Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Levemir
100 U/ml solution for injection in cartridge.
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
1 ml of the solution contains 100 U insulin detemir* (equivalent to 14.2 mg). 1 cartridge contains 3 ml
equivalent to 300 U.
*Insulin detemir is produced by recombinant DNA technology in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Solution for injection in cartridge. Penfill.
Clear, colourless, neutral solution.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults, adolescents and children aged 6–17 years.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The potency of insulin analogues, including insulin detemir, is expressed in units (U), whereas the
potency of insulin human is expressed in international units (IU). 1 unit (U) insulin detemir
corresponds to 1 international unit (IU) of insulin human.
In combination with oral antidiabetic medicinal products it is recommended to use Levemir once daily,
initially at a dose of 10 U or 0.1-0.2 U/kg. The dose of Levemir should be titrated based on individual
patients’ needs.
Based on study results, the following titration guideline is recommended:
Average pre-breakfast SMPG*
> 10.0 mmol/l (180 mg/dl)
9.1-10.0 mmol/l (163-180 mg/dl)
8.1-9.0 mmol/l (145-162 mg/dl)
7.1-8.0 mmol/l (127-144 mg/dl)
6.1-7.0 mmol/l (109-126 mg/dl)
3.1-4.0 mmol/l (56-72 mg/dl)
< 3.1 mmol/l (< 56 mg/dl)
* Self Monitored Plasma Glucose
When Levemir is used as part of a basal-bolus insulin regimen Levemir
should be administered once
or twice
daily depending on patients’ needs. Dose of Levemir
should be adjusted individually.












Adjustment of dose may be necessary if patients undertake increased physical activity, change their
usual diet or during concomitant illness.
Elderly (≥ 65 years old)
Levemir can be used in elderly patients. As with all insulin medicinal products, in elderly patients,
glucose monitoring should be intensified and the insulin detemir dose adjusted on an individual basis.
Renal and hepatic impairment
Renal or hepatic impairment may reduce the patient’s insulin requirements.
As with all insulin medicinal products, in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, glucose
monitoring should be intensified and the insulin detemir dose adjusted on an individual basis.
The efficacy and safety of Levemir were demonstrated in children and adolescents aged 6 to 17 years
in studies up to 6 months (see section 5.1).
As with all insulin medicinal products, in children and adolescents, glucose monitoring should be
intensified and the insulin detemir dose adjusted on an individual basis.
The efficacy and safety of Levemir have not been studied in children below the age of 6 years.
Levemir should only be used in this age group under careful medical supervision.
Transfer from other insulin medicinal products
When transferring from other intermediate or long-acting insulin medicinal products adjustment of the
dose and timing of administration may be necessary (see section 4.4).
As with all insulin medicinal products, close glucose monitoring is recommended during the transfer
and in the initial weeks thereafter (see section 4.4).
Concomitant antidiabetic treatment may need to be adjusted (dose and/or timing of oral antidiabetic
medicinal products or concurrent short/rapid-acting insulin medicinal products).
Levemir is a long-acting insulin analogue used as a basal insulin. Levemir is for subcutaneous
administration only. Levemir must not be administered intravenously, as it may result in severe
hypoglycaemia. Intramuscular administration should also be avoided. Levemir is not to be used in
insulin infusion pumps
.
Levemir
is administered subcutaneously by injection in the abdominal wall, the thigh, the upper arm,
the deltoid region or the gluteal region. Injection sites should always be rotated within the same
anatomic region in order to avoid lipodystrophy. As with all insulin medicinal products the duration of
action will vary according to the dose, injection site, blood flow, temperature and level of physical
activity. The injection can be given at any time during the day, but at the same time each day. For
patients who require twice daily dosing to optimise blood glucose control, the evening dose can be
administered in the evening or at bedtime.
Levemir Penfill is designed to be used with Novo Nordisk insulin delivery systems and NovoFine or
NovoTwist needles. The patient should be advised not to use any counterfeit needles.
Levemir Penfill is accompanied by a package leaflet with detailed instructions for use to be followed.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients (see section 6.1).
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Before travelling between different time zones, the patient should seek the doctor’s advice since this
may mean that the patient has to take the insulin and meals at different times.
Inadequate dosing or discontinuation of treatment, especially in type 1 diabetes, may lead to
hyperglycaemia and diabetic ketoacidosis. Usually the first symptoms of hyperglycaemia develop
gradually over a period of hours or days. They include thirst, increased frequency of urination, nausea,
vomiting, drowsiness, flushed dry skin, dry mouth, loss of appetite as well as acetone odour of breath.
In type 1 diabetes, untreated hyperglycaemic events eventually lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, which is
potentially lethal.
Omission of a meal or unplanned, strenuous physical exercise may lead to hypoglycaemia.
Hypoglycaemia may occur if the insulin dose is too high in relation to the insulin requirement (see
sections 4.8 and 4.9).
Patients, whose blood glucose control is greatly improved, e.g. by intensified insulin therapy, may
experience a change in their usual warning symptoms of hypoglycaemia, and should be advised
accordingly. Usual warning symptoms may disappear in patients with longstanding diabetes.
Concomitant illness, especially infections and feverish conditions, usually increases the patient's
insulin requirements. Concomitant diseases in the kidney, liver or affecting the adrenal, pituitary or
thyroid gland can require changes in insulin dose.
When patients are transferred between different types of insulin medicinal products, the early warning
symptoms of hypoglycaemia may change or become less pronounced than those experienced with
their previous insulin.
Transfer from other insulin medicinal products
Transferring a patient to another type or brand of insulin should be done under strict medical
supervision. Changes in strength, brand (manufacturer), type, origin (animal, human, human insulin
analogue) and/or method of manufacture (recombinant DNA versus animal source insulin) may result
in the need for a change in dose. Patients transferred to Levemir from another type of insulin
may
require a change in dose from that used with their usual insulin medicinal products. If an adjustment is
needed, it may occur with the first dose or during the first few weeks or months.
As with any insulin therapy, injection site reactions may occur and include pain, redness, hives,
inflammation, bruising, swelling and itching. Continuous rotation of the injection site within a given
area may help to reduce or prevent these reactions. Reactions usually resolve in a few days to a few
weeks. On rare occasions, injection site reactions may require discontinuation of Levemir.
There are limited data in patients with severe hypoalbuminaemia. Careful monitoring is recommended
in these patients.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
A number of medicinal products are known to interact with the glucose metabolism.
The following substances may reduce the patient’s insulin requirements:
Oral antidiabetic medicinal products, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI), beta-blockers, angiotensin
converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, salicylates, anabolic steroids and sulphonamides.
The following substances may increase the patient’s insulin requirements:
Oral contraceptives, thiazides, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, sympathomimetics, growth hormone
and danazol.
Beta-blockers may mask the symptoms of hypoglycaemia.
Octreotide/lanreotide may either increase or decrease the insulin requirement.
Alcohol may intensify or reduce the hypoglycaemic effect of insulin.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
There is no clinical experience with insulin detemir during pregnancy.
Animal reproduction studies have not revealed any differences between insulin detemir and insulin
human regarding embryotoxicity and teratogenicity. Caution should be exercised when prescribing to
pregnant women.
In general, intensified blood glucose control and monitoring of pregnant women with diabetes are
recommended throughout pregnancy and when contemplating pregnancy. Insulin requirements usually
fall in the first trimester and increase subsequently during the second and third trimester. After
delivery, insulin requirements normally return rapidly to pre-pregnancy values.
There is no clinical experience with insulin detemir during breast-feeding. Caution should be exercised
when prescribing to breast-feeding women. Breast-feeding women may require adjustments in insulin
dose and diet.
Animal reproduction studies with insulin detemir have not revealed any adverse effects on fertility.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The patient’s ability to concentrate and react may be impaired as a result of hypoglycaemia. This may
constitute a risk in situations where these abilities are of special importance (e.g. driving or using
machines).
Patients should be advised to take precautions to avoid hypoglycaemia while driving. This is
particularly important in those who have reduced or absent awareness of the warning signs of
hypoglycaemia or have frequent episodes of hypoglycaemia. The advisability of driving should be
considered in these circumstances.
a. Summary of the safety profile
Adverse reactions observed in patients using Levemir are mainly due to the pharmacologic effect of
insulin. The overall percentage of treated patients expected to experience adverse reactions is
estimated to be 12%.
The most frequently reported adverse reaction during treatment is hypoglycaemia, please see section c
below.
From clinical investigations, it is known that major hypoglycaemia, defined as requirement for third
party intervention, occurs in approximately 6% of the patients treated with Levemir.
Injection site reactions are seen more frequently during treatment with Levemir than with insulin
human. These reactions include pain, redness, hives, inflammation, bruising, swelling and itching at
the injection site. Most of the injection site reactions are minor and of a transitory nature, i.e. they
normally disappear during continued treatment in a few days to a few weeks.
At the beginning of the insulin treatment, refraction anomalies and oedema may occur; these reactions
are usually of transitory nature. Fast improvement in blood glucose control may be associated with
acute painful neuropathy, which is usually reversible. Intensification of insulin therapy with abrupt
improvement in glycaemic control may be associated with temporary worsening of diabetic
retinopathy, while long-term improved glycaemic control decreases the risk of progression of diabetic
retinopathy.
b. Tabulated list of adverse reactions
Adverse reactions listed below are based on clinical trial data and classified according to MedDRA
frequency and System Organ Class. Frequency categories are defined according to the following
convention: Very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100);
rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000); very rare (< 1/10,000); not known (cannot be estimated from the
available data).
Uncommon – Allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions,
urticaria, rash, eruptions*
Very rare – Anaphylactic reactions*
Metabolism and nutrition
disorders
Very common – Hypoglycaemia*
Rare – Peripheral neuropathy
Uncommon – Refraction disorders
Uncommon – Diabetic retinopathy
Skin and subcutaneous tissue
disorders
Uncommon – Lipodystrophy*
General disorders and
administration site conditions
Common – Injection site reactions
c. Description of selected adverse reactions
Allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions, urticaria, rash, eruptions
Allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions, urticaria, rash and eruptions are uncommon when
Levemir is used in basal-bolus regimen. However, when used in combination with oral antidiabetic












medicinal products, three clinical studies have shown a frequency of common (2.2% of allergic
reactions and potentially allergic reactions have been observed).
Anaphylactic reactions
The occurrence of generalised hypersensitivity reactions (including generalised skin rash, itching,
sweating, gastrointestinal upset, angioneurotic oedema, difficulties in breathing, palpitation and
reduction in blood pressure) is very rare but can potentially be life threatening.
Hypoglycaemia
The most frequently reported adverse reaction is hypoglycaemia. It may occur if the insulin dose is too
high in relation to the insulin requirement. Severe hypoglycaemia may lead to unconsciousness and/or
convulsions and may result in temporary or permanent impairment of brain function or even death.
The symptoms of hypoglycaemia usually occur suddenly. They may include cold sweats, cool pale
skin, fatigue, nervousness or tremor, anxiousness, unusual tiredness or weakness, confusion, difficulty
in concentration, drowsiness, excessive hunger, vision changes, headache, nausea and palpitation.
Lipodystrophy
Lipodystrophy is reported as uncommon. It may occur at the injection site as a consequence of failure
to rotate injection sites within an area.
Based on post-marketing sources and clinical trials, the frequency, type and severity of adverse
reactions observed in the paediatric population do not indicate any differences to the broader
experience in the general population.
e. Other special populations
Based on post-marketing sources and clinical trials, the frequency, type and severity of adverse
reactions observed in the elderly patients and in patients with renal or hepatic impairment do not
indicate any differences to the broader experience in the general population.
A specific overdose for insulin cannot be defined, however, hypoglycaemia may develop over
sequential stages if too high doses relative to the patient’s requirement are administered:
Mild hypoglycaemic episodes can be treated by oral administration of glucose or sugary
products. It is therefore recommended that the diabetic patient always carries sugar-containing
products.
Severe hypoglycaemic episodes, where the patient has become unconscious, can be treated with
glucagon (0.5 to 1 mg) given intramuscularly or subcutaneously, by a trained person, or with
glucose given intravenously by a healthcare professional. Glucose must be given intravenously,
if the patient does not respond to glucagon within 10 to 15 minutes. Upon regaining
consciousness, administration of oral carbohydrates is recommended for the patient in order to
prevent a relapse.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Drugs used in diabetes. Insulins and analogues for injection, long-acting:
ATC code: A10AE05.
Insulin detemir
is a soluble, long-acting insulin analogue with a prolonged duration of effect used as a
basal insulin.
The blood glucose lowering effect of insulin detemir
is due to the facilitated uptake of glucose
following binding of insulin to receptors on muscle and fat cells and to the simultaneous inhibition of
glucose output from the liver.
The time action profile of insulin detemir
is statistically significantly less variable and therefore more
predictable than for NPH (Neutral Protamine Hagedorn) insulin as seen from the within-subject
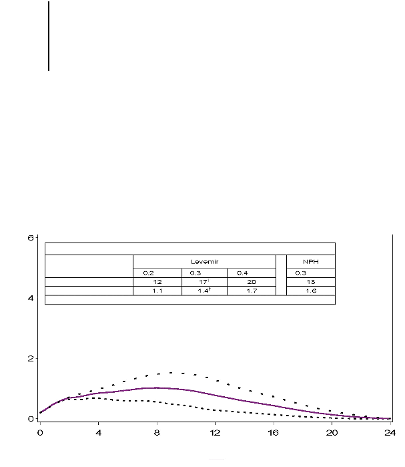
Coefficients of Variation (CV) for the total and maximum pharmacodynamic effect in Table 1.
Table 1
. Within-subject variability of the time action profile of insul
in detemir and NPH insulin
** Glucose Infusion Rate p-value < 0.001 for all comparisons with
The prolonged action of insulin detemir
is mediated by the strong self-association of insulin detemir
molecules at the injection site and albumin binding via the fatty acid side-chain. Insulin detemir is
distributed more slowly to peripheral target tissues compared to NPH insulin. These combined
mechanisms of protraction provide a more reproducible absorption and action profile of insulin
detemir
compared to NPH insulin.
Pharmacodynamic Parameters for Levemir and NPH
Duration of action (hr)
GIR
max
(mg/kg/min)
†
estimated values
Time Since Insulin Injection (hours)
Levemir ….. 0.2 U/kg 0.3 U/kg . . . .0.4 U/kg
Figure 1. Activity profiles of Levemir
in patients with type 1 diabetes.
The duration of action is up to 24 hours depending on dose providing an opportunity for once or twice
daily administration. If administered twice daily, steady state will occur after 2-3 dose administrations.
For doses in the interval of 0.2 - 0.4 U/kg, Levemir
exerts more than 50% of its maximum effect from
3-4 hours and up to approximately 14 hours after dose administration.
Dose proportionality in pharmacodynamic response (maximum effect, duration of action, total effect)
is observed after subcutaneous administration.
Lower day-to-day variability in FPG was demonstrated during treatment with Levemir compared to
NPH in long-term clinical trials.
Studies in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with basal insulin in combination with oral antidiabetic
medicinal products demonstrated that glycaemic control (HbA
1c
) with Levemir is comparable to NPH
insulin and insulin glargine and associated with less weight gain, please see Table 2 below. In the





