Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
INCRELEX 10 mg/ml solution for injection.
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each ml contains 10 mg of mecasermin.
Each vial contains 40 mg of mecasermin.
Mecasermin is a recombinant DNA-derived human insulin-like growth factor-1(IGF-1) produced in
Escherichia coli
.
Excipients:
One ml contains 9 mg of benzyl alcohol.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Aqueous, clear and colourless solution.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
For the long-term treatment of growth failure in children and adolescents with severe primary insulin-
like growth factor-1 deficiency (Primary IGFD).
Severe Primary IGFD is defined by:
•
height standard deviation score ≤ –3.0 and
•
basal IGF-1 levels below the 2.5
th
percentile for age and gender and
•
GH sufficiency.
•
Exclusion of secondary forms of IGF-1 deficiency, such as malnutrition, hypothyroidism,
or chronic treatment with pharmacologic doses of anti-inflammatory steroids.
Severe Primary IGFD includes patients with mutations in the GH receptor (GHR), post-GHR signaling
pathway, and IGF-1 gene defects; they are not GH deficient, and therefore, they cannot be expected to
respond adequately to exogenous GH treatment. It is recommended to confirm the diagnosis by
conducting an IGF-1 generation test.
4.2
Posology and method of administration
Treatment with INCRELEX should be directed by physicians who are experienced in the diagnosis
and management of patients with growth disorders.
The dose should be individualised for each patient. The recommended starting dose of mecasermin is
0.04 mg/kg twice daily by subcutaneous injection. If no significant treatment-related adverse events
occur for at least one week, the dose may be raised in increments of 0.04 mg/kg to the maximum dose
of 0.12 mg/kg given twice daily. Doses greater than 0.12 mg/kg given twice daily have not been
evaluated in children with severe Primary IGFD.
If the recommended dose is not tolerated by the subject, treatment with a lower dose can be
considered. Treatment success should be evaluated based on height velocities. The lowest dose that
was associated with substantial growth increases on an individual basis was 0.04 mg/kg BID.
INCRELEX should be administered shortly before or after a meal or snack. If hypoglycaemia occurs
with recommended doses, despite adequate food intake, the dose should be reduced. If the patient is
unable to eat, for any reason, INCRELEX should be withheld. The dose of mecasermin should never
be increased to make up for one or more omitted doses.
Injection sites should be rotated to a different site with each injection.
INCRELEX should be administered using sterile disposable syringes and injection needles. The
syringes should be of small enough volume that the prescribed dose can be withdrawn from the vial
with reasonable accuracy.
INCRELEX is not recommended for use in children below age 2 due to a lack of data on safety and
efficacy (see section 5.1).
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
Intravenous administration.
Active or suspected neoplasia. Therapy should be discontinued if evidence of neoplasia develops.
Benzyl alcohol must not be given to premature babies or neonates.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Thyroid and nutritional deficiencies should be corrected before initiating INCRELEX treatment.
INCRELEX is not a substitute for GH treatment.
INCRELEX should not be used for growth promotion in patients with closed epiphyses.
INCRELEX should be administered shortly before or after a meal or snack, because it may have
insulin-like hypoglycaemic effects. Special attention should be paid to young children, children with a
history of hypoglycaemia and children with inconsistent food intake. Patients should avoid engaging
in any high-risk activities within 2-3 hours after dosing, particularly at the initiation of INCRELEX
treatment, until a well tolerated dose of INCRELEX has been established. If a person with severe
hypoglycemia is unconscious or otherwise unable to ingest food normally, an injection of glucagon
may be required. Persons with a history of severe hypoglycemia should have glucagon available. At
the time of initial prescription, physicians should educate parents on the signs, symptoms and
treatment of hypoglycaemia, including injection of glucagon.
Doses of insulin and/or other hypoglycaemic agents may need to be reduced for diabetic subjects
using INCRELEX.
Echocardiogram is recommended before initiation of INCRELEX treatment in all patients. Patients
who terminate treatment should also have an echocardiogram. Patients with abnormal echocardiogram
findings or cardiovascular symptoms should be followed regularly with echocardiogram procedures.
Lymphoid tissue (e.g., tonsillar) hypertrophy associated with complications, such as snoring, sleep
apnoea, and chronic middle-ear effusions have been reported with the use of INCRELEX. Patients
should have examinations periodically and at the occurrence of clinical symptoms to rule out such
potential complications or to initiate appropriate treatment.
Intracranial hypertension (IH) with papilloedema, visual changes, headache, nausea and/or vomiting
has been reported in patients treated with INCRELEX, as has been reported with therapeutic GH
administration. IH-associated signs and symptoms resolved after interruption of dosing. Funduscopic
examination is recommended at the initiation, periodically during the course of INCRELEX therapy
and at the occurrence of clinical symptoms.
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis and progression of scoliosis can occur in patients who experience
rapid growth. These conditions and other symptoms and signs known to be associated with GH
treatment in general should be monitored during INCRELEX treatment. Any patient with the onset of
a limp or complaint of hip or knee pain should be evaluated.
In post-marketing experience in patients treated with INCRELEX, cases of hypersensitivity, urticaria,
pruritus and erythema have been reported. These have been observed both as being systemic and/or
local to the injection site. A small number of cases indicative of anaphylaxis requiring hospitalization
have been reported. Parents and patients should be informed that such reactions are possible and that if
a systemic allergic reaction occurs, treatment should be interrupted and prompt medical attention
should be sought.
Treatment should be reconsidered if after a year patients remain non-responsive.
Persons who have allergic reactions to injected IGF-1, who have unexpectedly high blood values of
IGF-1 after injection, or who fail to show a growth response may be having an antibody response to
injected IGF-1. In such instances, follow the instructions for antibody testing.
INCRELEX contains 9 mg/ml benzyl alcohol as a preservative.
Benzyl alcohol may cause toxic reactions and anaphylactoid reactions in infants and children up to 3
years old.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No interaction studies have been performed.
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
A negative pregnancy test and education about adequate contraception are recommended for all
women of child bearing potential prior to treatment with INCRELEX.
There are no adequate data for the use of mecasermin in pregnant women.
Animal studies are insufficient with respect to pregnancy (see section 5.3). The potential risk for
humans is unknown.
INCRELEX should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary.
Breast-feeding while taking INCRELEX is not recommended.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed. However,
hypoglycaemia may impair the ability to drive or use machines.
An integrated safety database from clinical studies contains 76 subjects with severe Primary IGFD
treated for a mean duration of 4.4 years and representing 321 subject-years.
Hypoglycaemia is the most frequently reported adverse drug reaction. The thirty-six subjects (47%)
who had one or more episodes of hypoglycaemia included 4 subjects who had hypoglycaemic seizure
on one or more occasion. Of the 36 subjects, 12 (33%) had a history of hypoglycaemia prior to
beginning treatment. The frequency of hypoglycaemia was highest in the first month of treatment, and
episodes were more frequent in younger children. Symptomatic hypoglycaemia was generally avoided
when a meal or snack was consumed either shortly before or after the administration of INCRELEX.
Injection site hypertrophy occurred in 24 subjects (32%).
This reaction was generally associated with
lack of proper rotation of injections. When injections were properly dispersed, the condition resolved.
Tonsillar hypertrophy was noted in 12 (16%) subjects, particularly in the first 1 to 2 years of therapy
with lesser tonsillar growth in subsequent years.
Snoring, generally beginning in the first year of treatment, was reported in 17 subjects (22%).
Hypoacusis was reported in 15 subjects (20%).
Intracranial hypertension occurred in three subjects (4%). In two subjects the events resolved without
interruption of INCRELEX treatment. INCRELEX treatment was discontinued in the third subject and
resumed later at a lower dose without recurrence. Fourteen subjects (18%) had headache considered
related to study drug.
During clinical trials in other indications totalling approximately 300 patients, reports of local and/or
systemic hypersensitivity were received for 8% of patients. All cases were mild or moderate in
severity and none was serious.
As with all protein pharmaceuticals, some patients may develop antibodies to INCRELEX. Anti-IGF-1
antibodies were observed in 11 of 23 children with severe Primary IGFD tested during the first year of
therapy. No attenuation of growth was observed as a consequence of the development of antibodies.
Table 1 contains very common (≥ 1/10) and common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10) adverse reactions for which
there is at least a reasonable suspicion of a causal relationship to INCRELEX treatment which
occurred in clinical trials. Within each frequency grouping, undesirable effects are presented in order
of decreasing seriousness.
Table 1: Adverse Drug Reactions in Clinical Trials
Cardiac murmur, abnormal
tympanometry, abnormal
echocardiogram, increased
alanine aminotransferase*,
increased aspartate
aminotransferase*, increased
weight
Cardiomegaly, ventricular
hypertrophy, atrial
hypertrophy*, tachycardia,
tachycardia paroxysmal*,
mitral valve incompetence*,
tricuspid valve
incompetence*
Congenital, Familial and Genetic
Disorders
Congenital jaw malformation,
pigmented naevus*
Blood and Lymphatic System
Disorders
Convulsions, febrile
convulsion*, benign
intracranial hypertension, loss
of consciousness*, sleep
apnoea syndrome, dizziness,
tremor*, restless leg
syndrome*
Papilloedema, reduced visual
acuity*, myopia*
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders
Otorrhoea, ear disorder*,
middle ear disorder*,
tympanic membrane
disorder*, ear pain, ear
congestion*, fluid in middle
ear
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal
Disorders
Tonsillar hypertrophy,
snoring
Adenoidal hypertrophy, nasal
turbinate hypertrophy*,
dyspnoea*, nasal mucosal
disorder*, obstructive airway
disorder*, abnormal
respiration*, nasal
congestion, mouth breathing















