Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Kentera 3.9 mg / 24 hours transdermal patch
2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each transdermal patch contains 36 mg of oxybutynin. The area of the patch is 39 cm
2
, releasing a
nominal 3.9 mg of oxybutynin per 24 hours.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Transdermal patch. The patch is a clear plastic with an adhesive backing, protected by a release liner
that is to be removed prior to application.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Symptomatic treatment of urge incontinence and/or increased urinary frequency and urgency as may
occur in adult patients with unstable bladder.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
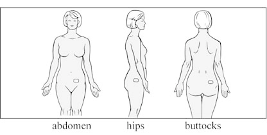
The patch should be applied to dry, intact skin on the abdomen, hip, or buttock immediately after
removal from the protective sachet. A new application site should be selected with each new patch to
avoid reapplication to the same site within 7 days.
The recommended dose is one 3.9 mg transdermal patch applied twice weekly (every 3 to 4 days).
There is no experience in children
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
Kentera is contraindicated in patients with urinary retention, severe gastro-intestinal condition,
myasthenia gravis or narrow-angle glaucoma and in patients who are at risk for these conditions.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Kentera should be used with caution in patients with hepatic or renal impairment. The use of Kentera
in patients with hepatic impairment should be carefully monitored. Other causes of frequent urination
(heart failure or renal disease) should be assessed before treatment with Kentera. If urinary tract
infection is present, an appropriate antibacterial therapy should be started.
Urinary retention:
Anticholinergic products should be administered with caution to patients with
clinically significant bladder outflow obstruction because of the risk of urinary retention.
Kentera should be used with caution in elderly patients, who may be more sensitive to the effects of
centrally acting anticholinergics and exhibit differences in pharmacokinetics.
Oral administration of oxybutynin may warrant the following cautionary statements, but these events
were not observed during clinical trials with Kentera:
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Anticholinergic medicinal products may decrease gastrointestinal motility
and should be used with caution in patients with gastrointestinal obstructive disorders because of the
risk of gastric retention. Also in conditions such as ulcerative colitis, and intestinal atony.
Anticholinergic medicinal products should be used with caution in patients who have hiatus
hernia/gastro-oesophageal reflux and/or who are concurrently taking medicinal products (such as
bisphosphonates) that can cause or exacerbate oesophagitis.
Anticholinergic medicinal products should be used with caution in patients who have autonomic
neuropathy, cognitive impairment or Parkinson's disease
Patients should be informed that heat prostration (fever and heat stroke due to decreased sweating) can
occur when anticholinergics such as oxybutynin are used in a hot environment.
Oxybutynin may exacerbate the symptoms of hyperthyroidism, coronary heart disease, congestive
heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, tachycardia, hypertension and prostatic hypertrophy
Oxybutynin may lead to suppressed salivary secretions which could result in dental caries,
parodontosis or oral candidiasis.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
The concomitant use of oxybutynin with other anticholinergic medicinal products or with other agents
that compete for CYP3A4 enzyme metabolism may increase the frequency or severity of dry mouth,
constipation, and drowsiness.
Anticholinergic agents may potentially alter the absorption of some concomitantly administered
medicinal products due to anticholinergic effects on gastrointestinal motility. As oxybutynin is
metabolised by cytochrome P 450 isoenzyme CYP 3A4, interactions with medicinal products that
inhibit this isoenzyme cannot be ruled out. This should be borne in mind when using azole antifungals
(e.g. ketoconasole) or macrolide antibiotics (e.g. erythromycin) concurrently with oxybutynin.
The anticholinergic activity of oxybutynin is increased by concurrent use of other anticholinergics or
medicinal products with anticholinergic activity, such as amantadine and other anticholinergic
antiparkinsonian medicinal products (e.g. biperiden, levodopa), antihistamines, antipsychotics (e.g.
phenothiazines, butyrophenones, clozapine), quinidine, tricyclic antidepressants, atropine and related
compounds like atropinic antispasmodics, dipyridamole.
Patients should be informed that alcohol may enhance the drowsiness caused by anticholinergic agents
such as oxybutynin (see section 4.7).
Oxybutynin may antagonize prokinetic therapies.
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
There are no adequate data on the use of oxybutynin transdermal patch in pregnant women.
Studies in animals have shown minor reproductive toxicity (see section 5.3). Kentera should not be
used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary.
When oxybutynin is used during breast-feeding, a small amount is excreted in the mother’s milk. Use
of oxybutynin while breast-feeding is therefore not recommended.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
Because Kentera may produce drowsiness, somnolence, or blurred vision, patients should be advised
to exercise caution when driving or using machinery (see section 4.5).