study versus insulin glargine, insulin detemir was allowed to be administered once or twice daily
whereas insulin glargine was to be administered once a day, 55% of the insulin detemir-treated
subjects completed the 52 weeks of treatment on the twice daily regimen.
Table 2. Change in body weight after insulin treatment
Study duration Insulin detemir
once daily
Insulin detemir
twice daily
NPH insulin Insulin glargine
In trials with the use of oral antidiabetic medicinal products combination therapy Levemir treatment
resulted in a 61-65% lower risk of minor nocturnal hypoglycaemia compared to NPH insulin.
In long-term treatment trials in patients with type 1 diabetes, fasting plasma glucose was improved
with Levemir
compared with NPH insulin when given as basal/bolus therapy including in children and
adolescents aged 6 to 17 years. Glycaemic control (HbA
1c
) with Levemir
is comparable to NPH
insulin, with a lower risk of nocturnal hypoglycaemia and no associated weight gain.
In clinical trials using basal bolus insulin therapy, the overall rates of hypoglycaemia with Levemir
and NPH insulin were similar. Analyses of nocturnal hypoglycaemia in patients with type 1 diabetes
showed a significantly lower risk of minor nocturnal hypoglycaemia (able to self-treat and confirmed
by capillary blood glucose less than 2.8 mmol/l or 3.1 mmol/l if expressed as plasma glucose) than
with NPH insulin, whereas no difference was seen in type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, the overall risk of
nocturnal hypoglycaemia in children and adolescents aged 6 to 17 years with type 1 diabetes was
significantly lower with Levemir compared to NPH insulin.
Antibody development has been observed with the use of Levemir. However, this does not appear to
have any impact on glycaemic control.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Maximum serum concentration is reached between 6 and 8 hours after administration.
When
administered twice daily, steady state serum concentrations are reached after 2-3 dose administrations.
Within-patient variation in absorption is lower for Levemir
than for other basal insulin preparations.
The absolute bioavailability of insulin detemir when administered subcutaneous is approximately
60%.
An apparent volume of distribution for insulin detemir
(approximately 0.1 l/kg) indicates that a high
fraction of insulin detemir
is circulating in the blood.
The results of the
in vitro
and
in vivo
protein binding studies suggest that there is no clinically relevant
interaction between insulin detemir and fatty acids or other protein bound medicinal products.
Degradation of insulin detemir
is similar to that of insulin human; all metabolites formed are inactive.
The terminal half-life after subcutaneous administration is determined by the rate of absorption from
the subcutaneous tissue. The terminal half-life is between 5 and 7 hours depending on the dose.










Dose proportionality in serum concentrations (maximum concentration, extent of absorption) is
observed after subcutaneous administration in the therapeutic dose range.
Elderly (≥ 65 years old)
There was no clinically relevant difference in pharmacokinetics of insulin detemir between elderly and
young subjects.
Renal and hepatic impairment
There was no clinically relevant difference in pharmacokinetics of insulin detemir between subjects
with renal or hepatic impairment and healthy subjects. As the pharmacokinetics of insulin detemir has
not been studied extensively in these populations, it is advised to monitor plasma glucose closely in
these populations.
Gender
There are no clinically relevant differences between genders in pharmacokinetic properties of insulin
detemir.
The pharmacokinetic properties of insulin detemir were investigated in children (6–12 years) and
adolescents (13–17 years) and compared to adults with type 1 diabetes. There was no clinically
relevant difference in pharmacokinetic properties.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety
pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity and toxicity to reproduction and development.
Receptor affinity data and
in vitro
mitogenicity tests revealed no evidence of an increased mitogenic
potential compared to insulin human.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Glycerol
Phenol
Metacresol
Zinc acetate
Disodium phosphate dihydrate
Sodium chloride
Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment)
Sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment)
Water for injections
Substances added to Levemir may cause degradation of insulin detemir, e.g. if the medicinal product
contains thiols or sulphites. Levemir
should not be added to infusion fluids.
This medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products.
After first opening: A maximum of 6 weeks when stored below 30°C.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C). Keep away from the cooling element. Do not freeze.
Keep the cartridge in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
After first opening or carried as a spare: Do not refrigerate. Store below 30°C.
Levemir must be protected from excessive heat and light.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
3 ml solution in cartridge (type 1 glass) with a plunger (bromobutyl) and a stopper
(bromobutyl/polyisoprene) in a carton.
Pack sizes of 1, 5 and 10 cartridges. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Needles and Levemir Penfill must not be shared. The cartridge must not be refilled.
Levemir
must not be used if it does not appear clear and colourless.
Levemir
which has been frozen must not be used.
The patient should be advised to discard the needle after each injection.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd
Denmark
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/04/278/001
EU/1/04/278/002
EU/1/04/278/003
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 01 June 2004
Date of last renewal: 16 April 2009
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines
Agency
http://www.ema.europa.eu
.
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Levemir
100 U/ml solution for injection in pre-filled pen.
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
1 ml of the solution contains 100 U insulin detemir* (equivalent to 14.2 mg). 1 pre-filled pen contains
3 ml equivalent to 300 U.
*Insulin detemir is produced by recombinant DNA technology in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Solution for injection in pre-filled pen. FlexPen.
Clear, colourless, neutral solution.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults, adolescents and children aged 6–17 years.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The potency of insulin analogues, including insulin detemir, is expressed in units (U), whereas the
potency of insulin human is expressed in international units (IU). 1 unit (U) insulin detemir
corresponds to 1 international unit (IU) of insulin human.
In combination with oral antidiabetic medicinal products it is recommended to use Levemir once daily,
initially at a dose of 10 U or 0.1-0.2 U/kg. The dose of Levemir should be titrated based on individual
patients’ needs.
Based on study results, the following titration guideline is recommended:
Average pre-breakfast SMPG*
> 10.0 mmol/l (180 mg/dl)
9.1-10.0 mmol/l (163-180 mg/dl)
8.1-9.0 mmol/l (145-162 mg/dl)
7.1-8.0 mmol/l (127-144 mg/dl)
6.1-7.0 mmol/l (109-126 mg/dl)
3.1-4.0 mmol/l (56-72 mg/dl)
< 3.1 mmol/l (< 56 mg/dl)
* Self Monitored Plasma Glucose
When Levemir is used as part of a basal-bolus insulin regimen Levemir
should be administered once
or twice
daily depending on patients’ needs. Dose of Levemir
should be adjusted individually.












Adjustment of dose may be necessary if patients undertake increased physical activity, change their
usual diet or during concomitant illness.
Elderly (≥
65
years old)
Levemir can be used in elderly patients. As with all insulin medicinal products, in elderly patients,
glucose monitoring should be intensified and the insulin detemir dose adjusted on an individual basis.
Renal and hepatic impairment
Renal or hepatic impairment may reduce the patient’s insulin requirements.
As with all insulin medicinal products, in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, glucose
monitoring should be intensified and the insulin detemir dose adjusted on an individual basis.
The efficacy and safety of Levemir were demonstrated in children and adolescents aged 6 to 17 years
in studies up to 6 months (see section 5.1).
As with all insulin medicinal products, in children and adolescents, glucose monitoring should be
intensified and the insulin detemir dose adjusted on an individual basis.
The efficacy and safety of Levemir have not been studied in children below the age of 6 years.
Levemir should only be used in this age group under careful medical supervision.
Transfer from other insulin medicinal products
When transferring
from other intermediate or long-acting insulin medicinal products adjustment of the
dose and timing of administration may be necessary (see section 4.4).
As with all insulin medicinal products, close glucose monitoring is recommended during the transfer
and in the initial weeks thereafter (see section 4.4).
Concomitant antidiabetic treatment may need to be adjusted (dose and/or timing of oral antidiabetic
medicinal products or concurrent short/rapid-acting insulin medicinal products).
Levemir is a long-acting insulin analogue used as a basal insulin. Levemir is for subcutaneous
administration only. Levemir must not be administered intravenously, as it may result in severe
hypoglycaemia. Intramuscular administration should also be avoided. Levemir is not to be used in
insulin infusion pumps
.
Levemir
is administered subcutaneously by injection in the abdominal wall, the thigh, the upper arm,
the deltoid region or the gluteal region. Injection sites should always be rotated within the same
anatomic region in order to avoid lipodystrophy. As with all insulin medicinal products the duration of
action will vary according to the dose, injection site, blood flow, temperature and level of physical
activity. The injection can be given at any time during the day, but at the same time each day. For
patients who require twice daily dosing to optimise blood glucose control, the evening dose can be
administered in the evening or at bedtime.
Levemir FlexPen are pre-filled pens designed to be used with NovoFine or NovoTwist disposable
needles up to a length of 8 mm. FlexPen delivers 1-60 units in increments of 1 unit. The patient
should be advised not to use any counterfeit needles.
Levemir FlexPen is colour-coded and accompanied by a package leaflet with detailed instructions for
use to be followed.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients (see section 6.1).
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Before travelling between different time zones, the patient should seek the doctor’s advice since this
may mean that the patient has to take the insulin and meals at different times.
Inadequate dosing or discontinuation of treatment, especially in type 1 diabetes, may lead to
hyperglycaemia and diabetic ketoacidosis. Usually the first symptoms of hyperglycaemia develop
gradually over a period of hours or days. They include thirst, increased frequency of urination, nausea,
vomiting, drowsiness, flushed dry skin, dry mouth, loss of appetite as well as acetone odour of breath.
In type 1 diabetes, untreated hyperglycaemic events eventually lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, which is
potentially lethal.
Omission of a meal or unplanned, strenuous physical exercise may lead to hypoglycaemia.
Hypoglycaemia may occur if the insulin dose is too high in relation to the insulin requirement (see
sections 4.8 and 4.9).
Patients, whose blood glucose control is greatly improved, e.g. by intensified insulin therapy, may
experience a change in their usual warning symptoms of hypoglycaemia, and should be advised
accordingly. Usual warning symptoms may disappear in patients with longstanding diabetes.
Concomitant illness, especially infections and feverish conditions, usually increases the patient's
insulin requirements. Concomitant diseases in the kidney, liver or affecting the adrenal, pituitary or
thyroid gland can require changes in insulin dose.
When patients are transferred between different types of insulin medicinal products, the early warning
symptoms of hypoglycaemia may change or become less pronounced than those experienced with
their previous insulin.
Transfer from other insulin medicinal products
Transferring a patient to another type or brand of insulin should be done under strict medical
supervision. Changes in strength, brand (manufacturer), type, origin (animal, human, human insulin
analogue) and/or method of manufacture (recombinant DNA versus animal source insulin) may result
in the need for a change in dose. Patients transferred to Levemir from another type of insulin
may
require a change in dose from that used with their usual insulin medicinal products. If an adjustment is
needed, it may occur with the first dose or during the first few weeks or months.
As with any insulin therapy, injection site reactions may occur and include pain, redness, hives,
inflammation, bruising, swelling and itching. Continuous rotation of the injection site within a given
area may help to reduce or prevent these reactions. Reactions usually resolve in a few days to a few
weeks. On rare occasions, injection site reactions may require discontinuation of Levemir.
There are limited data in patients with severe hypoalbuminaemia. Careful monitoring is recommended
in these patients.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
A number of medicinal products are known to interact with the glucose metabolism.
The following substances may reduce the patient’s insulin requirements:
Oral antidiabetic medicinal products, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI), beta-blockers, angiotensin
converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, salicylates, anabolic steroids and sulphonamides.
The following substances may increase the patient’s insulin requirements:
Oral contraceptives, thiazides, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, sympathomimetics, growth hormone
and danazol.
Beta-blockers may mask the symptoms of hypoglycaemia.
Octreotide/lanreotide may either increase or decrease the insulin requirement.
Alcohol may intensify or reduce the hypoglycaemic effect of insulin.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
There is no clinical experience with insulin detemir during pregnancy.
Animal reproduction studies have not revealed any differences between insulin detemir and insulin
human regarding embryotoxicity and teratogenicity. Caution should be exercised when prescribing to
pregnant women.
In general, intensified blood glucose control and monitoring of pregnant women with diabetes are
recommended throughout pregnancy and when contemplating pregnancy. Insulin requirements usually
fall in the first trimester and increase subsequently during the second and third trimester. After
delivery, insulin requirements normally return rapidly to pre-pregnancy values.
There is no clinical experience with insulin detemir during breast-feeding. Caution should be exercised
when prescribing to breast-feeding women. Breast-feeding women may require adjustments in insulin
dose and diet.
Animal reproduction studies with insulin detemir have not revealed any adverse effects on fertility.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The patient’s ability to concentrate and react may be impaired as a result of hypoglycaemia. This may
constitute a risk in situations where these abilities are of special importance (e.g. driving or using
machines).
Patients should be advised to take precautions to avoid hypoglycaemia while driving. This is
particularly important in those who have reduced or absent awareness of the warning signs of
hypoglycaemia or have frequent episodes of hypoglycaemia. The advisability of driving should be
considered in these circumstances.
a. Summary of the safety profile
Adverse reactions observed in patients using Levemir are mainly due to the pharmacologic effect of
insulin. The overall percentage of treated patients expected to experience adverse reactions is
estimated to be 12%.
The most frequently reported adverse reaction during treatment is hypoglycaemia, please see section c
below.
From clinical investigations, it is known that major hypoglycaemia, defined as requirement for third
party intervention, occurs in approximately 6% of the patients treated with Levemir.
Injection site reactions are seen more frequently during treatment with Levemir than with insulin
human. These reactions include pain, redness, hives, inflammation, bruising, swelling and itching at
the injection site. Most of the injection site reactions are minor and of a transitory nature, i.e. they
normally disappear during continued treatment in a few days to a few weeks.
At the beginning of the insulin treatment, refraction anomalies and oedema may occur; these reactions
are usually of transitory nature. Fast improvement in blood glucose control may be associated with
acute painful neuropathy, which is usually reversible. Intensification of insulin therapy with abrupt
improvement in glycaemic control may be associated with temporary worsening of diabetic
retinopathy, while long-term improved glycaemic control decreases the risk of progression of diabetic
retinopathy.
b. Tabulated list of adverse reactions
Adverse reactions listed below are based on clinical trial data and classified according to MedDRA
frequency and System Organ Class. Frequency categories are defined according to the following
convention: Very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100);
rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000); very rare (< 1/10,000); not known (cannot be estimated from the
available data).
Uncommon – Allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions,
urticaria, rash, eruptions*
Very rare – Anaphylactic reactions*
Metabolism and nutrition
disorders
Very common – Hypoglycaemia*
Rare – Peripheral neuropathy
Uncommon – Refraction disorders
Uncommon – Diabetic retinopathy
Skin and subcutaneous tissue
disorders
Uncommon – Lipodystrophy*
General disorders and
administration site conditions
Common – Injection site reactions
c. Description of selected adverse reactions












Allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions, urticaria, rash, eruptions
Allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions, urticaria, rash and eruptions are uncommon when
Levemir is used in basal-bolus regimen. However, when used in combination with oral antidiabetic
medicinal products, three clinical studies have shown a frequency of common (2.2% of allergic
reactions and potentially allergic reactions have been observed).
Anaphylactic reactions
The occurrence of generalised hypersensitivity reactions (including generalised skin rash, itching,
sweating, gastrointestinal upset, angioneurotic oedema, difficulties in breathing, palpitation and
reduction in blood pressure) is very rare but can potentially be life threatening.
Hypoglycaemia
The most frequently reported adverse reaction is hypoglycaemia. It may occur if the insulin dose is too
high in relation to the insulin requirement. Severe hypoglycaemia may lead to unconsciousness and/or
convulsions and may result in temporary or permanent impairment of brain function or even death.
The symptoms of hypoglycaemia usually occur suddenly. They may include cold sweats, cool pale
skin, fatigue, nervousness or tremor, anxiousness, unusual tiredness or weakness, confusion, difficulty
in concentration, drowsiness, excessive hunger, vision changes, headache, nausea and palpitation.
Lipodystrophy
Lipodystrophy is reported as uncommon. It may occur at the injection site as a consequence of failure
to rotate injection sites within an area.
Based on post-marketing sources and clinical trials, the frequency, type and severity of adverse
reactions observed in the paediatric population do not indicate any differences to the broader
experience in the general population.
e. Other special populations
Based on post-marketing sources and clinical trials, the frequency, type and severity of adverse
reactions observed in the elderly patients and in patients with renal or hepatic impairment do not
indicate any differences to the broader experience in the general population.
A specific overdose for insulin cannot be defined, however, hypoglycaemia may develop over
sequential stages if too high doses relative to the patient’s requirement are administered:
Mild hypoglycaemic episodes can be treated by oral administration of glucose or sugary
products. It is therefore recommended that the diabetic patient always carries sugar-containing
products.
Severe hypoglycaemic episodes, where the patient has become unconscious, can be treated with
glucagon (0.5 to 1 mg) given intramuscularly or subcutaneously, by a trained person, or with
glucose given intravenously by a healthcare professional. Glucose must be given intravenously,
if the patient does not respond to glucagon within 10 to 15 minutes. Upon regaining
consciousness, administration of oral carbohydrates is recommended for the patient in order to
prevent a relapse.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Drugs used in diabetes. Insulins and analogues for injection, long-acting:
ATC code: A10AE05.
Insulin detemir
is a soluble, long-acting insulin analogue with a prolonged duration of effect used as a
basal insulin.
The blood glucose lowering effect of insulin detemir
is due to the facilitated uptake of glucose
following binding of insulin to receptors on muscle and fat cells and to the simultaneous inhibition of
glucose output from the liver.
The time action profile of insulin detemir
is statistically significantly less variable and therefore more
predictable than for NPH (Neutral Protamine Hagedorn) insulin as seen from the within-subject
Coefficients of Variation (CV) for the total and maximum pharmacodynamic effect in Table 1.
NPH insulin
CV (%)
AUC
GIR,0-24h
* 27 68
GIR
max
** 23 46
*Area under the curve ** Glucose Infusion Rate p-value < 0.001 for all comparisons with insulin
detemir
The prolonged action of insulin detemir is mediated by the strong self-association of insulin detemir
molecules at the injection site and albumin binding via the fatty acid side-chain. Insulin detemir is
distributed more slowly to peripheral target tissues compared to NPH insulin. These combined
mechanisms of protraction provide a more reproducible absorption and action profile of insulin
detemir
compared to NPH insulin.
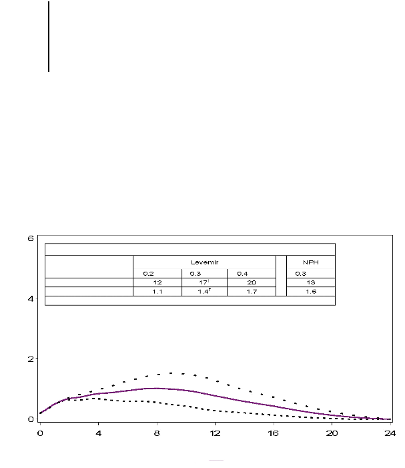
Pharmacodynamic Parameters for Levemir and NPH
Duration of action (hr)
GIR
max
(mg/kg/min)
†
estimated values
Figure 1. Activity profiles of Levemir
in patients with type 1 diabetes.
The duration of action is up to 24 hours depending on dose providing an opportunity for once or twice
daily administration. If administered twice daily, steady state will occur after 2-3 dose administrations.
For doses in the interval of 0.2 - 0.4 U/kg, Levemir
exerts more than 50% of its maximum effect from
3-4 hours and up to approximately 14 hours after dose administration.
Dose proportionality in pharmacodynamic response (maximum effect, duration of action, total effect)
is observed after subcutaneous administration.
Lower day-to-day variability in FPG was demonstrated during treatment with Levemir compared to
NPH in long-term clinical trials.
Table 1
. Within-subject variability of the time action profile of insul
in detemir and NPH insulin
Pharmacodynamic Endpoint
Time Since Insulin Injection (hours)
Levemir ….. 0.2 U/kg 0.3 U/kg . . . .0.4 U/kg




Studies in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with basal insulin in combination with oral antidiabetic
medicinal products demonstrated that glycaemic control (HbA
1c
) with Levemir is comparable to NPH
insulin and insulin glargine and associated with less weight gain, please see Table 2 below. In the
study versus insulin glargine, insulin detemir was allowed to be administered once or twice daily
whereas insulin glargine was to be administered once a day, 55% of the insulin detemir-treated
subjects completed the 52 weeks of treatment on the twice daily regimen.
Table 2. Change in body weight after insulin treatment
Study duration Insulin detemir
once daily
Insulin detemir
twice daily
NPH insulin Insulin glargine
In trials with the use of oral antidiabetic medicinal products combination therapy Levemir treatment
resulted in a 61-65% lower risk of minor nocturnal hypoglycaemia compared to NPH insulin.
In long-term treatment trials in patients with type 1 diabetes, fasting plasma glucose was improved
with Levemir
compared with NPH insulin when given as basal/bolus therapy including in children and
adolescents aged 6 to 17 years. Glycaemic control (HbA
1c
) with Levemir
is comparable to NPH
insulin, with a lower risk of nocturnal hypoglycaemia and no associated weight gain.
In clinical trials using basal bolus insulin therapy, the overall rates of hypoglycaemia with Levemir
and NPH insulin were similar. Analyses of nocturnal hypoglycaemia in patients with type 1 diabetes
showed a significantly lower risk of minor nocturnal hypoglycaemia (able to self-treat and confirmed
by capillary blood glucose less than 2.8 mmol/l or 3.1 mmol/l if expressed as plasma glucose) than
with NPH insulin, whereas no difference was seen in type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, the overall risk of
nocturnal hypoglycaemia in children and adolescents aged 6 to 17 years with type 1 diabetes was
significantly lower with Levemir compared to NPH insulin.
Antibody development has been observed with the use of Levemir. However, this does not appear to
have any impact on glycaemic control.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Maximum serum concentration is reached between 6 and 8 hours after administration. When
administered twice daily, steady state serum concentrations are reached after 2-3 dose administrations.
Within-patient variation in absorption is lower for Levemir
than for other basal insulin preparations.
The absolute bioavailability of insulin detemir when administered subcutaneous is approximately
60%.
An apparent volume of distribution for insulin detemir
(approximately 0.1 l/kg) indicates that a high
fraction of insulin detemir
is circulating in the blood.
The results of the
in vitro
and
in vivo
protein binding studies suggest that there is no clinically relevant
interaction between insulin detemir and fatty acids or other protein bound medicinal products.
Degradation of insulin detemir
is similar to that of insulin human; all metabolites formed are inactive.










The terminal half-life after subcutaneous administration is determined by the rate of absorption from
the subcutaneous tissue. The terminal half-life is between 5 and 7 hours depending on the dose.
Dose proportionality in serum concentrations (maximum concentration, extent of absorption) is
observed after subcutaneous administration in the therapeutic dose range.
Elderly (≥ 65
years old)
There was no clinically relevant difference in pharmacokinetics of insulin detemir
between elderly and
young subjects.
Renal and hepatic impairment
There was no clinically relevant difference in pharmacokinetics of insulin detemir between subjects
with renal or hepatic impairment and healthy subjects. As the pharmacokinetics of insulin detemir has
not been studied extensively in these populations, it is advised to monitor plasma glucose closely in
these populations.
Gender
There are no clinically relevant differences between genders in pharmacokinetic properties of insulin
detemir.
The pharmacokinetic properties of insulin detemir were investigated in children (6–12 years) and
adolescents (13–17 years) and compared to adults with type 1 diabetes. There was no clinically
relevant difference in pharmacokinetic properties.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety
pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity and toxicity to reproduction and development.
Receptor affinity data and
in vitro
mitogenicity tests revealed no evidence of an increased mitogenic
potential compared to insulin human.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Glycerol
Phenol
Metacresol
Zinc acetate
Disodium phosphate dihydrate
Sodium chloride
Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment)
Sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment)
Water for injections
Substances added to Levemir may cause degradation of insulin detemir, e.g. if the medicinal product
contains thiols or sulphites. Levemir
should not be added to infusion fluids.
This medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products.
After first opening: A maximum of 6 weeks when stored below 30°C.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C). Keep away from the cooling element. Do not freeze.
Keep the cap on FlexPen in order to protect from light.
After first opening or carried as a spare: Do not refrigerate. Store below 30°C.
Levemir must be protected from excessive heat and light.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
3 ml solution in cartridge (type 1 glass) with a plunger (bromobutyl) and a stopper
(bromobutyl/polyisoprene) contained in a pre-filled multidose disposable pen made of polypropylene
in a carton.
Pack sizes of 1 (with or without needles), 5 (without needles)
and 10 (without needles) pre-filled pens.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Needles and Levemir FlexPen must not be shared. The cartridge must not be refilled.
Levemir
must not be used if it does not appear clear and colourless.
Levemir
which has been frozen must not be used.
The patient should be advised to discard the needle after each injection.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd
Denmark
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/04/278/004
EU/1/04/278/005
EU/1/04/278/006
EU/1/04/278/010
EU/1/04/278/011
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 01 June 2004
Date of last renewal: 16 April 2009
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines
Agency
http://www.ema.europa.eu
.
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Levemir
100 U/ml solution for injection in pre-filled pen.
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
1 ml of the solution contains 100 U insulin detemir* (equivalent to 14.2 mg). 1 pre-filled pen contains
3 ml equivalent to 300 U.
*Insulin detemir is produced by recombinant DNA technology in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Solution for injection in pre-filled pen. InnoLet.
Clear, colourless, neutral solution.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults, adolescents and children aged 6–17 years.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The potency of insulin analogues, including insulin detemir, is expressed in units (U), whereas the
potency of insulin human is expressed in international units (IU). 1 unit (U) insulin detemir
corresponds to 1 international unit (IU) of insulin human.
In combination with oral antidiabetic medicinal products it is recommended to use Levemir once daily,
initially at a dose of 10 U or 0.1-0.2 U/kg. The dose of Levemir should be titrated based on individual
patients’ needs.
Based on study results, the following titration guideline is recommended:
Average pre-breakfast SMPG*
> 10.0 mmol/l (180 mg/dl)
9.1-10.0 mmol/l (163-180 mg/dl)
8.1-9.0 mmol/l (145-162 mg/dl)
7.1-8.0 mmol/l (127-144 mg/dl)
6.1-7.0 mmol/l (109-126 mg/dl)
3.1-4.0 mmol/l (56-72 mg/dl)
< 3.1 mmol/l (< 56 mg/dl)
* Self Monitored Plasma Glucose
When Levemir is used as part of a basal-bolus insulin regimen Levemir
should be administered once
or twice
daily depending on patients’ needs. Dose of Levemir
should be adjusted individually.












