Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Ilaris 150 mg powder for solution for injection
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
One vial contains 150 mg of canakinumab*.
After reconstitution, each ml of solution contains 150 mg canakinumab.
* fully human monoclonal antibody produced in mouse hybridoma Sp2/0 cells by recombinant DNA
technology
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Powder for solution for injection.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Ilaris is indicated for the treatment of Cryopyrin-Associated Periodic Syndromes (CAPS) in adults,
adolescents and children aged 4 years and older with body weight above 15 kg, including:
−
Muckle-Wells Syndrome (MWS),
Neonatal-Onset Multisystem Inflammatory Disease (NOMID) / Chronic Infantile Neurological,
Cutaneous, Articular Syndrome (CINCA),
Severe forms of Familial Cold Autoinflammatory Syndrome (FCAS) / Familial Cold Urticaria
(FCU) presenting with signs and symptoms beyond cold-induced urticarial skin rash.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Treatment should be initiated and supervised by a specialist physician experienced in the diagnosis
and treatment of CAPS.
After proper training in the correct injection technique, patients may self-inject Ilaris if their physician
determines that it is appropriate and with medical follow-up as necessary.
Adults, adolescents and children aged 4 years and older
The recommended dose of Ilaris is 150 mg for CAPS patients with body weight > 40 kg and 2 mg/kg
for CAPS patients with body weight ≥ 15 kg and ≤ 40 kg. This is administered every eight weeks as a
single dose via subcutaneous injection.
If a satisfactory clinical response (resolution of rash and other generalised inflammatory symptoms)
has not been achieved 7 days after treatment start, a second dose of Ilaris at 150 mg or 2 mg/kg can be
considered. If a full treatment response is subsequently achieved, the intensified dosing regimen of
300 mg and 4 mg/kg should be maintained. No experience exists for doses > 600 mg every 8 weeks.
Clinical experience with dosing at intervals of less than 4 weeks is limited.
Special populations
Paediatric population
Ilaris is not recommended for use in children below 4 years of age or with body weight below 15 kg
due to a lack of clinical data.
Elderly
Clinical experience in patients above 65 years is limited, therefore caution is recommended.
Hepatic impairment
Ilaris has not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment.
Renal impairment
No dose adjustment is needed in patients with renal impairment. However, clinical experience in such
patients is limited.
For instructions on use and handling of the reconstituted solution, see section 6.6.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
Active, severe infections (see section 4.4).
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Serious infections
Ilaris may be associated with an increased incidence of serious infections. Therefore patients should be
monitored carefully for signs and symptoms of infections during and after treatment with Ilaris.
Physicians should exercise caution when administering Ilaris to patients with infections, a history of
recurring infections, or underlying conditions which may predispose them to infections. Treatment
with Ilaris should not be continued or initiated in patients with severe infections requiring medical
intervention.
Infections, predominantly of the upper respiratory tract, in some instances serious, have been reported
more frequently with Ilaris than with placebo. All infections responded to standard therapy.
In
canakinumab-treated patients with serious and systemic infections, a physiological inflammatory
response was maintained as evidenced by concomitant C-reactive protein (CRP) elevation and fever.
A blunted inflammatory response to infections cannot be excluded and increased vigilance is therefore
recommended. No unusual or opportunistic infections were reported with Ilaris.
Concomitant use of Ilaris with tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors is not recommended because
this may increase the risk of serious infections (see section 4.5).
PPD (purified protein derivative) skin test
In approximately 12% of CAPS patients tested with a PPD skin test in clinical trials, follow-up testing
yielded a positive test result while treated with Ilaris without clinical evidence of a latent or active
tuberculosis infection. Before initiation of therapy, all patients must be evaluated for both active and
latent tuberculosis infection. Particularly in adult patients, this evaluation should include a detailed
medical history and appropriate screening tests. Patients must be monitored closely for signs and
symptoms of tuberculosis during and after treatment with Ilaris. In the event of conversion from a
negative to a positive PPD test, especially in high-risk patients, alternative means of screening for a
tuberculosis infection should be considered.
Neutropenia
Neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count [ANC] < 1.5 x 10
9
/l) has been observed commonly with
another medicinal product that inhibits IL-1 used in a patient population (rheumatoid arthritis) other
than CAPS. Neutropenia was observed commonly in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (not an
approved use) who were administered Ilaris subcutaneously in clinical studies. Treatment with Ilaris
should not be initiated in patients with neutropenia. It is recommended that neutrophil counts be
assessed prior to initiating treatment, after 1 to 2 months, and periodically thereafter while receiving
Ilaris. If a patient becomes neutropenic the ANC should be monitored closely and treatment
discontinuation should be considered.
Malignancies
The risk for the development of malignancies with anti-interleukin (IL)-1 therapy is unknown. A
potential risk cannot be excluded in patients treated with Ilaris.
Hypersensitivity reactions
Cases suggestive of hypersensitivity reactions with Ilaris therapy have been reported in clinical trials.
The majority of these events were mild in severity. No anaphylactoid or anaphylactic reactions have
been reported. However, the risk of severe hypersensitivity reactions, which is not uncommon for
injectable proteins, cannot be excluded (see section 4.3).
Hepatic function
Rare, mild, transient and asymptomatic cases of elevations of serum transaminases or bilirubin have
been reported in clinical trials.
Vaccinations
No data are available on the risk of secondary transmission of infection by live (attenuated) vaccines
in patients receiving Ilaris. Therefore, live vaccines should not be given concurrently with Ilaris unless
the benefits clearly outweigh the risks (see section 4.5).
Prior to initiation of Ilaris therapy, adult and paediatric patients should receive all recommended
vaccinations, as appropriate, including pneumococcal vaccine and inactivated influenza vaccine.
Mutation in NLRP3 gene
