzeon containing group
(12.4 patients with event per 100 patient-years) compared with OB alone regimen (5.6 patients with
event per 100 patient-years). When using a higher threshold for eosinophilia (>1.4 x 10
9
/l), the patient
exposure adjusted rate of eosinophilia is equal in both groups (1.8 patients with event per 100 patient-
years).
Table 3: Exposure adjusted Grade 3 & 4 laboratory abnormalities among patients on
Fuzeon+OB and OB alone regimens, reported at more than 2 patients with event per
100 patient years
Laboratory Parameters
Grading
Fuzeon+OB regimen
Per 100 patient years
OB alone regimen
Per 100 patient years
n
(Total Exposure patient years)
Haemoglobin
Gr. 3 (6.5-7.9 g/dL)
Creatinine phosphokinase
Gr. 3 (>5-10 x ULN)
No case of overdose has been reported. The highest dose administered to 12 patients in a clinical trial
was 180 mg as a single dose subcutaneously. These patients did not experience any adverse reactions
that were not seen with the recommended dose. In an Early Access Program study, one patient
administered 180 mg of Fuzeon as a single dose on one occasion. He did not experience an adverse
reaction as a result.
There is no specific antidote for overdose with enfuvirtide. Treatment of overdose should consist of
general supportive measures.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Other antivirals, ATC code: J05AX07
Mechanism of Action:
Enfuvirtide is a member of the therapeutic class called fusion inhibitors. It is an
inhibitor of the structural rearrangement of HIV-1 gp41 and functions by specifically binding to this
virus protein extracellularly thereby blocking fusion between the viral cell membrane and the target
cell membrane, preventing the viral RNA from entering into the target cell.
Antiviral activity
in vitro
: The susceptibility to enfuvirtide of 612 HIV recombinants containing the
env genes from HIV RNA samples taken at baseline from patients in Phase III studies gave a
geometric mean EC
50
of 0.259 μg/ml (geometric mean + 2SD = 1.96 μg/ml) in a recombinant
phenotype HIV entry assay. Enfuvirtide also inhibited HIV-1 envelope mediated cell-cell fusion.
Combination studies of enfuvirtide with representative members of the various antiretroviral classes
exhibited additive to synergistic antiviral activities and an absence of antagonism. The relationship
between the
in vitro
susceptibility of HIV-1 to enfuvirtide and inhibition of HIV-1 replication in
humans has not been established.
Antiretroviral drug resistance:
Incomplete viral suppression may lead to the development of drug
resistance to one or more components of the regimen.














In Vitro
resistance to enfuvirtide
: HIV-1 isolates with reduced susceptibility to enfuvirtide have been
selected
in vitro
which harbour substitutions in amino acids (aa) 36-38 of the gp41 ectodomain. These
substitutions were correlated with varying levels of reduced enfuvirtide susceptibility in HIV site-
directed mutants.
In Vivo
resistance to enfuvirtide
: In phase III clinical studies HIV recombinants containing the env
genes from HIV RNA samples taken up to week 24 from 187 patients showed >4 fold reduced
susceptibility to enfuvirtide compared with the corresponding pre-treatment samples. Of these,
185 (98.9%) env genes carried specific substitutions in region of aa 36 - 45 of gp41. The substitutions
observed in decreasing frequency were at aa positions 38, 43, 36, 40, 42 and 45. Specific single
substitutions at these residues in gp41 each resulted in a range of decreases from baseline in
recombinant viral susceptibility to enfuvirtide. The geometric mean changes ranged from 15.2 fold for
V38M to 41.6 fold for V38A. There were insufficient examples of multiple substitutions to determine
any consistent patterns of substitutions or their effect on viral susceptibility to enfuvirtide. The
relationship of these substitutions to
in vivo
effectiveness of enfuvirtide has not been established.
Decrease in viral sensitivity was correlated to the degree of pre-treatment resistance to background
therapy. (See table 5)
Cross-resistance
: Due to its novel viral target enfuvirtide is equally active
in vitro
against both
wild-type laboratory and clinical isolates and those with resistance to 1, 2 or 3 other classes of
antiretrovirals (nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase
inhibitors and protease inhibitors). Conversely, mutations in aa 36-45 of gp41 which give resistance to
enfuvirtide would not be expected to give cross resistance to other classes of antiretrovirals.
Clinical Pharmacodynamic data
Studies in Antiretroviral Experienced Patients:
The clinical activity of Fuzeon (in combination with
other antiretroviral agents) on plasma HIV RNA levels and CD4 counts have been investigated in two
randomised, multicenter, controlled studies (TORO 1 and TORO 2) of Fuzeon of 48 weeks duration.
995 patients comprised the intent-to-treat population. Patient demographics include a median baseline
HIV-1 RNA of 5.2 log
10
copies/ml and 5.1 log
10
copies/ml and median baseline CD4 cell count of
88 cells/mm
3
and 97 cells/mm
3
for Fuzeon + OB and OB, respectively. Patients had prior exposure to
a median of 12 antiretrovirals for a median of 7 years. All patients received an optimised background
(OB) regimen consisting of 3 to 5 antiretroviral agents selected on the basis of the patient's prior
treatment history, as well as baseline genotypic and phenotypic viral resistance measurements.
The proportion of patients achieving viral load of <400 copies/ml at week 48 was 30.4% among
patients on the Fuzeon+OB regimen compared to 12% among patients receiving OB regimen only.
The mean CD4 cell count increase was greater in patients on the Fuzeon + OB regimen than in
patients on OB regimen only. (see Table 4)
Outcomes of randomised treatment at week 48 (pooled studies TORO 1 and TORO
2, ITT)
Outcomes
Fuzeon +OB
90 mg bid
(N=661)
HIV-1 RNA
Log Change from baseline
(log
10
copies/ml)
*
CD4+ cell count
Change from baseline
(cells/mm
3
)
#
HIV RNA
>
1 log below
Baseline
**
247 (37.4%) 57 (17.1%) Odds Ratio
3.02
HIV RNA <400 copies/ml
**
201 (30.4%) 40 (12.0%) Odds Ratio
3.45
26 (7.8%) Odds Ratio
2.77
Discontinued due to adverse
reactions/intercurrent
illness/labs
†
Discontinued due to injection
site reactions
†
Discontinued due to other
reasons
†φ§
Based on results from pooled data of TORO 1 and TORO 2 on ITT population, week 48 viral load for subjects who were lost to
follow-up, discontinued therapy, or had virological failure replaced by their last observation (LOCF).
Last value carried forward.
M-H test: Discontinuations or virological failure considered as failures.
Percentages based on safety population Fuzeon+background (N=663) and background (N=334). Denominator for non-switch
patients: N=112.
As per the judgment of the investigator.
Includes discontinuations from loss to follow-up, treatment refusal, and other reasons.
Fuzeon+OB therapy was associated with a higher proportion of patients reaching <400 copies/ml
(or <50 copies/ml) across all subgroups based on baseline CD4, baseline HIV-1 RNA, number of prior
antiretrovirals (ARVs) or number of active ARVs in the OB regimen. However, subjects with baseline
CD4 >100 cells/mm
3
, baseline HIV-1 RNA <5.0 log
10
copies/ml, ≤ 10 prior ARVs, and/or other active
ARVs in their OB regimen were more likely to achieve a HIV-1 RNA of <400 copies/ml
(or <50 copies/ml) on either treatment. (see Table 5)






