Adjustment of dose may be necessary if patients undertake increased physical activity, change their
usual diet or during concomitant illness.
Elderly (≥
65
years old)
Levemir can be used in elderly patients. As with all insulin medicinal products, in elderly patients,
glucose monitoring should be intensified and the insulin detemir dose adjusted on an individual basis.
Renal and hepatic impairment
Renal or hepatic impairment may reduce the patient’s insulin requirements.
As with all insulin medicinal products, in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, glucose
monitoring should be intensified and the insulin detemir dose adjusted on an individual basis.
The efficacy and safety of Levemir were demonstrated in children and adolescents aged 6 to 17 years
in studies up to 6 months (see section 5.1).
As with all insulin medicinal products, in children and adolescents, glucose monitoring should be
intensified and the insulin detemir dose adjusted on an individual basis.
The efficacy and safety of Levemir have not been studied in children below the age of 6 years.
Levemir should only be used in this age group under careful medical supervision.
Transfer from other insulin medicinal products
When transferring
from other intermediate or long-acting insulin medicinal products adjustment of the
dose and timing of administration may be necessary (see section 4.4).
As with all insulin medicinal products, close glucose monitoring is recommended during the transfer
and in the initial weeks thereafter (see section 4.4).
Concomitant antidiabetic treatment may need to be adjusted (dose and/or timing of oral antidiabetic
medicinal products or concurrent short/rapid-acting insulin medicinal products).
Levemir is a long-acting insulin analogue used as a basal insulin. Levemir is for subcutaneous
administration only. Levemir must not be administered intravenously, as it may result in severe
hypoglycaemia. Intramuscular administration should also be avoided. Levemir is not to be used in
insulin infusion pumps
.
Levemir
is administered subcutaneously by injection in the abdominal wall, the thigh, the upper arm,
the deltoid region or the gluteal region. Injection sites should always be rotated within the same
anatomic region in order to avoid lipodystrophy. As with all insulin medicinal products the duration of
action will vary according to the dose, injection site, blood flow, temperature and level of physical
activity. The injection can be given at any time during the day, but at the same time each day. For
patients who require twice daily dosing to optimise blood glucose control, the evening dose can be
administered in the evening or at bedtime.
Levemir InnoLet are pre-filled pens designed to be used with NovoFine disposable needles up to a
length of 8 mm. InnoLet delivers 1-50 units in increments of 1 unit. The patient should be advised not
to use any counterfeit needles.
Levemir InnoLet is accompanied by a package leaflet with detailed instructions for use to be followed.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients (see section 6.1).
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Before travelling between different time zones, the patient should seek the doctor’s advice since this
may mean that the patient has to take the insulin and meals at different times.
Inadequate dosing or discontinuation of treatment, especially in type 1 diabetes, may lead to
hyperglycaemia and diabetic ketoacidosis. Usually the first symptoms of hyperglycaemia develop
gradually over a period of hours or days. They include thirst, increased frequency of urination, nausea,
vomiting, drowsiness, flushed dry skin, dry mouth, loss of appetite as well as acetone odour of breath.
In type 1 diabetes, untreated hyperglycaemic events eventually lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, which is
potentially lethal.
Omission of a meal or unplanned, strenuous physical exercise may lead to hypoglycaemia.
Hypoglycaemia may occur if the insulin dose is too high in relation to the insulin requirement (see
sections 4.8 and 4.9).
Patients, whose blood glucose control is greatly improved, e.g. by intensified insulin therapy, may
experience a change in their usual warning symptoms of hypoglycaemia, and should be advised
accordingly. Usual warning symptoms may disappear in patients with longstanding diabetes.
Concomitant illness, especially infections and feverish conditions, usually increases the patient's
insulin requirements. Concomitant diseases in the kidney, liver or affecting the adrenal, pituitary or
thyroid gland can require changes in insulin dose.
When patients are transferred between different types of insulin medicinal products, the early warning
symptoms of hypoglycaemia may change or become less pronounced than those experienced with
their previous insulin.
Transfer from other insulin medicinal products
Transferring a patient to another type or brand of insulin should be done under strict medical
supervision. Changes in strength, brand (manufacturer), type, origin (animal, human, human insulin
analogue) and/or method of manufacture (recombinant DNA versus animal source insulin) may result
in the need for a change in dose. Patients transferred to Levemir
from another type of insulin may
require a change in dose from that used with their usual insulin medicinal products. If an adjustment is
needed, it may occur with the first dose or during the first few weeks or months.
As with any insulin therapy, injection site reactions may occur and include pain, redness, hives,
inflammation, bruising, swelling and itching. Continuous rotation of the injection site within a given
area may help to reduce or prevent these reactions. Reactions usually resolve in a few days to a few
weeks. On rare occasions, injection site reactions may require discontinuation of Levemir.
There are limited data in patients with severe hypoalbuminaemia. Careful monitoring is recommended
in these patients.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
A number of medicinal products are known to interact with the glucose metabolism.
The following substances may reduce the patient’s insulin requirements:
Oral antidiabetic medicinal products, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI), beta-blockers, angiotensin
converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, salicylates, anabolic steroids and sulphonamides.
The following substances may increase the patient’s insulin requirements:
Oral contraceptives, thiazides, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, sympathomimetics, growth hormone
and danazol.
Beta-blockers may mask the symptoms of hypoglycaemia.
Octreotide/lanreotide may either increase or decrease the insulin requirement.
Alcohol may intensify or reduce the hypoglycaemic effect of insulin.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
There is no clinical experience with insulin detemir during pregnancy.
Animal reproduction studies have not revealed any differences between insulin detemir and insulin
human regarding embryotoxicity and teratogenicity. Caution should be exercised when prescribing to
pregnant women.
In general, intensified blood glucose control and monitoring of pregnant women with diabetes are
recommended throughout pregnancy and when contemplating pregnancy. Insulin requirements usually
fall in the first trimester and increase subsequently during the second and third trimester. After
delivery, insulin requirements normally return rapidly to pre-pregnancy values.
There is no clinical experience with insulin detemir during breast-feeding. Caution should be exercised
when prescribing to breast-feeding women. Breast-feeding women may require adjustments in insulin
dose and diet.
Animal reproduction studies with insulin detemir have not revealed any adverse effects on fertility.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The patient’s ability to concentrate and react may be impaired as a result of hypoglycaemia. This may
constitute a risk in situations where these abilities are of special importance (e.g. driving or using
machines).
Patients should be advised to take precautions to avoid hypoglycaemia while driving. This is
particularly important in those who have reduced or absent awareness of the warning signs of
hypoglycaemia or have frequent episodes of hypoglycaemia. The advisability of driving should be
considered in these circumstances.
a. Summary of the safety profile
Adverse reactions observed in patients using Levemir are mainly due to the pharmacologic effect of
insulin. The overall percentage of treated patients expected to experience adverse reactions is
estimated to be 12%.
The most frequently reported adverse reaction during treatment is hypoglycaemia, please see section c
below.
From clinical investigations, it is known that major hypoglycaemia, defined as requirement for third
party intervention, occurs in approximately 6% of the patients treated with Levemir.
Injection site reactions are seen more frequently during treatment with Levemir than with insulin
human. These reactions include pain, redness, hives, inflammation, bruising, swelling and itching at
the injection site. Most of the injection site reactions are minor and of a transitory nature, i.e. they
normally disappear during continued treatment in a few days to a few weeks.
At the beginning of the insulin treatment, refraction anomalies and oedema may occur; these reactions
are usually of transitory nature. Fast improvement in blood glucose control may be associated with
acute painful neuropathy, which is usually reversible. Intensification of insulin therapy with abrupt
improvement in glycaemic control may be associated with temporary worsening of diabetic
retinopathy, while long-term improved glycaemic control decreases the risk of progression of diabetic
retinopathy.
b. Tabulated list of adverse reactions
Adverse reactions listed below are based on clinical trial data and classified according to MedDRA
frequency and System Organ Class. Frequency categories are defined according to the following
convention: Very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100);
rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000); very rare (< 1/10,000); not known (cannot be estimated from the
available data).
Uncommon – Allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions,
urticaria, rash, eruptions*
Very rare – Anaphylactic reactions*
Metabolism and nutrition
disorders
Very common – Hypoglycaemia*
Rare – Peripheral neuropathy
Uncommon – Refraction disorders
Uncommon – Diabetic retinopathy
Skin and subcutaneous tissue
disorders
Uncommon – Lipodystrophy*
General disorders and
administration site conditions
Common – Injection site reactions
c. Description of selected adverse reactions












Allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions, urticaria, rash, eruptions
Allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions, urticaria, rash and eruptions are uncommon when
Levemir is used in basal-bolus regimen. However, when used in combination with oral antidiabetic
medicinal products, three clinical studies have shown a frequency of common (2.2% of allergic
reactions and potentially allergic reactions have been observed).
Anaphylactic reactions
The occurrence of generalised hypersensitivity reactions (including generalised skin rash, itching,
sweating, gastrointestinal upset, angioneurotic oedema, difficulties in breathing, palpitation and
reduction in blood pressure) is very rare but can potentially be life threatening.
Hypoglycaemia
The most frequently reported adverse reaction is hypoglycaemia. It may occur if the insulin dose is too
high in relation to the insulin requirement. Severe hypoglycaemia may lead to unconsciousness and/or
convulsions and may result in temporary or permanent impairment of brain function or even death.
The symptoms of hypoglycaemia usually occur suddenly. They may include cold sweats, cool pale
skin, fatigue, nervousness or tremor, anxiousness, unusual tiredness or weakness, confusion, difficulty
in concentration, drowsiness, excessive hunger, vision changes, headache, nausea and palpitation.
Lipodystrophy
Lipodystrophy is reported as uncommon. It may occur at the injection site as a consequence of failure
to rotate injection sites within an area.
Based on post-marketing sources and clinical trials, the frequency, type and severity of adverse
reactions observed in the paediatric population do not indicate any differences to the broader
experience in the general population.
e. Other special populations
Based on post-marketing sources and clinical trials, the frequency, type and severity of adverse
reactions observed in the elderly patients and in patients with renal or hepatic impairment do not
indicate any differences to the broader experience in the general population.
A specific overdose for insulin cannot be defined, however, hypoglycaemia may develop over
sequential stages if too high doses relative to the patient’s requirement are administered:
Mild hypoglycaemic episodes can be treated by oral administration of glucose or sugary
products. It is therefore recommended that the diabetic patient always carries sugar-containing
products.
Severe hypoglycaemic episodes, where the patient has become unconscious, can be treated with
glucagon (0.5 to 1 mg) given intramuscularly or subcutaneously by a trained person, or with
glucose given intravenously, by a healthcare professional. Glucose must be given intravenously,
if the patient does not respond to glucagon within 10 to 15 minutes. Upon regaining
consciousness, administration of oral carbohydrates is recommended for the patient in order to
prevent a relapse.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Drugs used in diabetes. Insulins and analogues for injection, long-acting:
ATC code: A10AE05.
Insulin detemir
is a soluble, long-acting insulin analogue with a prolonged duration of effect used as a
basal insulin.
The blood glucose lowering effect of insulin detemir
is due to the facilitated uptake of glucose
following binding of insulin to receptors on muscle and fat cells and to the simultaneous inhibition of
glucose output from the liver.
The time action profile of insulin detemir
is statistically significantly less variable and therefore more
predictable than for NPH (Neutral Protamine Hagedorn) insulin as seen from the within-subject
Coefficients of Variation (CV) for the total and maximum pharmacodynamic effect in Table 1.
Table 1
. Within-subject variability of the time action profile of insul
in detemir and NPH insulin
NPH insulin
CV (%)
AUC
GIR,0-24h
* 27 68
GIR
max
** 23 46
*Area under the curve ** Glucose Infusion Rate p-value < 0.001 for all comparisons with insulin
detemir
The prolonged action of insulin detemir
is mediated by the strong self-association of insulin detemir
molecules at the injection site and albumin binding via the fatty acid side-chain. Insulin detemir is
distributed more slowly to peripheral target tissues compared to NPH insulin. These combined
mechanisms of protraction provide a more reproducible absorption and action profile of insulin
detemir
compared to NPH insulin.
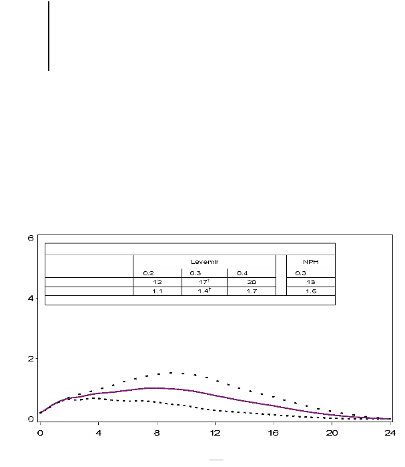
Pharmacodynamic Parameters for Levemir and NPH
Duration of action (hr)
GIR
max
(mg/kg/min)
†
estimated values
Figure 1. Activity profiles of Levemir
in patients with type 1 diabetes.
The duration of action is up to 24 hours depending on dose providing an opportunity for once or twice
daily administration. If administered twice daily, steady state will occur after 2-3 dose administrations.
For doses in the interval of 0.2 - 0.4 U/kg, Levemir
exerts more than 50% of its maximum effect from
3-4 hours and up to approximately 14 hours after dose administration.
Dose proportionality in pharmacodynamic response (maximum effect, duration of action, total effect)
is observed after subcutaneous administration.
Lower day-to-day variability in FPG was demonstrated during treatment with Levemir compared to
NPH in long-term clinical trials.
Time Since Insulin Injection (hours)
Levemir ….. 0.2 U/kg 0.3 U/kg . . . .0.4 U/kg