The most commonly reported adverse drug reactions were application site reactions, occurring in
23.1% of patients. Other commonly occurring adverse drug reactions reported were dry mouth (8.6%),
constipation (3.9%), diarrhoea (3.2%), headache (3.0%), dizziness (2.3%) and blurred vision (2.3%).
Adverse reactions known to be associated with anticholinergic therapy, but not observed with Kentera
during clinical studies are anorexia, vomiting, reflux oesophagitis, decreased sweating, heat stroke,
decreased lacrimation, mydriasis, tachycardia, arrhythmia, disorientation, poor ability to concentrate,
fatigue, nightmares, restlessness, convulsion, intraocular hypertension and induction of glaucoma,
confusion, anxiety, paranoia, hallucinations, photosensitivity, erectile dysfunction.
The adverse reactions reported below are classified according to frequency of occurrence as follows:
•
Common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10)
Uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100)
Infections and infestations
Common:
-
Upper respiratory tract infection, fungal infection
Ear and labyrinth disorders
Common:
-
Cardiac disorders
Uncommon:
-
Vascular disorders
Uncommon:
-
Gastrointestinal disorders
Common:
-
Dry mouth, constipation, diarrhoea, nausea, abdominal pain
Abdominal discomfort, dyspepsia
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Uncommon:
-
Renal and urinary disorders
Uncommon:
-
Urinary retention, dysuria
General disorders and administration site conditions
Very common:
-
Application site pruritis
Application site erythema, application site reaction, application site rash, headache,
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
Uncommon:
-
Plasma concentration of oxybutynin declines within 1 to 2 hours after removal of transdermal
system(s). Patients should be monitored until symptoms resolve. Overdosage with oxybutynin has
been associated with anticholinergic effects including central nervous system (CNS) excitation,
flushing, fever, dehydration, cardiac arrhythmia, vomiting, and urinary retention. Ingestion of 100 mg
oral oxybutynin chloride in association with alcohol has been reported in a 13 year old boy who
experienced memory loss, and in a 34 year old woman who developed stupor, followed by
disorientation and agitation on awakening, dilated pupils, dry skin, cardiac arrhythmia, and retention of
urine. Both patients recovered fully with symptomatic treatment.
No cases of overdose have been reported with Kentera.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: urinary antispasmodic, ATC code: G04B D04.
Mechanism of action: oxybutynin acts as a competitive antagonist of acetylcholine at post-ganglionic
muscarinic receptors, resulting in relaxation of bladder smooth muscle.
Pharmacodynamic effects:
In patients with overactive bladder, characterised by detrusor muscle instability or hyperreflexia,
cystometric studies have demonstrated that oxybutynin increases maximum urinary bladder capacity
and increases the volume to first detrusor contraction. Oxybutynin thus decreases urinary urgency and
the frequency of both incontinence episodes and voluntary urination.
Oxybutynin is a racemic (50:50) mixture of R- and S-isomers. Antimuscarinic activity resides
predominantly in the R-isomer. The R-isomer of oxybutynin shows greater selectivity for the M
1
and
M
3
muscarinic subtypes (predominant in bladder detrusor muscle and parotid gland) compared to the
M
2
subtype (predominant in cardiac tissue). The active metabolite, N-desethyloxybutynin, has
pharmacological activity on the human detrusor muscle that is similar to that of oxybutynin
in vitro
studies, but has a greater binding affinity for parotid tissue than oxybutynin. The free base form of
oxybutynin is pharmacologically equivalent to oxybutynin hydrochloride.
Clinical efficacy:
A total of 957 patients with urge urinary incontinence were evaluated in three controlled studies
comparing Kentera to either placebo, oral oxybutynin and/or tolterodine long acting capsules.
Reductions in weekly incontinence episodes, urinary frequency, and urinary void volume were
evaluated. Kentera led to consistent improvements in overactive bladder symptoms compared with
placebo.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Kentera has a concentration of oxybutynin sufficient to maintain continuous transport over the 3 to 4
day dosing interval. Oxybutynin is transported across intact skin and into the systemic circulation by
passive diffusion across the stratum corneum. Following the application of Kentera, oxybutynin
plasma concentration increases for approximately 24 to 48 hours, reaching average maximum
concentrations of 3 to 4 ng/ml. Steady-state conditions are reached during the second application of the
transdermal patch. Thereafter, steady concentrations are maintained for up to 96 hours. The difference
in AUC and C
max
of oxybutynin and the active metabolite N-desethyloxybutynin following
transdermal administration of Kentera on either the abdomen, buttocks or hip is not clinically relevant.
