Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Infanrix hexa, Powder and suspension for suspension for injection in a pre-filled syringe.
Diphtheria (D), tetanus (T), pertussis (acellular, component) (Pa), hepatitis B (rDNA) (HBV),
poliomyelitis (inactivated) (IPV) and Haemophilus
type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine (adsorbed).
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
After reconstitution, 1 dose (0.5 ml) contains:
Bordetella pertussis
antigens
Filamentous Haemagglutinin
1
Hepatitis B surface antigen
2,3
type 1 (Mahoney strain)
4
type 3 (Saukett strain)
4
Haemophilus type b polysaccharide
(polyribosylribitol phosphate)
3
conjugated to tetanus toxoid as carrier protein 20-40 micrograms
1
adsorbed on aluminium hydroxide, hydrated (Al(OH)
3
) 0.5 milligrams Al
2
produced in yeast cells (
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
) by recombinant DNA technology
3
adsorbed on aluminium phosphate (AlPO
4
)
4
propagated in VERO cells
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Powder and suspension for suspension for injection in a pre-filled syringe.
The diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, inactivated poliomyelitis (DTPa-HBV-IPV)
component is a turbid white suspension.
The lyophilised
Haemophilus influenzae
type b (Hib) component is a white powder.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Infanrix hexa is indicated for primary and booster vaccination of infants against diphtheria, tetanus,
pertussis, hepatitis B, poliomyelitis and disease caused by
Haemophilus influenzae
type b.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The primary vaccination schedule consists of three doses of 0.5 ml (such as 2, 3, 4 months; 3, 4, 5
months; 2, 4, 6 months) or two doses (such as 3, 5 months). There should be an interval of at least 1
month between doses.
The Expanded Program on Immunisation schedule (at 6, 10, 14 weeks of age) may only be used if a
dose of hepatitis B vaccine has been given at birth.
Locally established immunoprophylactic measures against hepatitis B should be maintained.
Where a dose of hepatitis B vaccine is given at birth, Infanrix hexa can be used as a replacement for
supplementary doses of hepatitis B vaccine from the age of six weeks. If a second dose of hepatitis B
vaccine is required before this age, monovalent hepatitis B vaccine should be used.
After a vaccination with 2 doses (e.g. 3, 5 months) of Infanrix hexa a booster dose must be given at
least 6 months after the last priming dose, preferably between 11 and 13 months of age.
After vaccination with 3 doses (e.g. 2, 3, 4 months; 3, 4, 5 months; 2, 4, 6 months) of Infanrix hexa a
booster dose must be given at least 6 months after the last priming dose and preferably before 18
months of age.
Booster doses should be given in accordance with the official recommendations, but, as a minimum, a
dose of Hib conjugate vaccine must be administered.
Infanrix hexa can be considered for the booster if the composition is in accordance with the official
recommendations.
Paediatric population
There is no relevant use of Infanrix hexa in children over 36 months.
Method of administration
Infanrix hexa is for deep intramuscular injection, preferably at alternating sites for subsequent
injections.
Hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any of the excipients or neomycin and polymyxin.
Hypersensitivity after previous administration of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, polio or
Hib vaccines.
Infanrix hexa is contraindicated if the infant has experienced an encephalopathy of unknown
aetiology, occurring within 7 days following previous vaccination with pertussis containing vaccine.
In these circumstances pertussis vaccination should be discontinued and the vaccination course should
be continued with diphtheria-tetanus, hepatitis B, polio and Hib vaccines.
As with other vaccines, administration of Infanrix hexa should be postponed in subjects suffering from
acute severe febrile illness. The presence of a minor infection is not a contraindication.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Vaccination should be preceded by a review of the medical history (especially with regard to previous
vaccination and possible occurrence of undesirable events) and a clinical examination.
If any of the following events are known to have occurred in temporal relation to receipt of pertussis-
containing vaccine, the decision to give further doses of pertussis-containing vaccines should be
carefully considered:
Temperature of ≥ 40.0°C within 48 hours, not due to another identifiable cause.
Collapse or shock-like state (hypotonic-hyporesponsiveness episode) within 48 hours of
vaccination.
Persistent, inconsolable crying lasting ≥ 3 hours, occurring within 48 hours of vaccination.
Convulsions with or without fever, occurring within 3 days of vaccination.
There may be circumstances, such as a high incidence of pertussis, when the potential benefits
outweigh possible risks.
As for any vaccination, the risk-benefit of immunising with Infanrix hexa or deferring this vaccination
should be weighed carefully in an infant or in a child suffering from a new onset or progression of a
severe neurological disorder.
As with all injectable vaccines, appropriate medical treatment and supervision should always be
readily available in case of a rare anaphylactic event following the administration of the vaccine.
Infanrix hexa should be administered with caution to subjects with thrombocytopenia or a bleeding
disorder since bleeding may occur following an intramuscular administration to these subjects.
Infanrix hexa should under no circumstances be administered intravascularly or intradermally.
Infanrix hexa will not prevent disease caused by pathogens other than
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
,
Clostridium tetani
,
Bordetella pertussis
, hepatitis B virus, poliovirus or
Haemophilus influenzae
type
b. However, it can be expected that hepatitis D will be prevented by immunisation as hepatitis D
(caused by the delta agent) does not occur in the absence of hepatitis B infection.
As with any vaccine, a protective immune response may not be elicited in all vaccinees (see section
5.1).
A history of febrile convulsions, a family history of convulsions or Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
(SIDS) do not constitute a contraindication for the use of Infanrix hexa. Vaccinees with a history of
febrile convulsions should be closely followed up as such adverse events may occur within 2 to 3 days
post vaccination.
HIV infection is not considered as a contraindication. The expected immunological response may not
be obtained after vaccination of immunosuppressed patients.
Since the Hib capsular polysaccharide antigen is excreted in the urine, a positive urine test can be
observed within 1-2 weeks following vaccination. Other tests should be performed in order to confirm
Hib infection during this period.
When Infanrix hexa is co-administered with Prevenar (pneumococcal saccharide conjugated vaccine,
adsorbed), the physician should be aware that data from clinical studies indicate that the rate of febrile
reactions was higher compared to that occurring following the administration of Infanrix hexa alone.
These reactions were mostly moderate (less than or equal to 39°C) and transient (see section 4.8).
Antipyretic treatment should be initiated according to local treatment guidelines.
Limited data in 169 premature infants indicate that Infanrix hexa can be given to premature children.
However, a lower immune response may be observed and the level of clinical protection remains
unknown.
The potential risk of apnoea and the need for respiratory monitoring for 48-72h should be considered
when administering the primary immunisation series to very premature infants (born ≤ 28 weeks of
gestation) and particularly for those with a previous history of respiratory immaturity.
As the benefit of the vaccination is high in this group of infants, vaccination should not be withheld or
delayed.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
There are insufficient data with regard to the efficacy and safety of simultaneous administration of
Infanrix hexa and Measles-Mumps-Rubella vaccine to allow any recommendation to be made.
Data on concomitant administration of Infanrix hexa with Prevenar (pneumococcal saccharide
conjugated vaccine, adsorbed) have shown no clinically relevant interference in the antibody response
to each of the individual antigens when given as a 3 dose primary vaccination.
As with other vaccines it may be expected that in patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy, an
adequate response may not be achieved.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
As Infanrix hexa is not intended for use in adults, adequate human data on use during pregnancy or
lactation and adequate animal reproduction studies are
not available.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The safety profile presented below is based on data from more than 16,000 subjects.
As has been observed for DTPa and DTPa-containing combinations, an increase in local
reactogenicity and fever was reported after booster vaccination with Infanrix hexa with respect to the
primary course.
Clinical trials on co-administration:
In clinical studies in which some of the vaccinees received Infanrix hexa concomitantly with Prevenar
as a booster (4th) dose of both vaccines, fever ≥ 38.0°C was reported following 43.4% of doses in
infants receiving Prevenar and Infanrix hexa at the same time as compared to 30.5% of doses in
infants receiving the hexavalent vaccine alone. Fever of greater than 39.5°C was observed following
2.6% and 1.5% of doses in infants receiving Infanrix hexa with or without Prevenar, respectively, (see
section 4.4). The incidence of fever following co-administration of the two vaccines in the primary
series was lower than that observed after the booster dose.
Tabulated summary of adverse reactions (clinical trials):
Within each frequency grouping, undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness.
Frequencies per dose are defined as follows:
Very common: (≥1/10)
Common:
Nervous system disorders:
Uncommon: somnolence
Very rare: convulsions (with or without fever)
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Uncommon: cough
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common: diarrhoea, vomiting
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Rare: rash
Very rare: dermatitis
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Very common: appetite lost
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Very common: fever ≥ 38°C, local swelling at the injection site (≤ 50 mm), fatigue, pain, redness
Common: fever >39.5°C, injection site reactions, including induration, local swelling at the injection
site (> 50 mm)*, injection site reaction
Uncommon: diffuse swelling of the injected limb, sometimes involving the adjacent joint*
Psychiatric disorders:
Very common: crying abnormal, irritability, restlessness
Common: nervousness
Post marketing surveillance:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Lymphadenopathy
Nervous system disorders:
Collapse or shock-like state (hypotonic-hyporesponsiveness episode)
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:
Apnoea [see section 4.4 for apnoea in very premature infants (≤ 28 weeks of gestation)]
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Angioedema
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Swelling of the entire injected limb*, extensive swelling reactions, injection site mass, injection site
vesicles
Immune system disorders
Anaphylactic reactions, anaphylactoid reactions (including urticaria), allergic reactions (including
pruritus)
* Children primed with acellular pertussis vaccines are more likely to experience swelling reactions
after booster administration in comparison with children primed with whole cell vaccines. These
reactions resolve over an average of 4 days.
Experience with hepatitis B vaccine:
In extremely rare cases, paralysis, neuropathy, Guillain-Barré syndrome, encephalopathy, encephalitis
and meningitis have been reported. The causal relationship to the vaccine has not been established.
Thrombocytopenia has been reported with hepatitis B vaccines.
No case of overdose has been reported.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmaco-therapeutic group: Bacterial and viral vaccines combined, ATC code J07CA09
Results obtained in the clinical studies for each of the components are summarised in the tables below:
Percentage of subjects with antibody titres ≥ assay cut-off one month after primary vaccination
with Infanrix hexa
Anti-diphtheria
(0.1 IU/ml)
†
Anti-tetanus
(0.1 IU/ml)
†
Anti-Polio type 1
(1/8 dilution)
†
Anti-Polio type 2
(1/8 dilution)
†
Anti-Polio type 3
(1/8 dilution)
†
N = number of subjects
* in a subgroup of infants not administered hepatitis B vaccine at birth, 77.7% of subjects had anti-
HBs titres ≥ 10 mIU/ml
† cut-off accepted as indicative of protection




















Percentage of subjects with antibody titres ≥ assay cut-off one month after booster vaccination
with Infanrix hexa
Booster vaccination at 11
months of age following a 3-5
month primary course
N=532
Booster vaccination during the
second year of life following a
three dose primary course
N= 2009
Anti-diphtheria
(0.1 IU/ml)
†
Anti-tetanus
(0.1 IU/ml)
†
Anti-Polio type 1
(1/8 dilution)
†
Anti-Polio type 2
(1/8 dilution)
†
Anti-Polio type 3
(1/8 dilution)
†
N = number of subjects
† cut-off accepted as indicative of protection
As the immune response to pertussis antigens following Infanrix hexa administration is equivalent to
that of Infanrix, the protective efficacy of the two vaccines is expected to be equivalent.
The clinical protection of the
pertussis component of Infanrix, against WHO-defined typical pertussis
(≥ 21 days of paroxysmal cough) was demonstrated in:
-
a prospective blinded household contact study performed in Germany (3, 4, 5 months schedule).
Based on data collected from secondary contacts in households where there was an index case with
typical pertussis, the protective efficacy of the vaccine was 88.7%.
-
a NIH sponsored efficacy study performed in Italy (2, 4, 6 months schedule. The vaccine efficacy
was found to be 84%. In a follow-up of the same cohort, the efficacy was confirmed up to 60
months after completion of primary vaccination without administration of a booster dose of
pertussis.
Results of long term follow-up in Sweden demonstrate that acellular pertussis vaccines are efficacious
in infants when administered according to the 3 and 5 months primary vaccination schedule, with a
booster dose administered at approximately 12 months. However, data indicate that protection against
pertussis may be waning at 7-8 years of age with this 3-5-12 months schedule. This suggests that a
second booster dose of pertussis vaccine is warranted in children aged 5-7 years who have previously
been vaccinated following this particular schedule.
