Proportion of patients
achieving <400 copies/ml and <50 copies/ml at Week 48 by
subgroup (pooled TORO 1 and TORO 2, ITT)
HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/ml
Fuzeon + OB
90 mg bid
(N=661)
Fuzeon + OB
90 mg bid
(N=661)
BL HIV-1 RNA < 5.0
log
10
1
copies/ml
BL HIV-1 RNA ≥ 5.0
log
10
1
copies/ml
0 Active ARVs in
background
1,2
1 Active ARV in
background
1,2
≥ 2 Active ARVs in
background
1,2
1
Discontinuations or virological failures considered as failures.
2
Based on GSS score.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
The pharmacokinetic properties of enfuvirtide have been evaluated in HIV-1-infected adult and
paediatric patients.
Absorption:
The
absolute bioavailability after subcutaneous administration of enfuvirtide 90 mg in the
abdomen was 84.3 ± 15.5%. Mean (± SD) C
max
was 4.59 ± 1.5 μg/ml, AUC was 55.8 ± 12.1 μg*hr/ml.
The subcutaneous absorption of enfuvirtide is proportional to the administered dose over the 45 to
180 mg dose range. Subcutaneous absorption at the 90 mg dose is comparable when injected into
abdomen, thigh or arm. In four separate studies (N= 9 to 12) the mean steady state trough plasma
concentration ranged from 2.6 to 3.4 μg/ml.
Distribution:
The steady state volume of distribution with intravenous administration of a 90 mg dose
of enfuvirtide was 5.5 ± 1.1 l. Enfuvirtide is 92% bound to plasma proteins in HIV
infected plasma
over a plasma concentration range of 2 to 10 μg/ml. It is bound predominantly to albumin and to a
lower extent to α-1 acid glycoprotein. In
in vitro
studies, enfuvirtide was not displaced from its
binding sites by other medicinal products, nor did enfuvirtide displace other medicinal products from
their binding sites. In HIV patients, enfuvirtide levels in the cerebrospinal fluid have been reported to
be negligible.
Metabolism:
As a peptide, enfuvirtide is expected to undergo catabolism to its constituent amino acids,
with subsequent recycling of the amino acids in the body pool.
In vitro
human microsomal studies and
in
in vivo
studies indicate that enfuvirtide is not an inhibitor of CYP450 enzymes. In
in vitro
human
microsomal and hepatocyte studies, hydrolysis of the amide group of the C-terminus amino acid,
phenylalanine results in a deamidated metabolite and the formation of this metabolite is not NADPH
dependent. This metabolite is detected in human plasma following administration of enfuvirtide, with
an AUC ranging from 2.4 to 15% of the enfuvirtide AUC.
Elimination:
Clearance of enfuvirtide after intravenous administration 90 mg was 1.4 ± 0.28 l/h and
the elimination half-life was 3.2 ± 0.42 h. Following a 90 mg subcutaneous dose of enfuvirtide the

















half-life of enfuvirtide is 3.8 ± 0.6 h. Mass balance studies to determine elimination pathway(s) of
enfuvirtide have not been performed in humans.
Hepatic Insufficiency:
The pharmacokinetics of enfuvirtide have not been studied in patients with
hepatic impairment.
Renal Insufficiency:
Analysis of plasma concentration data from patients in clinical trials indicated
that the clearance of enfuvirtide is not affected to any clinically relevant extent in patients with mild to
moderate renal impairment. In a renal impairment study AUC of enfuvirtide was increased on average
by 43-62% in patients with severe or end stage renal disease compared to patients with normal renal
function. Hemodialysis did not significantly alter enfuvirtide clearance. Less than 13% of the dose was
removed during hemodialysis. No dose adjustment is required for patients with impaired renal
function.
Elderly:
The pharmacokinetics of enfuvirtide have not been formally studied in elderly patients over
65 years of age.
Gender and Weight:
Analysis of plasma concentration data from patients in clinical trials indicated
that the clearance of enfuvirtide is 20% lower in females than males irrespective of weight and is
increased with increased body weight irrespective of gender (20% higher in a 100 kg and 20% lower
in a 40 kg body weight patient relative to a 70 kg reference patient). However, these changes are not
clinically significant and no dose adjustment is required.
Race:
Analysis of plasma concentration data from patients in clinical trials indicated that the clearance
of enfuvirtide was not different in Afro-Americans compared to Caucasians. Other PK studies suggest
no difference between Asians and Caucasians after adjusting exposure for body weight.
Paediatric Patients
:
The pharmacokinetics of enfuvirtide have been studied in 37 paediatric patients. A
dose of 2 mg/kg bid (maximum 90 mg bid) provided enfuvirtide plasma concentrations similar to
those obtained in adult patients receiving 90 mg bid dosage. In 25 paediatric patients ranging in age
from 5 to 16 years and receiving the 2 mg/kg bid dose into the upper arm, anterior thigh or abdomen,
the mean steady-state AUC was 54.3 ± 23.5 μg*h/ml, C
max
was 6.14 ± 2.48 μg/ml, and C
trough
was
2.93 ± 1.55 μg/ml.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety
pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity and late embryonal development. Long-term
animal carcinogenicity studies have not been performed.
Studies in guinea pigs indicated a potential for enfuvirtide to produce delayed contact hypersensitivity.
In a rat model on the resistance to influenza infection, an impairment of IFN-γ production was
observed. The resistance to influenza and streptococcal infection in rats was only weakly
compromised. The clinical relevance of these findings is unknown.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Powder
Sodium carbonate
Mannitol
Sodium hydroxide
Hydrochloric Acid
This medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products except those mentioned in
section 6.6.
Shelf life after reconstitution:
After reconstitution: Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 48 hours at 5°C when protected from
light.
From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. If not used
immediately, in-use storage times and conditions prior to use are the responsibility of the user and
would normally not be longer than 24 hours at 2 to 8°C, unless reconstitution has taken place in
controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light. For storage conditions of the
reconstituted medicinal product, see section 6.3.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
3 ml vial, colourless glass type 1
lyophilisate stopper, rubber (latex free)
Pack sizes
Each pack contains 60 vials of Fuzeon.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal
Any unused product should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Patients should be instructed on the use and administration of Fuzeon by a healthcare professional
before using for the first time.
Fuzeon must only be reconstituted with 1.1 ml water for injections. Patients must be instructed to add
the water for injections and then gently tap the vial with their fingertip until the powder begins to
dissolve. They must
never shake the vial or turn it upside down to mix—this will cause excessive
foaming
. After the powder begins to dissolve they can set the vial aside to allow it to completely
dissolve. The powder may take up to 45 minutes to dissolve into solution. The patient can gently roll
the vial between their hands after adding the water for injections until it is fully dissolved and this may
reduce the time it takes for the powder to dissolve. Before the solution is withdrawn for
administration, the patient should inspect the vial visually to ensure that the contents are fully in
solution, and that the solution is clear and without bubbles or particulate matter. If there is evidence of
particulate matter, the vial must not be used and should be discarded or returned to the pharmacy.
Fuzeon contains no preservative. Once reconstituted, the solution should be injected immediately. If
the reconstituted solution cannot be injected immediately, it must be kept refrigerated until use and
used within 24 hours. Refrigerated reconstituted solution should be brought to room temperature
before injection.
1 ml of the reconstituted solution should be injected subcutaneously in the upper arm, abdomen or
anterior thigh. The injection should be given at a site different from the preceding injection site and
aluminum seal with flip-off cap
where there is no current injection site reaction. A vial is suitable for single use only; unused portions
must be discarded.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Roche Registration Limited
6 Falcon Way
Shire Park
Welwyn Garden City
AL7 1TW
United Kingdom
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation:
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the web site of the European Medicines
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
A. MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
Roche Pharma AG, Emil-Barrell-Str. 1, D-79639 Grenzach-Wyhlen, Germany
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to restricted medical prescription (See Annex I: Summary of Product
Characteristics, section 4.2.)
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
The Marketing Authorisation Holder will submit the PSURs on a yearly basis
ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Fuzeon 90 mg/ml powder and solvent for solution for injection
Enfuvirtide
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains 108 mg enfuvirtide.
1 ml of reconstituted solutions contains 90 mg enfuvirtide.
Each vial with powder also contains sodium carbonate (anhydrous), mannitol, sodium hydroxide and
hydrochloric acid.
Each solvent vial contains 2 ml Water for Injections.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder and solvent for solution for injection
Contents of the box:
60 vials with powder for solution for injection
60 vials with solvent
60 3 ml syringes
60 1 ml syringes
180 alcohol swabs
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous use
Read the package leaflet before use
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY



