Clinical experience in patients without a confirmed mutation in the NLRP3 gene is limited.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Interactions between Ilaris and other medicinal products have not been investigated in formal studies.
An increased incidence of serious infections has been associated with administration of another IL-1
blocker in combination with TNF inhibitors. Use of Ilaris with TNF inhibitors is not recommended
because this may increase the risk of serious infections.
The expression of hepatic CYP450 enzymes may be suppressed by the cytokines that stimulate
chronic inflammation, such as IL-1 beta. Thus, CYP450 expression may be reversed when potent
cytokine inhibitory therapy, such as canakinumab, is introduced. This is clinically relevant for
CYP450 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index where the dose is individually adjusted. On
initiation of canakinumab in patients being treated with this type of medicinal product, therapeutic
monitoring of the effect or of the active substance concentration should be performed and the
individual dose of the medicinal product adjusted as necessary.
No data are available on either the effects of live vaccination or the secondary transmission of
infection by live vaccines in patients receiving Ilaris. Therefore, live vaccines should not be given
concurrently with Ilaris unless the benefits clearly outweigh the risks. Should vaccination with live
vaccines be indicated after initiation of Ilaris treatment, the recommendation is to wait for at least
3 months after the last Ilaris injection and before the next one (see section 4.4).
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
There is a limited amount of data from the use of canakinumab in pregnant women. Animal studies do
not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to reproductive toxicity (see section 5.3).
The risk for the foetus/mother is unknown. Women should use effective contraceptives during
treatment with Ilaris and for up to 3 months after the last dose. Women who are pregnant or who
desire to become pregnant should therefore only be treated after a thorough benefit-risk evaluation.
Lactation
It is not known whether canakinumab is excreted in human milk. The decision whether to breast-feed
during Ilaris therapy should therefore only be taken after a thorough benefit-risk evaluation.
Animal studies have shown that a murine anti-murine IL-1 beta antibody had no undesirable effects on
development in nursing mouse pups and that the antibody was transferred to them (see section 5.3).
Fertility
Formal studies of the potential effect of Ilaris on human fertility have not been conducted.
Canakinumab had no effect on male fertility parameters in marmosets (
C. jacchus
). A murine anti-
murine IL-1 beta antibody had no undesirable effects on fertility in male or female mice (see section
5.3).
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The ability to drive and operate machines may be impaired by some symptoms associated with CAPS.
Patients who experience vertigo during Ilaris treatment should wait for this to resolve completely
before driving or operating machines.
Summary of the safety profile
Approximately 830 subjects have been treated with Ilaris in blinded and open-label clinical trials in
patients with CAPS, patients with other diseases, and healthy volunteers. Safety data from 104 CAPS
patients is available. A total of 10 serious adverse reactions that were considered by the investigator as
related to treatment were reported during the clinical programme in CAPS, of which the most frequent
events were infections (3) and vertigo (2). The most frequently reported adverse events included upper
respiratory tract infections and nasopharyngitis across all CAPS studies. Dose and duration of
treatment have no impact on the type or frequency of adverse events.
A total of 104 adult and paediatric CAPS patients (including FCAS/FCU, MWS, and
NOMID/CINCA) have received Ilaris in clinical trials. The safety of canakinumab compared with
placebo was investigated in a pivotal phase III trial that consisted of an 8-week, open-label period
(Part I), a 24-week, randomised, double-blind and placebo-controlled withdrawal period (Part II), and
a 16-week open label period on canakinumab (Part III). All patients were treated with Ilaris 150 mg
subcutaneous or 2 mg/kg if body weight was ≥ 15 kg and ≤ 40 kg.
Adverse reactions are listed according to MedDRA system organ class and frequency category.
Frequency categories are defined using the following convention: very common (≥ 1/10); common
(≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100); rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000); very rare
(< 1/10,000); not known (cannot be estimated from the available data). Within each frequency
grouping, adverse reactions are presented in order of decreasing seriousness.
Tabulated summary of reported adverse drug reactions from pivotal CAPS clinical
trial
Infections and infestations
Very common
Urinary tract infection 0
Upper respiratory tract
infection
Ear and labyrinth disorders
Very common
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Very common
Injection site reaction
#
3 (8.6%)
# Solicited through physician questionnaires
*
All events resolved despite continued treatment with Ilaris.
Cases suggestive of hypersensitivity reactions with Ilaris therapy have been reported in patients treated
with canakinumab in clinical trials. The majority of these events were mild in severity. No
anaphylactoid or anaphylactic reactions have been reported.
During clinical trials with canakinumab mean values for hemoglobin increased and decreased for
white blood cell, neutrophils and platelets. These changes were potentially due to a decrease in
inflammation and not considered to be of clinical relevance.
Elevations of transaminases have been observed rarely in CAPS patients.
Asymptomatic and mild elevations of serum bilirubin have been observed in CAPS patients treated
with canakinumab without concomitant elevations of transaminases.
Paediatric population
Twenty-three paediatric CAPS patients (4-17 years of age) demonstrated similar efficacy and safety to
adult patients. Specifically, the overall frequency and severity of infectious episodes in paediatric
patients were comparable to that in the adult population. Infection of the upper respiratory tract was
the most frequently reported infection.
No case of overdose has been reported.
In case of overdose, it is recommended for the patient to be monitored for any signs or symptoms of
adverse reactions, and appropriate symptomatic treatment instituted immediately.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Interleukin inhibitors, ATC code: L04AC08
This medicinal product has been authorised under “Exceptional Circumstances”. This means that due
to the rarity of the disease it has not been possible to obtain complete information on this medicinal
product. The European Medicines Agency (EMEA) will review any new information which may
become available every year and this SPC will be updated as necessary.