Protective antibodies against hepatitis B have been shown to persist for at least 3.5 years in more than
90% of children administered four doses of Infanrix hexa. Antibody levels were not different from
what was observed in a parallel cohort administered 4 doses of monovalent hepatitis B vaccine
.
The effectiveness of the Hib component of Infanrix hexa has been, and continues to be, investigated
via an extensive post-marketing surveillance study conducted in Germany. Over a five year follow-up
period, the effectiveness of the Hib components of two hexavalent vaccines, of which one was
Infanrix hexa, was 90.4% for a full primary series and 100% for a booster dose (irrespective of
priming).
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Evaluation of pharmacokinetic properties is not required for vaccines.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety, specific
toxicity, repeated dose toxicity and compatibility of ingredients.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Hib powder:
Lactose anhydrous
DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension:
Sodium chloride (NaCl)
Medium 199 containing principally amino acids, mineral salts, vitamins
Water for injections
For adjuvants, see section 2.
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal
products.
After reconstitution: an immediate use is recommended. However the stability has been demonstrated
for 8 hours at 21°C after reconstitution.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C).
Do not freeze.
Store in the original package, in order to protect from light.
For storage conditions of the reconstituted medicinal product, see section 6.3.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
Powder in a vial (type I glass) with a stopper (butyl).
0.5 ml of suspension in a pre-filled syringe (type I glass) with plunger stoppers (butyl).
Pack sizes of 1, 10, 20 and 50 with or without needles.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Upon storage, a white deposit and clear supernatant may be observed in the syringe containing the
DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension. This does not constitute a sign of deterioration.
The syringe should be well shaken in order to obtain a homogeneous turbid white suspension.
The DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension should be inspected visually for any foreign particulate matter and/or
abnormal physical appearance. In the event of either being observed, discard the vaccine.
The vaccine is reconstituted by adding the contents of the syringe to the vial containing the Hib
powder. After the addition of the DTPa-HBV-IPV vaccine to the powder, the mixture should be well
shaken until the powder is completely dissolved.
The reconstituted vaccine presents as a slightly more cloudy suspension than the liquid component
alone. This is normal and does not impair the performance of the vaccine. In the event of other
variation being observed, discard the vaccine.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals s.a.
Rue de l'Institut 89
B-1330 Rixensart, Belgium
8. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S
EU/1/00/152/001
EU/1/00/152/002
EU/1/00/152/003
EU/1/00/152/004
EU/1/00/152/005
EU/1/00/152/006
EU/1/00/152/007
EU/1/00/152/008
9. DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 23 October 2000
Date of latest renewal: 23 October 2005
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Infanrix hexa, Powder and suspension for suspension for injection in a pre-filled syringe.
Diphtheria (D), tetanus (T), pertussis (acellular, component) (Pa), hepatitis B (rDNA) (HBV),
poliomyelitis (inactivated) (IPV) and Haemophilus
type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine (adsorbed).
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
After reconstitution, 1 dose (0.5 ml) contains:
Bordetella pertussis
antigens
Pertussis toxoid
1
Filamentous Haemagglutinin
1
Hepatitis B surface antigen
2,3
Poliovirus (inactivated)
type 1 (Mahoney strain)
4
type 3 (Saukett strain)
4
Haemophilus
type b polysaccharide
(polyribosylribitol phosphate)
3
conjugated to tetanus toxoid as carrier protein 20-40 micrograms
1
adsorbed on aluminium hydroxide, hydrated (Al(OH)
3
) 0.5 milligrams Al
2
produced in yeast cells (
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
) by recombinant DNA technology
3
adsorbed on aluminium phosphate (AlPO
4
)
4
propagated in VERO cells
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Powder and suspension for suspension for injection in a pre-filled syringe.
The diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, inactivated poliomyelitis (DTPa-HBV-IPV)
component is a turbid white suspension.
The lyophilised
Haemophilus influenzae
type b (Hib) component is a white powder.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Infanrix hexa is indicated for primary and booster vaccination of infants against diphtheria, tetanus,
pertussis, hepatitis B, poliomyelitis and disease caused by
Haemophilus influenzae
type b.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The primary vaccination schedule consists of three doses of 0.5 ml (such as 2, 3, 4 months; 3, 4, 5
months; 2, 4, 6 months) or two doses (such as 3, 5 months). There should be an interval of at least 1
month between doses.
The Expanded Program on Immunisation schedule (at 6, 10, 14 weeks of age) may only be used if a
dose of hepatitis B vaccine has been given at birth.
Locally established immunoprophylactic measures against hepatitis B should be maintained.
Where a dose of hepatitis B vaccine is given at birth, Infanrix hexa can be used as a replacement for
supplementary doses of hepatitis B vaccine from the age of six weeks. If a second dose of hepatitis B
vaccine is required before this age, monovalent hepatitis B vaccine should be used.
After a vaccination with 2 doses (e.g. 3, 5 months) of Infanrix hexa a booster dose must be given at
least 6 months after the last priming dose, preferably between 11 and 13 months of age.
After vaccination with 3 doses (e.g. 2, 3, 4 months; 3, 4, 5 months; 2, 4, 6 months) of Infanrix hexa a
booster dose must be given at least 6 months after the last priming dose and preferably before 18
months of age.
Booster doses should be given in accordance with the official recommendations, but, as a minimum, a
dose of Hib conjugate vaccine must be administered.
Infanrix hexa can be considered for the booster if the composition is in accordance with the official
recommendations.
There is no relevant use of Infanrix hexa in children over 36 months.
Method of administration
Infanrix hexa is for deep intramuscular injection, preferably at alternating sites for subsequent
injections.
Hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any of the excipients or neomycin and polymyxin.
Hypersensitivity after previous administration of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, polio or
Hib vaccines.
Infanrix hexa is contraindicated if the infant has experienced an encephalopathy of unknown
aetiology, occurring within 7 days following previous vaccination with pertussis containing vaccine.
In these circumstances pertussis vaccination should be discontinued and the vaccination course should
be continued with diphtheria-tetanus, hepatitis B, polio and Hib vaccines.
As with other vaccines, administration of Infanrix hexa should be postponed in subjects suffering from
acute severe febrile illness. The presence of a minor infection is not a contraindication.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Vaccination should be preceded by a review of the medical history (especially with regard to previous
vaccination and possible occurrence of undesirable events) and a clinical examination.
If any of the following events are known to have occurred in temporal relation to receipt of pertussis-
containing vaccine, the decision to give further doses of pertussis-containing vaccines should be
carefully considered:
Temperature of ≥ 40.0°C within 48 hours, not due to another identifiable cause.
Collapse or shock-like state (hypotonic-hyporesponsiveness episode) within 48 hours of
vaccination.
Persistent, inconsolable crying lasting ≥ 3 hours, occurring within 48 hours of vaccination.
Convulsions with or without fever, occurring within 3 days of vaccination.
There may be circumstances, such as a high incidence of pertussis, when the potential benefits
outweigh possible risks.
As for any vaccination, the risk-benefit of immunising with Infanrix hexa or deferring this vaccination
should be weighed carefully in an infant or in a child suffering from a new onset or progression of a
severe neurological disorder.
As with all injectable vaccines, appropriate medical treatment and supervision should always be
readily available in case of a rare anaphylactic event following the administration of the vaccine.
Infanrix hexa should be administered with caution to subjects with thrombocytopenia or a bleeding
disorder since bleeding may occur following an intramuscular administration to these subjects.
Infanrix hexa should under no circumstances be administered intravascularly or intradermally.
Infanrix hexa will not prevent disease caused by pathogens other than
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
,
Clostridium tetani
,
Bordetella pertussis
, hepatitis B virus, poliovirus or
Haemophilus influenzae
type
b. However, it can be expected that hepatitis D will be prevented by immunisation as hepatitis D
(caused by the delta agent) does not occur in the absence of hepatitis B infection.
As with any vaccine, a protective immune response may not be elicited in all vaccinees (see section
5.1).
A history of febrile convulsions, a family history of convulsions or Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
(SIDS) do not constitute a contraindication for the use of Infanrix hexa. Vaccinees with a history of
febrile convulsions should be closely followed up as such adverse events may occur within 2 to 3 days
post vaccination.
HIV infection is not considered as a contraindication. The expected immunological response may not
be obtained after vaccination of immunosuppressed patients.
Since the Hib capsular polysaccharide antigen is excreted in the urine, a positive urine test can be
observed within 1-2 weeks following vaccination. Other tests should be performed in order to confirm
Hib infection during this period.
When Infanrix hexa is co-administered with Prevenar (pneumococcal saccharide conjugated vaccine,
adsorbed), the physician should be aware that data from clinical studies indicate that the rate of febrile
reactions was higher compared to that occurring following the administration of Infanrix hexa alone.
These reactions were mostly moderate (less than or equal to 39°C) and transient (see section 4.8).
Antipyretic treatment should be initiated according to local treatment guidelines.
Limited data in 169 premature infants indicate that Infanrix hexa can be given to premature children.
However, a lower immune response may be observed and the level of clinical protection remains
unknown.
The potential risk of apnoea and the need for respiratory monitoring for 48-72h should be considered
when administering the primary immunisation series to very premature infants (born ≤ 28 weeks of
gestation) and particularly for those with a previous history of respiratory immaturity.
As the benefit of the vaccination is high in this group of infants, vaccination should not be withheld or
delayed.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
There are insufficient data with regard to the efficacy and safety of simultaneous administration of
Infanrix hexa and Measles-Mumps-Rubella vaccine to allow any recommendation to be made.
Data on concomitant administration of Infanrix hexa with Prevenar (pneumococcal saccharide
conjugated vaccine, adsorbed) have shown no clinically relevant interference in the antibody response
to each of the individual antigens when given as a 3 dose primary vaccination.
As with other vaccines, it may be expected that in patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy, an
adequate response may not be achieved.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
As Infanrix hexa is not intended for use in adults, adequate human data on use during pregnancy or
lactation and adequate animal reproduction studies are
not available.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The safety profile presented below is based on data from more than 16,000 subjects.
As has been observed for DTPa and DTPa-containing combinations, an increase in local
reactogenicity and fever was reported after booster vaccination with Infanrix hexa with respect to the
primary course.
Clinical trials on co-administration:
In clinical studies in which some of the vaccinees received Infanrix hexa concomitantly with Prevenar
as a booster (4th) dose of both vaccines, fever ≥ 38.0°C was reported following 43.4% of doses in
infants receiving Prevenar and Infanrix hexa at the same time as compared to 30.5% of doses in
infants receiving the hexavalent vaccine alone. Fever of greater than 39.5°C was observed following
2.6% and 1.5% of doses in infants receiving Infanrix hexa with or without Prevenar, respectively, (see
section 4.4). The incidence of fever following co-administration of the two vaccines in the primary
series was lower than that observed after the booster dose.
Tabulated summary of adverse reactions (clinical trials):
Within each frequency grouping, undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness.
Frequencies per dose are defined as follows:
Very common: (≥1/10)
Common:
Nervous system disorders:
Uncommon: somnolence
Very rare: convulsions (with or without fever)
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common: diarrhoea, vomiting
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Rare: rash
Very rare: dermatitis
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Very common: appetite lost
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Very common: fever ≥ 38°C, local swelling at the injection site (≤ 50 mm), fatigue, pain, redness
Common: fever >39.5°C, injection site reactions, including induration, local swelling at the injection
site (> 50 mm)*, injection site reaction
Uncommon: diffuse swelling of the injected limb, sometimes involving the adjacent joint*
Psychiatric disorders:
Very common: crying abnormal, irritability, restlessness
Common: nervousness
Post marketing surveillance:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Lymphadenopathy
Nervous system disorders:
Collapse or shock-like state (hypotonic-hyporesponsiveness episode)
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:
Apnoea [see section 4.4 for apnoea in very premature infants (≤ 28 weeks of gestation)]
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Angioedema
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Swelling of the entire injected limb*, extensive swelling reactions, injection site mass, injection site
vesicles
Immune system disorders
Anaphylactic reactions, anaphylactoid reactions (including urticaria), allergic reactions (including
pruritus)
* Children primed with acellular pertussis vaccines are more likely to experience swelling reactions
after booster administration in comparison with children primed with whole cell vaccines. These
reactions resolve over an average of 4 days.
Experience with hepatitis B vaccine:
In extremely rare cases, paralysis, neuropathy, Guillain-Barré syndrome, encephalopathy, encephalitis
and meningitis have been reported. The causal relationship to the vaccine has not been established.
Thrombocytopenia has been reported with hepatitis B vaccines.
No case of overdose has been reported.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmaco-therapeutic group: Bacterial and viral vaccines combined, ATC code J07CA09
Results obtained in the clinical studies for each of the components are summarised in the tables below:
Percentage of subjects with antibody titres ≥ assay cut-off one month after primary vaccination
with Infanrix hexa
Anti-diphtheria
(0.1 IU/ml)
†
Anti-tetanus
(0.1 IU/ml)
†
Anti-Polio type 1
(1/8 dilution) †
Anti-Polio type 2
(1/8 dilution)
†
Anti-Polio type 3
(1/8 dilution)
†
N = number of subjects
* in a subgroup of infants not administered hepatitis B vaccine at birth, 77.7% of subjects had anti-
HBs titres ≥ 10 mIU/ml
† cut-off accepted as indicative of protection




