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light
After reconstitution store in a refrigerator
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
The remaining Water for Injections in the solvent vial after withdrawal of the 1.1 ml required for
reconstitution has to be discarded
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Roche Registration Limited
6 Falcon Way
Shire Park
Welwyn Garden City
AL7 1TW
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
Justification for not including Braille accepted




















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE IMMEDIATE PACKAGING
IMMEDIATE OUTER CARTON FOR FUZEON VIALS
WITHIN
PACK 1
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Fuzeon 90 mg/ml powder for solution for injection
Enfuvirtide
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains 108 mg enfuvirtide.
1 ml of reconstituted solution contains 90 mg of enfuvirtide.
Each vial also contains sodium carbonate (anhydrous), mannitol, sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric
acid.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder for solution for injection
60 vials with powder for solution for injection
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous use
Read the package leaflet before use
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light
After reconstitution store in a refrigerator





























10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Roche Registration Limited
6 Falcon Way
Shire Park
Welwyn Garden City
AL7 1TW
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
Justification for not including Braille accepted


















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE IMMEDIATE PACKAGING
IMMEDIATE OUTER CARTON FOR WATER FOR INJECTIONS VIALS WITHIN PACK 1
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Solvent for solution
Water for Injections
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Solvent for parenteral use
Contained in this box are 60 vials of 2 ml water for injections
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
This water for injections is intended for the reconstitution of Fuzeon 90 mg/ml powder for solution for
injection to obtain a solution for subcutaneous use
Read the package leaflet before use
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
The remaining Water for Injections in the solvent vial after withdrawal of the 1.1 ml required for
reconstitution has to be discarded



























11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Roche Registration Limited
6 Falcon Way
Shire Park
Welwyn Garden City
AL7 1TW
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
Justification for not including Braille accepted
















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Fuzeon 90 mg/ml powder and solvent for solution for injection
Enfuvirtide
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains 108 mg enfuvirtide.
1 ml of reconstituted solution contains 90 mg of enfuvirtide.
Each vial with powder contains sodium carbonate (anhydrous), mannitol, sodium hydroxide and
hydrochloric acid.
Each solvent vial contains 2 ml water for injections.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder and solvent for solution for injection
Contents of this box:
60 vials with powder for solution for injection
60 vials with solvent
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous use
Read the package leaflet before use
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY



























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light
After reconstitution store in a refrigerator
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
The remaining Water for Injections in the solvent vial after withdrawal of the 1.1 ml required for
reconstitution has to be discarded
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Roche Registration Limited
6 Falcon Way
Shire Park
Welwyn Garden City
AL7 1TW
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
Justification for not including Braille accepted




















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE IMMEDIATE PACKAGING
IMMEDIATE OUTER CARTON FOR FUZEON VIALS
WITHIN
PACK 2
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Fuzeon 90 mg/ml powder for solution for injection
Enfuvirtide
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each Fuzeon vial contains 108 mg enfuvirtide.
1 ml of reconstituted solution contains 90 mg enfuvirtide.
Each vial also contains sodium carbonate (anhydrous), mannitol, sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric
acid.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder for solution for injection
60 vials with powder for solution for injection
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous use
Read the package leaflet before use
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light
After reconstitution store in a refrigerator





























10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Roche Registration Limited
6 Falcon Way
Shire Park
Welwyn Garden City
AL7 1TW
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
Justification for not including Braille accepted


















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE IMMEDIATE PACKAGING
IMMEDIATE OUTER CARTON FOR WATER FOR INJECTIONS VIALS
WITHIN PACK 2
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Solvent for parenteral use
Contained in this box are 60 vials of 2 ml water for injections
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
This water for injections is intended for reconstitution of Fuzeon 90 mg/ml powder for solution for
injection to obtain a solution for subcutaneous use
Read the package leaflet before use
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
The remaining Water for Injections in the solvent vial after withdrawal of the 1.1 ml required for
reconstitution has to be discarded

























11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Roche Registration Limited
6 Falcon Way
Shire Park
Welwyn Garden City
AL7 1TW
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
Justification for not including Braille accepted
















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
OUTER CARTON FOR PACKAGE TO CONTAIN FUZEON VIALS ONLY
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Fuzeon 90 mg/ml powder for solution for injection
Enfuvirtide
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains 108 mg enfuvirtide.
1 ml of reconstituted solution contains 90 mg enfuvirtide.
Each vial also contains sodium carbonate (anhydrous), mannitol, sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric
acid.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder for solution for injection
60 vials with powder for solution for injection
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous use
Read the package leaflet before use
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light
After reconstitution store in a refrigerator





























10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Roche Registration Limited
6 Falcon Way
Shire Park
Welwyn Garden City
AL7 1TW
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
Justification for not including Braille accepted


