Mechanism of action
Canakinumab is a fully human monoclonal anti-human interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) antibody of the
IgG1/κ isotype. Canakinumab binds with high affinity specifically to human IL-1 beta and neutralises
the biological activity of human IL-1 beta by blocking its interaction with IL-1 receptors, thereby
preventing IL-1 beta-induced gene activation and the production of inflammatory mediators.
Pharmacodynamic effects
In clinical studies, CAPS patients who have uncontrolled over-production of IL-1 beta show a rapid
response to therapy with canakinumab, i.e. laboratory parameters such as high C-reactive protein
(CRP) and serum amyloid A (SAA), high neutrophil and platelet counts, and leukocytosis rapidly
returned to normal.
Clinical data
The efficacy and safety of canakinumab have been demonstrated in patients with varying degrees of
disease severity and different CAPS phenotypes (including FCAS/FCU, MWS, and NOMID/CINCA).
Only patients with confirmed NLRP3 mutation were included in the pivotal study.
In the Phase I/II study, treatment with canakinumab had a rapid onset of action, with disappearance or
clinically significant improvement of symptoms within one day after dosing. Laboratory parameters
such as high CRP and SAA, high neutrophils and platelet counts normalised rapidly within days of
canakinumab injection.
The pivotal study consisted of a 48-week three-part multicentre study, i.e. an 8-week open-label period
(Part I), a 24-week randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled withdrawal period (Part II), followed
by a 16-week open-label period (Part III). The aim of the study was to assess efficacy, safety, and
tolerability of canakinumab (150 mg or 2 mg/kg every 8 weeks) in patients with CAPS.
Part I: A complete clinical and biomarker response to canakinumab (defined as composite of
physician’s global assessment on autoinflammatory and on skin disease ≤ minimal and CRP or
SAA values < 10 mg/litre) was observed in 97% of patients and appeared within 7 days of
initiation of treatment. Significant improvements were seen in physician’s clinical assessment of
autoinflammatory disease activity: global assessment of autoinflammatory disease activity,
assessment of skin disease (urticarial skin rash), arthralgia, myalgia, headache/migraine,
conjunctivitis, fatigue/malaise, assessment of other related symptoms, and patient’s assessment
of symptoms.
Part II: In the withdrawal period of the pivotal study, the primary endpoint was defined as the
proportion of patients with a disease relapse/flare: none (0%) of the patients randomised to
canakinumab flared, compared with 81% of the patients randomised to placebo.
Part III: Patients treated with placebo in Part II who flared regained and maintained clinical and
serological response following entry into the open-label canakinumab extension.
Tabulated summary of efficacy in Phase III trial, pivotal placebo-controlled
withdrawal period (Part II)
Phase III trial, pivotal placebo-controlled withdrawal period (Part II)
Proportion of patients with disease flare in Part II
* mean (median) change from beginning of Part II
Sustained efficacy for more than 3 years was observed for the initial four patients with continued
administration of canakinumab.
No antibodies to canakinumab have been detected in CAPS patients treated with canakinumab.
Paediatric population
The CAPS trials with canakinumab included a total of 23 paediatric patients with an age range from 4
to 17 years (approximately half of them treated on an mg/kg basis). Overall, the efficacy, safety and
tolerability profile of canakinumab in paediatric patients was comparable to adult patients.
The European Medicines Agency has deferred the obligation to submit the results of studies with Ilaris
in one or more subsets of the paediatric population in Cryopyrin Associated Periodic Syndromes
(CAPS). See section 4.2 for information on paediatric use.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
The peak serum canakinumab concentration (C
max
) occurred approximately 7 days following single
subcutaneous administration of 150 mg in adult CAPS patients. The mean terminal half-life was
26 days. Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, the absolute bioavailability of subcutaneous
canakinumab was estimated to be 70%. The clearance (CL) and distribution volume (V
ss
) of
canakinumab varied according to body weight and were estimated to be 0.174 l/day and 6.01 litres,
respectively, in a typical CAPS patient of body weight 70 kg. The expected accumulation ratio was
1.3-fold following 6 months of subcutaneous administration of 150 mg canakinumab every 8 weeks.
Exposure parameters (such as AUC and C
max
) increased in proportion to dose over the dose range of
0.30 to 10.0 mg/kg given as intravenous infusion or from 150 to 300 mg as subcutaneous injection.
There was no indication of accelerated clearance or time-dependent change in the pharmacokinetic
properties of canakinumab following repeated administration. No gender or age-related
pharmacokinetic differences were observed after correction for body weight.
Paediatric population
Peak concentrations of canakinumab occurred between 2 to 7 days following single subcutaneous
administration of canakinumab 150 mg or 2 mg/kg in paediatric patients. The terminal half-life ranged
from 22.9 to 25.7 days, similar to the pharmacokinetic properties observed in adults.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on cross-reactivity, repeated dose,
immunotoxicity, reproductive and juvenile toxicity studies performed with canakinumab or a murine
anti-murine IL-1 beta antibody.