Percentage of subjects with antibody titres ≥ assay cut-off one month after booster vaccination
with Infanrix hexa
Booster vaccination at 11
months of age following a 3-5
month primary course
N=532
Booster vaccination during the
second year of life following a
three dose primary course
N= 2009
Anti-diphtheria
(0.1 IU/ml)
†
Anti-tetanus
(0.1 IU/ml)
†
Anti-Polio type 1
(1/8 dilution)
†
Anti-Polio type 2
(1/8 dilution)
†
Anti-Polio type 3
(1/8 dilution)
†
N = number of subjects
† cut-off accepted as indicative of protection
As the immune response to pertussis antigens following Infanrix hexa administration is equivalent to
that of Infanrix, the protective efficacy of the two vaccines is expected to be equivalent.
The clinical protection of the
pertussis component of Infanrix, against WHO-defined typical pertussis
(≥ 21 days of paroxysmal cough) was demonstrated in:
-
a prospective blinded household contact study performed in Germany (3, 4, 5 months schedule).
Based on data collected from secondary contacts in households where there was an index case with
typical pertussis, the protective efficacy of the vaccine was 88.7%.
-
a NIH sponsored efficacy study performed in Italy (2, 4, 6 months schedule. The vaccine efficacy
was found to be 84%. In a follow-up of the same cohort, the efficacy was confirmed up to 60
months after completion of primary vaccination without administration of a booster dose of
pertussis.
Results of long term follow-up in Sweden demonstrate that acellular pertussis vaccines are efficacious
in infants when administered according to the 3 and 5 months primary vaccination schedule, with a
booster dose administered at approximately 12 months. However, data indicate that protection against
pertussis may be waning at 7-8 years of age with this 3-5-12 months schedule. This suggests that a
second booster dose of pertussis vaccine is warranted in children aged 5-7 years who have previously
been vaccinated following this particular schedule.
Protective antibodies against hepatitis B have been shown to persist for at least 3.5 years in more than
90% of children administered four doses of Infanrix hexa. Antibody levels were not different from
what was observed in a parallel cohort administered 4 doses of monovalent hepatitis B vaccine
.
















The effectiveness of the Hib component of Infanrix hexa has been, and continues to be, investigated
via an extensive post-marketing surveillance study conducted in Germany.
Over a five year follow-up
period, the effectiveness of the Hib components of two hexavalent vaccines, of which one was
Infanrix hexa, was 90.4% for a full primary series and 100% for a booster dose (irrespective of
priming).
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Evaluation of pharmacokinetic properties is not required for vaccines.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety, specific
toxicity, repeated dose toxicity and compatibility of ingredients.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Hib powder:
Lactose anhydrous
DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension:
Sodium chloride (NaCl)
Medium 199 containing principally amino acids, mineral salts, vitamins
Water for injections
For adjuvants, see section 2.
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal
products.
After reconstitution: an immediate use is recommended. However the stability has been demonstrated
for 8 hours at 21°C after reconstitution.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C).
Do not freeze.
Store in the original package, in order to protect from light.
For storage conditions of the reconstituted medicinal product, see section 6.3.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
Powder in a vial (type I glass) with Bioset® with a stopper (butyl).
0.5 ml of suspension in pre-filled syringe (type I glass) with plunger stoppers (butyl).
Pack sizes of 1, 10, 20 and 50 with or without needles.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Upon storage, a white deposit and clear supernatant may be observed in the syringe containing the
DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension. This does not constitute a sign of deterioration.
The syringe should be well shaken in order to obtain a homogeneous turbid white suspension.
The DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension should be inspected visually for any foreign particulate matter and/or
abnormal physical appearance. In the event of either being observed, discard the vaccine.
The vaccine is reconstituted by adding the contents of the syringe to the vial containing the Hib
powder. It is good clinical practice to only inject a vaccine when it has reached room temperature. In
addition, a vial at room temperature ensures sufficient elasticity of the rubber closure to minimise any
coring of rubber particles. To achieve this, the vial should be kept at room temperature (25 ± 3 °C) for
at least five minutes before connecting the syringe and reconstituting the vaccine. For reconstitution,
twist and remove the plastic cover from the Bioset® and remove the cap from the syringe. Before
connecting the syringe onto the Bioset®, make sure the two containers are aligned (see Picture 1).
Connect the syringe onto the Bioset® by twisting it. Push downwards until syringe“clicks” into
position. Inject the contents of the syringe into the vial. Mix thoroughly until the Hib powder is
completely dissolved. Aspirate the reconstituted vaccine back into the syringe. Unscrew the syringe
from Bioset® and affix a needle for vaccine administration.
The reconstituted vaccine presents as a slightly more cloudy suspension than the liquid component
alone. This is normal and does not impair the performance of the vaccine. In the event of other
variation being observed, discard the vaccine.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals s.a.
Rue de l'Institut 89
B-1330 Rixensart, Belgium
8. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S
EU/1/00/152/009
EU/1/00/152/010
EU/1/00/152/011
EU/1/00/152/012
EU/1/00/152/013

EU/1/00/152/014
EU/1/00/152/015
EU/1/00/152/016
EU/1/00/152/017
EU/1/00/152/018
9. DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 23 October 2000
Date of latest renewal: 23 October 2005
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Infanrix hexa, Powder and suspension for suspension for injection.
Diphtheria (D), tetanus (T), pertussis (acellular, component) (Pa), hepatitis B (rDNA) (HBV),
poliomyelitis (inactivated) (IPV) and Haemophilus
type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine (adsorbed).
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
After reconstitution, 1 dose (0.5 ml) contains:
Bordetella pertussis
antigens
Filamentous Haemagglutinin
1
Hepatitis B surface antigen
2,3
type 1 (Mahoney strain)
4
type 3 (Saukett strain)
4
Haemophilus type b polysaccharide
(polyribosylribitol phosphate)
3
conjugated to tetanus toxoid as carrier protein 20-40 micrograms
1
adsorbed on aluminium hydroxide, hydrated (Al(OH)
3
) 0.5 milligrams Al
2
produced in yeast cells (
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
) by recombinant DNA technology
3
adsorbed on aluminium phosphate (AlPO
4
)
4
propagated in VERO cells
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Powder and suspension for suspension for injection.
The diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, inactivated poliomyelitis (DTPa-HBV-IPV)
component is a turbid white suspension.
The lyophilised
Haemophilus influenzae
type b (Hib) component is a white powder.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Infanrix hexa is indicated for primary and booster vaccination of infants against diphtheria, tetanus,
pertussis, hepatitis B, poliomyelitis and disease caused by
Haemophilus influenzae
type b.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The primary vaccination schedule consists of three doses of 0.5 ml (such as 2, 3, 4 months; 3, 4, 5
months; 2, 4, 6 months) or two doses (such as 3, 5 months). There should be an interval of at least 1
month between doses.
The Expanded Program on Immunisation schedule (at 6, 10, 14 weeks of age) may only be used if a
dose of hepatitis B vaccine has been given at birth.
Locally established immunoprophylactic measures against hepatitis B should be maintained.
Where a dose of hepatitis B vaccine is given at birth, Infanrix hexa can be used as a replacement for
supplementary doses of hepatitis B vaccine from the age of six weeks. If a second dose of hepatitis B
vaccine is required before this age, monovalent hepatitis B vaccine should be used.
After a vaccination with 2 doses (e.g. 3, 5 months) of Infanrix hexa a booster dose must be given at
least 6 months after the last priming dose, preferably between 11 and 13 months of age.
After vaccination with 3 doses (e.g. 2, 3, 4 months; 3, 4, 5 months; 2, 4, 6 months) of Infanrix hexa a
booster dose must be given at least 6 months after the last priming dose and preferably before 18
months of age.
Booster doses should be given in accordance with the official recommendations, but, as a minimum, a
dose of Hib conjugate vaccine must be administered.
Infanrix hexa can be considered for the booster if the composition is in accordance with the official
recommendations.
There is no relevant use of Infanrix hexa in children over 36 months.
Infanrix hexa is for deep intramuscular injection, preferably at alternating sites for subsequent
injections.
Hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any of the excipients or neomycin and polymyxin.
Hypersensitivity after previous administration of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, polio or
Hib vaccines.
Infanrix hexa is contraindicated if the infant has experienced an encephalopathy of unknown
aetiology, occurring within 7 days following previous vaccination with pertussis containing vaccine.
In these circumstances pertussis vaccination should be discontinued and the vaccination course should
be continued with diphtheria-tetanus, hepatitis B, polio and Hib vaccines.
As with other vaccines, administration of Infanrix hexa should be postponed in subjects suffering from
acute severe febrile illness. The presence of a minor infection is not a contraindication.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Vaccination should be preceded by a review of the medical history (especially with regard to previous
vaccination and possible occurrence of undesirable events) and a clinical examination.
If any of the following events are known to have occurred in temporal relation to receipt of pertussis-
containing vaccine, the decision to give further doses of pertussis-containing vaccines should be
carefully considered:
Temperature of ≥ 40.0°C within 48 hours, not due to another identifiable cause.
Collapse or shock-like state (hypotonic-hyporesponsiveness episode) within 48 hours of
vaccination.
Persistent, inconsolable crying lasting ≥ 3 hours, occurring within 48 hours of vaccination.
Convulsions with or without fever, occurring within 3 days of vaccination.
There may be circumstances, such as a high incidence of pertussis, when the potential benefits
outweigh possible risks.
As for any vaccination, the risk-benefit of immunising with Infanrix hexa or deferring this vaccination
should be weighed carefully in an infant or in a child suffering from a new onset or progression of a
severe neurological disorder.
As with all injectable vaccines, appropriate medical treatment and supervision should always be
readily available in case of a rare anaphylactic event following the administration of the vaccine.
Infanrix hexa should be administered with caution to subjects with thrombocytopenia or a bleeding
disorder since bleeding may occur following an intramuscular administration to these subjects.
Infanrix hexa should under no circumstances be administered intravascularly or intradermally.
Infanrix hexa will not prevent disease caused by pathogens other than
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
,
Clostridium tetani
,
Bordetella pertussis
, hepatitis B virus, poliovirus or
Haemophilus influenzae
type
b. However, it can be expected that hepatitis D will be prevented by immunisation as hepatitis D
(caused by the delta agent) does not occur in the absence of hepatitis B infection.
As with any vaccine, a protective immune response may not be elicited in all vaccinees (see section
5.1).
A history of febrile convulsions, a family history of convulsions or Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
(SIDS) do not constitute a contraindication for the use of Infanrix hexa. Vaccinees with a history of
febrile convulsions should be closely followed up as such adverse events may occur within 2 to 3 days
post vaccination.
HIV infection is not considered as a contraindication. The expected immunological response may not
be obtained after vaccination of immunosuppressed patients.
Since the Hib capsular polysaccharide antigen is excreted in the urine, a positive urine test can be
observed within 1-2 weeks following vaccination. Other tests should be performed in order to confirm
Hib infection during this period.
When Infanrix hexa is co-administered with Prevenar (pneumococcal saccharide conjugated vaccine,
adsorbed), the physician should be aware that data from clinical studies indicate that the rate of febrile
reactions was higher compared to that occurring following the administration of Infanrix hexa alone.
These reactions were mostly moderate (less than or equal to 39°C) and transient (see section 4.8).
Antipyretic treatment should be initiated according to local treatment guidelines.
Limited data in 169 premature infants indicate that Infanrix hexa can be given to premature children.
However, a lower immune response may be observed and the level of clinical protection remains
unknown.
The potential risk of apnoea and the need for respiratory monitoring for 48-72h should be considered
when administering the primary immunisation series to very premature infants (born ≤ 28 weeks of
gestation) and particularly for those with a previous history of respiratory immaturity.
As the benefit of the vaccination is high in this group of infants, vaccination should not be withheld or
delayed.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
There are insufficient data with regard to the efficacy and safety of simultaneous administration of
Infanrix hexa and Measles-Mumps-Rubella vaccine to allow any recommendation to be made.
Data on concomitant administration of Infanrix hexa with Prevenar (pneumococcal saccharide
conjugated vaccine, adsorbed) have shown no clinically relevant interference in the antibody response
to each of the individual antigens when given as a 3 dose primary vaccination.
As with other vaccines it may be expected that in patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy, an
adequate response may not be achieved.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
As Infanrix hexa is not intended for use in adults, adequate human data on use during pregnancy or
lactation and adequate animal reproduction studies are
not available.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The safety profile presented below is based on data from more than 16,000 subjects.
As has been observed for DTPa and DTPa-containing combinations, an increase in local
reactogenicity and fever was reported after booster vaccination with Infanrix hexa with respect to the
primary course.
Clinical trials on co-administration:
In clinical studies in which some of the vaccinees received Infanrix hexa concomitantly with Prevenar
as a booster (4th) dose of both vaccines, fever ≥ 38.0°C was reported following 43.4% of doses in
infants receiving Prevenar and Infanrix hexa at the same time as compared to 30.5% of doses in
infants receiving the hexavalent vaccine alone. Fever of greater than 39.5°C was observed following
2.6% and 1.5% of doses in infants receiving Infanrix hexa with or without Prevenar, respectively, (see
section 4.4). The incidence of fever following co-administration of the two vaccines in the primary
series was lower than that observed after the booster dose.
Tabulated summary of adverse reactions (clinical trials):
Within each frequency grouping, undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness.
Frequencies per dose are defined as follows:
Very common: (≥1/10)
Common:
Nervous system disorders:
Uncommon: somnolence
Very rare: convulsions (with or without fever)
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Uncommon: cough
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common: diarrhoea, vomiting
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Rare: rash
Very rare: dermatitis
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Very common: appetite lost
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Very common: fever ≥ 38°C, local swelling at the injection site (≤ 50 mm), fatigue, pain, redness
Common: fever >39.5°C, injection site reactions, including induration, local swelling at the injection
site (> 50 mm)*, injection site reaction
Uncommon: diffuse swelling of the injected limb, sometimes involving the adjacent joint*
Psychiatric disorders:
Very common: crying abnormal, irritability, restlessness
Common: nervousness
Post marketing surveillance:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Lymphadenopathy
Nervous system disorders:
Collapse or shock-like state (hypotonic-hyporesponsiveness episode)
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:
Apnoea [see section 4.4 for apnoea in very premature infants (≤ 28 weeks of gestation)]
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Angioedema
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Swelling of the entire injected limb*, extensive swelling reactions, injection site mass, injection site
vesicles
Immune system disorders
Anaphylactic reactions, anaphylactoid reactions (including urticaria), allergic reactions (including
pruritus)
* Children primed with acellular pertussis vaccines are more likely to experience swelling reactions
after booster administration in comparison with children primed with whole cell vaccines. These
reactions resolve over an average of 4 days.
Experience with hepatitis B vaccine:
In extremely rare cases, paralysis, neuropathy, Guillain-Barré syndrome, encephalopathy, encephalitis
and meningitis have been reported. The causal relationship to the vaccine has not been established.
Thrombocytopenia has been reported with hepatitis B vaccines.
No case of overdose has been reported.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmaco-therapeutic group: Bacterial and viral vaccines combined, ATC code J07CA09
Results obtained in the clinical studies for each of the components are summarised in the tables below:
Percentage of subjects with antibody titres ≥ assay cut-off one month after primary vaccination
with Infanrix hexa
Anti-diphtheria
(0.1 IU/ml)
†
Anti-tetanus
(0.1 IU/ml)
†
Anti-Polio type 1
(1/8 dilution)
†
Anti-Polio type 2
(1/8 dilution)
†
Anti-Polio type 3
(1/8 dilution)
†
N = number of subjects
* in a subgroup of infants not administered hepatitis B vaccine at birth, 77.7% of subjects had anti-
HBs titres ≥ 10 mIU/ml
† cut-off accepted as indicative of protection




