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Fuzeon 90 mg/ml powder and solvent for solution for injection
Enfuvirtide
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
-
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you personally. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm
them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
What Fuzeon is and what it is used for
WHAT FUZEON IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
What Fuzeon is
Fuzeon inhibits the entry of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) into the cells that HIV attacks
(called CD4 or T-cells) in your blood. It works by preventing the HIV from making contact with the
affected cell membrane. This means that the HIV cannot enter the cell and then it cannot multiply.
This is because HIV needs the DNA in the host cell so it can multiply.
When Fuzeon should be used
Fuzeon is used in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products by persons who are
infected with HIV, the virus which causes AIDS. Your doctor has prescribed Fuzeon to help control
your HIV infection. Fuzeon is not a cure for HIV infection. Never use or share used needles.
if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to enfuvirtide or any of the other ingredients of Fuzeon. (see
section 6).
Take special care with Fuzeon:
if you have any other medical conditions,
if you have had any lung disease in the past; are currently, or have been, an intravenous drug
user; are a smoker,
if you have a history of any kidney problems.
Fuzeon does not reduce the risk of passing HIV to others through sexual contact or blood
contamination. It is important to continue to take appropriate precautions to prevent passing HIV to
others. Fuzeon is not a cure for HIV infection.
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
In some patients with advanced HIV infection (AIDS) and a history of opportunistic infections, signs
and symptoms of inflammation from previous infections may occur soon after anti-HIV treatment is
started. It is believed that these symptoms are due to a recovery of the body’s immune system. This
improvement enables the body to fight infections that may have been present with no obvious
symptoms. Patients with chronic hepatitis B and C and treated with antiretroviral therapy are at an
increased risk for serious liver problems. If you notice any symptoms of infection, please inform your
doctor immediately.
Bone problems
Some patients taking combination antiretroviral therapy may develop a bone disease called
osteonecrosis (death of bone tissue caused by loss of blood supply to the bone). The length of
combination antiretroviral therapy, corticosteroid use, alcohol consumption, severe
immunosuppression, higher body mass index, among others, may be some of the many risk factors for
developing this disease. Signs of osteonecrosis are joint stiffness, aches and pains (especially of the
hip, knee and shoulder) and difficulty in movement. If you notice any of these symptoms please
inform your doctor.
Taking other medicines
Please inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines,
even those not prescribed. Fuzeon has been shown not to interact with your other anti-HIV medicines
or rifampicin (an antibiotic).
Using Fuzeon with food and drink
You can take Fuzeon with or without food but you still need to follow the instructions given in the
package leaflets for your other medicines.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Pregnant women and breast-feeding mothers should not take Fuzeon unless specifically directed to by
their doctor. Be sure to tell your doctor immediately if you are or may be pregnant or if you are breast-
feeding a baby. HIV-infected women should not breast-feed their infants because of the risk that your
baby can be infected with HIV through your breast milk. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice
before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
Fuzeon has not been specifically tested for its possible effects on your ability to drive a car or operate
machines. However, if you feel dizzy while taking Fuzeon then please do not drive nor operate
machines.
Always use Fuzeon exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor or
pharmacist if you are not sure.
The usual dose is 90 mg twice a day
, given as a 1 ml subcutaneous (just below the skin) injection.
See further instructions on how to use Fuzeon at the end of this leaflet. There you will find instructions
on how to prepare Fuzeon and how to give yourself an injection.
If you take more Fuzeon than you should
There is no specific antidote for overdose with Fuzeon. If you take more than the recommended dose
please consult your doctor.
If you forget to take Fuzeon
Take the dose as soon as you remember and then take your next dose at its regular time. Do not take
the forgotten dose if it is less than 6 hours before you are going to take your next regular dose and
never take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
Like all medicines, Fuzeon can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The side effect that you may experience most commonly when taking Fuzeon, are reactions at the
place on your body where you have given yourself the injection. You will probably experience one or
more of the following mild to moderate reactions at the place where you inject your medicine:
● itchiness
● swelling
● redness
● pain or tenderness
● hardened skin or bumps.
These reactions can appear within the first week of treatment and generally do not get worse with
continued use of Fuzeon. Reactions at an individual injection site usually last for equal to or less than
7 days. If you experience reactions at an injection site, it is important not to stop taking Fuzeon until
you have talked with your doctor about any concerns you may have.
Injection site reactions may be worse when injections are repeated in the same place on the body, or
when the injection is given deeper than intended (for example, into a muscle). In rare instances,
patients experienced an infection at an individual injection site. To reduce the risk of infection, it is
important that you follow the Fuzeon Injection Instructions provided below.
Apart from reactions at the injection site, the side effects most frequently reported in patients receiving
antiretroviral treatment with or without Fuzeon are diarrhoea and feeling sick.
Very common side effects
(affects more than 1 in 10 persons)
are pain and numbness in hands, feet or
legs, and loss of weight.
Common side effects
(affects 1 to 10 users in 100)
are
● inflammation of the sinuses (cavities in the forehead),
● local swelling on the skin,
● reactions at injection sites,
● pneumonia,
● ear infection,
● swollen glands,
● decreased appetite,
● anorexia,
● increased blood fat values,
● diabetes,
● feeling anxious or irritated,
● nightmares,
● feeling dizzy,
● lack of concentration,
● tremor (shaking),
● inflamed eye lids,
● nasal congestion,
● inflammation of the pancreas,
● heart burn,
● dry skin,
● eczema,
● redness of the skin,
● acne,
● muscle pain,
● kidney stones,
● 'flu-like' symptoms,
● feeling weak
● blood in the urine.
Hypersensitivity (allergy) to Fuzeon is rare
(affects 1 to 10 users in 10,000)
. However if you develop
symptoms that may suggest that you are allergic to this medicine then you must stop taking it straight
away and tell your doctor as soon as possible. Symptoms that you should look out for are rash, a high
temperature or chill, feeling sick or being sick and sweating and shaking. These symptoms do not
definitely mean you are allergic to this medicine but you must discuss them with your doctor.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Fuzeon after the expiry date which is stated on the label of either the Fuzeon or the Water
for Injections Vials after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
Once the solution has been prepared for your injection it should be used immediately. If it is not used
immediately it must be stored in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C) and used within 24 hours.
Do not use Fuzeon if you notice any particles in the powder or the solution once the water for injection
has been added. Also do not use the water for injections if you see any particles in the vial or if the
water is cloudy.
The active substance is enfuvirtide. Each vial contains 108 mg enfuvirtide. After reconstitution
with the solvent provided 1 ml of reconstituted solution contains 90 mg enfuvirtide.
The other ingredients are:
Powder
Sodium Carbonate, anhydrous
Mannitol
Sodium Hydroxide
Hydrochloric Acid
Solvent
Water for Injections
This medicinal product contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per dose, i.e. essentially ‘sodium-
free’.
What Fuzeon looks like and contents of the pack
Fuzeon powder and solvent for solution for injection comes in a carton containing:
60 vials of Fuzeon
60 vials of Water for Injections that is used to reconstitute the Fuzeon powder
60 3 ml syringes
60 1 ml syringes
180 alcohol swabs.
This pack provides you with everything you need to prepare and take your Fuzeon for 30 days of
injections.
Fuzeon is also available in a carton containing 60 vials of Fuzeon and 60 vials of Water for Injections.
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Roche Registration Limited
6 Falcon Way
Shire Park
Welwyn Garden City
AL7 1TW
United Kingdom
The Manufacturer responsible for batch release is
Roche Pharma AG
Emil-Barell-Str. 1,
D-79639 Grenzach-Wyhlen
Germany
For any information about this medicinal product, please contact the local representative of the
Marketing Authorisation Holder:
België/Belgique/Belgien
N.V. Roche S.A.
Tél/Tel: +32 (0) 2 525 82 11
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
(Voir/siehe Belgique/Belgien)
България
Рош България ЕООД
Тел: +359 2 818 44 44
Magyarország
Roche (Magyarország) Kft.
Tel: +36 - 23 446 800
Česká republika
Roche s. r. o.
Tel: +420 - 2 20382111
Malta
(See United Kingdom)
Danmark
Roche a/s
Tlf: +45 - 36 39 99 99
Nederland
Roche Nederland B.V.
Tel: +31 (0) 348 438050
Deutschland
Roche Pharma AG
Tel: +49 (0) 7624 140
Norge
Roche Norge AS
Tlf: +47 - 22 78 90 00
Eesti
Roche Eesti OÜ
Tel: + 372 6 177 380
Österreich
Roche Austria GmbH
Tel: +43 (0) 1 27739
Ελλάδα
Roche (Hellas) A.E.
Τηλ: +30 210 61 66 100
Polska
Roche Polska Sp.z o.o.
Tel: +48 - 22 345 18 88
España
Roche Farma S.A.
Tel: +34 - 91 324 81 00
Portugal
Roche Farmacêutica Química, Lda
Tel: +351 - 21 425 70 00
France
Roche
Tél: +33 (0) 1 46 40 50 00
România
Roche România S.R.L.
Tel: +40 21 206 47 01
Ireland
Roche Products (Ireland) Ltd.
Tel: +353 (0) 1 469 0700
Slovenija
Roche farmacevtska družba d.o.o.
Tel: +386 - 1 360 26 00
Ísland
Roche a/s
c/o Icepharma hf
Sími: +354 540 8000
Slovenská republika
Roche Slovensko, s.r.o.
Tel: +421 - 2 52638201
Italia
Roche S.p.A.
Tel: +39 - 039 2471
Suomi/Finland
Roche Oy
Puh/Tel: +358 (0) 10 554 500
Kύπρος
Γ.Α.Σταμάτης & Σια Λτδ.
Τηλ: +357 - 22 76 62 76
Sverige
Roche AB
Tel: +46 (0) 8 726 1200
Latvija
Roche Latvija SIA
Tel: +371 – 6 7039831
United Kingdom
Roche Products Ltd.
Tel: +44 (0) 1707 366000
Lietuva
UAB “Roche Lietuva”
Tel: +370 5 2546799
This leaflet was last approved in
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency web site:
Always take Fuzeon exactly as your doctor has instructed you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist
if you are unsure.
The usual dose is 90 mg twice a day
, given as a 1 ml subcutaneous (just below the skin) injection
into the upper arm, anterior thigh or abdomen. Each injection should be given at a site different from
the last place you injected and never where there is still an injection site reaction from an earlier dose.
You should not inject your medicine into moles, scar tissue, bruises or your navel.
When to take Fuzeon
It is best to take Fuzeon at the same time each day if you can. Try and space the doses evenly apart
whenever it is convenient for you. First thing in the morning and again in the evening are good times.
The following is a basic, step-by-step guide to injecting your medicine. Please contact your doctor or
pharmacist if you have any questions about Fuzeon administration.
How long should you take Fuzeon for?
You should keep taking your medicine until your doctor tells you to stop. If you stop and interrupt
your treatment with Fuzeon this may lead to the HIV in your blood becoming resistant to it quicker
than if you take it regularly and without treatment interruptions. The HIV virus in your blood may
eventually become resistant to Fuzeon and your blood levels of virus begin to rise. This is when your
doctor may decide to no longer keep treating you with Fuzeon. Your doctor should discuss this with
you at that time.
What to do if you are left-handed
The illustrations in this leaflet show individuals who are right-handed. If you are left-handed, do what
comes naturally to you. You will probably find it most comfortable to hold the syringe in your left
hand and hold the vial between thumb and forefinger of your right hand.
When to have a carer help you
Certain injection sites, such as the upper arms, can be difficult to use at first. Have your partner, a
friend, or a family member with you if you need help. To reduce the risk of needlestick injury, you
should have a carer attend an injection training session with your healthcare provider.
Your syringes
The syringes supplied with this medicine have a coloured needle protection device that is attached to
the needle. This safety device covers the needle after use and reduces the risk of needle-stick injuries.
Although these syringes offer this safety feature, it is important that you dispose of used syringes
properly and according to the instructions given to you by your healthcare provider.
Wash your hands well to reduce the risk of bacterial infections. Do not touch anything except
the medicine and supplies.
When handling the syringe, do not touch the needle. Do not touch the tops of the vials once they
have been cleaned with alcohol swabs.
Make sure none of the items in your kit have been opened. Do not use opened materials.
Never use a syringe with a bent or damaged needle.
Never mix your medicine with tap water.
Never inject your medicine with other injectable medicines.
The only recommended route of injection is subcutaneous (under the skin). Fuzeon should
not
be given intravenously (directly into your veins) or intramuscularly (directly into your muscle).
Throw away used syringes into your dedicated waste container with a lid for the safe disposal of
waste materials. Consult your doctor if you have any questions about safe disposal of these
items.