Since canakinumab binds to marmoset (
C. jacchus
) and human IL-1 beta with a similar affinity, the
safety of canakinumab has been studied in the marmoset. No undesirable effects of canakinumab were
seen following twice weekly administration to marmosets for up to 26 weeks or in an embryofoetal
developmental toxicity study in pregnant marmosets, at exposure in excess of human clinical levels. In
addition, no antibodies to canakinumab were detected in these studies. No non-specific tissue cross-
reactivity was demonstrated when canakinumab was applied to normal human tissues.
Formal carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with canakinumab.
In an embryofoetal development study in marmosets canakinumab showed no maternal toxicity,
embryotoxicity or teratogenicity when administered throughout organogenesis.
No undesirable effects of a murine anti-murine IL-1 beta antibody were seen in a complete set of
reproductive and juvenile studies in mice. Anti-murine IL-1 beta did not elicit adverse events on foetal
or neonatal growth when administered throughout late gestation, delivery and nursing (see section
4.6). The high dose used in these studies was in excess of the maximally effective dose in terms of IL-
1 beta suppression and activity.
An immunotoxicology study in mice with a murine anti-murine IL-1 beta antibody showed that
neutralising IL-1 beta has no effects on immune parameters and caused no impairment of immune
function in mice.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Sucrose
Histidine
Histidine hydrochloride monohydrate
Polysorbate 80
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal
products.
After reconstitution, from a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. If
not used immediately, in-use storage times and conditions prior to use are the responsibility of the user
and would normally not be longer than 24 hours at 2°C - 8°C.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C).
Do not freeze.
Store in the original package in order to protect from light.
For storage conditions of the reconstituted medicinal product, see section 6.3.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
150 mg of powder for solution for injection in a vial (type I glass) with a stopper (coated chlorobutyl
rubber) and flip-off cap (aluminium).
Packs containing 1 vial or multipacks containing 4 (4x1) vials.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Instructions for reconstitution
Using aseptic technique, reconstitute each vial of Ilaris at room temperature by slowly injecting 1.0 ml
water for injections with a 1 ml syringe and an 18 G x 2 inch (50 mm) needle. Swirl the vial slowly at
an angle of about 45° for approximately 1 minute and allow to stand for about 5 minutes. Then gently
turn the vial upside down and back again ten times. If possible, avoid touching the rubber stopper with
your fingers. Allow to stand for about 15 minutes at room temperature to obtain a clear to opalescent
solution. Do not shake. Do not use if particles are present in the solution.
Tap the side of the vial to remove any residual liquid from the stopper. The solution should be free of
visible particles and clear to opalescent. The solution should be colourless or may have a slight
brownish-yellow tint. If the solution has a distinctly brown discolouration it should not be used. If not
used immediately after reconstitution, the solution should be kept at 2°C to 8°C and used within
24 hours.
Instructions for administration
Carefully withdraw the required volume depending on the dose to be administered (0.2 ml to 1.0 ml)
and subcutaneously inject using a 27 G x 0.5 inch (13 mm) needle.
The following are suitable injection sites: upper thigh, abdomen, upper arm or buttocks. Broken skin
and areas which are bruised or covered by a rash should be avoided. Injection into scar-tissue should
be avoided as this may result in insufficient exposure to Ilaris.
Ilaris vials are for single use only.
Disposal
Patients or their caregivers should be instructed on the appropriate procedure for disposal of the vials,
syringes and needles in accordance with local requirements.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Novartis Europharm Limited
Wimblehurst Road
Horsham
West Sussex, RH12 5AB
United Kingdom
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
MANUFACTURER OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE
SUBSTANCE AND MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION
HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH RELEASE
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
SPECIFIC OBLIGATIONS TO BE FULFILLED BY THE
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
A. MANUFACTURER OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE SUBSTANCE AND
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer of the biological active substance
Novartis Pharma S.A.S.
Centre de Biotechnologie
8, rue de l’Industrie
68330 Huningue
France
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
Novartis Pharma GmbH
Roonstrasse 25
D-90429 Nürnberg
Germany
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to restricted medical prescription. (See Annex I: Summary of Product
Characteristics).
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
The Marketing Authorisation Holder (MAH) shall ensure that, prior to launch, all physicians who are
expected to prescribe/use Ilaris are provided with a physician information pack containing the
following:
•
The Summary of Product Characteristics
•
Physician information
•
Patient Alert Card
The physician information should contain the following key messages:
•
The risk of serious infections, including opportunistic bacterial, viral and fungal infections in
patients treated with Ilaris;
•
The risk of acute injection-related reactions;
•
The need to instruct patients on proper techniques for self-administration when the patient is
willing and capable to do so, and guidance for Health Care Professionals on how to report
administration errors;
•
The identified or potential risk of immunogenicity that might lead to immune-mediated
symptoms;
•
The need for Health Care Professionals to perform an annual clinical assessment of patients
regarding a potential increased risk for the development of malignancies;
•
The need to measure neutrophil counts prior to initiating treatment, after 1 to 2 months and
periodically thereafter while receiving Ilaris as treatment with Ilaris should not be initiated in
patients with neutropenia;
•
The need to monitor patients for changes in their lipid profiles;
•
The unknown safety of Ilaris in pregnant and lactating women, thus the need for physicians to
discuss this risk with patients if they become or plan to become pregnant;
•
The proper patient management as regards the interaction with vaccination;
•
The possibility to include patients in the registry study to facilitate the collection of long term
efficacy and safety data;
•
The role and use of patient alert card.
Pharmacovigilance system
The MAH must ensure that the system of pharmacovigilance, as described in version 8.0 presented in
Module 1.8.1. of the Marketing Authorisation Application, is in place and functioning before and
whilst the product is on the market.
Risk Management Plan
The MAH commits to performing the studies and additional pharmacovigilance activities detailed in
the Pharmacovigilance Plan, as agreed in version 1.1 (14 May 2009) of the Risk Management Plan
(RMP) presented in Module 1.8.2. of the Marketing Authorisation Application and any subsequent
updates of the RMP agreed by the CHMP.
As per the CHMP Guideline on Risk Management Systems for medicinal products for human use, the
updated RMP should be submitted at the same time as the next Periodic Safety Update Report
(PSUR).
In addition, an updated RMP should be submitted
•
When new information is received that may impact on the current Safety Specification,
Pharmacovigilance Plan or risk minimisation activities
Within 60 days of an important (pharmacovigilance or risk minimisation) milestone being
reached
At the request of the EMEA
C. SPECIFIC OBLIGATIONS TO BE FULFILLED BY THE MARKETING
AUTHORISATION HOLDER
The Marketing Authorisation Holder shall complete the following programme of studies within the
specified time frame, the results of which shall form the basis of the annual reassessment of the
benefit/risk profile.
The Applicant is requested to provide regular safety and efficacy
data from the Global Registry for both adults and children. The
fact that a limited number of paediatric patients were included in
the clinical studies combined with the lack of data on the effect of
long term IL-1ß suppression is a concern in view of the orphan
nature of the condition. The Applicant will need to propose a plan
to collect data from the registry on safety and efficacy in children;
particularly risk of infection and possible impairment of immune
reactions such as response to vaccinations and growth.
In addition the Applicant is requested to assess cases for whom
there is loss of efficacy to determine whether this is due to
changes over time in PK/PD or antibody development.
The Applicant is required to provide updates on the recruitment
rates and any intermediary results with the PSURs.
The patients should be included in the Registry until both
following conditions are met: 5 years recruitment period and
200 patients included.
Further PK steady state exposure data (AUC, C
max
, C
min
during
steady state) especially for paediatric subjects is required. The
Applicant is requested to commit to a PK study in children.
1. Areas: Quality, Non-clinical, Clinical, Pharmacovigilance system, Risk Management Plan and
Pharmacovigilance
2. Due date for the specific obligation or for the first interim report if a precise date cannot be committed to.







ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
UNIT PACK CARTON (INCLUDING BLUE BOX)
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Ilaris 150 mg powder for solution for injection
Canakinumab
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
One vial contains 150 mg canakinumab.
Also contains: sucrose, histidine, histidine hydrochloride monohydrate, polysorbate 80.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder for solution for injection.
1 vial of powder.
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous use.
Single use.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
After reconstitution, from a microbiological point of view immediate use is recommended. However
in-use stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 2-8°C.




















SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
Do not freeze.
Store in the original package in order to protect from light.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Novartis Europharm Limited
Wimblehurst Road
Horsham
West Sussex, RH12 5AB
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE




















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
OUTER CARTON OF MULTIPACK (INCLUDING BLUE BOX)
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Ilaris 150 mg powder for solution for injection
Canakinumab
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
One vial contains 150 mg canakinumab.
Also contains: sucrose, histidine, histidine hydrochloride monohydrate, polysorbate 80.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder for solution for injection.
Multipack comprising 4 intermediate packs, each containing 1 vial of powder.
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous use.
Single use.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
After reconstitution, from a microbiological point of view immediate use is recommended. However
in-use stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 2-8°C.




















SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
Do not freeze.
Store in the original package in order to protect from light.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Novartis Europharm Limited
Wimblehurst Road
Horsham
West Sussex, RH12 5AB
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE




















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
INTERMEDIATE CARTON OF MULTIPACK (WITHOUT BLUE BOX)
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Ilaris 150 mg powder for solution for injection
Canakinumab
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
One vial contains 150 mg canakinumab.
Also contains: sucrose, histidine, histidine hydrochloride monohydrate, polysorbate 80.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder for solution for injection.
Component of a multipack comprising 4 intermediate packs, each containing 1 vial.
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous use.
Single use.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
After reconstitution, from a microbiological point of view immediate use is recommended. However
in-use stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 2-8°C.




















SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
Do not freeze.
Store in the original package in order to protect from light.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Novartis Europharm Limited
Wimblehurst Road
Horsham
West Sussex, RH12 5AB
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE



