Percentage of subjects with antibody titres ≥ assay cut-off one month after booster vaccination
with Infanrix hexa
Booster vaccination at 11
months of age following a 3-5
month primary course
N=532
Booster vaccination during the
second year of life following a
three dose primary course
N= 2009
Anti-diphtheria
(0.1 IU/ml)
†
Anti-tetanus
(0.1 IU/ml)
†
Anti-Polio type 1
(1/8 dilution)
†
Anti-Polio type 2
(1/8 dilution)
†
Anti-Polio type 3
(1/8 dilution)
†
N = number of subjects
† cut-off accepted as indicative of protection
As the immune response to pertussis antigens following Infanrix hexa administration is equivalent to
that of Infanrix, the protective efficacy of the two vaccines is expected to be equivalent.
The clinical protection of the
pertussis component of Infanrix, against WHO-defined typical pertussis
(≥ 21 days of paroxysmal cough) was demonstrated in:
-
a prospective blinded household contact study performed in Germany (3, 4, 5 months schedule).
Based on data collected from secondary contacts in households where there was an index case with
typical pertussis, the protective efficacy of the vaccine was 88.7%.
-
a NIH sponsored efficacy study performed in Italy (2, 4, 6 months schedule. The vaccine efficacy
was found to be 84%. In a follow-up of the same cohort, the efficacy was confirmed up to 60
months after completion of primary vaccination without administration of a booster dose of
pertussis.
Results of long term follow-up in Sweden demonstrate that acellular pertussis vaccines are efficacious
in infants when administered according to the 3 and 5 months primary vaccination schedule, with a
booster dose administered at approximately 12 months. However, data indicate that protection against
pertussis may be waning at 7-8 years of age with this 3-5-12 months schedule. This suggests that a
second booster dose of pertussis vaccine is warranted in children aged 5-7 years who have previously
been vaccinated following this particular schedule.
















Protective antibodies against hepatitis B have been shown to persist for at least 3.5 years in more than
90% of children administered four doses of Infanrix hexa. Antibody levels were not different from
what was observed in a parallel cohort administered 4 doses of monovalent hepatitis B vaccine
.
The effectiveness of the Hib component of Infanrix hexa has been, and continues to be, investigated
via an extensive post-marketing surveillance study conducted in Germany. Over a five year follow-up
period, the effectiveness of the Hib components of two hexavalent vaccines, of which one was
Infanrix hexa, was 90.4% for a full primary series and 100% for a booster dose (irrespective of
priming).
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Evaluation of pharmacokinetic properties is not required for vaccines.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety, specific
toxicity, repeated dose toxicity and compatibility of ingredients.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Hib powder:
Lactose anhydrous
DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension:
Sodium chloride (NaCl)
Medium 199 containing principally amino acids, mineral salts, vitamins
Water for injections
For adjuvants, see section 2.
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal
products.
After reconstitution: an immediate use is recommended. However the stability has been demonstrated
for 8 hours at 21°C after reconstitution.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C).
Do not freeze.
Store in the original package, in order to protect from light.
For storage conditions of the reconstituted medicinal product, see section 6.3.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
Powder in a vial (type I glass) with a stopper (butyl).
0.5 ml of suspension in a vial (type I glass) with a stopper (butyl).
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Upon storage, a white deposit and clear supernatant may be observed in the vial containing the DTPa-
HBV-IPV suspension. This does not constitute a sign of deterioration.
The DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension should be well shaken in order to obtain a homogeneous turbid white
suspension and should be inspected visually for any foreign particulate matter and/or abnormal
physical appearance. In the event of either being observed, discard the vaccine.
The vaccine is reconstituted by adding the contents of the vial containing the DTPa-HBV-IPV
suspension by means of a syringe to the vial containing the Hib powder. After the addition of the
DTPa-HBV-IPV vaccine to the Hib powder, the mixture should be well shaken until the powder is
completely dissolved.
The reconstituted vaccine presents as a slightly more cloudy suspension than the liquid component
alone. This is normal and does not impair the performance of the vaccine. In the event of other
variation being observed, discard the vaccine.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals s.a.
Rue de l'Institut 89
B-1330 Rixensart, Belgium
8. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S
9. DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 23 October 2000
Date of latest renewal: 23 October 2005
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
ANNEX II
A. MANUFACTURERS OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE SUBSTANCES AND
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR
BATCH RELEASE
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
A. MANUFACTURERS OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE SUBSTANCES AND
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturers of the biological active substances
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals s.a.
Rue de l’Institut 89,
1330 Rixensart
Belgium
Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics GmbH & Co. KG
Emil-von-Behring-Str. 76,
D-35041 Marburg
Germany
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals s.a.
Rue de l’Institut 89,
1330 Rixensart
Belgium
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Pharmacovigilance system
The MAH must ensure that the system of pharmacovigilance, as described in version 3.06
presented in Module 1.8.1. of the Marketing Authorisation, is in place and functioning before
and whilst the product is on the market.
PSURs
The holder of marketing authorisation will continue to submit annual PSURs
The holder of the marketing authorisation must inform the European Commission about the marketing
plans for the medicinal product authorised by this decision.
Official batch release: in accordance with Article 114 of Directive 2001/83/EC as amended, the
official batch release will be undertaken by a state laboratory or a laboratory designated for that
purpose.
ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
1 VIAL AND 1 PRE-FILLED SYRINGE WITHOUT NEEDLE
10 VIALS AND 10 PRE-FILLED SYRINGES WITHOUT NEEDLES
20 VIALS AND 20 PRE-FILLED SYRINGES WITHOUT NEEDLES
50 VIALS AND 50 PRE-FILLED SYRINGES WITHOUT NEEDLES
1 VIAL AND 1 PRE-FILLED SYRINGE WITH 2 NEEDLES
10 VIALS AND 10 PRE-FILLED SYRINGES WITH 20 NEEDLES
20 VIALS AND 20 PRE-FILLED SYRINGES WITH 40 NEEDLES
50 VIALS AND 50 PRE-FILLED SYRINGES WITH 100 NEEDLES
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Infanrix hexa – Powder and suspension for suspension for injection in a pre-filled syringe
Diphtheria (D), tetanus (T), pertussis (acellular component) (Pa), hepatitis B (rDNA) (HBV),
poliomyelitis (inactivated) (IPV) and Haemophilus
type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine (adsorbed)
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
After reconstitution, 1 dose (0.5 ml):
Diphtheria toxoid
1
Bordetella pertussis
antigens
(Pertussis toxoid
1
, Filamentous haemagglutinin
1
, Pertactin
1
)
Hepatitis B surface antigen
2
Poliovirus (inactivated) type 1, 2, 3
Haemophilus
type b polysaccharide
(polyribosylribitol phosphate)
2
conjugated to tetanus toxoid as carrier protein
Lactose anhydrous
Sodium chloride
Medium 199 containing principally amino acids, mineral salts, vitamins
Water for injections
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder and suspension for suspension for injection in a pre-filled syringe
Vial: powder
Pre-filled syringe: suspension
1 vial and 1 pre-filled syringe
1 dose (0.5 ml)


