Gather all of the following supplies:
One vial of Fuzeon (glass container with white powder inside)
One vial of water for injections (glass container with clear and colourless liquid inside)
One 3 ml syringe (larger syringe) with a 25 mm needle
One 1 ml syringe (smaller syringe) with a 13 mm needle
Dedicated waste container with a lid for the safe disposal of the waste materials.
Open Syringe Packages and Remove Vial Caps
Throw away packages and vial caps into the rubbish.
Place syringes and vials onto a clean surface.
After washing hands, do not touch anything except the injection supplies and the injection site.
Wipe each vial top with a fresh alcohol pad. Let the tops air-dry.
Be sure not to touch the rubber tops after cleaning them. If you touch them, be sure to clean
them again.
Draw Up Water for Injections
Pick up the
3 ml large syringe
. Using your index finger, push back the coloured needle protection
device towards the syringe.
To ensure that the needle is secure, hold the clear plastic cap and tighten the needle/cap assembly with
a gentle clockwise twist. Do not use too much force as the needle may loosen.
To remove the clear plastic cap push towards the syringe and then pull the cap off.

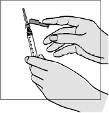




Insert the syringe needle into the rubber top of the vial of water for injections and press the plunger,
injecting the air.
Turn the vial upside down. Make sure the tip of the needle is always below the surface of the water for
injections to help keep any air bubbles from entering the syringe.
Slowly pull back the plunger until the water reaches the 1.1 ml mark.
Please be aware that the vial
contains an excess of water for injections (2 ml); you only have to withdraw 1.1 ml of it to
prepare your medication properly.
Tap the syringe gently to make any air bubbles rise to the top.
If excess air enters the syringe, gently press the plunger to force any air back into the vial and
withdraw the water again, making sure you have 1.1 ml of water for injections in the syringe.
Remove the needle from the vial,
making sure you never touch the needle with your fingers
or any other object
.
Throw away the vial into the rubbish. The solvent vial is intended for single use only and the
remaining water for injections in the vial after withdrawal of the volume required for
reconstitution has to be discarded.
Injecting Water For Injections Into Fuzeon Powder
Gently tap the vial of Fuzeon to loosen the powder.
Hold the water-filled syringe by the barrel and push the needle through the rubber top of the vial
at a slight angle.
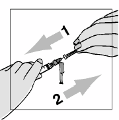
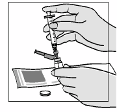


Press the syringe plunger in slowly. Allow the water to flow slowly down the inside of the vial.
Be
careful not to forcefully shoot water into the powder, since this can cause foaming. If foaming
occurs, it may take longer for the powder to dissolve completely.
After all of the sterile water for injections has been added to the vial of Fuzeon, remove the
syringe from the vial.
Hold the barrel of the syringe with one hand and gently press the coloured needle protection
device down on a
flat surface
until it covers the needle. You will hear a click.
Do not use your
free hand to press the device over the needle.
Throw away the syringe into a dedicated waste container.
Mixing the Water with the Fuzeon Powder
Gently tap the vial with your fingertip until the powder begins to dissolve.
Never shake the vial
or turn it upside down to mix—this will cause excessive foaming
. After the powder begins to
dissolve you can set the vial aside to allow it to completely dissolve. The powder may take up to
45 minutes to dissolve in to solution. The vial can also be gently rolled between your hands
after adding the water for injections until it is fully dissolved and this may reduce the time it
takes for the powder to dissolve.
If you accidentally touch the rubber stopper, be sure to clean it again with a new alcohol swab.
Make sure the powder has dissolved completely, allowing any bubbles that may have formed to
settle. If bubbles still exist, gently tap the side of the vial to help settle them.
As with all injectable medicines, it is important to inspect the solution for particles. If you
notice any particles in the solution, do not use it. You should throw away the vial into the
dedicated waste container with a lid or return it to the pharmacy. Start again with a new vial of
Fuzeon powder.
Once a dose is mixed with water for injections, it must be used immediately or stored in a
refrigerator and used within 24 hours. Allow the solution to return to room temperature before
using.
If you are preparing both of your daily doses at one time, be sure to use new syringes, water for
injections, and Fuzeon for each dose.
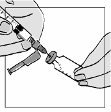
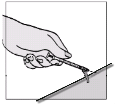
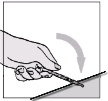