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Ilaris 150 mg powder for solution for injection
Canakinumab
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
-
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
What Ilaris is and what it is used for
WHAT ILARIS IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Ilaris is used in adults, adolescents and children aged 4 years and older with body weight above 15 kg
to treat the following auto-inflammatory diseases, which are collectively known as Cryopyrin-
Associated Periodic Syndromes (CAPS):
−
Muckle-Wells Syndrome (MWS),
Neonatal-Onset Multisystem Inflammatory Disease (NOMID), also called Chronic Infantile
Neurological, Cutaneous, Articular Syndrome (CINCA),
Severe forms of Familial Cold Autoinflammatory Syndrome (FCAS) / Familial Cold Urticaria
(FCU) presenting with signs and symptoms beyond cold-induced urticarial skin rash.
Ilaris belongs to a group of medicines called interleukin inhibitors. The active substance in Ilaris is
canakinumab, a fully-human monoclonal antibody. It blocks the activity of a substance called
interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta). In patients with CAPS, the body produces excessive amounts of IL-1
beta. This may lead to symptoms such as fever, headache, fatigue, skin rash, or painful joints and
muscles. By blocking the activity of IL-1 beta, canakinumab leads to an improvement in these
symptoms.
If you have any questions about how Ilaris works or why this medicine has been prescribed for you,
ask your doctor.
Do not use Ilaris
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to canakinumab or any of the other ingredients of Ilaris listed
in section 6 of this leaflet.
-
if you have an active, severe infection.
If you think you may be allergic or have an infection, do not use Ilaris and ask your doctor for advice.
Take special care with Ilaris
Before using Ilaris
, tell your doctor if any of the following applies to you:
−
if you currently have an infection or if you have a history of recurring infections or a condition
which makes you vulnerable to infections.
−
if you require vaccinations. You are advised to avoid a certain type of vaccination (also called
live vaccines) while being treated with Ilaris (see also “Using other medicines”).
During treatment with Ilaris, tell your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following
symptoms
:
−
prolonged fever (i.e. fever lasting longer than 3 days) or any other symptoms possibly related to
an infection, such as prolonged cough, prolonged headache or localised redness, warmth or
swelling of your skin.
−
signs of an allergic reaction such as difficulty breathing, nausea, dizziness, skin rash,
palpitations or low blood pressure.
−
signs of liver disorders such as yellow skin and eyes, nausea, loss of appetite, dark-coloured
urine and light-coloured stools.
Ilaris is not recommended for children younger than 4 years of age or who weigh less than 15 kg.
Using other medicines
Please tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other
medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
−
You are advised to avoid a certain type of vaccination known as “live vaccines” while being
treated with Ilaris. Your doctor may want to check your vaccination history and give you any
vaccinations that you have missed before you start treatment with Ilaris. Should vaccination
with live vaccines be necessary after initiation of Ilaris treatment, you are recommended to wait
for at least 3 months after the last Ilaris injection and before the next one.
Medicines called tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors predominantly used in rheumatoid and
autoimmune diseases (such as etanercept, adalimumab or infliximab) should not be used with
Ilaris because this may increase the risk of infections.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
−
Ilaris has not been studied in pregnant women. You are advised to avoid becoming pregnant and
must use adequate contraception while using Ilaris and for at least 3 months after the last Ilaris
treatment. It is important to tell your doctor if you are pregnant, if you think you may be
pregnant or if you plan to get pregnant. Your doctor will discuss with you the potential risk of
taking Ilaris during pregnancy.
It is not known whether Ilaris passes into human milk. Your doctor will discuss with you the
potential risks of taking Ilaris before breast-feeding.
Driving and using machines
Some symptoms associated with CAPS or with Ilaris treatment, such as a spinning sensation (known
as vertigo), may affect your ability to drive or use machines. If you feel a spinning sensation, do not
drive or operate any tools or machines until you are feeling normal again.
Ask your doctor, nurse or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Always use Ilaris exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor, nurse or
pharmacist if you are not sure.
Ilaris is intended for subcutaneous use. This means that it is injected through a short needle into the
fatty tissue just under the skin.
How much Ilaris to use
The recommended dose of Ilaris for CAPS patients is:
−
150 mg for patients with body weight of more than 40 kg.
−
2 mg/kg for patients with body weight between 15 kg and 40 kg.
Ilaris is injected as a single dose every 8 weeks.
If you have not sufficiently responded to treatment after 7 days, your doctor may consider giving you
a repeat dose of 150 mg or 2 mg/kg. After this you will continue to receive this higher dose of 300 mg
or 4 mg/kg.
Injecting Ilaris yourself
After proper training in the correct injection technique, you may inject Ilaris yourself.
−
You and your doctor should decide together whether or not you will inject Ilaris yourself.
−
Your doctor or nurse will show you how to inject yourself.
−
Do not try to inject yourself if you have not been properly trained or if you are not sure how to
do it.
For instructions on how to inject yourself with Ilaris, please read the section “Instructions for use” at
the end of this leaflet. If you have any questions, contact your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
How long to use Ilaris
You should continue using Ilaris for as long as your doctor tells you.
If you use more Ilaris than you should
−
If you accidentally inject more Ilaris than the recommended dose, it is unlikely to be serious, but
you should inform your doctor, nurse or pharmacist as soon as possible.
You should not inject Ilaris earlier than 8 weeks after the previous dose, unless your doctor tells
you to. If you accidentally inject Ilaris sooner than you should, you should also inform your
doctor, nurse or pharmacist as soon as possible.
If you forget to use Ilaris
If you have forgotten to use a dose of Ilaris, inject the next dose as soon as you remember, then contact
your doctor to discuss when you should take the next dose. You should then continue with injections
at 8-week intervals as before.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
Like all medicines, Ilaris may cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Most of the side
effects are mild to moderate and will generally disappear a few days to a few weeks after treatment.
Side effects may occur with certain frequencies, which are defined as follows:
Very common:
affects more than 1 user in 10
affects 1 to 10 users in 100
affects 1 to 10 users in 1,000
affects 1 to 10 users in 10,000
affects less than 1 user in 10,000
frequency cannot be estimated from the available data.
Potentially serious side effects (very common):
−
Prolonged fever (i.e. fever lasting longer than 3 days) or any other symptoms possibly related to
an infection, such as prolonged cough, prolonged headache or localised redness, warmth or
swelling of your skin.
If you experience any of these,
tell your doctor immediately
.