Gastrointestinal Disorders
Vomiting, retching*,
abdominal pain*, upper
abdominal pain*, abdominal
distension*, dysphagia*
Renal and Urinary Disorders
Nephrolithiasis*,
hydronephrosis*, renal colic*
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue
Disorders
Skin hypertrophy,
acrochordons*, abnormal hair
texture*
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue
Disorders
Arthralgia, pain in extremity,
myalgia, scoliosis*, spinal
deformity*, soft tissue
disorder*, muscle cramp*,
flank pain*, musculoskeletal
stiffness*
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders Hypoglycaemia
Hypoglycaemic seizure,
hyperglycaemia,
hyperlipidaemia*, obesity*
Infections and Infestations
Febrile infection*, upper
respiratory tract infection*,
otitis media, otitis media
serous, chronic otitis media
serous *, otitis externa*,
pharyngitis*, tonsillitis, ear
infection, oral candidiasis*
Surgical and Medical Procedures
Adenotonsillectomy*,
adenoidectomy, ear tube
insertion
General Disorders and Administration
Site Conditions
Injection site hypertrophy
Mucosal membrane
hyperplasia, hypertrophy,
injection site pain, injection
site bruising, injection site
fibrosis*, injection site
reaction*, injection site
swelling*, injection site
induration*, injection site
pigmentation changes*,
mucosal oedema*, asthenia*,
lethargy*, chest discomfort*
Reproductive System and Breast
Disorders
Gynaecomastia, ovarian cyst*
