STEP 3: PREPARING FOR THE INJECTION
Injection sites include the abdomen, upper thighs, and upper arms. Each injection should be given at a
site different from the last place you injected and never where there is still an injection site reaction
from an earlier dose. You should not inject your medicine into moles, scar tissue, bruises or your
navel.
Choose a different area from where you last injected yourself, and then check for any places where
you may have a reaction (press the skin to see if there are any hard bumps). It is much better to avoid
these areas. Also avoid areas that could become irritated by your belt or the waistline of your clothing.
Cleansing the Injection Site
Cleanse the area for injection thoroughly with an alcohol swab in a circular motion, working outward.
Allow to air-dry completely.
Drawing Up Fuzeon into the 1 ml Syringe
Wipe the top of the Fuzeon vial again with a new alcohol swab.
Pick up the
1 ml small syringe
. Using your index finger, push back the coloured needle protection
device towards the syringe.
To ensure that the needle is secure, hold the plastic cap and tighten the needle/cap assembly by slightly
turning and pushing it towards the syringe.
To remove the clear plastic cap push towards the syringe and then pull the cap off.
Draw back 1 ml of air. Be careful not to pull the plunger too fast past the 1 ml marker and/or out of the
barrel.
Insert the syringe needle into the rubber top of the Fuzeon vial and press the plunger, injecting the air.
Gently turn the vial upside down.


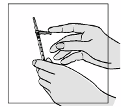
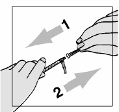


Make sure the tip of the needle is always below the surface of the solution to help keep air
bubbles from entering the syringe.
Slowly pull back the plunger until the solution reaches the 1.0 ml
mark. Be careful not to pull the plunger too fast past the 1 ml marker and/or out of the barrel.
Tap the syringe gently to make any air bubbles rise to the top.
If excess air enters the syringe, gently press the plunger to inject the air back into the vial and
withdraw the solution again, making sure you have 1.0 ml of solution in the syringe (whatever
volume your doctor prescribed, if different). This step may be repeated until the correct amount
of solution is in the syringe.
Remove the syringe from the vial.
Tip:
Your healthcare provider may suggest different injection techniques that will work best for you.
Pinch as much of a skin fold as possible without making yourself uncomfortable.
Pierce the skin at a 45-degree angle.
When the needle is in, release the skin, and using the same hand, hold on to the syringe barrel to help
steady it and prevent shifting.
Using the thumb, depress the plunger in to inject the solution.
After the dose is fully delivered, remove the needle from the skin.
Hold the barrel of the syringe with one hand and gently press the coloured needle protection
device down on a
flat surface
until it covers the needle. You will hear a click.
Do not use your
free hand to press the device over the needle.

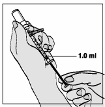
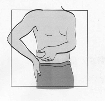
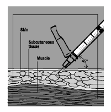



Throw away the syringe into a dedicated waste container with a lid.
Cover the injection site with a sticking plaster if any blood is present.
STEP 5: DISPOSING OF USED SUPPLIES
Throw away all used syringes directly into the dedicated waste container with a lid. Keep the cover of
this container tight and keep the dedicated waste container with a lid out of the reach of children.
Check with your doctor or pharmacist about proper disposal of the container.
In addition, you should safely dispose of all used alcohol swabs and vials, even if the vials contain
unused amounts of medicine or water for injections. The vials of Fuzeon and water for injections
should only be used once. Used supplies other than syringes (alcohol swabs and empty vials) may be
disposed of into the rubbish as long as no blood is visible. If blood is visible, dispose of the items into
the dedicated waste container with a lid.
If you have any questions or concerns about the safe disposal of these materials, please call your
doctor or pharmacist.
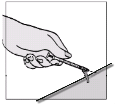
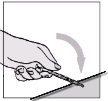



PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Fuzeon 90 mg/ml powder for solution for injection
Enfuvirtide
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
-
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you personally. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm
them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
What Fuzeon is and what it is used for
WHAT FUZEON IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
What Fuzeon is
Fuzeon inhibits the entry of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) into the cells that HIV attacks
(called CD4 or T-cells) in your blood. It works by preventing the HIV from making contact with the
affected cell membrane. This means that the HIV cannot enter the cell and then it cannot multiply.
This is because HIV needs the DNA in the host cell so it can multiply.
When Fuzeon should be used
Fuzeon is used in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products by persons who are
infected with HIV, the virus which causes AIDS. Your doctor has prescribed Fuzeon to help control
your HIV infection. Fuzeon is not a cure for HIV infection. Never use or share used needles.
if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to enfuvirtide or any of the other ingredients of Fuzeon (see
section 6).
Take special care with Fuzeon:
if you have any other medical conditions,
if you have had any lung disease in the past; are currently, or have been, an intravenous drug
user; are a smoker,
if you have a history of any kidney problems.
Fuzeon does not reduce the risk of passing HIV to others through sexual contact or blood
contamination. It is important to continue to take appropriate precautions to prevent passing HIV to
others. Fuzeon is not a cure for HIV infection.
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
In some patients with advanced HIV infection (AIDS) and a history of opportunistic infections, signs
and symptoms of inflammation from previous infections may occur soon after anti-HIV treatment is
started. It is believed that these symptoms are due to a recovery of the body’s immune system. This
improvement enables the body to fight infections that may have been present with no obvious
symptoms. Patients with chronic hepatitis B and C and treated with antiretroviral therapy are at an
increased risk for serious liver problems. If you notice any symptoms of infection, please inform your
doctor immediately.
Bone problems
Some patients taking combination antiretroviral therapy may develop a bone disease called
osteonecrosis (death of bone tissue caused by loss of blood supply to the bone). The length of
combination antiretroviral therapy, corticosteroid use, alcohol consumption, severe
immunosuppression, higher body mass index, among others, may be some of the many risk factors for
developing this disease. Signs of osteonecrosis are joint stiffness, aches and pains (especially of the
hip, knee and shoulder) and difficulty in movement. If you notice any of these symptoms please
inform your doctor.
Taking other medicines
Please inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines,
even those not prescribed. Fuzeon has been shown not to interact with your other anti-HIV medicines
or rifampicin (an antibiotic).
Using Fuzeon with food and drink
You can take Fuzeon with or without food but you still need to follow the instructions given in the
package leaflets for your other medicines.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Pregnant women and breast-feeding mothers should not take Fuzeon unless specifically directed to by
their doctor. Be sure to tell your doctor immediately if you are or may be pregnant or if you are breast-
feeding a baby. HIV-infected women should not breast-feed their infants because of the risk that your
baby can be infected with HIV through your breast milk. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice
before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
Fuzeon has not been specifically tested for its possible effects on your ability to drive a car or operate
machines. However, if you feel dizzy while taking Fuzeon then please do not drive nor operate
machines.
Always use Fuzeon exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor or
pharmacist if you are not sure.
The usual dose is 90 mg twice a day
, given as a l ml subcutaneous (just below the skin) injection.
See further instructions on how to use Fuzeon at the end of this leaflet. There you will find instructions
on how to prepare Fuzeon and how to give yourself an injection.
If you take more Fuzeon than you should
There is no specific antidote for overdose with Fuzeon. If you take more than the recommended dose
please consult your doctor.
If you forget to take Fuzeon
Take the dose as soon as you remember and then take your next dose at its regular time. Do not take
the forgotten dose if it is less than 6 hours before you are going to take your next regular dose and
never take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
Like all medicines, Fuzeon can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The side effect that you may experience most commonly when taking Fuzeon, are reactions at the
place on your body where you have given yourself the injection. You will probably experience one or
more of the following mild to moderate reactions at the place where you inject your medicine:
● itchiness
● swelling
● redness
● pain or tenderness
● hardened skin or bumps.
These reactions can appear within the first week of treatment and generally do not get worse with
continued use of Fuzeon. Reactions at an individual injection site usually last for equal to or less than
7 days. If you experience reactions at an injection site, it is important not to stop taking Fuzeon until
you have talked with your doctor about any concerns you may have.
Injection site reactions may be worse when injections are repeated in the same place on the body, or
when the injection is given deeper than intended (for example, into a muscle). In rare instances,
patients experienced an infection at an individual injection site. To reduce the risk of infection, it is
important that you follow the Fuzeon Injection Instructions provided below.
Apart from reactions at the injection site, the side effects most frequently reported in patients receiving
antiretroviral treatment with or without Fuzeon are diarrhoea and feeling sick.
Very common side effects
(affects more than 1 in 10 persons)
are pain and numbness in hands, feet or
legs, and loss of weight.
Common side effects
(affects 1 to 10 users in 100)
are:
● inflammation of the sinuses (cavities in the forehead),
● local swelling on the skin,
● reactions at injection sites
● pneumonia,
● ear infection,
● swollen glands,
● decreased appetite,
● anorexia,
● increased blood fat values,
● diabetes,
● feeling anxious or irritated,
● nightmares,
● feeling dizzy,
● lack of concentration,
● tremor (shaking),
● inflamed eye lids,
● nasal congestion,
● inflammation of the pancreas,
● heart burn,
● dry skin,
● eczema,
● redness of the skin,
● acne,
● muscle pain,
● kidney stones,
● 'flu-like' symptoms,
● feeling weak
● blood in the urine.
Hypersensitivity (allergy) to Fuzeon is rare
(affects 1 to 10 users in 10,000)
. However if you develop
symptoms that may suggest that you are allergic to this medicine then you must stop taking it straight
away and tell your doctor as soon as possible. Symptoms that you should look out for are rash, a high
temperature or chill, feeling sick or being sick and sweating and shaking. These symptoms do not
definitely mean you are allergic to this medicine but you must discuss them with your doctor.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Fuzeon after the expiry date which is stated on the label of the Fuzeon Vials after EXP.
The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
Once the solution has been prepared for your injection it should be used immediately. If it is not used
immediately it must be stored in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C) and used within 24 hours.
Do not use Fuzeon if you notice any particles in the powder or the solution once the water for
injections has been added.
The active substance is enfuvirtide. Each vial contains 108 mg enfuvirtide. After reconstitution
with the solvent 1 ml of reconstituted solution contains 90 mg enfuvirtide.
The other ingredients are:
Sodium Carbonate, anhydrous
Mannitol
Sodium Hydroxide
Hydrochloric Acid
This medicinal product contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per dose, i.e. essentially ‘sodium-
free’.
What Fuzeon looks like and contents of the pack
Fuzeon powder for solution for injection comes in a carton containing 60 vials of your medicine.
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Roche Registration Limited
6 Falcon Way
Shire Park
Welwyn Garden City
AL7 1TW
United Kingdom
The Manufacturer responsible for batch release is
Roche Pharma AG
Emil-Barell-Str. 1,
D-79639 Grenzach-Wyhlen
Germany
For any information about this medicinal product, please contact the local representative of the
Marketing Authorisation Holder:
België/Belgique/Belgien
N.V. Roche S.A.
Tél/Tel: +32 (0) 2 525 82 11
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
(Voir/siehe Belgique/Belgien)
България
Рош България ЕООД
Тел: +359 2 818 44 44
Magyarország
Roche (Magyarország) Kft.
Tel: +36 - 23 446 800
Česká republika
Roche s. r. o.
Tel: +420 - 2 20382111
Malta
(See United Kingdom)
Danmark
Roche a/s
Tlf: +45 - 36 39 99 99
Nederland
Roche Nederland B.V.
Tel: +31 (0) 348 438050
Deutschland
Roche Pharma AG
Tel: +49 (0) 7624 140
Norge
Roche Norge AS
Tlf: +47 - 22 78 90 00
Eesti
Roche Eesti OÜ
Tel: + 372 - 6 177 380
Österreich
Roche Austria GmbH
Tel: +43 (0) 1 27739
Ελλάδα
Roche (Hellas) A.E.
Τηλ: +30 210 61 66 100
Polska
Roche Polska Sp.z o.o.
Tel: +48 - 22 345 18 88
España
Roche Farma S.A.
Tel: +34 - 91 324 81 00
Portugal
Roche Farmacêutica Química, Lda
Tel: +351 - 21 425 70 00
France
Roche
Tél: +33 (0) 1 46 40 50 00
România
Roche România S.R.L.
Tel: +40 21 206 47 01
Ireland
Roche Products (Ireland) Ltd.
Tel: +353 (0) 1 469 0700
Slovenija
Roche farmacevtska družba d.o.o.
Tel: +386 - 1 360 26 00
Ísland
Roche a/s
c/o Icepharma hf
Sími: +354 540 8000
Slovenská republika
Roche Slovensko, s.r.o.
Tel: +421 - 2 52638201
Italia
Roche S.p.A.
Tel: +39 - 039 2471
Suomi/Finland
Roche Oy
Puh/Tel: +358 (0) 10 554 500
Kύπρος
Γ.Α.Σταμάτης & Σια Λτδ.
Τηλ: +357 - 22 76 62 76
Sverige
Roche AB
Tel: +46 (0) 8 726 1200
Latvija
Roche Latvija SIA
Tel: +371 – 6 7039831
United Kingdom
Roche Products Ltd.
Tel: +44 (0) 1707 366000
Lietuva
UAB “Roche Lietuva”
Tel: +370 5 2546799
This leaflet was last approved in
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency web site:
Always take Fuzeon exactly as your doctor has instructed you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist
if you are unsure.
The usual dose is 90 mg twice a day
, given as a 1 ml subcutaneous (just below the skin) injection
into the upper arm, anterior thigh or abdomen. Each injection should be given at a site different from
the last place you injected and never where there is still an injection site reaction from an earlier dose.
You should not inject your medicine into moles, scar tissue, bruises or your navel.
When to take Fuzeon
It is best to take Fuzeon at the same time each day if you can. Try and space the doses evenly apart
whenever it is convenient for you. First thing in the morning and again in the evening are good times.
The following is a basic, step-by-step guide to injecting your medicine. Please contact your doctor or
pharmacist if you have any questions about Fuzeon administration.
How long should you take Fuzeon For
?
You should keep taking your medicine until your doctor tells you to stop. If you stop and interrupt
your treatment with Fuzeon this may lead to the HIV in your blood becoming resistant to it quicker
than if you take it regularly and without treatment interruptions. The HIV virus in your blood may
eventually become resistant to Fuzeon and your blood levels of virus begin to rise. This is when your
doctor may decide to no longer keep treating you with Fuzeon. Your doctor should discuss this with
you at that time.
What to do if you are left-handed
The illustrations in this leaflet show individuals who are right-handed. If you are left-handed, do what
comes naturally to you. You will probably find it most comfortable to hold the syringe in your left
hand and hold the vial between thumb and forefinger of your right hand.
When to have a carer help you
Certain injection sites, such as the upper arms, can be difficult to use at first. Have your partner, a
friend, or a family member with you if you need help. To reduce the risk of needlestick injury, you
should have a carer attend an injection training session with your healthcare provider.
Wash your hands well to reduce the risk of bacterial infections. Do not touch anything except
the medicine and supplies.
When handling syringes, do not touch the needle. Do not touch the tops of the vials once they
have been cleaned with alcohol swabs.
Make sure none of the items that you need for your injection have been opened. Do not use
opened materials.
Never mix your medicine with tap water.
Never inject your medicine with other injectable medicines.
The only recommended route of injection is subcutaneous (under the skin). Fuzeon should
not
be given intravenously (directly into your veins) or intramuscularly (directly into your muscle).
Discard used syringes into your dedicated container with a lid for the safe disposal of waste
materials. Consult your doctor if you have any questions about safe disposal of these items.
Gather all of the following supplies that you will need to prepare and give yourself an injection. You
need to ask your pharmacist or doctor if you need to find out where to get the water for injections, the
3 ml and 1 ml syringes, alcohol swabs and dedicated waste container with a lid:
One vial of water for injections
One 3 ml syringe (larger syringe) with a 25 mm needle
One 1 ml syringe (smaller syringe) with a 13 mm needle
Dedicated waste container with a lid for the safe disposal of the waste materials.
Open Syringe Packages and Remove Vial Caps
Throw away packages and vial caps into the rubbish.
Place syringes and vials onto a clean surface.
After washing hands, do not touch anything except the injection supplies and the injection site.