Very common side effects:
−
Spinning sensation (vertigo).
Injection site reaction (such as redness, swelling, warmth and itching).
Sore throat and nose (nasopharyngitis).
Potential side effects:
These side effects could potentially occur but have either not been reported as a side effect with Ilaris
or have been reported rarely during the use of Ilaris but seem to be unrelated to Ilaris.
−
Signs of an allergic reaction such as difficulty breathing, nausea, dizziness, skin rash,
palpitations or low blood pressure. If you experience any of these symptoms,
tell your doctor
immediately
.
Signs of liver disorders such as yellow skin and eyes, nausea, loss of appetite, dark-coloured
urine and light-coloured stools.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist
.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Ilaris after the expiry date which is stated on the label and carton. The expiry date refers to
the last day of that month.
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C).
Do not freeze.
Store in the original package in order to protect from light.
After reconstitution, from a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately.
However, chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 2°C - 8°C.
Do not use Ilaris if you notice that the solution is not clear to opalescent or contains particles.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
The active substance is canakinumab. One vial of powder contains 150 mg canakinumab.
The other ingredients are:
sucrose, histidine, histidine hydrochloride monohydrate, polysorbate
80.
What Ilaris looks like and contents of the pack
−
Ilaris is supplied as a powder for solution for injection in a 150 mg glass vial.
Ilaris is available in packs containing one vial or multipacks comprising four intermediate
packs, each containing one vial. Not all pack sizes may be marketed in your country.
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Novartis Europharm Limited
Wimblehurst Road
Horsham
West Sussex, RH12 5AB
United Kingdom
Manufacturer
Novartis Pharma GmbH
Roonstrasse 25
D-90429 Nuremberg
Germany
For any information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the Marketing
Authorisation Holder:
België/Belgique/Belgien
Novartis Pharma N.V.
Tél/Tel: +32 2 246 16 11
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
Novartis Pharma N.V.
Tél/Tel: +32 2 246 16 11
България
Novartis Pharma Services Inc.
Тел.: +359 2 489 98 28
Magyarország
Novartis Hungária Kft. Pharma
Tel.: +36 1 457 65 00
Česká republika
Novartis s.r.o.
Tel: +420 225 775 111
Malta
Novartis Pharma Services Inc.
Tel: +356 2298 3217
Danmark
Novartis Healthcare A/S
Tlf: +45 39 16 84 00
Nederland
Novartis Pharma B.V.
Tel: +31 26 37 82 111
Deutschland
Novartis Pharma GmbH
Tel: +49 911 273 0
Norge
Novartis Norge AS
Tlf: +47 23 05 20 00
Eesti
Novartis Pharma Services Inc.
Tel: +372 66 30 810
Österreich
Novartis Pharma GmbH
Tel: +43 1 86 6570
Ελλάδα
Novartis (Hellas) A.E.B.E.
Τηλ: +30 210 281 17 12
Polska
Novartis Poland Sp. z o.o.
Tel.: +48 22 550 8888
España
Novartis Farmacéutica, S.A.
Tel: +34 93 306 42 00
Portugal
Novartis Farma - Produtos Farmacêuticos, S.A.
Tel: +351 21 000 8600
France
Novartis Pharma S.A.S.
Tél: +33 1 55 47 66 00
România
Novartis Pharma Services Inc.
Tel: +40 21 31299 01
Ireland
Novartis Ireland Limited
Tel: +353 1 260 12 55
Slovenija
Novartis Pharma Services Inc.
Tel: +386 1 300 75 50
Ísland
Vistor hf.
Sími: +354 535 7000
Slovenská republika
Novartis Slovakia s.r.o.
Tel: +421 2 5542 5439
Italia
Novartis Farma S.p.A.
Tel: +39 02 96 54 1
Suomi/Finland
Novartis Finland Oy
Puh/Tel: +358 9 61 33 22 11
Κύπρος
Δημητριάδης και Παπαέλληνας Λτδ
Τηλ: +357 22 690 690
Sverige
Novartis Sverige AB
Tel: +46 8 732 32 00
Latvija
Novartis Pharma Services Inc.
Tel: +371 67 887 070
United Kingdom
Novartis Pharmaceuticals UK Ltd.
Tel: +44 1276 698370
Lietuva
Novartis Pharma Services Inc.
Tel: +370 5 269 16 50
This leaflet was last approved in
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF ILARIS POWDER FOR SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
Please note that the preparation of the injection at room temperature takes about 30 minutes.
See also section 3, “Injecting Ilaris yourself”.
Read these instructions all the way through before beginning.
Find a clean place in which to prepare and administer the injection.
Wash your hands with soap and water.
Check the expiry dates on the vial and syringes. Do not use after the expiry date which is stated
on the label and carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Always use new, unopened needles and syringes. Avoid touching the needles and the tops of the
vials.
Gather together the necessary items
Included in the pack
One vial of Ilaris powder for solution for injection (keep refrigerated)
Not included in the pack
−
one vial (or ampoule) of sterile water for injection (“water”) (do not refrigerate)
one 18 G x 2 inch (50 mm) needle for reconstituting the powder (“transfer needle”)
one 27 G x 0.5 inch (13 mm) needle for injecting (“injection needle”)
a proper disposal container for used needles, syringe and vials (sharps container)
1.
Remove the protective caps from the Ilaris and
water vials. Do not touch the vial stoppers. Clean
the stoppers with the alcohol swab.
2.
Open the wrappers containing the syringe and the
transfer needle (bigger one) and attach the needle
to the syringe.
3.
Carefully remove the cap from the transfer needle
and set the cap aside. Pull the plunger all the way
down to the 1.0 ml mark, filling the syringe with
air. Insert the needle into the water vial through the
centre of the rubber stopper (Fig. 1).
4.
Gently push the plunger all the way down until air
is injected into the vial.