Depression*, sleep terror,
nervousness, abnormal
behaviour*, disorientation*
* = occurred in only 1 subject (1%)
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of INCRELEX.
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible
to reliably estimate their frequency.
-
Systemic hypersensitivity:
anaphylaxis, generalized urticaria, angioedema, dyspnoea
The symptoms in the cases indicative of anaphylaxis included hives, angioedema and dyspnoea. Some
patients required hospitalization. Upon re-administration, symptoms did not re-occur in all patients.
-
Local allergic reactions at the injection site:
pruritis, urticaria.
No case of overdose has been reported.
Acute overdose could lead to hypoglycaemia. Long-term overdose may result in signs and symptoms
of acromegaly or gigantism.
Treatment of acute overdose of mecasermin should be directed at alleviating any hypoglycaemic
effects. Oral glucose or food should be consumed. If the overdose results in loss of consciousness,
intravenous glucose or parenteral glucagon may be required to reverse the hypoglycaemic effects.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Somatropin and agonists, ATC code: H01AC03
This medicinal product has been authorised under “Exceptional Circumstances”.
This means that due to the rarity of the disease it has not been possible to obtain complete information
on this medicinal product.
The European Medicines Agency (EMEA) will review any new information which may
become available every year and this SPC will be updated as necessary.
Mecasermin is a human insulin-like growth factor-1 (rhIGF-1) produced by recombinant DNA
technology. IGF-1 consists of 70 amino acids in a single chain with three intramolecular disulfide
bridges and a molecular weight of 7649 daltons. The amino acid sequence of the product is identical to
that of endogenous human IGF-1. The rhIGF-1 protein is synthesised in bacteria (
E. coli
) that have
been modified by the addition of the gene for human IGF-1.
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) is the principal hormonal mediator of statural growth. Under
normal circumstances, growth hormone (GH) binds to its receptor in the liver and other tissues, and
stimulates the synthesis/secretion of IGF-1. In target tissues the Type 1 IGF-1 receptor, which is
homologous to the insulin receptor, is activated by IGF-1, leading to intracellular signaling which
stimulates multiple processes leading to statural growth. The metabolic actions of IGF-1 are in part
directed at stimulating the uptake of glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids so that metabolism supports
growing tissues.








The following actions have been demonstrated for endogenous human IGF-1:
•
Skeletal growth is accomplished at the epiphyseal plates at the ends of a growing bone.
Growth and metabolism of epiphyseal plate cells are directly stimulated by GH and IGF-1.
•
Organ growth: treatment of IGF-1 deficient rats with rhIGF-1 results in whole body and
organ growth.
•
Cell growth: IGF-1 receptors are present on most types of cells and tissues. IGF-1 has
mitogenic activity that leads to an increased number of cells in the body.
IGF-1 suppresses hepatic glucose production, stimulates peripheral glucose utilization, and can reduce
blood glucose and cause hypoglycaemia.
IGF-1 has inhibitory effects on insulin secretion.
Circulating IGF-1 plays an important role in the acquisition and maintenance of bone mass.
IGF-1
increases bone density.
Five clinical studies (4 open-label and 1 double-blind, placebo-controlled) were conducted with
INCRELEX. Subcutaneous doses of mecasermin, generally ranging from 60 to 120 µg/kg given twice
daily (BID), were administered to 76 paediatric subjects with severe Primary IGFD. Patients were
enrolled in the studies on the basis of extreme short stature, slow growth rates, low IGF-1 serum
concentrations, and normal GH secretion. Baseline characteristics for the patients evaluated in the
primary and secondary efficacy analyses from the combined studies were (mean ± SD): chronological
age (years): 6.8 ± 3.8; height (cm): 85.0 ± 15.3; height standard deviation score (SDS): -6.7 ± 1.8;
height velocity (cm/yr): 2.8 ± 1.8; height velocity SDS: -3.3 ± 1.7; IGF-1 (ng/ml): 21.9 ± 24.8; IGF-1
SDS: -4.4 ± 2.0; and bone age (years): 3.9 ± 2.8. Sixty-two subjects had at least one year of treatment.
Of these, 53 (85%) had Laron syndrome-like phenotype; 7 (11%) had GH gene deletion, and 1 (2%)
had neutralizing antibodies to GH. Thirty-eight (61%) of the subjects were male; 49 (79%) were
Caucasian. Fifty-six (90%) of the subjects were prepubertal at baseline.
Annual results for height velocity, height velocity SDS, and height SDS are shown in Table 2. Pre-
treatment height velocity data were available for 59 subjects. The height velocities at a given year of
treatment were compared by paired t-tests to the pre-treatment height velocities of the same subjects
completing that treatment year.
Table 2: Annual Height Results by Number of Years Treated with INCRELEX
Pre-Tx Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Year 7 Year 8
2.8 (1.8) 8.0 (2.2) 5.8 (1.4) 5.5 (1.9) 4.7 (1.4) 4.7 (1.6) 4.8 (1.5) 4.6 (1.5) 4.5 (1.2)
Mean (SD) for change
from pre-Tx
P-value for change
from pre-Tx [1]
<0.0001 <0.0001 <0.0001 <0.0001 0.0015 0.0009 0.0897 0.2135
-3.3 (1.7) 1.9 (2.9) -0.2
(1.6)
Mean (SD) for change
from pre-Tx
P-value for change
from pre-Tx [1]
Mean (SD) for change
from pre-Tx
P-value for change
from pre-Tx [1]
Pre-Tx = Pre-treatment; SD = Standard Deviation; SDS = Standard Deviation Score
[1] P-values for comparison versus pre-Tx values were computed using paired t-tests.
Forty-seven subjects were included in an analysis of the effects of INCRELEX on bone age
advancement. The mean ± SD change in chronological age was 5.1 ± 3.0 years and the mean ± SD
change in bone age was 5.8 ± 2.9 years.
Efficacy is dose dependent. For subjects receiving doses between 100 and 120 µg/kg BID, the mean
first year height velocity was approximately 8.7 cm/yr.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
The absolute subcutaneous bioavailability of mecasermin in severe Primary IGFD subjects has not
been determined. The bioavailability of mecasermin after subcutaneous administration in healthy
subjects has been reported to be approximately 100%.


