Studies in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with basal insulin in combination with oral antidiabetic
medicinal products demonstrated that glycaemic control (HbA
1c
) with Levemir is comparable to NPH
insulin and insulin glargine and associated with less weight gain, please see Table 2 below. In the
study versus insulin glargine, insulin detemir was allowed to be administered once or twice daily
whereas insulin glargine was to be administered once a day, 55% of the insulin detemir-treated
subjects completed the 52 weeks of treatment on the twice daily regimen.
Table 2. Change in body weight after insulin treatment
Study duration Insulin detemir
once daily
Insulin detemir
twice daily
NPH insulin Insulin glargine
In trials with the use of oral antidiabetic medicinal products combination therapy Levemir treatment
resulted in a 61-65% lower risk of minor nocturnal hypoglycaemia compared to NPH insulin.
In long-term treatment trials in patients with type 1 diabetes, fasting plasma glucose was improved
with Levemir
compared with NPH insulin when given as basal/bolus therapy including in children and
adolescents aged 6 to 17 years. Glycaemic control (HbA
1c
) with Levemir
is comparable to NPH
insulin, with a lower risk of nocturnal hypoglycaemia and no associated weight gain.
In clinical trials using basal bolus insulin therapy, the overall rates of hypoglycaemia with Levemir
and NPH insulin were similar. Analyses of nocturnal hypoglycaemia in patients with type 1 diabetes
showed a significantly lower risk of minor nocturnal hypoglycaemia (able to self-treat and confirmed
by capillary blood glucose less than 2.8 mmol/l or 3.1 mmol/l if expressed as plasma glucose) than
with NPH insulin, whereas no difference was seen in type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, the overall risk of
nocturnal hypoglycaemia in children and adolescents aged 6 to 17 years with type 1 diabetes was
significantly lower with Levemir compared to NPH insulin.
Antibody development has been observed with the use of Levemir. However, this does not appear to
have any impact on glycaemic control.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Maximum serum concentration is reached between 6 and 8 hours after administration. When
administered twice daily, steady state serum concentrations are reached after 2-3 dose administrations.
Within-patient variation in absorption is lower for Levemir
than for other basal insulin preparations.
The absolute bioavailability of insulin detemir when administered subcutaneous is approximately
60%.
An apparent volume of distribution for insulin detemir (approximately 0.1 l/kg) indicates that a high
fraction of insulin detemir
is circulating in the blood.
The results of the
in vitro
and
in vivo
protein binding studies suggest that there is no clinically relevant
interaction between insulin detemir and fatty acids or other protein bound medicinal products.
Degradation of insulin detemir
is similar to that of insulin human; all metabolites formed are inactive.










The terminal half-life after subcutaneous administration is determined by the rate of absorption from
the subcutaneous tissue. The terminal half-life is between 5 and 7 hours depending on the dose.
Dose proportionality in serum concentrations (maximum concentration, extent of absorption) is
observed after subcutaneous administration in the therapeutic dose range.
Elderly (≥ 65
years old)
There was no clinically relevant difference in pharmacokinetics of insulin detemir
between elderly and
young subjects.
Renal and hepatic impairment
There was no clinically relevant difference in pharmacokinetics of insulin detemir between subjects
with renal or hepatic impairment and healthy subjects. As the pharmacokinetics of insulin detemir has
not been studied extensively in these populations, it is advised to monitor plasma glucose closely in
these populations.
Gender
There are no clinically relevant differences between genders in pharmacokinetic properties of insulin
detemir.
The pharmacokinetic properties of insulin detemir were investigated in children (6–12 years) and
adolescents (13–17 years) and compared to adults with type 1 diabetes. There was no clinically
relevant difference in pharmacokinetic properties.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety
pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity and toxicity to reproduction and development.
Receptor affinity data and
in vitro
mitogenicity tests revealed no evidence of an increased mitogenic
potential compared to insulin human.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Glycerol
Phenol
Metacresol
Zinc acetate
Disodium phosphate dihydrate
Sodium chloride
Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment)
Sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment)
Water for injections
Substances added to Levemir may cause degradation of insulin detemir, e.g. if the medicinal product
contains thiols or sulphites. Levemir
should not be added to infusion fluids.
This medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products.
After first opening: A maximum of 6 weeks when stored below 30°C.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C). Keep away from the cooling element. Do not freeze.
Keep the cap on InnoLet in order to protect from light.
After first opening or carried as a spare: Do not refrigerate. Store below 30°C.
Levemir must be protected from excessive heat and light.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
3 ml solution in cartridge (type 1 glass) with a plunger (bromobutyl) and a stopper
(bromobutyl/polyisoprene) contained in a pre-filled multidose disposable pen made of polypropylene
in a carton.
Pack sizes of 1, 5 and 10 pre-filled pens. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Needles and Levemir InnoLet must not be shared. The cartridge must not be refilled.
Levemir
must not be used if it does not appear clear and colourless.
Levemir
which has been frozen must not be used.
The patient should be advised to discard the needle after each injection.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd
Denmark
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/04/278/007
EU/1/04/278/008
EU/1/04/278/009
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 01 June 2004
Date of last renewal: 16 April 2009
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines
Agency
http://www.ema.europa.eu
.
A. MANUFACTURER OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE
SUBSTANCE AND MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION
HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH RELEASE
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
MANUFACTURER OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE SUBSTANCE AND
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer of the biological active substance
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd
Denmark
Novo Nordisk A/S
Hallas Allé
DK-4400 Kalundborg
Denmark
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd
Denmark
Levemir Penfill and FlexPen
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd
Denmark
Novo Nordisk Production SAS
45, Avenue d’Orléans
F-28002 Chartres
France
The printed package leaflet of the medicinal product must state the name and address of the
manufacturer responsible for the release of the concerned batch.
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
The MAH must ensure that the system of pharmacovigilance, as described in version 9
presented in Module 1.8.1 of the Marketing Authorisation Application, is in place and
functioning before and whilst the product is on the market.
Risk Management Plan
The MAH commits to performing the studies and additional pharmacovigilance activities
detailed in the Pharmacovigilance Plan, as agreed in version 1.0 (as of 22 September 2009) of
the Risk Management Plan (RMP) presented in Module 1.8.2 of the Marketing Authorisation
Application and any subsequent updates of the RMP agreed by the CHMP.
As per the CHMP Guideline on Risk Management Systems for medicinal products for human
use, any updated RMP should be submitted at the same time as the next Periodic Safety Update
Report (PSUR).
In addition, an updated RMP should be submitted:
•
When new information is received that may impact the current Safety Specification,
Pharmacovigilance Plan or risk minimisation activities.
Within 60 days of an important (pharmacovigilance or risk minimisation) milestone
At the request of the European MedicinesAgency.
ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
OUTER CARTON (CARTRIDGE. Penfill)
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Levemir
100 U/ml solution for injection in cartridge
Insulin detemir
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE
1 cartridge of 3 ml contains 300 U
1 ml solution contains 100 U insulin detemir (equivalent to 14.2 mg),
glycerol, phenol, metacresol, zinc acetate, disodium phosphate dihydrate, sodium chloride,
hydrochloric acid/sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment and water for injections
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Solution for injection in cartridge. Penfill.
1 x 3 ml
5 x 3 ml
10 x 3 ml
METHOD AND ROUTE OF ADMINISTRATION
Read the package leaflet before use
Subcutaneous use
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNINGS, IF NECESSARY
Use only clear, colourless solution.
Single patient use only
EXP
After first opening: Use within 6 weeks






























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C)
Do not freeze
Keep the cartridge in the outer carton in order to protect from light
After first opening: Do not refrigerate. Store below 30°C
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
Discard the needle after each injection
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd
Denmark
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBERS
EU/1/04/278/001 1 cartridge of 3 ml
EU/1/04/278/002 5 cartridges of 3 ml
EU/1/04/278/003 10 cartridges of 3 ml
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE






















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
OUTER CARTON (PRE-FILLED PEN. FlexPen)
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Levemir 100 U/ml solution for injection in pre-filled pen
Insulin detemir
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE
1 pre-filled pen of 3 ml contains 300 U
1 ml solution contains 100 U insulin detemir (equivalent to 14.2 mg),
glycerol, phenol, metacresol, zinc acetate, disodium phosphate dihydrate, sodium chloride,
hydrochloric acid/sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment and water for injections
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Solution for injection in pre-filled pen. FlexPen.
1 x 3 ml
5 x 3 ml
10 x 3 ml
1 x 3 ml + 7 NovoFine needles
1 x 3 ml + 7 NovoTwist needles
METHOD AND ROUTE OF ADMINISTRATION
Needles are not included.
Read the package leaflet before use
Subcutaneous use
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNINGS, IF NECESSARY
Use only clear, colourless solution.
Single patient use only
Designed to be used with NovoFine or NovoTwist disposable needles up to a length of 8 mm































EXP
After first opening: Use within 6 weeks
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C)
Do not freeze
Keep the cap on in order to protect from light
After first opening: Do not refrigerate. Store below 30°C
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
Discard the needle after each injection
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd
Denmark
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBERS
EU/1/04/278/004 1 pen of 3 ml
EU/1/04/278/005 5 pens of 3 ml
EU/1/04/278/006 10 pens of 3 ml
EU/1/04/278/010 1 pen of 3 ml and 7 NovoFine needles
EU/1/04/278/011 1 pen of 3 ml and 7 NovoTwist needles
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE























PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
OUTER CARTON (PRE-FILLED PEN. InnoLet)
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Levemir
100 U/ml solution for injection in pre-filled pen
Insulin detemir
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE
1 pre-filled pen of 3 ml contains 300 U
1 ml solution contains 100 U insulin detemir (equivalent to 14.2 mg),
glycerol, phenol, metacresol, zinc acetate, disodium phosphate dihydrate, sodium chloride,
hydrochloric acid/sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment and water for injections
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Solution for injection in pre-filled pen. InnoLet.
1 x 3 ml
5 x 3 ml
10 x 3 ml
METHOD AND ROUTE OF ADMINISTRATION
Needles are not included.
Read the package leaflet before use
Subcutaneous use
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNINGS, IF NECESSARY
Use only clear, colourless solution.
Single patient use only
Designed to be used with NovoFine disposable needles up to a length of 8 mm






























After first opening: Use within 6 weeks
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C)
Do not freeze
Keep the cap on in order to protect from light
After first opening: Do not refrigerate. Store below 30°C
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
Discard the needle after each injection
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd
Denmark
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBERS
EU/1/04/278/007 1 pen of 3 ml
EU/1/04/278/008 5 pens of 3 ml
EU/1/04/278/009 10 pens of 3 ml
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE






