10 vials and 10 pre-filled syringes
10 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
20 vials and 20 pre-filled syringes
20 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
50 vials and 50 pre-filled syringes
50 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
1 vial and 1 pre-filled syringe + 2 needles
1 dose (0.5 ml)
10 vials and 10 pre-filled syringes + 20 needles
10 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
20 vials and 20 pre-filled syringes + 40 needles
20 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
50 vials and 50 pre-filled syringes + 100 needles
50 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Read the package leaflet before use
Intramuscular use
Shake before use
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator
Do not freeze
Store in the original package in order to protect from light
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE














11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals s.a.
Rue de l’Institut 89
B-1330 Rixensart, Belgium
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/00/152/002 - 10 vials and 10 pre-filled syringes without needles
EU/1/00/152/003 - 20 vials and 20 pre-filled syringes without needles
EU/1/00/152/004 - 50 vials and 50 pre-filled syringes without needles
EU/1/00/152/005 - 1 vial and 1 pre-filled syringe with 2 needles
EU/1/00/152/006 - 10 vials and 10 pre-filled syringes with 20 needles
EU/1/00/152/007 - 20 vials and 20 pre-filled syringes with 40 needles
EU/1/00/152/008 - 50 vials and 50 pre-filled syringes with 100 needles
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
Justification for not including Braille accepted
EU/1/00/152/001 - 1 vial and 1 pre-filled syringe without needle



















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
1 VIAL WITH BIOSET
®
AND 1 PRE-FILLED SYRINGE WITHOUT NEEDLE
10 VIALS WITH BIOSET
®
AND 10 PRE-FILLED SYRINGES WITHOUT NEEDLES
20 VIALS WITH BIOSET
®
AND 20 PRE-FILLED SYRINGES WITHOUT NEEDLES
50 VIALS WITH BIOSET
®
AND 50 PRE-FILLED SYRINGES WITHOUT NEEDLES
1 VIAL WITH BIOSET
®
AND 1 PRE-FILLED SYRINGE WITH 1 NEEDLE
10 VIALS WITH BIOSET
®
AND 10 PRE-FILLED SYRINGES WITH 10 NEEDLES
20 VIALS WITH BIOSET
®
AND 20 PRE-FILLED SYRINGES WITH 20 NEEDLES
50 VIALS WITH BIOSET
®
AND 50 PRE-FILLED SYRINGES WITH 50 NEEDLES
1 VIAL WITH BIOSET
®
AND 1 PRE-FILLED SYRINGE WITH 2 NEEDLES
10 VIALS WITH BIOSET
®
AND 10 PRE-FILLED SYRINGES WITH 20 NEEDLES
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Infanrix hexa – Powder and suspension for suspension for injection in a pre-filled syringe
Diphtheria (D), tetanus (T), pertussis (acellular, component) (Pa), hepatitis B (rDNA) (HBV),
poliomyelitis (inactivated) (IPV) and Haemophilus
type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine (adsorbed)
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
After reconstitution, 1 dose (0.5 ml):
Diphtheria toxoid
1
Pertussis
antigens
(Pertussis toxoid
1
, Filamentous haemagglutinin
1
, Pertactin
1
)
Hepatitis B surface antigen
2
Poliovirus (inactivated ) type 1, 2, 3
Haemophilus
type b polysaccharide
(polyribosylribitol phosphate)
2
conjugated to tetanus toxoid as carrier protein
Lactose anhydrous
Sodium chloride
Medium 199 containing principally amino acids, mineral salts, vitamins
Water for injections
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder and suspension for suspension for injection in a pre-filled syringe
Vial with Bioset® Cap: powder
Pre-filled syringe: suspension
1 vial with bioset® and 1 pre-filled syringe
1 dose (0.5 ml)



















10 vials with bioset® and 10 pre-filled syringes
10 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
20 vials with bioset® and 20 pre-filled syringes
20 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
50 vials with bioset® and 50 pre-filled syringes
50 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
1 vial with bioset® and 1 pre-filled syringe + 1 needle
1 dose (0.5 ml)
10 vials with bioset® and 10 pre-filled syringes + 10 needles
10 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
20 vials with bioset® and 20 pre-filled syringes + 20 needles
20 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
50 vials with bioset® and 50 pre-filled syringes + 50 needles
50 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
1 vial with bioset® and 1 pre-filled syringe + 2 needles
1 dose (0.5 ml)
10 vials with bioset® and 10 pre-filled syringes + 20 needles
10 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Read the package leaflet before use
Intramuscular use
Shake before use
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator
Do not freeze
Store in the original package in order to protect from light











10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals s.a.
Rue de l’Institut 89
B-1330 Rixensart, Belgium
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/00/152/009 - 1 vial with bioset® and 1 pre-filled syringe without needle
EU/1/00/152/010 - 10 vials with bioset® and 10 pre-filled syringes without needles
EU/1/00/152/011 - 20 vials with bioset® and 20 pre-filled syringes without needles
EU/1/00/152/012 - 50 vials with bioset® and 50 pre-filled syringes without needles
EU/1/00/152/013 - 1 vial with bioset® and 1 pre-filled syringe with 1 needle
EU/1/00/152/014 - 10 vials with bioset® and 10 pre-filled syringes with 10 needles
EU/1/00/152/015 - 20 vials with bioset® and 20 pre-filled syringes with 20 needles
EU/1/00/152/016 - 50 vials with bioset® and 50 pre-filled syringes with 50 needles
EU/1/00/152/017 - 1 vial with bioset® and 1 pre-filled syringe with 2 needles
EU/1/00/152/018 - 10 vials with bioset® and 10 pre-filled syringes with 20 needles
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
Justification for not including Braille accepted





















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
1 VIAL AND 1 VIAL 50 VIALS AND 50 VIALS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Infanrix hexa – Powder and suspension for suspension for injection
Diphtheria (D), tetanus (T), pertussis (acellular component) (Pa), hepatitis B (rDNA) (HBV),
poliomyelitis (inactivated) (IPV) and Haemophilus
type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine (adsorbed)
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
After reconstitution, 1 dose (0.5 ml):
Diphtheria toxoid
1
Bordetella pertussis
antigens
(Pertussis toxoid
1
, Filamentous haemagglutinin
1
, Pertactin
1
)
Hepatitis B surface antigen
2
Poliovirus (inactivated) type 1, 2, 3
Haemophilus
type b polysaccharide
(polyribosylribitol phosphate)
2
conjugated to tetanus toxoid as carrier protein
Lactose anhydrous
Sodium chloride
Medium 199 containing principally amino acids, mineral salts, vitamins
Water for injections
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder and suspension for suspension for injection
Vial: powder
Vial: suspension
1 vial and 1 vial
1 dose (0.5 ml)
50 vials and 50 vials
50 x 1 dose (0.5 ml)
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Read the package leaflet before use
Intramuscular use
Shake before use























SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator
Do not freeze
Store in the original package in order to protect from light
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals s.a.
Rue de l’Institut 89
B-1330 Rixensart, Belgium
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE

