In blood, IGF-1 is bound to six IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs), with ~80% bound as a complex with
IGFBP-3 and an acid-labile subunit. IGFBP-3 is reduced in subjects with severe Primary IGFD,
resulting in increased clearance of IGF-1 in these subjects relative to healthy subjects. The total IGF-1
volume of distribution (mean ± SD) after subcutaneous administration of INCRELEX in 12 subjects
with severe Primary IGFD is estimated to be 0.257 (± 0.073) l/kg at a mecasermin dose of
0.045 mg/kg, and is estimated to increase as the dose of mecasermin increases. Limited information is
available on the concentration of unbound IGF-1 after the administration of INCRELEX.
Both the liver and the kidney have been shown to metabolise IGF-1.
The mean terminal t
1/2
of total IGF-1 after single subcutaneous administration of 0.12 mg/kg in three
paediatric subjects with severe Primary IGFD is estimated to be 5.8 hours. Clearance of total IGF-1 is
inversely proportional to serum IGFBP-3 levels and total IGF-1 systemic clearance (CL/F) is
estimated to be 0.04 l/hr/kg at 3
mg/l IGFBP-3 in 12 subjects.
CHARACTERISTICS IN SPECIAL POPULATIONS
The pharmacokinetics of INCRELEX have not been studied in subjects greater than 65 years of age.
The pharmacokinetics of INCRELEX have not been studied in subjects younger than 12 years of age.
In children over 12 years old with Primary IGFD and in healthy adults there were no apparent
differences between males and females in the pharmacokinetics of INCRELEX.
No information is available.
No studies have been conducted in children with renal impairment.
No studies have been conducted to determine the effect of hepatic impairment on the
pharmacokinetics of mecasermin.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety
pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity or genotoxicity.
Adverse reactions not observed in clinical studies, but seen in animals at exposure levels similar to
clinical exposure levels and with possible relevance to clinical use were as follows:
In rats and rabbits reproductive toxicity was studied after intravenous but not after subcutaneous
application (the normal clinical route). These studies did not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects
with respect to fertility and pregnancy, but due to the different route of application the relevance of
these findings is unclear. Placental transfer of mecasermin was not studied.
Mecasermin was administered subcutaneously to Sprague Dawley rats at doses of 0, 0.25, 1, 4, and
10 mg/kg/day for up to 2 years. An increased incidence of adrenal medullary hyperplasia and
pheochromocytoma was observed in male rats at doses of 1 mg/kg/day and above (≥ 1 times the
clinical exposure with the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] based on AUC) and female
rats at all dose levels (≥ 0.3 times the clinical exposure with the MRHD based on AUC).
An increased incidence of keratoacanthoma in the skin was observed in male rats at doses of 4 and
10 mg/kg/day (≥ 4 times the exposure with the MRHD based on AUC). An increased incidence of
mammary gland carcinoma in both male and female rats was observed in animals treated with
10 mg/kg/day (7 times the exposure with the MRHD based on AUC). Excess mortality secondary to
IGF-1 induced hypoglycaemia was observed in the carcinogenesis studies.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Benzyl alcohol
Sodium chloride
Polysorbate 20
Glacial acetic acid
Sodium acetate
Water for injections
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal
products.
After opening:
Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 30 days at 2°C to 8°C.
From a microbiological point of view, once opened, the product may be stored for a maximum of
30 days at 2°C to 8°C. Other in-use storage times and conditions are the responsibility of the user.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C).
Do not freeze.
Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
6.5
Nature and contents of container
4 ml of solution in a 5 ml vial (type I glass) closed with a latex-free stopper (bromobutyl/isoprene
polymer) and a seal (lacquered plastic).
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
INCRELEX is supplied as a sterile solution with preservative for multiple use.
The solution should be clear immediately after removal from the refrigerator. If the solution is cloudy,
or contains particulate matter, it must not be injected.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Ipsen Pharma
65, quai Georges Gorse
92100 Boulogne-Billancourt
France
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 03/08/2007
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
MANUFACTURER OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE
SUBSTANCE AND MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION
HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH RELEASE
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
SPECIFIC OBLIGATIONS TO BE FULFILLED BY THE
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
A. MANUFACTURER OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE SUBSTANCE AND
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer of the biological active substance
Lonza Baltimore, Inc.
5901 East Lombard Street
Baltimore, Maryland 21224
USA
Name and address of the manufacturer(s) responsible for batch release
Beaufour Ipsen Industrie
Rue d'Ethe Virton
28100 Dreux
France
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to restricted medical prescription (See Annex I: Summary of Product
Characteristics, section 4.2).
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
The MAH must ensure that, at launch, all physicians who are expected to prescribe INCRELEX are
provided with a “physician information pack” containing the following:
Product information
Physician information about INCRELEX (information card, dosing guide, and a dose calculator)
Patient information pack
The physician information about INCRELEX should contain the following key elements:
•
To educate parents on the signs, symptoms and treatment of hypoglycaemia, including
injection of glucagon.
•
That patients should have examinations of the ears, nose and throat periodically and at the
occurrence of clinical symptoms to rule out such potential complications or to initiate
appropriate treatment.
•
To perform a routine funduscopic examination prior to beginning treatment and periodically
during treatment or at the occurrence of clinical symptoms.
•
INCRELEX is contraindicated in the presence of active or suspected neoplasia, and therapy
should be discontinued if evidence of neoplasia develops.
•
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis and progression of scoliosis can occur in patients who
experience rapid growth. These conditions should be monitored during INCRELEX treatment.
•
To inform parents and patients that systemic allergic reactions are possible and that if this
occurs treatment should be interrupted and prompt medical attention should be sought.
•
Immunogenicity sampling information.