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Levemir 100 U/ml solution for injection in cartridge
Insulin detemir
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine
–
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
What Levemir is and what it is used for
WHAT LEVEMIR IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Levemir
is a modern insulin (insulin analogue) with a long-acting effect. Modern insulins are
improved versions of insulin human.
Levemir is used to treat diabetes mellitus in adults, adolescents and children aged 6 years and above.
Diabetes mellitus is a disease where your body does not produce enough insulin to control the level of
your blood sugar. Levemir may be used in combination with oral antidiabetic medicines or with meal-
related rapid acting insulin medicines.
Levemir has a long and steady blood-sugar-lowering action starting within a few hours (3-4). Levemir
provides 24 hours of basal insulin coverage after injection.
► If you are allergic
(hypersensitive) to insulin detemir or any of the other ingredients in Levemir
(see 6 Further information).
► If you suspect hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar) is starting (see
3
How to use Levemir).
► In insulin infusion pumps.
► If the cartridge or the device containing the cartridge is dropped, damaged or crushed.
► If it has not been stored correctly or been frozen (see 5 How to store Levemir).
► If the insulin does not appear water clear and colourless.
► Check the label to make sure it is the right type of insulin.
► Always check the cartridge, including the rubber plunger (stopper). Do not use it if any damage
is seen or if there is a gap between the rubber plunger and the white label band. Take it back to
your supplier. See your delivery system manual for further instructions.
► Always use a new needle for each injection to prevent contamination.
► Needles and Levemir Penfill must not be shared.
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
Take special care with Levemir
► If you have trouble with your kidneys or liver, or with your adrenal, pituitary or thyroid glands.
► If you exercise more than usual or if you want to change your usual diet, as this may affect your
blood sugar level.
► If you are ill, carry on taking your insulin and consult your doctor.
► If you are going abroad: travelling over time zones may affect your insulin needs and the timing
of your injections. Consult your doctor if you are planning such travelling.
► If you have very low albumin you need to carefully monitor your blood sugar level. Discuss this
with your doctor.
Some medicines affect the way glucose works in your body and this may influence your insulin dose.
Listed below are the most common medicines, which may affect your insulin treatment. Tell your
doctor, nurse or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines, including
medicines obtained without a prescription. In particular, you should tell your doctor if you are using
any medicine as mentioned below that affects your blood sugar level.
If you take any of the medicines below, your blood sugar level may fall (hypoglycaemia):
•
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) (used to treat depression)
Beta-blockers (used to treat high blood pressure)
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (used to treat certain heart conditions or high
blood pressure)
Salicylates (used to relieve pain and lower fever)
Anabolic steroids (such as testosterone)
Sulphonamides (used to treat infections)
If you take any of the medicines below, your blood sugar level may rise (hyperglycaemia):
•
Oral contraceptives (birth control pills)
Thiazides (used to treat high blood pressure or excessive fluid retention)
Thyroid hormones (used to treat thyroid gland disorders)
Sympathomimetics (such as epinephrine [adrenaline], or salbutamol, terbutaline used to treat
asthma)
Growth hormone (medicine for stimulation of skeletal and somatic growth and pronounced
influence on the body’s metabolic processes)
Danazol (medicine acting on ovulation)
Octreotide and lanreotide (used for treatment of acromegaly, a rare hormonal disorder that usually
occurs in middle-aged adults, caused by the pituitary gland producing excess growth hormone) may
either increase or decrease your sugar level.
Beta-blockers (used to treat high blood pressure) may weaken or suppress entirely the first warning
symptoms which help you to recognise a hypoglycaemia.
Taking Levemir with food and drink
► If you drink alcohol, your need for insulin may change, as your blood sugar level may either
rise or fall. Careful monitoring is recommended.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Other medicines for the treatment of diabetes
Glucocorticoids (such as ‘cortisone’ used to treat inflammation)
► If you are pregnant, planning a pregnancy or breast-feeding
please contact your doctor for
advice. Your insulin dose may need to be changed during pregnancy particularly after delivery.
Careful control of your diabetes, and prevention of hypoglycaemia, is important for the health
of your baby.
Driving and using machines
If your blood sugar is low or high, your concentration and ability to react might be affected and
therefore also your ability to drive or operate a machine. Bear in mind that you could endanger
yourself or others. Please ask your doctor whether you can drive a car:
► If you have frequent hypoglycaemia.
► If you find it hard to recognise hypoglycaemia.
Important information about some of the ingredients in Levemir
Levemir contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per dose, i.e. Levemir is essentially ‘sodium-free’.
Talk about your insulin dose with your doctor and nurse. Make sure you get Levemir Penfill as your
doctor and nurse have told you to use and follow their advice carefully
.
If your doctor has switched you
from one type or brand of insulin to another, your dose may have to
be adjusted by your doctor. Do not change your insulin unless your doctor tells you to.
Levemir can be used in children and adolescents 6 years and above.
There is no experience with the use of Levemir in children below the age of 6 years. Therefore, only
use Levemir in children below this age, if your doctor has specifically told you to.
Use in special populations
If you have reduced kidney or liver function, or if you are above 65 years of age, you need to check
your blood glucose more regularly and discuss changes in your insulin dose with your doctor.
Frequency of administration
When Levemir is used in combination with an oral antidiabetic medicine, Levemir should be
administered once a day. When Levemir is used as part of a basal-bolus insulin regimen Levemir
should be administered once or twice
daily depending on patients’ needs. Dose of Levemir
should be
adjusted individually. The injection can be given at any time during the day, but at the same time each
day. For patients who require twice daily dosing to optimise blood glucose control, the evening dose
can be administered in the evening or at bedtime.
Levemir
is for injection under the skin (subcutaneously). Never inject your insulin directly into a vein
(intravenously) or muscle (intramuscular). Always vary the sites you inject within the same region, to
avoid lumps (see 4 Possible side effects). The best places to give yourself an injection are: the front of
your thighs, the front of your waist (abdomen), or the upper arm. You should always measure your
blood glucose regularly.
Inject the insulin under the skin. Use the injection technique advised by your doctor or nurse
and as described in your delivery system manual.
Keep the needle under your skin for at least 6 seconds to make sure that the full dose has been
delivered.
After each injection
be sure to remove and discard the needle
and store Levemir without the
needle attached. Otherwise the liquid may leak out, which can cause inaccurate dosing.
Do not refill the cartridge.
Levemir Penfill cartridges are designed to be used with Novo Nordisk insulin delivery systems and
NovoFine or NovoTwist needles. Be sure you are not using any counterfeit needles. Ask your
pharmacist.
If you are treated with Levemir
Penfill and another insulin Penfill cartridge, you should use two
insulin delivery systems, one for each type of insulin.
If you take more Levemir than you should
If you take too much insulin your blood sugar gets too low (this is called hypoglycaemia or hypo).
This may also happen:
•
If you eat too little or miss a meal.
If you exercise more than usual.
The warning signs of a hypo may come on suddenly and can include: cold sweat; cool pale skin;
headache; rapid heart beat; feeling sick; feeling very hungry; temporary changes in vision; drowsiness;
unusual tiredness and weakness; nervousness or tremor; feeling anxious; feeling confused; difficulty in
concentrating.
If you feel a hypo coming on: take a high sugar snack and then measure your blood sugar.
If your blood sugar is too low: eat glucose tablets or another high sugar snack (sweets, biscuits, fruit
juice), then rest.
Always carry glucose tablets, sweets, biscuits or fruit juice with you, just in case.
When the symptoms of hypoglycaemia have disappeared or when your blood glucose level is
stabilised continue insulin treatment.
Tell relevant people you have diabetes and what the consequences may be, including the risk of
passing out (becoming unconscious) due to a hypo.
Tell relevant people that if you pass out, they must turn you on your side and get medical help straight
away. They must not give you any food or drink. It could choke you.
You may recover more quickly from unconsciousness with an injection of the hormone glucagon by
someone who knows how to use it. If you are given glucagon you will need glucose or a sugary snack
as soon as you are conscious. If you do not respond to glucagon treatment, you will have to be treated
in a hospital. Contact your doctor or an emergency ward after an injection of glucagon: you need to
find the reason for your hypo to avoid getting more.
► If prolonged severe hypoglycaemia is not treated, it can cause brain damage (temporary or
permanent) and even death.
► If you have a hypo that makes you pass out, or a lot of hypos, talk to your doctor. The amount
or timing of insulin, food or exercise may need to be adjusted.
If you forget to take Levemir
If you forget to take your insulin
your blood sugar may get too high (this is called hyperglycaemia).
This may also happen:
•
If you repeatedly take less insulin than you need.
If you get an infection or a fever.
If you eat more than usual.
If you exercise less than usual.
The warning signs appear gradually. They include: increased urination; feeling thirsty; losing your
appetite; feeling sick (nausea or vomiting); feeling drowsy or tired; flushed, dry skin; dry mouth and a
fruity (acetone) smell of the breath.
If you get any of these signs:
test your blood sugar level, test your urine for ketones if you can, then
seek medical advice immediately.
These may be signs of a very serious condition called diabetic ketoacidosis. If you do not treat it, this
could lead to diabetic coma and eventually death.
If you stop taking Levemir
This could lead to severe hyperglycaemia (very high blood sugar) and ketoacidosis (build-up of acid in
the blood because the body is breaking down fat instead of sugar). Do not stop taking your insulin
without speaking to a doctor, who will tell you what needs to be done.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Like all medicines, Levemir
can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Side effects may occur with certain frequencies, which are defined as follows:
•
Very common: affects more than 1 user in 10
Uncommon: affects 1 to 10 users in 1,000
Rare: affects 1 to 10 users in 10,000
Very rare: affects less than 1 user in 10,000
Not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia). See the advice in “If you take more Levemir than you should”
under 3 How to use Levemir.
Injection site
reactions (pain, redness, hives, inflammation, bruising, swelling and itching). These
usually disappear after a few weeks of taking your insulin. If they do not disappear see your doctor. If
you have serious or continuing reactions, you may need to stop using Levemir and use another insulin.
Allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions, see below*
Signs of allergy (allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions). Hives and rash may occur.
*Allergic reactions and potentially allergic reactions are uncommon side effects when Levemir is used
in combinations with a rapid acting insulin (basal-bolus). However, when used in combination with
oral antidiabetic medicines, three clinical studies have shown a frequency of common.
Seek medical advice immediately:
► If the above signs of allergy appear, or
► If you suddenly feel unwell and you: start sweating; start being sick (vomiting); have difficulty
in breathing; have a rapid heart beat; feel dizzy.
Vision problems. When you first start your insulin treatment, it may disturb your vision, but the
disturbance is usually temporary.
Changes at the injection site (lipodystrophy). If you inject yourself too often at the same site, fatty
tissue under the skin at this site may shrink (lipoatrophy) or thicken (lipohypertrophy). Changing the
Common: affects 1 to 10 users in 100
site with each injection may help to prevent such skin changes. If you notice your skin pitting or
thickening at the injection site, tell your doctor or nurse because these reactions can become more
severe, or they may change the absorption of your insulin if you inject in such a site.
Swollen joints. When you start taking insulin, water retention may cause swelling around your ankles
and other joints. Normally this soon disappears.
Disturbed sensation (peripheral neuropathy). Fast improvement in blood glucose control may cause
disturbed sensation (numbness, weakness or pain) in legs or arms. These symptoms normally
disappear.
Serious allergic reaction to Levemir
or one of its ingredients (called a generalised allergic reaction).
See also the warning in 2 Before you use Levemir.
If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Levemir
after the expiry date which is
stated on the cartridge label and carton after ‘EXP.’
The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Levemir
Penfill that is not being used is to be stored in the refrigerator at 2°C - 8°C, away from the
cooling element. Do not freeze
.
Levemir
Penfill that is being used or carried as a spare is not to be kept in the refrigerator. You can
carry it with you and keep it at room temperature (below 30°C) for up to 6 weeks.
Always keep the cartridge in the outer carton when you are not using it in order to protect it from light.
Levemir
must be protected from excessive heat and light.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
The active substance is insulin detemir. Each ml contains 100 U of insulin detemir. Each
cartridge contains 300 U of insulin detemir in 3 ml solution for injection. 1 unit (U) insulin
detemir corresponds to 1 international unit (IU) of insulin human.
The other ingredients are:
glycerol, phenol, metacresol, zinc acetate, disodium phosphate
dihydrate, sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide and water for injections.
What Levemir looks like and contents of the pack
Levemir comes as a clear, colourless, aqueous solution.
Pack sizes of 1, 5 and 10 cartridges of 3 ml. Not all packs may be marketed.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd, Denmark
The manufacturer can be identified by the batch number printed on the slip of the carton and on the
label:
If the second and third characters are S6, P5, K7, or ZF, Novo Nordisk A/S, Novo Allé, DK-
2880 Bagsværd, Denmark is the manufacturer.
If the second and third characters are H7 or T6, Novo Nordisk Production SAS, 45 Avenue
d’Orléans F-28002 Chartres, France is the manufacturer.
This leaflet was last approved
in
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the website of the European Medicines Agency
http://www.ema.europa.eu
.
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Levemir 100 U/ml solution for injection in pre-filled pen
Insulin detemir
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine
–
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
What Levemir is and what it is used for
WHAT LEVEMIR
IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Levemir
is a modern insulin (insulin analogue) with a long-acting effect. Modern insulins are
improved versions of insulin human.
Levemir is used to treat diabetes mellitus in adults, adolescents and children aged 6 years and above.
Diabetes mellitus is a disease where your body does not produce enough insulin to control the level of
your blood sugar. Levemir may be used in combination with oral antidiabetic medicines or with meal-
related rapid acting insulin medicines.
Levemir has a long and steady blood-sugar-lowering action starting within a few hours (3-4). Levemir
provides 24 hours of basal insulin coverage after injection.