Distribution
Oxybutynin is widely distributed in body tissues following systemic absorption. The volume of
distribution was estimated to be 193 l after intravenous administration of 5 mg oxybutynin
hydrochloride.
Metabolism
Oxybutynin administered orally is metabolised primarily by the cytochrome P450 enzyme systems,
particularly CYP3A4, found mostly in the liver and gut wall. Metabolites include
phenylcyclohexylglycolic acid, which is pharmacologically inactive, and N-desethyloxybutynin, which
is pharmacologically active. Transdermal administration of oxybutynin bypasses the first-pass
gastrointestinal and hepatic metabolism, reducing the formation of the N-desethyl metabolite.
Excretion
Oxybutynin is extensively metabolised by the liver, see above with less than 0.1% of the administered
dose excreted unchanged in the urine. Also, less than 0.1% of the administered dose is excreted as the
metabolite N-desethyloxybutynin.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Pre-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on studies for acute toxicology, repeat
dose toxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenic potential and local toxicity. At a concentration of 0.4
mg/kg/day oxybutynin administered subcutaneously, the occurrence of organ anomalies is
significantly increased, but is observed only in the presence of maternal toxicity. Kentera delivers
approximately 0.08 mg/kg/day. However, in the absence of understanding the association between
maternal toxicity and developmental effect, the relevance to human safety cannot be addressed. In the
subcutaneous fertility study in rats, while no effects were reported in males, in females, fertility was
impaired and a NOAEL (no observed adverse effect level) of 5 mg/kg was identified.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Backing film
Clear polyester/ethylene-vinyl acetate (PET/EVA)
Middle layer
Triacetin
Acrylic copolymer adhesive solution containing 2-ethylhexyl acrylate N-vinyl pyrrolidone and
hexamethyleneglycol dimethacrylate polymer domains
Release Liner
Siliconised polyester
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Do not refrigerate or freeze.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
The transdermal patches are individually contained in LDPE/paper laminate sachets and supplied in
Patient Calendar Boxes of 2, 8 or 24 patches.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Apply immediately upon removal from the protective sachet. After use the patch still contains
substantial quantities of active ingredients. Remaining active ingredients of the patch may have
harmful effects if reaching the aquatic environment. Hence, after removal, the used patch should be
folded in half, adhesive side inwards so that the release membrane is not exposed, placed in the
original sachet and then discarded safely out of reach of children. Any used or unused patches should
be discarded according to local requirements or returned to the pharmacy. Used patches should not be
flushed down the toilet nor placed in liquid waste disposal systems.
Activities that may lead to excessive sweating, or exposure to water or extreme temperature may
contribute to adhesion problems. Do not expose the patch to the sun.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Nicobrand Limited
189 Castleroe Road
Coleraine
Northern Ireland
BT51 3RP
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 15/06/2004
Date of latest renewal: 15/06/2009
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this product is available on the website of the European Medicines Agency
(EMEA) http://www.emea.europa.eu
A.
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH RELEASE
B.
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
Nicobrand Limited
189 Castleroe Road
Coleraine
BT51 3RP
Northern Ireland
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Pharmacovigilance System:
The MAH must ensure that the system of pharmacovigilance, as described in version 1.2 presented in
Module 1.8.1 of the Marketing Authorisation, is in place and functioning before and whilst the product
is on the market.
ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
CARTON (Containing 2, 8 and 24 transdermal patches)
1.
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Kentera 3.9 mg / 24 hours transdermal patch
oxybutynin
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each transdermal patch releases 3.9 mg of oxybutynin per 24 hours. Each patch of 39 cm
2
contains
36 mg of oxybutynin.
Excipients: triacetin; acrylic adhesive (containing 2-ethylhexyl acrylate; N-vinyl pyrrolidone and
hexamethyleneglycol dimethacrylate polymer domains).
Backing: polyester/ethylene-vinyl acetate film; siliconised polyester film.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
2 transdermal patches
8 transdermal patches
24 transdermal patches
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
For transdermal use only.
Do not use if seal on sachet is broken
Apply immediately upon removal from sachet.
Read the package leaflet before use.