The patient information about INCRELEX should contain the following information:
•
That INCRELEX should be administered shortly before or after a meal or snack because it has
insulin-like hypoglycaemic effects.
•
The signs and symptoms of hypoglycaemia. Instructions on the treatment of hypoglycaemia.
That parents and caregivers should always ensure that the child has a source of sugar.
Instructions on the administration of glucagon should severe hypoglycaemia occur.
•
INCRELEX should not be administered if the patient is unable to eat for any reason. The dose
of INCRELEX should not be doubled to make up for one or more omitted doses.
•
To avoid engaging in any high-risk activities (such as vigorous physical activity) within 2 - 3
hours after dosing, particularly at the initiation of INCRELEX treatment, until a well-tolerated
dose of INCRELEX has been established.
•
Instructions to change and rotate the site of injection for each injection to avoid the
development of lipohypertrophy.
•
Instructions to report the onset or worsening of snoring that may indicate an increase in
growth of tonsils and/or adenoids following the beginning of treatment with INCRELEX.
•
To report the onset of severe headache blurred vision and associated nausea and vomiting to
their physician.
•
To report any onset of a limp or complaint of hip or knee pain to their physician so it can be
evaluated.
In addition there will be a dosing guide, and a dose calculator, for use by physician and patients to
include information on the individualised dose escalation to minimise the risk of medication errors and
hypoglycaemia.
•
OTHER CONDITIONS
Pharmacovigilance system
The MAH must ensure that the system of pharmacovigilance, as described in version 3 dated 3 June
2008 presented in Module 1.8.1. of the Marketing Authorisation Application, is in place and
functioning before and whilst the product is on the market.
Risk Management plan
The MAH commits to performing the studies and additional pharmacovigilance activities detailed in
the Pharmacovigilance Plan, as agreed in Version 2 of 1.9. of the Risk Management Plan (RMP)
presented in Module 1.8.2. of the Marketing Authorisation Application and any subsequent updates of
the RMP agreed by the CHMP
As per the CHMP Guideline on Risk Management Systems for medicinal products for human use, the
updated RMP should be submitted at the same time as the next Periodic Safety Update Report
(PSUR).
In addition, an updated RMP should be submitted
• When new information is received that may impact on the current Safety Specification,
Pharmacovigilance Plan or risk minimisation activities
• Within 60 days of an important (pharmacovigilance or risk minimisation) milestone being
reached
• At the request of the EMEA
C. SPECIFIC OBLIGATIONS TO BE FULFILLED BY THE MARKETING
AUTHORISATION HOLDER
The Marketing Authorisation Holder shall complete the following programme of studies within the
specified time frame, the results of which shall form the basis of the annual reassessment of the
benefit/risk profile.
•
To develop and validate an immunogenicity assay for assessing anti-IGF-I antibodies.
•
To perform one long-term safety study where mecasermin treatment is initiated in early phase of
childhood and continued to adulthood in order to investigate:
•
Long-term toxicity in patients undergoing developmental changes
•
Possible occurrence of malignancies as well as other risks
The next interim report shall be submitted by 31/12/2011, and subsequent interim reports will be
submitted every year until the final patient is followed for 5 years.
ANNEX III
LABELING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
INCRELEX 10 mg/ml solution for injection.
Mecasermin
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
One ml contains 10 mg of mecasermin.
Each vial contains 40 mg of mecasermin.
Other ingredients: benzyl alcohol, sodium chloride, polysorbate 20, glacial acetic acid, sodium acetate
and water for injections.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Solution for injection.
One multi-use vial of 4 ml.
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous use.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
EXP
After first opening, use within 30 days.




















SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator.
Do not freeze.
Keep vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Ipsen Pharma
65, quai Georges Gorse
92100 Boulogne-Billancourt
France
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE



