Justification for not including Braille accepted
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Infanrix hexa, Powder and suspension for suspension for injection in a pre-filled syringe
Diphtheria (D), tetanus (T), pertussis (acellular, component) (Pa), hepatitis B (rDNA) (HBV),
poliomyelitis (inactivated) (IPV) and Haemophilus
type b (HIB) conjugate vaccine (adsorbed).
Read all of this leaflet carefully before your child receives this vaccine.
-
Keep this leaflet until your child has finished the complete vaccination course. You may need to
read it again.
-
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or your pharmacist.
-
This vaccine has been prescribed for your child. Do not pass it on to others.
-
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
In this leaflet:
1.
What Infanrix hexa is and what it is used for
2.
Before your child receives Infanrix hexa
3.
How Infanrix hexa is given
4.
Possible side effects
5.
How to store Infanrix hexa
6.
1. WHAT Infanrix hexa IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Infanrix hexa is a vaccine used in children to prevent six diseases: diphtheria, tetanus (lockjaw),
pertussis (whooping cough), hepatitis B, poliomyelitis (Polio) and
Haemophilus influenzae
type b. The
vaccine works by causing the body to produce its own protection (antibodies) against these diseases.
•
Diphtheria:
Diphtheria mainly affects the airways and sometimes the skin. Generally the airways
become inflamed (swollen) causing severe breathing difficulties and sometimes suffocation. The
bacteria also release a toxin (poison), which can cause nerve damage, heart problems, and even
death.
•
Tetanus
(Lockjaw): Tetanus bacteria enter the body through cuts, scratches or wounds in the skin.
Wounds that are especially prone to infection are burns, fractures, deep wounds or wounds
contaminated with soil, dust, horse manure/dung or wood splinters. The bacteria release a toxin
(poison), which can cause muscle stiffness, painful muscle spasms, fits and even death. The muscle
spasms can be strong enough to cause bone fractures of the spine.
•
Pertussis
(Whooping cough): Pertussis is a highly infectious illness. The disease affects the
airways causing severe spells of coughing that may interfere with normal breathing. The coughing
is often accompanied by a “whooping” sound, hence the common name “whooping cough”. The
cough may last for 1-2 months or longer. Pertussis can also cause ear infections, bronchitis which
may last a long time, pneumonia, fits, brain damage and even death.
•
Hepatitis B:
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus. It causes the liver to become swollen
(inflamed). The virus is found in body fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal secretions, or saliva
(spit) of infected people.
•
Poliomyelitis (Polio):
Poliomyelitis, sometimes called simply “polio” is a viral infection that can
have variable effects. Often it causes only a mild illness but in some people it causes permanent
damage or even death. In its severest form, polio infection causes paralysis of the muscles (muscles
cannot move), including those muscles needed for breathing and walking. The limbs affected by
the disease may be painfully deformed.
•
Haemophilus influenzae
type b
(Hib): Hib infection most frequently causes brain inflammation
(swelling). There will be some type of serious complications such as: mental retardation, cerebral
palsy, deafness, epilepsy or partial blindness. Hib infection also causes inflammation of the throat.
It occasionally causes death by suffocation. Less commonly, the bacteria can also infect the blood,
heart, lungs, bones, joints, and tissues of the eyes and mouth.
Vaccination is the best way to protect against these diseases. None of the components in the vaccine
are infectious.
2. BEFORE YOUR CHILD RECEIVES Infanrix hexa
Infanrix hexa should not be given:
•
if your child has previously had any allergic reaction to Infanrix hexa, or any ingredient
contained in this vaccine. The active substances and other ingredients in Infanrix hexa are listed
at the end of the leaflet. Signs of an allergic reaction may include itchy skin rash, shortness of
breath and swelling of the face or tongue.
•
if your child has previously had an allergic reaction to any vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus,
pertussis (whooping cough), hepatitis B, poliomyelitis or
Haemophilus influenzae
type b
diseases.
•
if your child experienced problems of the nervous system within 7 days after previous
vaccination with a vaccine against pertussis (whooping cough) disease.
•
if your child has a severe infection with a high temperature (over 38°C). A minor infection such
as a cold should not be a problem, but talk to your doctor first.
Take special care with Infanrix hexa:
•
if after previously having Infanrix hexa or another vaccine against pertussis (whooping cough)
disease, your child had any problems, especially:
♦
A high temperature (over 40°C) within 48 hours of vaccination
♦
A collapse or shock-like state within 48 hours of vaccination
♦
Persistent crying lasting 3 hours or more within 48 hours of vaccination
♦
Seizures/fits with or without a high temperature within 3 days of vaccination
•
if your child is suffering from an undiagnosed or progressive disease of the brain or
uncontrolled epilepsy. After control of the disease the vaccine should be administered.
•
if your child has a bleeding problem or bruises easily
•
if your child has a tendency to seizures/fits due to a fever, or if there is a history in the family of
this
As with all vaccines, Infanrix hexa may not completely protect all people who are vaccinated.
Using other medicines or vaccines
Please tell your doctor if your child is taking or has recently taken any other medicines, including
medicines obtained without a prescription or has recently received any other vaccine.
Important information about some of the ingredients of Infanrix hexa
Please tell your doctor if your child has had an allergic reaction to neomycin and polymyxin
(antibiotics).
HOW Infanrix hexa IS GIVEN
Your child will receive a total of two or three injections with an interval of at least one month between
each one. Each injection is given on a separate visit. You will be informed by the doctor or nurse when
you should come back for subsequent injections.
If additional injections or “booster” are necessary, the doctor will tell you.
If your child misses a scheduled injection, talk to your doctor and arrange another visit.
Make sure your child finishes the complete vaccination course of three injections. If not, your child
may not be fully protected against the diseases.
The doctor will give Infanrix hexa as an injection into the muscle.
The vaccine should never be given into blood vessels or into the skin.
Like all medicines, Infanrix hexa can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
As with all injectable vaccines, there is an extremely small risk of serious allergic reactions
(anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions). Signs of serious allergic reactions may be:
•
rashes that may be itchy or blistering
•
swelling of the eyes and face
•
difficulty in breathing or swallowing
•
a sudden drop in blood pressure and loss of consciousness.
Such reactions will usually occur before leaving the doctor’s surgery. However, if your child gets any
of these symptoms you should contact a doctor urgently.
As with other vaccines against pertussis (whooping cough) disease, following side effects may occur
very rarely within 2 to 3 days after vaccination:
•
collapse or periods of unconsciousness or lack of awareness
•
seizures or fits with or without fever
If your child gets any of these side effects you should contact a doctor urgently.
Other side effects that have been reported are:
Very common
(These may occur in 1 in 10 doses or more of the vaccine)
•
loss of appetite
•
fever greater than or equal to 38°C
•
swelling, pain, redness at the injection site
•
tiredness
•
abnormal crying, irritability, restlessness.
Common
(These may occur in up to 1 in 10 doses of the vaccine)
•
diarrhoea, vomiting
•
fever greater than 39.5°C
•
swelling larger than 5 cm at the injection site, hard lump at the injection site
•
nervousness.
Uncommon
(These may occur in up to 1 in 100 doses of the vaccine)
•
sleepiness
•
cough
•
large swelling at the injected limb.
Rare
(These may occur in up to 1 in 1,000 doses of the vaccine)
•
rash.
Very rare
(These may occur in up to 1 in 10,000 doses of the vaccine)
•
swollen glands in the neck, armpit or groin (lymphadenopathy)
•
in babies born very prematurely (at or before 28 weeks of gestation) longer gaps than normal
between breaths may occur for 2-3 days after vaccination.
•
temporarily stopping breathing (apnoea)swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue or throat which
may cause difficulty in swallowing or breathing (angioedema)
•
dermatitis
•
swelling of the entire injected limb, vesicles at the injection site.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor or pharmacist.
5. HOW TO STORE Infanrix hexa
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Infanrix hexa after the expiry date which is stated on the carton. The expiry date refers to
the last day of that month.
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
Store in the original package in order to protect from light.
Do not freeze. Freezing destroys the vaccine.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
What Infanrix hexa contains
The active substances are:
Diphtheria toxoid
1
Bordetella pertussis
antigens
Pertussis toxoid
1
Filamentous Haemagglutinin
1
Hepatitis B surface antigen
2,3
Poliovirus (inactivated)
type 1 (Mahoney strain)
4
type 3 (Saukett strain)
4
Haemophilus
type b polysaccharide
(polyribosylribitol phosphate)
3
conjugated to tetanus toxoid as carrier protein 20-40 micrograms
1
adsorbed on aluminium hydroxide, hydrated (Al(OH)
3
) 0.5 milligrams Al
2
produced in yeast cells (
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
) by recombinant DNA technology
3
adsorbed on aluminium phosphate (AlPO
4
)
4
propagated in VERO cells
The other ingredients in Infanrix hexa are:
Hib powder:
lactose anhydrous
DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension:
sodium chloride (NaCl), medium 199 containing principally
amino acids, mineral salts, vitamins and water for injections
What Infanrix hexa looks like and contents of the pack
Powder and suspension for suspension for injection in a pre-filled syringe.
The diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, inactivated poliomyelitis (DTPa-HBV-IPV)
component is a white, slightly milky liquid presented in a pre-filled syringe (0.5 ml).
The Hib component is a white powder presented in a glass vial.
Both components must be mixed together before your child receives the vaccine. The mixed
appearance is a white, slightly milky liquid.
Infanrix hexa is available in packs of 1, 10, 20 and 50 with or without needles.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals s.a.
Rue de l’Institut 89
B-1330 Rixensart
Belgium
For any information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the Marketing
Authorisation Holder:
België/Belgique/Belgien
GlaxoSmithKline s.a./n.v.
Tél/Tel: + 32 2 656 21 11
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
GlaxoSmithKline s.a./n.v.
Tél/Tel: + 32 2 656 21 11
България
ГлаксоСмитКлайн ЕООД
ул. Димитър Манов бл.10
София 1408
Тел. + 359 2 953 10 34
Magyarország
GlaxoSmithKline Kft.
Tel.: + 36-1-2255300
Česká republika
GlaxoSmithKline s.r.o.
Tel: + 420 222 001 111
gsk.czmail@gsk.com
Malta
GlaxoSmithKline Malta
Tel: + 356 21 238131
Danmark
GlaxoSmithKline Pharma A/S
Tlf: + 45 36 35 91 00
Nederland
GlaxoSmithKline BV
Tel: + 31 (0)30 69 38 100
nlinfo@gsk.com
Deutschland
GlaxoSmithKline GmbH & Co. KG
Tel: + 49 (0)89 360448701
produkt.info@gsk.com
Norge
GlaxoSmithKline AS
Tlf: + 47 22 70 20 00
firmapost@gsk.no
Eesti
GlaxoSmithKline Eesti OÜ
Tel: +372 667 6900
estonia@gsk.com
Österreich
GlaxoSmithKline Pharma GmbH.
Tel: + 43 1 970 75-0
at.info@gsk.com
Ελλάδα
GlaxoSmithKline A.E.B.E
Tηλ: + 30 210 68 82 100
Polska
GSK Commercial Sp. z.o.o.
Tel.: + 48 (22) 576 9000
España
GlaxoSmithKline, S.A.
Tel: + 34 902 202 700
es-ci@gsk.com
Portugal
Smith Kline & French Portuguesa, Produtos
Farmacêuticos, Lda.
Tel: + 351 21 412 95 00
FI.PT@gsk.com
France
Laboratoire GlaxoSmithKline
Tél: + 33 (0) 1 39 17 84 44
diam@gsk.com
România
GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) SRL
Tel: +40 (0)21 3028 208
Ireland
GlaxoSmithKline (Ireland) Ltd
Tel: + 353 (0)1 4955000
Slovenija
GlaxoSmithKline d.o.o.
Tel: + 386 (0) 1 280 25 00
medical.x.si@gsk.com
Ísland
GlaxoSmithKline ehf.
Sími: +354-530 3700
Slovenská republika
GlaxoSmithKline Slovakia s.r.o.
Tel: +421 (0)2 48 26 11 11
recepcia.sk@gsk.com
Italia
GlaxoSmithKline S.p.A.
Tel:+ 39 04 59 21 81 11
Suomi/Finland
GlaxoSmithKline Oy
Puh/Tel: + 358 10 30 30 30
Finland.tuoteinfo@gsk.com
Κύπρος
GlaxoSmithKline (Cyprus) Ltd
Τηλ: + 357 22 39 70 00
Sverige
GlaxoSmithKline AB
Tel: + 46 (0)8 638 93 00
info.produkt@gsk.com
Latvija
GlaxoSmithKline Latvia SIA
Tel: + 371 67312687
lv-epasts@gsk.com
United Kingdom
GlaxoSmithKline UK
Tel: + 44 (0)808 100 9997
customercontactuk@gsk.com
Lietuva
GlaxoSmithKline Lietuva UAB
Tel. +370 5 264 90 00
info.lt@gsk.com
This leaflet was last approved in
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) web
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---
The following information is intended for medical or healthcare professionals only:
Upon storage, a white deposit and clear supernatant can be observed in the syringe containing the
DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension. This does not constitute a sign of deterioration.
The syringe should be well shaken in order to obtain a homogeneous turbid white suspension.
The DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension should be inspected visually for any foreign particulate matter and/or
variation of physical aspect. In the event of either being observed, discard the container.
The vaccine is reconstituted by adding the contents of the syringe to the vial containing the Hib
powder. After the addition of the DTPa-HBV-IPV vaccine to the powder,the mixture should then be
well shaken until the powder is completely dissolved.
The reconstituted vaccine presents as a slightly more cloudy suspension than the liquid component
alone. This is normal and does not impair the performance of the vaccine. In the event of other
variation being observed, discard the vaccine.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Infanrix hexa, Powder and suspension for suspension for injection
in a pre-filled syringe
Diphtheria (D), tetanus (T), pertussis (acellular, component) (Pa), hepatitis B (rDNA) (HBV),
poliomyelitis (inactivated) (IPV) and Haemophilus
type b (HIB) conjugate vaccine (adsorbed).