► If you are allergic
(hypersensitive) to insulin detemir or any of the other ingredients in Levemir
(see 6 Further information).
► If you suspect hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar) is starting (see 3 How to use Levemir).
► In insulin infusion pumps.
► If FlexPen is dropped, damaged or crushed.
► If it has not been stored correctly or been frozen (see 5 How to store Levemir).
► If the insulin does not appear water clear and colourless.
► Check the label to make sure it is the right type of insulin.
► Always use a new needle for each injection to prevent contamination.
► Needles and Levemir FlexPen must not be shared.
Take special care with Levemir
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
► If you have trouble with your kidneys or liver, or with your adrenal, pituitary or thyroid glands.
► If you exercise more than usual or if you want to change your usual diet, as this may affect your
blood sugar level.
► If you are ill, carry on taking your insulin and consult your doctor.
► If you are going abroad: travelling over time zones may affect your insulin needs and the timing
of your injections. Consult your doctor if you are planning such travelling.
► If you have very low albumin you need to carefully monitor your blood sugar level. Discuss this
with your doctor.
Some medicines affect the way glucose works in your body and this may influence your insulin dose.
Listed below are the most common medicines, which may affect your insulin treatment. Tell your
doctor, nurse or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines, including
medicines obtained without a prescription. In particular, you should tell your doctor if you are using
any medicine as mentioned below that affects your blood sugar level.
If you take any of the medicines below, your blood sugar level may fall (hypoglycaemia):
•
Other medicines for the treatment of diabetes
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) (used to treat depression)
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (used to treat certain heart conditions or high
blood pressure)
Salicylates (used to relieve pain and lower fever)
Sulphonamides (used to treat infections)
If you take any of the medicines below, your blood sugar level may rise (hyperglycaemia):
•
Oral contraceptives (birth control pills)
Thiazides (used to treat high blood pressure or excessive fluid retention)
Glucocorticoids (such as ‘cortisone’ used to treat inflammation)
Sympathomimetics (such as epinephrine [adrenaline], or salbutamol, terbutaline used to treat
asthma)
Growth hormone (medicine for stimulation of skeletal and somatic growth and pronounced
influence on the body’s metabolic processes)
Danazol (medicine acting on ovulation)
Octreotide and lanreotide (used for treatment of acromegaly, a rare hormonal disorder that usually
occurs in middle-aged adults, caused by the pituitary gland producing excess growth hormone) may
either increase or decrease your sugar level.
Beta-blockers (used to treat high blood pressure) may weaken or suppress entirely the first warning
symptoms which help you to recognise a hypoglycaemia.
Taking Levemir with food and drink
► If you drink alcohol, your need for insulin may change, as your blood sugar level may either
rise or fall. Careful monitoring is recommended.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
► If you are pregnant, planning a pregnancy or breast-feeding please contact your doctor for
advice. Your insulin dose may need to be changed during pregnancy particularly after delivery.
Careful control of your diabetes, and prevention of hypoglycaemia, is important for the health
of your baby.
Beta-blockers (used to treat high blood pressure)
Anabolic steroids (such as testosterone)
Thyroid hormones (used to treat thyroid gland disorders)
Driving and using machines
If your blood sugar is low or high, your concentration and ability to react might be affected and
therefore also your ability to drive or operate a machine. Bear in mind that you could endanger
yourself or others. Please ask your doctor whether you can drive a car:
► If you have frequent hypoglycaemia.
► If you find it hard to recognise hypoglycaemia.
Important information about some of the ingredients in Levemir
Levemir contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per dose, i.e. Levemir is essentially ‘sodium-free’.
Talk about your insulin dose with your doctor and nurse. Make sure you get the colour coded Levemir
FlexPen as your doctor and nurse have told you to use and follow their advice carefully
.
If your doctor has switched you
from one type or brand of insulin to another, your dose may have to
be adjusted by your doctor. Do not change your insulin unless your doctor tells you to.
Levemir can be used in children and adolescents 6 years and above.
There is no experience with the use of Levemir in children below the age of 6 years. Therefore, only
use Levemir in children below this age, if your doctor has specifically told you to.
Use in special populations
If you have reduced kidney or liver function, or if you are above 65 years of age, you need to check
your blood glucose more regularly and discuss changes in your insulin dose with your doctor.
Frequency of administration
When Levemir is used in combination with an oral antidiabetic medicine, Levemir should be
administered once a day. When Levemir is used as part of a basal-bolus insulin regimen Levemir
should be administered once or twice
daily depending on patients’ needs. Dose of Levemir
should be
adjusted individually. The injection can be given at any time during the day, but at the same time each
day. For patients who require twice daily dosing to optimise blood glucose control, the evening dose
can be administered in the evening or at bedtime.
Levemir
is for injection under the skin (subcutaneously). Never inject your insulin directly into a vein
(intravenously) or muscle (intramuscular). Always vary the sites you inject within the same region, to
avoid lumps (see 4 Possible side effects). The best places to give yourself an injection are: the front of
your thighs, the front of your waist (abdomen), or the upper arm. You should always measure your
blood glucose regularly.
If you take more Levemir than you should
If you take too much insulin your blood sugar gets too low (this is called hypoglycaemia or hypo).
This may also happen:
•
If you eat too little or miss a meal.
If you exercise more than usual.
The warning signs of a hypo may come on suddenly and can include: cold sweat; cool pale skin;
headache; rapid heart beat; feeling sick; feeling very hungry; temporary changes in vision; drowsiness;
unusual tiredness and weakness; nervousness or tremor; feeling anxious; feeling confused; difficulty in
concentrating.
If you feel a hypo coming on: take a high sugar snack and then measure your blood sugar.
If your blood sugar is too low: eat glucose tablets or another high sugar snack (sweets, biscuits, fruit
juice), then rest.
Always carry glucose tablets, sweets, biscuits or fruit juice with you, just in case.
When the symptoms of hypoglycaemia have disappeared or when your blood glucose level is
stabilised continue insulin treatment.
Tell relevant people you have diabetes and what the consequences may be, including the risk of
passing out (becoming unconscious) due to a hypo.
Tell relevant people that if you pass out, they must turn you on your side and get medical help straight
away. They must not give you any food or drink. It could choke you.
You may recover more quickly from unconsciousness with an injection of the hormone glucagon by
someone who knows how to use it. If you are given glucagon you will need glucose or a sugary snack
as soon as you are conscious. If you do not respond to glucagon treatment, you will have to be treated
in a hospital. Contact your doctor or an emergency ward after an injection of glucagon: you need to
find the reason for your hypo to avoid getting more.
► If prolonged severe hypoglycaemia is not treated, it can cause brain damage (temporary or
permanent) and even death.
► If you have a hypo that makes you pass out, or a lot of hypos, talk to your doctor. The amount
or timing of insulin, food or exercise may need to be adjusted.
If you forget to take Levemir
If you forget to take your insulin
your blood sugar may get too high (this is called hyperglycaemia).
This may also happen:
•
If you repeatedly take less insulin than you need.
If you get an infection or a fever.
If you exercise less than usual.
The warning signs appear gradually. They include: increased urination; feeling thirsty; losing your
appetite; feeling sick (nausea or vomiting); feeling drowsy or tired; flushed, dry skin; dry mouth and a
fruity (acetone) smell of the breath.
If you get any of these signs:
test your blood sugar level, test your urine for ketones if you can, then
seek medical advice immediately.
These may be signs of a very serious condition called diabetic ketoacidosis. If you do not treat it, this
could lead to diabetic coma and eventually death.
If you stop taking Levemir
This could lead to severe hyperglycaemia (very high blood sugar) and ketoacidosis (build-up of acid in
the blood because the body is breaking down fat instead of sugar). Do not stop taking your insulin
without speaking to a doctor, who will tell you what needs to be done.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
How to handle Levemir FlexPen
Levemir FlexPen is a pre-filled disposable pen containing insulin detemir.
If you eat more than usual.
Read the Levemir FlexPen instructions for use included in this package leaflet carefully. You
must use the pen as described in the Instructions for Use.
Like all medicines, Levemir
can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Side effects may occur with certain frequencies, which are defined as follows:
•
Very common: affects more than 1 user in 10
Uncommon: affects 1 to 10 users in 1,000
Rare: affects 1 to 10 users in 10,000
Very rare: affects less than 1 user in 10,000
Not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia). See the advice in “If you take more Levemir than you should”
under 3 How to use Levemir.
Injection site
reactions (pain, redness, hives, inflammation, bruising, swelling and itching). These
usually disappear after a few weeks of taking your insulin. If they do not disappear see your doctor. If
you have serious or continuing reactions, you may need to stop using Levemir and use another insulin.
Allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions, see below*
Signs of allergy (allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions). Hives and rash may occur.
*Allergic reactions and potentially allergic reactions are uncommon side effects when Levemir is used
in combinations with a rapid acting insulin (basal-bolus). However, when used in combination with
oral antidiabetic medicines, three clinical studies have shown a frequency of common.
Seek medical advice immediately:
► If the above signs of allergy appear, or
► If you suddenly feel unwell and you: start sweating; start being sick (vomiting); have difficulty
in breathing; have a rapid heart beat; feel dizzy.
Vision problems.
When you first start your insulin treatment, it may disturb your vision, but the
disturbance is usually temporary.
Changes at the injection site (lipodystrophy). If you inject yourself too often at the same site, fatty
tissue under the skin at this site may shrink (lipoatrophy) or thicken (lipohypertrophy). Changing the
site with each injection may help to prevent such skin changes. If you notice your skin pitting or
thickening at the injection site, tell your doctor or nurse because these reactions can become more
severe, or they may change the absorption of your insulin if you inject in such a site.
Swollen joints. When you start taking insulin, water retention may cause swelling around your ankles
and other joints. Normally this soon disappears.
Common: affects 1 to 10 users in 100
Disturbed sensation (peripheral neuropathy). Fast improvement in blood glucose control may cause
disturbed sensation (numbness, weakness or pain) in legs or arms. These symptoms normally
disappear.
Serious allergic reaction to Levemir
or one of its ingredients (called a generalised allergic reaction).
See also the warning in 2 Before you use Levemir
.
If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Levemir
after the expiry date which is
stated on the FlexPen label and carton after ‘EXP.’
The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Levemir
FlexPen that is not being used is to be stored in the refrigerator at 2°C - 8°C, away from the
cooling element. Do not freeze
.
Levemir
FlexPen that is being used or carried as a spare is not to be kept in the refrigerator. You can
carry it with you and keep it at room temperature (below 30°C) for up to 6 weeks.
Always keep the cap on your FlexPen when you are not using it in order to protect it from light.
Levemir
must be protected from excessive heat and light.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
The active substance is insulin detemir. Each ml contains 100 U of insulin detemir. Each pre-
filled pen contains 300 U of insulin detemir in 3 ml solution for injection. 1 unit (U) insulin
detemir corresponds to 1 international unit (IU) of insulin human.
The other ingredients are:
glycerol, phenol, metacresol, zinc acetate, disodium phosphate
dihydrate, sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide and water for injections.
What Levemir looks like and contents of the pack
Levemir comes as a clear, colourless, aqueous solution.
Pack sizes of 1 (with or without needles), 5 (without needles) and 10 (without needles) pre-filled pens
of 3 ml. Not all packs may be marketed.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd, Denmark
The manufacturer can be identified by the batch number printed on the slip of the carton and on the
label:
If the second and third characters are S6, P5, K7, or ZF, Novo Nordisk A/S, Novo Allé, DK-
2880 Bagsværd, Denmark is the manufacturer.
If the second and third characters are H7 or T6, Novo Nordisk Production SAS, 45 Avenue
d’Orléans F-28002 Chartres, France is the manufacturer.
Now turn over for information on how to use your FlexPen.
This leaflet was last approved in
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the website of the European Medicines Agency
http://www.ema.europa.eu
.
LEVEMIR solution for injection in a pre-filled pen. FlexPen. INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Please read the following instructions carefully before using your Levemir FlexPen.
Your FlexPen is a unique dial-a-dose insulin pen. You can select doses from 1 to 60 units in
increments of 1 unit. FlexPen is designed to be used with NovoFine or NovoTwist disposable needles
up to a length of 8 mm. Be sure you are not using any counterfeit needles. Ask your pharmacist.
Always carry a spare insulin delivery device in case your FlexPen is lost or damaged.
The colour of the pen in the illustrations differs from your FlexPen.
Your FlexPen is designed to work accurately and safely. It must be handled with care.
If it is dropped or crushed, there is a risk of damage and leakage of insulin.
You can clean the exterior of your FlexPen by wiping it with a medicinal swab. Do not soak it, wash
or lubricate it as it may damage the pen.
Do not refill your FlexPen.
Preparing your Levemir FlexPen
Check the label to make sure that your FlexPen contains the correct type of insulin.
B
Remove the protective tab from a new disposable needle.
Screw the needle straight and tightly onto your FlexPen.
C
Pull off the big outer needle cap and keep it for later.
D
Pull off the inner needle cap and dispose of it.
Always use a new needle for each injection to prevent contamination.
Be careful not to bend or damage the needle before use.
To reduce the risk of unexpected needle sticks, never put the inner needle cap back on when you
have removed it from the needle.
Checking the insulin flow
Prior to each injection, small amounts of air may collect in the cartridge during normal use. To
avoid injection of air and ensure proper dosing:
E
Turn the dose selector to select 2 units.
F
Hold your FlexPen with the needle pointing upwards and tap the cartridge gently with your finger a
few times to make any air bubbles collect at the top of the cartridge.
G
Keeping the needle upwards, press the push-button all the way in. The dose selector returns to 0.
A drop of insulin should appear at the needle tip. If not, change the needle and repeat the procedure no
more than 6 times.
If a drop of insulin still does not appear, the pen is defective, and you must use a new one.
Check that the dose selector is set at 0.
H
Turn the dose selector to select the number of units you need to inject.
The dose can be corrected either up or down by turning the dose selector in either direction until the
correct dose lines up with the pointer. When turning the dose selector be careful not to push the push-
button as insulin will come out.
You cannot select a dose larger than the number of units left in the cartridge.