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
INCRELEX 10 mg/ml solution for injection
Mecasermin
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
-
If you have further questions, please ask the doctor or pharmacist.
-
This medicine has been prescribed for you/your child. Do not pass it on to others. It may
harm them, even if their symptoms are the same.
-
If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this
leaflet, please tell the doctor or pharmacist.
1. What INCRELEX is and what it is used for
2. Before you use INCRELEX
3. How to use INCRELEX
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store INCRELEX
6. Further information
1.
WHAT INCRELEX IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
-
INCRELEX is a liquid that contains man-made insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), which
is similar to the IGF-1 made by your body.
-
INCRELEX is used to treat children or adolescents who are very short for their age
because their bodies do not make enough IGF-1. This condition is called primary IGF-1
deficiency.
2.
BEFORE YOU USE INCRELEX
-
if you/your child is allergic (hypersensitive) to mecasermin or any of the other ingredients
of INCRELEX.
-
if you/your child has cancer.
-
by injecting directly into a vein.
-
Benzyl alcohol must not be given to premature babies or neonates.
Take special care with INCRELEX
-
if you/your child has a curved spine (scoliosis). They should be monitored for progression
of their scoliosis.
-
if you/your child has enlarged tonsils (tonsillar hypertrophy). They should have
examinations periodically.
-
if you/your child has symptoms of increased pressure in the brain (intracranial
hypertension), such as headache with vomiting, contact the doctor for advice.
- if you/your child has a localised reaction at the injection site or generalised allergic
reaction with INCRELEX. Call the doctor as soon as possible if you/your child get a
localised rash. Get medical help immediately if you/your child has a generalised allergic
reaction (hives, trouble breathing, faintness or collapse and feeling generally unwell).
-
if you/your child has finished growing (the bone growth plates are closed).
-
the use of INCRELEX has not been studied in children under 2 years of age and is
therefore not recommended.
Especially tell the doctor if you/your child takes insulin or other anti-diabetes medicines. A dose
adjustment may be needed for these medicines.
Please tell the doctor or pharmacist if you/your child is taking or has recently taken any other
medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription, herbal medicines and vitamin
supplements.
Taking INCRELEX with food and drink
INCRELEX should be administered shortly before or after eating, because it may have insulin-like
hypoglycaemic effects and so it may decrease blood sugar levels.
The doses should be withheld when a meal or snack is omitted. The dose should never be increased to
make up for one or more omitted doses.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
INCRELEX therapy should be discontinued if pregnancy occurs.
INCRELEX should not be administered to a breast-feeding mother.
Driving and using machines
No studies of the effects of INCRELEX on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
However, hypoglycaemia may impair the ability to drive and use machines.
Patients should avoid engaging in any high-risk activities (e.g., driving, etc.) within 2-3 hours after
dosing, particularly at the initiation of INCRELEX treatment, until a dose of INCRELEX has been
established without occurrence of significant treatment-related adverse events.
Important information about some of the ingredients of INCRELEX
INCRELEX contains 9 mg per ml benzyl alcohol as a preservative.
Benzyl alcohol may cause toxic reactions and allergic reactions in infants and children up to 3 years
old.
Always use INCRELEX exactly as your/your child’s doctor has told you. You should check with
your/your child’s doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure. The typical dose is 0.04 to 0.12 mg/kg of
patient weight administered twice a day. See the ‘Instructions for Use’ at the end of this leaflet.
Inject INCRELEX just under your/your child’s skin shortly before or after a meal or snack. Do not
give you/your child’s dose of INCRELEX if you/your child cannot eat for any reason. Do not make up
the missed dose by giving two doses the next time.
Inject INCRELEX just below the skin in your/your child’s upper arm, upper leg (thigh), stomach area
(abdomen), or buttocks. Never inject it into a vein or muscle. Change the injection site for each
injection.
Only use INCRELEX that is clear and colourless.
Treatment with INCRELEX is a long-term therapy. For further information ask the doctor.
If you use more INCRELEX than you should
If more INCRELEX than recommended was injected, please tell the doctor.
Acute overdosage could lead to hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar). Long-term overdose may result in
enlargement of certain body parts (e.g., hands, feet, parts of the face) or excessive growth of the whole
body.
Treatment of acute overdose of INCRELEX should be directed at reversing hypoglycaemia. Sugar-
containing fluids or food should be consumed. If the patient is not awake or alert enough to drink
sugar-containing fluids, an injection of glucagon into the muscle may be necessary to reverse the low
blood sugar. Your doctor or nurse will instruct you how to give the injection of glucagon.
If you forget to use INCRELEX
Do not use a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop using INCRELEX
A disruption or early ending of treatment with INCRELEX may impair the success of the growth
therapy. Please ask the doctor for advice before stopping the treatment.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask the doctor or pharmacist.
Like all medicines, INCRELEX can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell the doctor or pharmacist.
The very common side effects (likely to occur in more than 1 out of 10 patients) which occurred in
clinical trials are listed below.
Hypoglycaemia (Low Blood Sugar):
INCRELEX, like insulin, may lower blood sugar levels. Signs of low blood sugar are: dizziness,
tiredness, restlessness, hunger, irritability, trouble concentrating, sweating, nausea and fast or irregular
heartbeats.
Severe hypoglycaemia may cause unconsciousness, seizures or death. If you/your child take
INCRELEX, you/your child should avoid participating in high risk activities (such as vigorous
physical activity) within 2 to 3 hours after INCRELEX injection, especially at the beginning of
INCRELEX treatment.
Before beginning treatment with INCRELEX the doctor or nurse will explain to you how to treat
hypoglycaemia. You/your child should always have a source of sugar such as orange juice, glucose
gel, sweets, or milk available in case symptoms of hypoglycaemia occur. For severe hypoglycaemia, if
you/your child is not responsive and cannot drink sugar-containing fluids, you should give an injection
of glucagon. The doctor or nurse will instruct you how to give the injection. Glucagon raises the blood
sugar when it is injected. It is important that you/your child have a well-balanced diet including
protein and fat such as meat and cheese in addition to sugar-containing foods.
Increased blood sugar has also been observed with INCRELEX treatment.
Reactions at the Injection Site:
Injecting INCRELEX can cause local lipoatrophy (loss of fat), lipohypertrophy (increase of fat), or
pain, redness or bruising at the injection site. Injection site reactions can be avoided by changing the
injection site at each injection (injection site rotation).
Enlarged tonsils:
INCRELEX may enlarge you/your child’s tonsils. Some signs of enlarged tonsils include: snoring,
difficulty breathing or swallowing, sleep apnea (a condition where breathing stops briefly during
sleep), or fluid in the middle ear, as well as infections of the ear. Sleep apnea can cause excessive
daytime sleepiness. Call the doctor should these symptoms bother you/your child. An infection of the