Sun/Wed
Mon/Thu
Tue/Fri
Wed/Sat
Thu/Sun
Fri/Mon
Sat/Tue
6. SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED
OUT OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY





























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Do not refrigerate or freeze.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Nicobrand Limited
189 Castleroe Road
Coleraine
Northern Ireland
BT51 3RP
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER (S)
EU/1/03/270/001 <8 transdermal patches>
EU/1/03/270/002 <24 transdermal patches>
EU/1/03/270/003 <2 transdermal patches>
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE

























MINIMUM PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON SMALL IMMEDIATE PACKAGING UNITS
SACHET (Contains 1 transdermal patch)
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Kentera 3.9 mg / 24 hours transdermal patch
oxybutynin
For transdermal use only.
Apply immediately upon removal from sachet.
Read the package leaflet before use.
CONTENTS BY WEIGHT, BY VOLUME OR BY UNIT
Contains 1 transdermal patch.
Do not refrigerate or freeze.



















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Kentera 3.9 mg / 24 hours transdermal patch
Oxybutynin
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using Kentera.
If you have further questions, please ask your doctor or your pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them even if
their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
What Kentera is and what it is used for
1.
WHAT KENTERA IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Kentera is used in adults to control the symptoms of urge incontinence and/or increased urinary
frequency and urgency.
Kentera works by allowing the bladder to expand and accommodate more urine.
2.
BEFORE YOU USE KENTERA
If you are hypersensitive (allergic) to oxybutynin or any of the ingredients of Kentera.
If you have a rare condition called myasthenia gravis that makes the muscles in the body
become weak and tire easily.
If you experience incomplete bladder emptying during urination, the use of oxybutynin may
increase this problem. You should discuss this problem with your doctor before using Kentera.
If you have digestion problems caused by reduced emptying of the stomach after a meal you
should consult your doctor before using Kentera.
If you have glaucoma or a family history of glaucoma, tell your doctor.
Take special care with Kentera:
If you have any of the following:
-
Generalized muscle weakness
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
Since treatment with oxybutynin may cause decreased perspiration, there is an increased risk of fever
and heat stroke if you are exposed to high environmental temperatures.
Kentera is not recommended for use in children or adolescents.
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines,
including medicines obtained without a prescription.
Applying the Kentera patch at the same time as taking other medicines that have similar side effects
such as dry mouth, constipation and drowsiness, may increase how often and how severe these side
effects are experienced.
Oxybutynin may slow the digestive tract and thereby influence the adsorption of other oral medicines,
or the use of this medicine together with other medicines may increase the effect of oxybutynin.
Especially:
-
Ketoconasole, itraconazole or fluconazole (used for the treatment of fungal infections).
Biperiden, levodopa, or amantadine (used to treat Parkinson’s disease).
Antihistamines (used in the treatment of allergies such as hayfever).
Phenothiazines or clozapine (used to treat mental illness).
Tricyclic antidepressants (used to treat depression).
Dipyridamole (used to treat blood clotting problems).
Atropine and other anticholinergic medicines (used for treatment in stomach disorders such as
irritable bowel syndrome).
Using Kentera with food and drink
Oxybutynin may cause drowsiness or blurred vision. Drowsiness may be increased by consumption of
alcohol.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Ask your doctor for advice before taking any medicine.
Kentera should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary.
When oxybutynin is used during breast-feeding, a small amount is excreted in the mother’s milk. Use
of oxybutynin while breast-feeding is therefore not recommended.
Driving and using machines
Because Kentera may produce drowsiness, somnolence, or blurred vision, patients should be advised
to exercise caution when driving or using machinery.
Always use Kentera exactly as your doctor has instructed you. You should check with your doctor or
pharmacist if you are not sure.
Apply a new Kentera patch twice weekly (every 3 to 4 days) according to the instructions for use.
Change the patch on the same two days every week, for example, every Sunday and Wednesday or
Monday and Thursday. Printed on the inside flap of your Kentera package, you will find a Kentera
calendar checklist that will help you to remember your dosing schedule. Mark the schedule you plan to
Erythromycin a macrolide antibiotic (used to treat bacterial infections).
follow and remember always to change your patch on the same two days of the week you have chosen
on your calendar. Make sure to wear only one patch at a time and wear your patch continuously, until
it is time to apply a new one.
Apply the patch to a clean, dry, smooth area of skin on your abdomen, hips or buttocks. Avoid placing
the patch in the waistline area to prevent tight clothing from rubbing against the patch. Do not expose
the patch to the sun. Place the patch underneath your clothing. Rotate application sites with each new
application. Do not apply a patch to the same place on your body for at least 1 week.