Read all of this leaflet carefully before your child receives this vaccine.
-
Keep this leaflet until your child has finished the complete vaccination course. You may need to
read it again.
-
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or your pharmacist.
-
This vaccine has been prescribed for your child. Do not pass it on to others.
-
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
In this leaflet
:
1.
What Infanrix hexa is and what it is used for
2.
Before your child receives Infanrix hexa
3.
How Infanrix hexa is given
4.
Possible side effects
5.
How to store Infanrix hexa
6.
1. WHAT Infanrix hexa IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Infanrix hexa is a vaccine used in children to prevent six diseases: diphtheria, tetanus (lockjaw),
pertussis (whooping cough), hepatitis B, poliomyelitis (Polio) and
Haemophilus influenzae
type b. The
vaccine works by causing the body to produce its own protection (antibodies) against these diseases.
•
Diphtheria:
Diphtheria mainly affects the airways and sometimes the skin. Generally the airways
become inflamed (swollen) causing severe breathing difficulties and sometimes suffocation. The
bacteria also release a toxin (poison), which can cause nerve damage, heart problems, and even
death.
•
Tetanus
(Lockjaw): Tetanus bacteria enter the body through cuts, scratches or wounds in the skin.
Wounds that are especially prone to infection are burns, fractures, deep wounds or wounds
contaminated with soil, dust, horse manure/dung or wood splinters. The bacteria release a toxin
(poison), which can cause muscle stiffness, painful muscle spasms, fits and even death. The muscle
spasms can be strong enough to cause bone fractures of the spine.
•
Pertussis
(Whooping cough): Pertussis is a highly infectious illness. The disease affects the
airways causing severe spells of coughing that may interfere with normal breathing. The coughing
is often accompanied by a “whooping” sound, hence the common name “whooping cough”. The
cough may last for 1-2 months or longer. Pertussis can also cause ear infections, bronchitis which
may last a long time, pneumonia, fits, brain damage and even death.
•
Hepatitis
B:
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus. It causes the liver to become swollen
(inflamed). The virus is found in body fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal secretions, or saliva
(spit) of infected people.
•
Poliomyelitis (Polio):
Poliomyelitis, sometimes called simply “polio” is a viral infection that can
have variable effects. Often it causes only a mild illness but in some people it causes permanent
damage or even death. In its severest form, polio infection causes paralysis of the muscles (muscles
cannot move), including those muscles needed for breathing and walking. The limbs affected by
the disease may be painfully deformed.
•
Haemophilus influenzae
type b
(Hib)
: Hib infection most frequently causes brain inflammation
(swelling). There will be some type of serious complications such as: mental retardation, cerebral
palsy, deafness, epilepsy or partial blindness. Hib infection also causes inflammation of the throat.
It occasionally causes death by suffocation. Less commonly, the bacteria can also infect the blood,
heart, lungs, bones, joints, and tissues of the eyes and mouth.
Vaccination is the best way to protect against these diseases. None of the components in the vaccine
are infectious.
2. BEFORE YOUR CHILD RECEIVES Infanrix hexa
Infanrix hexa should not be given:
•
if your child has previously had any allergic reaction to Infanrix hexa, or any ingredient
contained in this vaccine. The active substances and other ingredients in Infanrix hexa are listed
at the end of the leaflet. Signs of an allergic reaction may include itchy skin rash, shortness of
breath and swelling of the face or tongue.
•
if your child has previously had an allergic reaction to any vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus,
pertussis (whooping cough), hepatitis B, poliomyelitis or
Haemophilus influenzae
type b
diseases.
•
if your child experienced problems of the nervous system within 7 days after previous
vaccination with a vaccine against pertussis (whooping cough) disease.
if your child has a severe infection with a high temperature (over 38°C). A minor infection such
as a cold should not be a problem, but talk to your doctor first.
Take special care with Infanrix hexa:
•
if after previously having Infanrix hexa or another vaccine against pertussis (whooping cough)
disease, your child had any problems, especially:
♦
A high temperature (over 40°C) within 48 hours of vaccination
♦
A collapse or shock-like state within 48 hours of vaccination
♦
Persistent crying lasting 3 hours or more within 48 hours of vaccination
♦
Seizures/fits with or without a high temperature within 3 days of vaccination
•
if your child is suffering from an undiagnosed or progressive disease of the brain or
uncontrolled epilepsy. After control of the disease the vaccine should be administered.
•
if your child has a bleeding problem or bruises easily
•
if your child has a tendency to seizures/fits due to a fever, or if there is a history in the family of
this
As with all vaccines, Infanrix hexa may not completely protect all people who are vaccinated.
Using other medicines or vaccines
Please tell your doctor if your child is taking or has recently taken any other medicines, including
medicines obtained without a prescription or has recently received any other vaccine.
Important information about some of the ingredients of Infanrix hexa
Please tell your doctor if your child has had an allergic reaction to neomycin and polymyxin
(antibiotics).
HOW Infanrix hexa IS GIVEN
Your child will receive a total of two or three injections with an interval of at least one month between
each one. Each injection is given on a separate visit. You will be informed by the doctor or nurse when
you should come back for subsequent injections.
If additional injections or “booster” are necessary, the doctor will tell you.
If your child misses a scheduled injection, talk to your doctor and arrange another visit.
Make sure your child finishes the complete vaccination course of three injections. If not, your child
may not be fully protected against the diseases.
The doctor will give Infanrix hexa as an injection into the muscle.
The vaccine should never be given into blood vessels or into the skin.
Like all medicines, Infanrix hexa can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
As with all injectable vaccines, there is an extremely small risk of serious allergic reactions
(anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions). Signs of serious allergic reactions may be:
•
rashes that may be itchy or blistering
•
swelling of the eyes and face
•
difficulty in breathing or swallowing
•
a sudden drop in blood pressure and loss of consciousness.
Such reactions will usually occur before leaving the doctor’s surgery. However, if your child gets any
of these symptoms you should contact a doctor urgently.
As with other vaccines against pertussis (whooping cough) disease, following side effects may occur
very rarely within 2 to 3 days after vaccination:
•
collapse or periods of unconsciousness or lack of awareness
•
seizures or fits with or without fever
If your child gets any of these side effects you should contact a doctor urgently.
Other side effects that have been reported are:
Very common
(These may occur in 1 in 10 doses or more of the vaccine)
•
loss of appetite
•
fever greater than or equal to 38°C
•
swelling, pain, redness at the injection site
•
tiredness
•
abnormal crying, irritability, restlessness.
Common
(These may occur in up to 1 in 10 doses of the vaccine)
•
diarrhoea, vomiting
•
fever greater than 39.5°C
•
swelling larger than 5 cm at the injection site, hard lump at the injection site
•
nervousness.
Uncommon
(These may occur in up to 1 in 100 doses of the vaccine)
•
sleepiness
•
cough
•
large swelling at the injected limb.
Rare
(These may occur in up to 1 in 1,000 doses of the vaccine)
•
rash.
Very rare
(These may occur in up to 1 in 10,000 doses of the vaccine)
•
swollen glands in the neck, armpit or groin (lymphadenopathy)
•
in babies born very prematurely (at or before 28 weeks of gestation) longer gaps than normal
between breaths may occur for 2-3 days after vaccination.
•
temporarily stopping breathing (apnoea)
•
swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue or throat which may cause difficulty in swallowing or
breathing (angioedema)
•
dermatitis
•
swelling of the entire injected limb, vesicles at the injection site.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor or pharmacist.
5. HOW TO STORE Infanrix hexa
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Infanrix hexa after the expiry date which is stated on the carton. The expiry date refers to
the last day of that month.
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
Store in the original package in order to protect from light.
Do not freeze. Freezing destroys the vaccine.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
What Infanrix hexa contains
The active substances are:
Diphtheria toxoid
1
Bordetella pertussis
antigens
Pertussis toxoid
1
Filamentous Haemagglutinin
1
Hepatitis B surface antigen
2,3
Poliovirus (inactivated)
type 1 (Mahoney strain)
4
type 3 (Saukett strain)
4
Haemophilus
type b polysaccharide
(polyribosylribitol phosphate)
3
conjugated to tetanus toxoid as carrier protein 20-40 micrograms
1
adsorbed on aluminium hydroxide, hydrated (Al(OH)
3
) 0.5 milligrams Al
2
produced in yeast cells (
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
) by recombinant DNA technology
3
adsorbed on aluminium phosphate (AlPO
4
)
4
propagated in VERO cells
The other ingredients in Infanrix hexa are:
Hib powder:
lactose anhydrous
DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension:
sodium chloride (NaCl), medium 199 containing principally
amino acids, mineral salts, vitamins and water for injections
What Infanrix hexa looks like and contents of the pack
Powder and suspension for suspension for injection in a pre-filled syringe.
The diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, inactivated poliomyelitis (DTPa-HBV-IPV)
component is a white, slightly milky liquid presented in a pre-filled syringe (0.5 ml).
The Hib component is a white powder presented in a glass vial with Bioset®.
Both components must be mixed together before your child receives the vaccine. The mixed
appearance is a white, slightly milky liquid.
Infanrix hexa is available in packs of 1, 10, 20 and 50 with or without needles.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals s.a.
Rue de l’Institut 89
B-1330 Rixensart
Belgium
For any information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the Marketing
Authorisation Holder:
België/Belgique/Belgien
GlaxoSmithKline s.a./n.v.
Tél/Tel: + 32 2 656 21 11
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
GlaxoSmithKline s.a./n.v.
Tél/Tel: + 32 2 656 21 11
България
ГлаксоСмитКлайн ЕООД
ул. Димитър Манов бл.10
София 1408
Тел. + 359 2 953 10 34
Magyarország
GlaxoSmithKline Kft.
Tel.: + 36-1-2255300
Česká republika
GlaxoSmithKline s.r.o.
Tel: + 420 222 001 111
gsk.czmail@gsk.com
Malta
GlaxoSmithKline Malta
Tel: + 356 21 238131
Danmark
GlaxoSmithKline Pharma A/S
Tlf: + 45 36 35 91 00
Nederland
GlaxoSmithKline BV
Tel: + 31 (0)30 69 38 100
nlinfo@gsk.com
Deutschland
GlaxoSmithKline GmbH & Co. KG
Tel: + 49 (0)89 360448701
Norge
GlaxoSmithKline AS
Tlf: + 47 22 70 20 00
Eesti
GlaxoSmithKline Eesti OÜ
Tel: +372 667 6900
estonia@gsk.com
Österreich
GlaxoSmithKline Pharma GmbH.
Tel: + 43 1 970 75-0
at.info@gsk.com
Ελλάδα
GlaxoSmithKline A.E.B.E
Tηλ: + 30 210 68 82 100
Polska
GSK Commercial Sp. z.o.o.
Tel.: + 48 (22) 576 9000
España
GlaxoSmithKline, S.A.
Tel: + 34 902 202 700
es-ci@gsk.com
Portugal
Smith Kline & French Portuguesa, Produtos
Farmacêuticos, Lda.
Tel: + 351 21 412 95 00
FI.PT@gsk.com
France
Laboratoire GlaxoSmithKline
Tél: + 33 (0) 1 39 17 84 44
diam@gsk.com
România
GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) SRL
Tel: +40 (0)21 3028 208
Ireland
GlaxoSmithKline (Ireland) Ltd
Tel: + 353 (0)1 4955000
Slovenija
GlaxoSmithKline d.o.o.
Tel: + 386 (0) 1 280 25 00
medical.x.si@gsk.com
Ísland
GlaxoSmithKline ehf.
Sími: +354-530 3700
Slovenská republika
GlaxoSmithKline Slovakia s.r.o.
Tel: +421 (0)2 48 26 11 11
recepcia.sk@gsk.com
Italia
GlaxoSmithKline S.p.A.
Tel:+ 39 04 59 21 81 11
Suomi/Finland
GlaxoSmithKline Oy
Puh/Tel: + 358 10 30 30 30
Finland.tuoteinfo@gsk.com
Κύπρος
GlaxoSmithKline (Cyprus) Ltd
Τηλ: + 357 22 39 70 00
Sverige
GlaxoSmithKline AB
Tel: + 46 (0)8 638 93 00
info.produkt@gsk.com
Latvija
GlaxoSmithKline Latvia SIA
Tel: + 371 67312687
lv-epasts@gsk.com
United Kingdom
GlaxoSmithKline UK
Tel: + 44 (0)808 100 9997
customercontactuk@gsk.com
Lietuva
GlaxoSmithKline Lietuva UAB
Tel. +370 5 264 90 00
info.lt@gsk.com
This leaflet was last approved in
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) web
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following information is intended for medical or healthcare professionals only:
Upon storage, a white deposit and clear supernatant can be observed in the syringe containing the
DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension. This does not constitute a sign of deterioration.
The syringe should be well shaken in order to obtain a homogeneous turbid white suspension.
The DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension should be inspected visually for any foreign particulate matter and/or
variation of physical aspect. In the event of either being observed, discard the container.
The Bioset® is a specially designed cap which simplifies reconstitution. It is good clinical practice to
only inject a vaccine when it has reached room temperature. In addition, a vial at room temperature
ensures sufficient elasticity of the rubber closure to minimise any coring of rubber particles. To
achieve this, the vial should be kept at room temperature (25 ± 3 °C) for at least five minutes before
connecting the syringe and reconstituting the vaccine. For reconstitution, twist the cover from the
Bioset® cap and remove the cap from the syringe. Before connecting the syringe onto the Bioset®,
make sure the two containers are aligned (see Picture 1). Connect the syringe onto the Bioset® by
twisting it. Push downwards until syringe ‘clicks’ into position. Inject liquid, mix thoroughly until
powder is completely dissolved. Aspirate reconstituted vaccine back into syringe. Unscrew syringe
from Bioset®. Affix a needle for administration.
The reconstituted vaccine presents as a slightly more cloudy suspension than the liquid component
alone. This is normal and does not impair the performance of the vaccine. In the event of other
variation being observed, discard the vaccine.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