Wipe each vial top with a fresh alcohol pad. Let the tops air-dry.
Be sure not to touch the rubber tops after cleaning them. If you touch them, be sure to clean
them again.
Draw Up Water for Injections
Pick up the
3 ml large syringe
.
To ensure that the needle is secure, hold the plastic cap and tighten the needle/cap assembly by slightly
turning and pushing it towards the syringe.
Remove the plastic cap and draw back 1.1 ml of air.
Insert the syringe needle into the rubber top of the vial of water for injections and press the plunger,
injecting the air.
Turn the vial upside down. Make sure the tip of the needle is always below the surface of the sterile
water to help keep any air bubbles from entering the syringe.
Slowly pull back the plunger until the water for injection reaches the 1.1 ml mark.
Tap the syringe gently to make any air bubbles rise to the top.
If excess air enters the syringe, gently press the plunger to force any air back into the vial and
withdraw the water for injections again, making sure you have 1.1 ml of water for injections in the
syringe.
Remove the needle from the vial,
making sure you never touch the needle with your fingers
or any other object
.
Throw away the water for injections vial into the rubbish. The water for injections vial is
intended for single use only.
Injecting Water for Injections Into the Fuzeon Powder
Gently tap the vial of Fuzeon to loosen the powder.
Hold the water-filled syringe by the barrel and push the needle through the rubber top of the Fuzeon
vial at a slight angle.

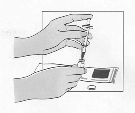




Press the syringe plunger in slowly. Allow the water to flow slowly down the inside of the vial.
Be
careful not to forcefully shoot water into the powder, since this can cause foaming. If foaming
occurs, it may take longer for the powder to dissolve completely
.
After all of the water for injections has been added to the vial of Fuzeon, throw the syringe into
a dedicated waste container.
Mixing the Water For Injections with the Fuzeon Powder
Gently tap the vial with your fingertip until the powder begins to dissolve.
Never shake the vial
or turn it upside down to mix—this will cause excessive foaming
. After the powder begins to
dissolve you can set the vial aside to allow it to completely dissolve. The powder may take up to
45 minutes to dissolve in to solution. The vial can also be gently rolled between your hands
after adding the water for injections until it is fully dissolved and this may reduce the time it
takes for the powder to dissolve.
If you accidentally touch the rubber stopper, be sure to clean it again with a new alcohol swab.
Make sure the powder has dissolved completely, allowing any bubbles that may have formed to
settle. If bubbles still exist, gently tap the side of the vial to help settle them.
As with all injectable medicines, it is important to inspect the solution for particles. If you
notice any particles in the solution, do not use it. You should throw away the vial into the
dedicated waste container with a lid or return it to the pharmacy. Start again with a new vial of
Fuzeon Powder.
Once a dose is mixed with water for injections, it must be used immediately or stored in a
refrigerator and used within 24 hours. Allow the solution to return to room temperature before
using.
If you are preparing both of your daily doses at one time, be sure to use new syringes, water for
injections and Fuzeon for each dose.
STEP 3: PREPARING FOR THE INJECTION
Injection sites include the abdomen, upper thighs, and upper arms. Each injection should be given at a
site different from the last place you injected and never where there is still an injection site reaction
from an earlier dose. You should not inject your medicine into moles, scar tissue, bruises or your
navel.

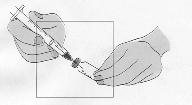

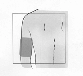




Choose a different area from where you last injected yourself, and then check for any places where
you may have a reaction (press the skin to see if there are any hard bumps). It is much better to avoid
these areas. Also avoid areas that could become irritated by your belt or the waistline of your clothing.
Cleansing the Injection Site
Cleanse the area for injection thoroughly with an alcohol swab in a circular motion, working outward.
Allow to air-dry completely.
Drawing Up Fuzeon into the 1 ml syringe
Wipe the top of the Fuzeon vial again with a new alcohol swab.
Pick up the
1 ml small syringe
.
To ensure that the needle is secure, hold the plastic cap and tighten the needle/cap assembly by slightly
turning and pushing it towards the syringe.
Remove the plastic cap and draw back 1 ml of air.
Insert the syringe needle into the rubber top of the Fuzeon vial and press the plunger, injecting the air.
Gently turn the vial upside down.
Make sure the tip of the needle is always below the surface of the
solution to help keep air bubbles from entering the syringe.
Slowly pull back the plunger until the
solution reaches the 1.0 ml mark.
Tap the syringe gently to make any air bubbles rise to the top.
If excess air enters the syringe, gently press the plunger to inject the air back into the vial and
withdraw the solution again, making sure you have 1.0 ml of solution in the syringe (whatever
volume your doctor prescribed, if different). This step may be repeated until the correct amount
of solution is in the syringe.
Remove the syringe from the vial.
STEP 4: INJECTING FUZEON
Tip: Your healthcare provider may suggest different injection techniques that will work best
for you.
Pinch as much of a skin fold as possible without making yourself uncomfortable.
Pierce the skin at a 45-degree angle.
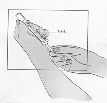
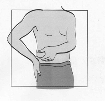



When the needle is in, release the skin, and using the same hand, hold on to the syringe barrel to help
steady it and prevent shifting.
Using the thumb, depress the plunger in to inject the medicine. After the dose is fully delivered
remove the needle from the skin.
Discard the syringe into a dedicated waste container with a lid.
Cover the injection site with a sticking plaster if any blood is present.
STEP 5: DISPOSING OF USED SUPPLIES
Throw away all used syringes directly into the dedicated waste container with a lid. Keep the cover of
this container tight and keep the container out of the reach of children. Check with your doctor or
pharmacist about proper disposal of the container.
In addition, you should safely dispose of all used alcohol swabs and vials, even if the vials contain
unused amounts of medicine or water for injections. The vials of Fuzeon are intended for single use
only. Used supplies other than syringes (alcohol swabs and empty vials) may be disposed of into the
rubbish as long as no blood is visible. If blood is visible, dispose of the items into the dedicated waste
container with a lid.
If you have any questions or concerns about the safe disposal of these materials, please call your
doctor or pharmacist.

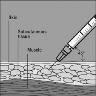



Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/fuzeon.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|






























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