tonsils has also been observed. The doctor should regularly examine your/your child’s tonsils.
Swelling inside the nose, enlarged thymus and lymph nodes have been seen with INCRELEX
treatment.
Hypoacusis (hearing loss)
Tell the doctor if you/your child develop hearing problems.
The common side effects (likely to occur in fewer than 1 out of 10 patients) which occurred in clinical
trials are listed below.
Heart abnormalities:
In some patients treated with INCRELEX, an ultrasound examination of the heart (echocardiogram)
showed an increased size of the heart muscle. Your doctor may perform an echocardiogram before,
during and after INCRELEX treatment.
Also, a racing pulse and heart valve abnormalities have been reported with INCRELEX treatment.
Intracranial hypertension (increased pressure in the brain):
INCRELEX, like growth hormone, can sometimes cause a temporary increase in pressure within the
brain. The symptoms of intracranial hypertension can include headache and nausea with vomiting.
Tell the doctor if you/your child has headache with vomiting. Your doctor can check to see if
intracranial hypertension is present. If it is present, your doctor may decide to temporarily reduce or
discontinue INCRELEX therapy. INCRELEX may be started again after the episode is over.
Vision disturbances have also been reported.
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis:
This is a situation where the top of the upper leg (femur) slips apart. Get medical attention for
you/your child immediately if you/your child develops a limp or has hip or knee pain.
Worsened scoliosis (caused by rapid growth):
If you/your child has scoliosis, you/your child will need to be checked often for an increase in the
curve of the spine. Pain and stiffness in muscles or joints, as well as jaw malformations, have also
been seen with INCRELEX treatment.
Infections:
Infections of the mouth, throat and the upper airways have been observed in children with Increlex
treatment. Such infections may be associated with fever.
Kidney disorders
:
Kidney stones have been reported, as well as associated pain and kidney swelling.
Reproductive system
:
Breast enlargement, as well as cysts in the ovaries, have been observed.
Stomach pain, difficulties swallowing, retching and vomiting have occurred with INCRELEX
treatment. Weight gain has also been reported, as have increases in blood fat and in liver enzyme
values.
Skin and hair changes:
Skin thickening, moles, skin tags, and abnormal hair texture have been seen with INCRELEX
treatment.
Other reported adverse events include lack of energy, depression, nervousness, disorientation, chest
discomfort, dizziness, trembling and restless legs.
During post-marketing experience the following adverse events have been reported: serious allergic
reactions (anaphylaxis) which can cause generalised hives, difficulty in breathing, dizziness, swelling
of the face and/or throat. Local allergic reactions at the injection site (itching, hives) have also been
reported. The frequency of these events occurring cannot be estimated from the available data.
Tell the doctor if you/your child develops serious allergic reactions.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use INCRELEX after the expiry date which is stated on the label after EXP. The expiry date
refers to the last day of the month.
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C). Do not freeze.
Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
After first use, the vial may be stored for up to 30 days at 2 to 8ºC.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
-
The active substance is mecasermin. One ml contains 10 mg of mecasermin. Each vial
contains 40 mg of mecasermin.
-
The other ingredients are: benzyl alcohol, sodium chloride, polysorbate 20, glacial acetic
acid, sodium acetate, and water for injections.
What INCRELEX looks like and contents of the pack
INCRELEX is a clear and colourless solution for injection supplied in a glass vial closed with a
stopper and a seal. The vial contains 4 ml of liquid.
INCRELEX is supplied as a pack containing one glass vial.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorisation Holder:
Ipsen Pharma
65, quai Georges Gorse
92100 Boulogne-Billancourt
Manufacturer:
Beaufour Ipsen Industrie
Rue d'Ethe Virton
28100 Dreux
France
For any information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the Marketing
Authorisation Holder.
België/Belgique/Belgien,
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
Ipsen NV
Guldensporenpark 87
B-9820 Merelbeke
België /
Belgique/Belgien
Tél/Tel: + 32 - 9 -243 96 00
Italia
Ipsen SpA
Via A. Figino, 16
I-20156 Milano
Tel: + 39 - 02 - 39 22 41
România,
Болгария
Beaufour Ipsen Pharma
Aleea Alexandru, nr.10, Ap.2-4, Sct.1
Bucuresti, 011821 - RO
Tel: + 40 21(0) 231 27 20
Latvija
Beaufour Ipsen Pharma
Bauskas 58
Riga LV 1004
Tel: +371 67622233
Česká republika
Ipsen Pharma
Evropská 136/810
CZ-160 00 Praha 6
Tel: + 420 242 481 821
Lietuva
Beaufour Ipsen Pharma Lietuvos filialas
Betygalos g. 2,
LT-47183 Kaunas
Tel. + 370 37 337854
Danmark, Norge, Suomi/Finland, Sverige,
Ísland
Institut Produits Synthèse (IPSEN) AB
Kista Science Tower
Färögatan 33
Magyarország
Beaufour Ipsen Pharma SAS Magyarországi
Kereskedelmi Képviselet
1133 Budapest,
Árbóc u. 6.
Tel: +36 1 555 5930
SE - 164 51 Kista
Sverige/Ruotsi/Svíþjóð
Tel/Tlf/Puh/Sími: +46 8 588 370 70
Deutschland, Österreich
Ipsen Pharma GmbH
Einsteinstr. 30
D-76275 Ettlingen
Deutschland
Tel: + 49 - 7243 184-80
Nederland
Ipsen Farmaceutica B.V.
Taurusavenue 33 B
NL-2132 LS Hoofddorp
Tel: + 31 23 55 41 600
Eesti
ESTOBIIN OÜ
Udeselja 4-4
11913, Tallinn, Estonia
Tel: +372 600 2996
Polska
Ipsen Poland Sp. z o.o.
Al. Jana Pawła II
29
PL-00- 867 Warszawa
Tel.: + 48 (0) 22 653 68 00
Ελλάδα, Κύπρος, Malta
Ipsen EΠΕ
Αγ. ∆ηµητρίου 63
Άλιµος
GR-17456 Αθήνα
Ελλάδα
Τηλ: + 30 - 210 - 984 3324
Portugal
Ipsen Portugal - Produtos Farmacêuticos S.A.
Alameda Fernão Lopes, n
o
16-11
o
, Miraflores
P-1495 - 190 Algés
Tel: + 351 - 21 - 412 3550
España
Ipsen Pharma S.A.
Ctra. Laureà Miró 395
Sant Feliu de Llobregat
E-08980 Barcelona
Tel: + 34 - 936 - 858 100
Slovenija
Pharmaswiss d.o.o
Dolenjska cesta 242c
SI-1000 Ljubljana
Tel: + 386 1 236 47 00
France
Ipsen Pharma
65 quai Georges Gorse
F-92100 Boulogne-Billancourt
Tel: +33 - 1 - 58 33 50 00
United Kingdom
Ipsen Ltd.
190 Bath Road
Slough, Berkshire
SL1 3XE
Tel: + 44 - (0)1753 - 62 77 00
Ireland
Ipsen Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
7 Upper Leeson Street
IRL-Dublin 4
Tel: + 353 - 1 - 668 1377
Slovenská republika
Liek s.r.o.
Hviezdoslavova 19
SK-903 01 Senec
Tel. +421 245 646 322
This leaflet was last approved in
This medicine has been authorised under “Exceptional Circumstances”.
This means that because of the rarity of this disease it has been impossible to get complete information
on this medicine.
The European Medicines Agency (EMEA) will review any new information on the medicine every
year and this leaflet will be updated as necessary.
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) web
site: http://www.emea.europa.eu/ There are also links to other websites about rare diseases and
treatments.
<------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
INCRELEX should be administered using sterile disposable syringes and injection needles. The
syringes should be of small enough volume that the prescribed dose can be withdrawn from the vial
with reasonable accuracy.
Wash your hands before getting INCRELEX ready for your/your child’s injection.
Use a new disposable needle and syringe every time you give a dose. Use syringes and needles
only once. Throw them away properly.
Never
share needles and syringes.
Check the liquid to make sure it is clear and colourless. Do not use after the expiry date or if it
is cloudy or if you see particles. If a vial freezes, dispose appropriately.
If you are using a new vial, remove the protective cap. Do not remove the rubber stopper.
Wipe the rubber stopper of the vial with an alcohol swab to prevent contamination of the vial by
germs that may be introduced by repeated needle insertions (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Wipe top
with alcohol