Each patch is individually sealed in a protective sachet. Please read all the information below before
you begin to apply Kentera
.
Step 1: Choose a spot for the patch that is:
Freshly washed, but dry and cool (wait a few minutes after taking a hot bath or shower).
Free of cuts, rashes or any other skin irritation.
Step 2: Open the sachet that contains the patch.
Tear open along arrows marked on the right side of the sachet as shown in drawing below.
Do not cut the sachet with scissors, which might damage the patch inside.
Apply immediately to your skin; do not keep or store the patch outside the sealed sachet.
Step 3: Apply one half of the patch to your skin.
Gently bend the patch and remove the first piece of protective liner, which covers the sticky
surface of the patch.
Without touching the sticky surface, firmly press the patch, adhesive face down, onto the part of
the abdomen, hips or buttocks you have selected for application.
Free of body powder, lotion, and oil.
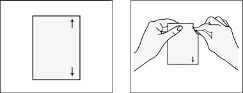
Step 4: Apply the second half of the patch to your skin.
Bend the patch back over itself. Press down on the liner firmly.
Push the liner forward a little to loosen the edge.
Grab the loose edge at either corner and peel off the second piece of the liner. Try not to touch
the sticky surface of the patch.
Press the entire patch firmly onto the skin with your fingertips. Press for at least 10 seconds to
make sure the patch will stay in place. Be sure all of it sticks to your skin, even around the
edges.
Discard the protective liners.
Bathing, showering, swimming and
exercise:
You should wear each patch all the time until you apply a new one. Baths, showers, swimming and
exercise should not affect the patch as long as you don’t rub the patch as you wash. Avoid soaking in a
hot bath for a long period of time, which can make the patch come off.
If the patch starts to lift off your skin, apply a little bit of pressure using your fingertips. The patch is
designed to re-stick. Very rarely will the patch come off completely. If it does, try putting the same
patch back on the same spot. If it sticks firmly all over, leave it on. If not, take it off and put a new
patch on a new spot. No matter what day this happens, continue with the twice-a-week schedule that
you have marked on your patch box.
If you forget to change the patch after 3-4 days:
As soon as you remember, remove the old patch and apply a new one to a new spot on your abdomen,
hips or buttocks. No matter what day this happens, continue with the same twice-a-week schedule for
your next patch, even if it means changing the new patch before 3 to 4 days have elapsed.
When changing the patch, remove the old patch slowly. Fold it in half (sticky sides together) and
throw it away to keep out of the reach of children and pets. Mild redness may be present at the
application site. This redness should disappear within several hours after removal of the patch. If
irritation persists, please contact your doctor.
Gently washing the application site with warm water and a mild soap should remove any adhesive that
remains on your skin after removal of the patch. A small amount of baby oil may also be used to
remove any excess residue. Rings of adhesive that become soiled may require a medical adhesive
removal pad that should be available from your pharmacist. Alcohol or other strong solvents may
cause skin irritation and should not be used.


After use the patch still contains substantial quantities of active ingredients. Remaining active
ingredients of the patch may have harmful effects if reaching the aquatic environment. Hence, after
removal, the used patch should be folded in half, adhesive side inwards so that the release membrane is
not exposed, placed in the original sachet and then discarded safely out of reach of children. Any used
or unused patches should be discarded according to local requirements or returned to the pharmacy.
Used patches should not be flushed down the toilet nor placed in liquid waste disposal systems.
If you use more Kentera than you should
The patient should not apply more than one patch at a time.
If you forget to use Kentera
Apply a Kentera patch as soon as you realise your patch is missing, or you have missed a scheduled
day of application.
If you stop using Kentera
Your urge incontinence may return and you may have increased urinary frequency if you decide to
stop using the patch. Continue to use Kentera as long as your doctor tells you to.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions on the use of this medical product.
Like all medicines, Kentera can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The frequency of possible side effects listed below is defined using the following convention:
-
Very common (affects more than 1 user in 10)
Uncommon (affects 1 to 10 users in 1,000)
Rare (affects 1 to 10 users in 10,000)
Very rare (affects less than 1 user in 10,000)
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data).
Very common side effect:
-
itching around the site of patch application
redness or rash at the site of patch application
upper respiratory tract or fungal infections
Common (affects 1 to 10 users in 100)
If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in the leaflet, please tell
your doctor.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Kentera after the date shown on the sachet and the carton.
Do not refrigerate or freeze.