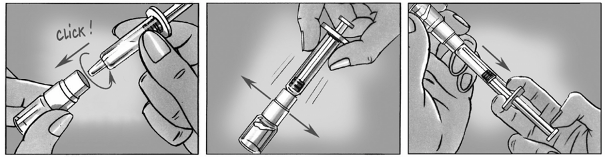
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Infanrix hexa, Powder and suspension for suspension for injection
Diphtheria (D), tetanus (T), pertussis (acellular, component) (Pa), hepatitis B (rDNA) (HBV),
poliomyelitis (inactivated) (IPV) and Haemophilus
type b (HIB) conjugate vaccine (adsorbed).
Read all of this leaflet carefully before your child receives this vaccine.
-
Keep this leaflet until your child has finished the complete vaccination course. You may need to
read it again.
-
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or your pharmacist.
-
This vaccine has been prescribed for your child. Do not pass it on to others.
-
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
What Infanrix hexa is and what it is used for
Before your child receives Infanrix hexa
How Infanrix hexa is given
How to store Infanrix hexa
1. WHAT Infanrix hexa IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Infanrix hexa is a vaccine used in children to prevent six diseases: diphtheria, tetanus (lockjaw),
pertussis (whooping cough), hepatitis B, poliomyelitis (Polio) and
Haemophilus influenzae
type b. The
vaccine works by causing the body to produce its own protection (antibodies) against these diseases.
•
Diphtheria:
Diphtheria mainly affects the airways and sometimes the skin. Generally the airways
become inflamed (swollen) causing severe breathing difficulties and sometimes suffocation. The
bacteria also release a toxin (poison), which can cause nerve damage, heart problems, and even
death.
•
Tetanus
(Lockjaw): Tetanus bacteria enter the body through cuts, scratches or wounds in the skin.
Wounds that are especially prone to infection are burns, fractures, deep wounds or wounds
contaminated with soil, dust, horse manure/dung or wood splinters. The bacteria release a toxin
(poison), which can cause muscle stiffness, painful muscle spasms, fits and even death. The muscle
spasms can be strong enough to cause bone fractures of the spine.
•
Pertussis
(Whooping cough): Pertussis is a highly infectious illness. The disease affects the
airways causing severe spells of coughing that may interfere with normal breathing. The coughing
is often accompanied by a “whooping” sound, hence the common name “whooping cough”. The
cough may last for 1-2 months or longer. Pertussis can also cause ear infections, bronchitis which
may last a long time, pneumonia, fits, brain damage and even death.
•
Hepatitis B:
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus. It causes the liver to become swollen
(inflamed). The virus is found in body fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal secretions, or saliva
(spit) of infected people.
•
Poliomyelitis (Polio):
Poliomyelitis, sometimes called simply “polio” is a viral infection that can
have variable effects. Often it causes only a mild illness but in some people it causes permanent
damage or even death. In its severest form, polio infection causes paralysis of the muscles (muscles
cannot move), including those muscles needed for breathing and walking. The limbs affected by
the disease may be painfully deformed.
•
Haemophilus influenzae
type b
(Hib): Hib infection most frequently causes brain inflammation
(swelling). There will be some type of serious complications such as: mental retardation, cerebral
palsy, deafness, epilepsy or partial blindness. Hib infection also causes inflammation of the throat.
It occasionally causes death by suffocation. Less commonly, the bacteria can also infect the blood,
heart, lungs, bones, joints, and tissues of the eyes and mouth.
Vaccination is the best way to protect against these diseases. None of the components in the vaccine
are infectious.
2. BEFORE YOUR CHILD RECEIVES Infanrix hexa
Infanrix hexa should not be given:
•
if your child has previously had any allergic reaction to Infanrix hexa, or any ingredient
contained in this vaccine. The active substances and other ingredients in Infanrix hexa are listed
at the end of the leaflet. Signs of an allergic reaction may include itchy skin rash, shortness of
breath and swelling of the face or tongue.
•
if your child has previously had an allergic reaction to any vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus,
pertussis (whooping cough), hepatitis B, poliomyelitis or
Haemophilus influenzae
type b
diseases.
•
if your child experienced problems of the nervous system within 7 days after previous
vaccination with a vaccine against pertussis (whooping cough) disease.
•
if your child has a severe infection with a high temperature (over 38°C). A minor infection such
as a cold should not be a problem, but talk to your doctor first.
Take special care with Infanrix hexa:
•
if after previously having Infanrix hexa or another vaccine against pertussis (whooping cough)
disease, your child had any problems, especially:
♦
A high temperature (over 40°C) within 48 hours of vaccination
♦
A collapse or shock-like state within 48 hours of vaccination
♦
Persistent crying lasting 3 hours or more within 48 hours of vaccination
♦
Seizures/fits with or without a high temperature within 3 days of vaccination
•
if your child is suffering from an undiagnosed or progressive disease of the brain or
uncontrolled epilepsy. After control of the disease the vaccine should be administered.
•
if your child has a bleeding problem or bruises easily
•
if your child has a tendency to seizures/fits due to a fever, or if there is a history in the family of
this
As with all vaccines, Infanrix hexa may not completely protect all people who are vaccinated.
Using other medicines or vaccines
Please tell your doctor if your child is taking or has recently taken any other medicines, including
medicines obtained without a prescription or has recently received any other vaccine.
Important information about some of the ingredients of Infanrix hexa
Please tell your doctor if your child has had an allergic reaction to neomycin and polymyxin
(antibiotics).
HOW Infanrix hexa IS GIVEN
Your child will receive a total of two or three injections with an interval of at least one month between
each one. Each injection is given on a separate visit. You will be informed by the doctor or nurse when
you should come back for subsequent injections.
If additional injections or “booster” are necessary, the doctor will tell you.
If your child misses a scheduled injection, talk to your doctor and arrange another visit.
Make sure your child finishes the complete vaccination course of three injections. If not, your child
may not be fully protected against the diseases.
The doctor will give Infanrix hexa as an injection into the muscle.
The vaccine should never be given into blood vessels or into the skin.
Like all medicines, Infanrix hexa can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
As with all injectable vaccines, there is an extremely small risk of serious allergic reactions
(anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions). Signs of serious allergic reactions may be:
•
rashes that may be itchy or blistering
•
swelling of the eyes and face
•
difficulty in breathing or swallowing
•
a sudden drop in blood pressure and loss of consciousness.
Such reactions will usually occur before leaving the doctor’s surgery. However, if your child gets any
of these symptoms you should contact a doctor urgently.
As with other vaccines against pertussis (whooping cough) disease, following side effects may occur
very rarely within 2 to 3 days after vaccination:
•
collapse or periods of unconsciousness or lack of awareness
•
seizures or fits with or without fever
If your child gets any of these side effects you should contact a doctor urgently.
Other side effects that have been reported are:
Very common
(These may occur in 1 in 10 doses or more of the vaccine)
•
loss of appetite
•
fever greater than or equal to 38°C
•
swelling, pain, redness at the injection site
•
tiredness
•
abnormal crying, irritability, restlessness.
Common
(These may occur in up to 1 in 10 doses of the vaccine)
•
diarrhoea, vomiting
•
fever greater than 39.5°C
•
swelling larger than 5 cm at the injection site, hard lump at the injection site
•
nervousness.
Uncommon
(These may occur in up to 1 in 100 doses of the vaccine)
•
sleepiness
•
cough
•
large swelling at the injected limb.
Rare
(These may occur in up to 1 in 1,000 doses of the vaccine)
•
rash.
Very rare
(These may occur in up to 1 in 10,000 doses of the vaccine)
•
swollen glands in the neck, armpit or groin (lymphadenopathy)
•
in babies born very prematurely (at or before 28 weeks of gestation) longer gaps than normal
between breaths may occur for 2-3 days after vaccination.
•
temporarily stopping breathing (apnoea)swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue or throat which
may cause difficulty in swallowing or breathing (angioedema)
•
dermatitis
•
swelling of the entire injected limb, vesicles at the injection site.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor or pharmacist.
5. HOW TO STORE Infanrix hexa
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Infanrix hexa after the expiry date which is stated on the carton. The expiry date refers to
the last day of that month.
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
Store in the original package in order to protect from light.
Do not freeze. Freezing destroys the vaccine.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
What Infanrix hexa contains
The active substances are:
Diphtheria toxoid
1
Bordetella pertussis
antigens
Pertussis toxoid
1
Filamentous Haemagglutinin
1
Hepatitis B surface antigen
2,3
Poliovirus (inactivated)
type 1 (Mahoney strain)
4
type 3 (Saukett strain)
4
Haemophilus
type b polysaccharide
(polyribosylribitol phosphate)
3
conjugated to tetanus toxoid as carrier protein 20-40 micrograms
1
adsorbed on aluminium hydroxide, hydrated (Al(OH)
3
) 0.5 milligrams Al
2
produced in yeast cells (
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
) by recombinant DNA technology
3
adsorbed on aluminium phosphate (AlPO
4
)
4
propagated in VERO cells
The other ingredients in Infanrix hexa are:
Hib powder:
lactose anhydrous
DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension:
sodium chloride (NaCl), medium 199 containing principally
amino acids, mineral salts, vitamins and water for injections
What Infanrix hexa looks like and contents of the pack
Powder and suspension for suspension for injection.
The diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, inactivated poliomyelitis (DTPa-HBV-IPV)
component is a white, slightly milky liquid presented in a glass vial (0.5 ml).
The Hib component is a white powder presented in a glass vial.
Both components must be mixed together before your child receives the vaccine. The mixed
appearance is a white, slightly milky liquid.
Infanrix hexa is available in packs of 1 and 50.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals s.a.
Rue de l’Institut 89
B-1330 Rixensart
Belgium
For any information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the Marketing
Authorisation Holder:
België/Belgique/Belgien
GlaxoSmithKline s.a./n.v.
Tél/Tel: + 32 2 656 21 11
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
GlaxoSmithKline s.a./n.v.
Tél/Tel: + 32 2 656 21 11
България
ГлаксоСмитКлайн ЕООД
ул. Димитър Манов бл.10
София 1408
Тел. + 359 2 953 10 34
Magyarország
GlaxoSmithKline Kft.
Tel.: + 36-1-2255300
Česká republika
GlaxoSmithKline s.r.o.
Tel: + 420 2 22 001 111
gsk.czmail@gsk.com
Malta
GlaxoSmithKline Malta
Tel: + 356 21 238131
Danmark
GlaxoSmithKline Pharma A/S
Tlf: + 45 36 35 91 00
Nederland
GlaxoSmithKline BV
Tel: + 31 (0)30 69 38 100
nlinfo@gsk.com
Deutschland
GlaxoSmithKline GmbH & Co. KG
Tel: + 49 (0)89 360448701
produkt.info@gsk.com
Norge
GlaxoSmithKline AS
Tlf: + 47 22 70 20 00
firmapost@gsk.no
Eesti
GlaxoSmithKline Eesti OÜ
Tel: +372 667 6900
estonia@gsk.com
Österreich
GlaxoSmithKline Pharma GmbH.
Tel: + 43 1 970 75-0
at.info@gsk.com
Ελλάδα
GlaxoSmithKline A.E.B.E
Tηλ: + 30 210 68 82 100
Polska
GSK Commercial Sp. z.o.o.
Tel.: + 48 (22) 576 9000
España
GlaxoSmithKline, S.A.
Tel: + 34 902 202 700
es-ci@gsk.com
Portugal
Smith Kline & French Portuguesa, Produtos
Farmacêuticos, Lda.
Tel: + 351 21 412 95 00
FI.PT@gsk.com
France
Laboratoire GlaxoSmithKline
Tél: + 33 (0) 1 39 17 84 44
diam@gsk.com
România
GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) SRL
Tel: +40 (0)21 3028 208
Ireland
GlaxoSmithKline (Ireland) Ltd
Tel: + 353 (0)1 4955000
Slovenija
GlaxoSmithKline d.o.o.
Tel: + 386 (0) 1 280 25 00
medical.x.si@gsk.com
Ísland
GlaxoSmithKline ehf.
Sími: +354-530 3700
Slovenská republika
GlaxoSmithKline Slovakia s.r.o.
Tel: +421 (0)2 48 26 11 11
recepcia.sk@gsk.com
Italia
GlaxoSmithKline S.p.A.
Tel:+ 39 04 59 21 81 11
Suomi/Finland
GlaxoSmithKline Oy
Puh/Tel: + 358 10 30 30 30
Finland.tuoteinfo@gsk.com
Κύπρος
GlaxoSmithKline (Cyprus) Ltd
Τηλ: + 357 22 39 70 00
Sverige
GlaxoSmithKline AB
Tel: + 46 (0)8 638 93 00
info.produkt@gsk.com
Latvija
GlaxoSmithKline Latvia SIA
Tel: + 371 67312687
lv-epasts@gsk.com
United Kingdom
GlaxoSmithKline UK
Tel: + 44 (0)808 100 9997
customercontactuk@gsk.com
Lietuva
GlaxoSmithKline Lietuva UAB
Tel. +370 5 264 90 00
info.lt@gsk.com
This leaflet was last approved in
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) web
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following information is intended for medical or healthcare professionals only:
Upon storage, a white deposit and clear supernatant may be observed in the vial containing the DTPa-
HBV-IPV suspension. This does not constitute a sign of deterioration.
The DTPa-HBV-IPV suspension should be well shaken in order to obtain a homogeneous turbid white
suspension and should be inspected visually for any foreign particulate matter and/or abnormal
physical appearance. In the event of either being observed, discard the vaccine.
The vaccine is reconstituted by adding the contents of the vial containing the DTPa-HBV-IPV
suspension by means of a syringe to the vial containing the Hib powder. After the addition of the
DTPa-HBV-IPV vaccine to the Hib powder, the mixture should be well shaken until the powder is
completely dissolved.
The reconstituted vaccine presents as a slightly more cloudy suspension than the liquid component
alone. This is normal and does not impair the performance of the vaccine. In the event of other
variation being observed, discard the vaccine.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/infanrix_hexa.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|
























































































































































































































































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