Before putting the needle into the vial, pull back on plunger to draw air into the syringe equal
to the prescribed dose. Put the needle through the rubber top of the vial and push the plunger to
inject air into the vial (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: Inject air
into vial
Leave the syringe in the vial and turn both upside down. Hold the syringe and vial firmly (see
Figure 3).
Figure 3: Prepare for
extraction




8. Make sure the tip of the needle is in the liquid (see Figure 4). Pull the plunger to withdraw the
correct dose into the syringe (see Figure 5).
Figure 5: Extract
correct dose
9. Before you take the needle out of the vial, check the syringe for air bubbles. If bubbles are in the
syringe, hold the vial and syringe with needle straight up and tap the side of the syringe until the
bubbles float to the top. Push the bubbles out with the plunger and draw liquid back in until you
have the correct dose (see Figure 6).
Figure 6: Remove air bubbles
and refill syringe
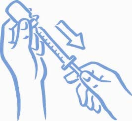




10. Remove the needle from the vial. Do not let the needle touch anything. You
are now ready to inject (see Figure 7).
Figure 7: Ready to
inject
Inject INCRELEX as instructed by the doctor.
Do not give the injection if you/your child is unable to eat shortly before or after the injection.
Decide on an injection area – upper arm, thigh, buttock, or abdomen (see below). The injection
site should be changed for each injection (rotate the injection site).
Use alcohol or soap and water to clean the skin where you are going to inject you/your child.
The injection site should be dry before you inject.


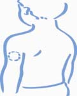


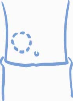

Lightly pinch the skin. Insert the needle in the way the doctor showed you. Release the skin (see
Figure A).
Figure A: Lightly pinch
the skin and inject as
instructed
Slowly push in the plunger of the syringe all the way, making sure you have injected all the
liquid. Pull the needle straight out and gently press on the spot where you injected you/your
child with gauze or a cotton ball for a few seconds.
Do not rub the area
(see Figure B).
Figure B: Press (don’t rub)
with gauze or cotton
5.
Follow the doctor’s instructions for throwing away the needle and syringe. Do not recap the
syringe. Used needle and syringe should be placed in a sharps container (such as a biohazard
container), hard plastic container (such as a detergent bottle), or metal container (such as an
empty coffee can). Such containers should be sealed and disposed of properly.



Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/increlex.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|










































































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