The used patches should be folded in half, adhesive side inwards so that the release membrane is not
exposed, placed in the original sachet and then discarded safely out of the reach of children. Any used
or unused patches should be discarded according to local requirements or returned to the pharmacy.
Used patches should not be flushed down the toilet nor placed in liquid waste disposal systems.
The active substance is oxybutynin. Each transdermal patch releases 3.9 mg of oxybutynin per
24 hours. Each patch of 39 cm
2
contains 36 mg of oxybutynin.
The other ingredients are: Each patch contains triacetin, and acrylic adhesive solution. The
oxybutynin, triacetin and acrylic adhesive are coated on clear PET/EVA backing film and covered
with a siliconised polyester release liner.
What Kentera looks like and contents of the pack
Kentera is a transdermal patch and it is packaged in cartons containing 2, 8, and 24 patches. Each
patch consists of a clear backing film that has the pharmaceutical ingredients coated on the side
containing the protective backing film. The backing film is to be removed prior to patch application.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Nicobrand Limited
189 Castleroe Road
Coleraine
Northern Ireland
BT51 3RP
For any information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the Marketing
Authorisation Holder.
België/Belgique/Belgien
Eurocept BV
Tél/Tel: +31 (0) 35 528 8377
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
Eurocept BV
Tél/Tel: +31 (0) 35 528 8377




България
Nicobrand Limited
A Subsidiary of Watson Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Великобритания (Обединеното кралство)
Teл.: +44 (0) 28 7086 8733
Magyarország
Nicobrand Limited
A Subsidiary of Watson Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Nagy-Britannia
Tel.: +44 (0) 28 7086 8733
Česká republika
Herbacos Recordati s.r.o.
Tel: +420 466 741 915
Malta
Nicobrand Limited
A Subsidiary of Watson Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Ir-Renju Unit
Tel: +44 (0) 28 7086 8733
Danmark
Orion Pharma A/S
Tlf: +45 49 12 66 00
Nederland
Eurocept BV
Tel: +31 (0) 35 528 8377
Deutschland
Merckle Recordati GmbH
Tel: +49 (0) 731 7047 0
Norge
Orion Pharma AS
Tlf: +47 40 00 42 10
Eesti
Nicobrand Limited
A Subsidiary of Watson Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Ühendkuningriik
Tel: +44 (0) 28 7086 8733
Österreich
Merckle Recordati GmbH
Deutschland
Tel: +49 (0) 731 7047 0
Ελλάδα
Recordati Hellas Pharmaceuticals A.E.
Τηλ: +30 210-6773822
Polska
Nicobrand Limited
A Subsidiary of Watson Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Wielka Brytania
Tel.: +44 (0) 28 7086 8733
España
Recordati España, S.L.
Tel: +34 91 6591550
Portugal
Jaba Recordati S.A.
Tel: +351 21 4329 500
France
Bouchara Recordati Laboratories
Tél: +33 (0) 1 45 19 10 00
România
Nicobrand Limited
A Subsidiary of Watson Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Marea Britanie
Tel: +44 (0) 28 7086 8733
Ireland
Recordati Ireland Ltd.
Tel: +44 (0) 845 0942936
Slovenija
Nicobrand Limited
A Subsidiary of Watson Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Velika Britanija
Tel: +44 (0) 28 7086 8733
Ísland
Nicobrand Limited
A Subsidiary of Watson Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Bretland
Sími: +44 (0) 28 7086 8733
Slovenská
republika
Herbacos Recordati s.r.o.
Česká republika
Tel: +420 466 741 915
Italia
Innova Pharma S.p.A.
Tel: +39 02 48787.1
Suomi/Finland
Orion Corporation
Puh/Tel: +358 10 4261














Κύπρος
Recordati Hellas Pharmaceuticals A.E.
Ελλάδα
Τηλ: +30 210-6773822
Sverige
Orion Pharma AB
Tel: +46 8 623 64 40
Latvija
Nicobrand Limited
A Subsidiary of Watson Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Lielbritānija
Tel: +44 (0) 28 7086 8733
United Kingdom
Orion Pharma (UK) Ltd
Tel: +44 (0) 1635 520300
Lietuva
Nicobrand Limited
A Subsidiary of Watson Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Jungtinė Karalystė
Tel: +44 (0) 28 7086 8733
This leaflet was approved in {MM/YYYY}
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) web
site: http://www.emea.europa.eu






Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/kentera.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|





































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