5.
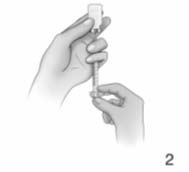
Invert the vial and syringe assembly and bring to
eye level (Fig. 2).
6.
Make sure the tip of the transfer needle is covered
by the water and slowly pull the syringe plunger
down to slightly past the 1.0 ml mark. If you see
bubbles in the syringe, remove bubbles as
instructed by your healthcare provider or
pharmacist.
7.
Make sure 1.0 ml of water is in the syringe, then
withdraw the needle from the vial. (There will be
water remaining in the vial.)
8.
Insert the transfer needle through the centre of the
stopper of the vial of Ilaris powder, taking care not
to touch the needle or the stopper. Slowly inject
1.0 ml of water in to the vial containing the Ilaris
powder (Fig. 3).
9.
Carefully remove the syringe with the transfer
needle from the vial and recap the needle as
instructed by your healthcare provider or
pharmacist.
10.
Without touching the rubber stopper, swirl (do not
shake) the vial slowly at an angle of about
45 degrees for approximately 1 minute (Fig. 4a).
Allow to stand for 5 minutes.
11.
Now, gently turn the vial upside down and back
again ten times, again taking care not to touch the
rubber stopper (Fig. 4b).
12.
Allow to stand for about 15 minutes at room
temperature to obtain a clear to opalescent solution.
Do not shake. Do not use if particles are present in
the solution.
13.
Make sure all of the solution is in the bottom of the
vial. If drops remain on the stopper, tap the side of
the vial to remove them. The solution should be
clear to opalescent and free of visible particles.
-
If not used immediately after reconstitution,
the solution should be stored in the
refrigerator (2°C to 8°C) and used within
24 hours.







14.
Clean the rubber stopper of the vial containing the
Ilaris solution with a new alcohol swab.
15.
Uncap the transfer needle again. Pull the plunger of
the syringe all the way down to the 1.0 ml mark,
filling the syringe with air. Insert the syringe
needle into the vial of Ilaris solution through the
centre of the rubber stopper (Fig. 5). Gently push
the plunger all the way down until air is injected
into the vial. Do not inject air into the medicine.
16.
Do not
invert the vial and syringe assembly
(Fig. 6a). Insert the needle all the way into the vial
until it reaches the bottom edge.
17.
Tip the vial to ensure that the required amount of
solution can be drawn into the syringe (Fig. 6b).
NOTE: The required amount depends on the dose
to be administered (0.2 ml to 1.0 ml). Your
healthcare provider will instruct you on the right
amount for you.
18.
Slowly pull the syringe plunger up to the correct
mark (0.2 ml to 1.0 ml), filling the syringe with
Ilaris solution. If there are air bubbles in the
syringe, remove bubbles as instructed by your
healthcare provider. Ensure that the correct amount
of solution is in the syringe.
19.
Remove the syringe and needle from the vial.
(There may be solution remaining in the vial.)
Recap the transfer needle as instructed by your
healthcare provider or pharmacist. Remove the
transfer needle from the syringe. Place the transfer
needle in the sharps container.
20.
Open the wrapper containing the injection needle
and attach the needle to the syringe. Set the syringe
aside.







21.
Choose an injection site on the upper thigh,
abdomen, upper arm or buttocks. Do not use an
area that has a rash or broken skin, or is bruised or
lumpy. Avoid injecting into scar-tissue as this may
lead to insufficient exposure to canakinumab.
Avoid injecting in to a vein.
22.
Clean the injection site with a new alcohol swab.
Allow the area to dry. Uncap the injection needle.
23.
Gently pinch the skin up at the injection site. Hold
the syringe at a 90-degree angle and in a single,
smooth motion, push the needle straight down
completely into the skin (Fig. 7).
24.
Keep the needle all the way in the skin while
slowly pushing the syringe plunger down until the
barrel is empty (Fig. 8). Release the pinched skin
and pull the needle straight out. Dispose of the
needle and syringe in the sharps container without
recapping or removing the needle.
25.
Do not rub the injection area. If bleeding occurs,
apply a clean, dry cotton swab over the area, and
press gently for 1 to 2 minutes, or until bleeding
stops (Fig. 9). Then apply an adhesive plaster.
26.
Safely dispose of needles and syringe in the sharps
container or as directed by your healthcare provider
or pharmacist (Fig. 10). Never reuse syringes or
needles.
27.
Properly dispose of vials containing remaining
water and Ilaris solution (if any) as directed by
your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Any
unused product or waste material should be
disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Keep the sharps container out of reach of children.
Dispose of it as directed by your healthcare provider or
pharmacist.










Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/ilaris.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|








































































































































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