Do not use the residual scale to measure your dose of insulin.
Insert the needle into your skin. Use the injection technique shown by your doctor or nurse.
I
Inject the dose by pressing the push-button all the way in until 0 lines up with the pointer. Be careful
only to push the push-button when injecting.
Turning the dose selector will not inject insulin.
J
Keep the push-button fully depressed after the injection until the needle has been withdrawn from the
skin.
The needle must remain under the skin for at least 6 seconds. This will ensure that the full dose has
been injected.
K
Lead the needle into the big outer needle cap without touching the big outer needle cap. When the
needle is covered, carefully push the big outer needle cap completely on and then unscrew the needle.
Dispose of it carefully and put the cap back on.

Always remove the needle after each injection and store your FlexPen without the needle
attached. Otherwise the liquid may leak out which can cause inaccurate dosing.
Caregivers should be most careful when handling used needles to avoid needle sticks.
Dispose of the used FlexPen carefully without the needle attached.
Needles and Levemir FlexPen must not be shared.
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Levemir 100 U/ml solution for injection in pre-filled pen
Insulin detemir
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine
–
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
What Levemir is and what it is used for
WHAT LEVEMIR IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Levemir
is a modern insulin (insulin analogue) with a long-acting effect. Modern insulins are
improved versions of insulin human.
Levemir is used to treat diabetes mellitus in adults, adolescents and children aged 6 years and above.
Diabetes mellitus is a disease where your body does not produce enough insulin to control the level of
your blood sugar. Levemir may be used in combination with oral antidiabetic medicines or with meal-
related rapid acting insulin medicines.
Levemir has a long and steady blood-sugar-lowering action starting within a few hours (3-4). Levemir
provides 24 hours of basal insulin coverage after injection.
► If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to insulin detemir or any of the other ingredients in Levemir
(see 6 Further information).
► If you suspect hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar) is starting (see 3 How to use Levemir).
► In insulin infusion pumps.
► If InnoLet is dropped, damaged or crushed.
► If it has not been stored correctly or been frozen (see 5 How to store Levemir).
► If the insulin does not appear water clear and colourless.
► Check the label to make sure it is the right type of insulin.
► Always use a new needle
for each injection to prevent contamination.
► Needles and Levemir InnoLet must not be shared.
Take special care with Levemir
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
► If you have trouble with your kidneys or liver, or with your adrenal, pituitary or thyroid glands.
► If you exercise more than usual or if you want to change your usual diet, as this may affect your
blood sugar level.
► If you are ill, carry on taking your insulin and consult your doctor.
► If you are going abroad: travelling over time zones may affect your insulin needs and the timing
of your injections. Consult your doctor if you are planning such travelling.
► If you have very low albumin you need to carefully monitor your blood sugar level. Discuss this
with your doctor.
Some medicines affect the way glucose works in your body and this may influence your insulin dose.
Listed below are the most common medicines, which may affect your insulin treatment. Tell your
doctor, nurse or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines, including
medicines obtained without a prescription. In particular, you should tell your doctor if you are using
any medicine as mentioned below that affects your blood sugar level.
If you take any of the medicines below, your blood sugar level may fall (hypoglycaemia):
•
Other medicines for the treatment of diabetes
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) (used to treat depression)
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (used to treat certain heart conditions or high
blood pressure)
Salicylates (used to relieve pain and lower fever)
Sulphonamides (used to treat infections)
If you take any of the medicines below, your blood sugar level may rise (hyperglycaemia):
•
Oral contraceptives (birth control pills)
Thiazides (used to treat high blood pressure or excessive fluid retention)
Glucocorticoids (such as ‘cortisone’ used to treat inflammation)
Sympathomimetics (such as epinephrine [adrenaline], or salbutamol, terbutaline used to treat
asthma)
Growth hormone (medicine for stimulation of skeletal and somatic growth and pronounced
influence on the body’s metabolic processes)
Danazol (medicine acting on ovulation)
Octreotide and lanreotide (used for treatment of acromegaly, a rare hormonal disorder that usually
occurs in middle-aged adults, caused by the pituitary gland producing excess growth hormone) may
either increase or decrease your sugar level.
Beta-blockers (used to treat high blood pressure) may weaken or suppress entirely the first warning
symptoms which help you to recognise a hypoglycaemia.
Taking Levemir with food and drink
► If you drink alcohol, your need for insulin may change, as your blood sugar level may either
rise or fall. Careful monitoring is recommended.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
► If you are pregnant, planning a pregnancy or breast-feeding
please contact your doctor for
advice. Your insulin dose may need to be changed during pregnancy particularly after delivery.
Careful control of your diabetes, and prevention of hypoglycaemia, is important for the health
of your baby.
Beta-blockers (used to treat high blood pressure)
Anabolic steroids (such as testosterone)
Thyroid hormones (used to treat thyroid gland disorders)
Driving and using machines
If your blood sugar is low or high, your concentration and ability to react might be affected and
therefore also your ability to drive or operate a machine. Bear in mind that you could endanger
yourself or others. Please ask your doctor whether you can drive a car:
► If you have frequent hypoglycaemia.
► If you find it hard to recognise hypoglycaemia.
Important information about some of the ingredients in Levemir
Levemir contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per dose, i.e. Levemir is essentially ‘sodium-free’.
Talk about your insulin dose with your doctor and nurse. Make sure you get Levemir InnoLet as your
doctor and nurse have told you to use and follow their advice carefully
.
If your doctor has switched you
from one type or brand of insulin to another, your dose may have to
be adjusted by your doctor. Do not change your insulin unless your doctor tells you to.
Levemir can be used in children and adolescents 6 years and above.
There is no experience with the use of Levemir in children below the age of 6 years. Therefore, only
use Levemir in children below this age, if your doctor has specifically told you to.
Use in special populations
If you have reduced kidney or liver function, or if you are above 65 years of age, you need to check
your blood glucose more regularly and discuss changes in your insulin dose with your doctor.
Frequency of administration
When Levemir is used in combination with an oral antidiabetic medicine, Levemir should be
administered once a day. When Levemir is used as part of a basal-bolus insulin regimen Levemir
should be administered once or twice
daily depending on patients’ needs. Dose of Levemir
should be
adjusted individually. The injection can be given at any time during the day, but at the same time each
day. For patients who require twice daily dosing to optimise blood glucose control, the evening dose
can be administered in the evening or at bedtime.
Levemir
is for injection under the skin (subcutaneously). Never inject your insulin directly into a vein
(intravenously) or muscle (intramuscular). Always vary the sites you inject within the same region, to
avoid lumps (see 4 Possible side effects). The best places to give yourself an injection are: the front of
your thighs, the front of your waist (abdomen), or the upper arm. You should always measure your
blood glucose regularly.
If you take more Levemir than you should
If you take too much insulin your blood sugar gets too low (this is called hypoglycaemia or hypo).
This may also happen:
•
If you eat too little or miss a meal.
If you exercise more than usual.
The warning signs of a hypo may come on suddenly and can include: cold sweat; cool pale skin;
headache; rapid heart beat; feeling sick; feeling very hungry; temporary changes in vision; drowsiness;
unusual tiredness and weakness; nervousness or tremor; feeling anxious; feeling confused; difficulty in
concentrating.
If you feel a hypo coming on: take a high sugar snack and then measure your blood sugar.
If your blood sugar is too low: eat glucose tablets or another high sugar snack (sweets, biscuits, fruit
juice), then rest.
Always carry glucose tablets, sweets, biscuits or fruit juice with you, just in case.
When the symptoms of hypoglycaemia have disappeared or when your blood glucose level is
stabilised continue insulin treatment.
Tell relevant people you have diabetes and what the consequences may be, including the risk of
passing out (becoming unconscious) due to a hypo.
Tell relevant people that if you pass out, they must turn you on your side and get medical help straight
away. They must not give you any food or drink. It could choke you.
You may recover more quickly from unconsciousness with an injection of the hormone glucagon by
someone who knows how to use it. If you are given glucagon you will need glucose or a sugary snack
as soon as you are conscious. If you do not respond to glucagon treatment, you will have to be treated
in a hospital. Contact your doctor or an emergency ward after an injection of glucagon: you need to
find the reason for your hypo to avoid getting more.
► If prolonged severe hypoglycaemia is not treated, it can cause brain damage (temporary or
permanent) and even death.
► If you have a hypo that makes you pass out, or a lot of hypos, talk to your doctor. The amount
or timing of insulin, food or exercise may need to be adjusted.
If you forget to take Levemir
If you forget to take your insulin
your blood sugar may get too high (this is called hyperglycaemia).
This may also happen:
•
If you repeatedly take less insulin than you need.
If you get an infection or a fever.
If you exercise less than usual.
The warning signs appear gradually. They include: increased urination; feeling thirsty; losing your
appetite; feeling sick (nausea or vomiting); feeling drowsy or tired; flushed, dry skin; dry mouth and a
fruity (acetone) smell of the breath.
If you get any of these signs:
test your blood sugar level, test your urine for ketones if you can, then
seek medical advice immediately.
These may be signs of a very serious condition called diabetic ketoacidosis. If you do not treat it, this
could lead to diabetic coma and eventually death.
If you stop taking Levemir
This could lead to severe hyperglycaemia (very high blood sugar) and ketoacidosis (build-up of acid in
the blood because the body is breaking down fat instead of sugar). Do not stop taking your insulin
without speaking to a doctor, who will tell you what needs to be done.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
How to handle Levemir InnoLet
Levemir InnoLet is a pre-filled disposable pen containing insulin detemir.
If you eat more than usual.
Read the Levemir InnoLet instructions for use included in this package leaflet carefully. You
must use the pen as described in the Instructions for Use.
Like all medicines, Levemir can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Side effects may occur with certain frequencies, which are defined as follows:
•
Very common: affects more than 1 user in 10
Common: affects 1 to 10 users in 100
Uncommon: affects 1 to 10 users in 1,000
Very rare: affects less than 1 user in 10,000
Not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia). See the advice in “If you take more Levemir than you should”
under 3 How to use Levemir.
Injection site
reactions (pain, redness, hives, inflammation, bruising, swelling and itching). These
usually disappear after a few weeks of taking your insulin. If they do not disappear see your doctor. If
you have serious or continuing reactions, you may need to stop using Levemir and use another insulin.
Allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions, see below*
Signs of allergy (allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions). Hives and rash may occur.
*Allergic reactions and potentially allergic reactions are uncommon side effects when Levemir is used
in combinations with a rapid acting insulin (basal-bolus). However, when used in combination with
oral antidiabetic medicines, three clinical studies have shown a frequency of common.
Seek medical advice immediately:
► If the above signs of allergy appear, or
► If you suddenly feel unwell and you: start sweating; start being sick (vomiting); have difficulty
in breathing; have a rapid heart beat; feel dizzy.
Vision problems.
When you first start your insulin treatment, it may disturb your vision, but the
disturbance is usually temporary.
Changes at the injection site (lipodystrophy). If you inject yourself too often at the same site, fatty
tissue under the skin at this site may shrink (lipoatrophy) or thicken (lipohypertrophy). Changing the
site with each injection may help to prevent such skin changes. If you notice your skin pitting or
thickening at the injection site, tell your doctor or nurse because these reactions can become more
severe, or they may change the absorption of your insulin if you inject in such a site.
Swollen joints. When you start taking insulin, water retention may cause swelling around your ankles
and other joints. Normally this soon disappears.
Disturbed sensation ( peripheral neuropathy). Fast improvement in blood glucose control may cause
disturbed sensation (numbness, weakness or pain) in legs or arms. These symptoms normally
disappear.
Rare: affects 1 to 10 users in 10,000
Serious allergic reaction to Levemir
or one of its ingredients (called a generalised allergic reaction).
See also the warning in 2 Before you use Levemir
.
If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Levemir
after the expiry date which is
stated on the InnoLet label and carton after ‘EXP.’
The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Levemir
InnoLet that is not being used is to be stored in the refrigerator at 2°C - 8°C, away from the
cooling element. Do not freeze
.
Levemir
InnoLet that is being used or carried as a spare is not to be kept in the refrigerator. You can
carry it with you and keep it at room temperature (below 30°C) for up to 6 weeks.
Always keep the cap on your InnoLet when you are not using it in order to protect it from light.
Levemir
must be protected from excessive heat and light.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
The active substance is insulin detemir. Each ml contains 100 U of insulin detemir. Each pre-
filled pen contains 300 U of insulin detemir in 3 ml solution for injection. 1 unit (U) insulin
detemir corresponds to 1 international unit (IU) of insulin human.
The other ingredients are:
glycerol, phenol, metacresol, zinc acetate, disodium phosphate
dihydrate, sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide and water for injections.
What Levemir looks like and contents of the pack
Levemir comes as a clear, colourless, aqueous solution.
Pack sizes of 1, 5 and 10 pre-filled pens of 3 ml. Not all packs may be marketed.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd, Denmark
Now turn over for information on how to use your InnoLet.
This leaflet was last approved in
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the website of the European Medicines Agency
http://www.ema.europa.eu
.
LEVEMIR solution for injection in a pre-filled pen. InnoLet. INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Please read the following instructions carefully before using your Levemir
InnoLet.
Your InnoLet is a simple, compact pre-filled pen able to deliver 1 to 50 units in increments of 1 unit.
InnoLet is designed to be used with NovoFine disposable needles up to a length of 8 mm. Be sure you
are not using any counterfeit needles. Ask your pharmacist. Always carry a spare insulin delivery
device in case your InnoLet is lost or damaged.
Check the label to be sure that your InnoLet contains the correct type of insulin. Take off the cap (as
shown by the arrow).
Always use a new needle for each injection to prevent contamination.
Screw the needle straight and tightly onto your
InnoLet (picture
A
).
Always use a new NovoFine disposable needle for each injection. Do not bend or damage the
needle before use.
Pull off the big outer needle cap and the inner needle cap. You may want to store the big outer
needle cap in the compartment.
Remove the protective tab from a NovoFine needle.
Priming to expel air
prior to each injection
Small amounts of air may collect in the needle and cartridge during normal use.
To avoid injection of air and ensure proper dosing:
•
Dial 2 units by turning the dose selector clockwise.
Hold your
InnoLet with the needle upwards and tap the cartridge gently with your finger a few
times (picture
B
) to make any air bubbles collect at the top of the cartridge.
A drop of insulin should appear at the needle tip. If not, change the needle and repeat the
procedure no more than 6 times.
If a drop of insulin still does not appear, the device is defective and must not be used.
B
Always check that the push-button is fully depressed and the dose selector is set to 0.
Dial the number of units required by turning the dose selector clockwise (picture
C
). Do not use
the residual scale to measure your dose of insulin.
You will hear a click for every single unit dialled. The dose can be corrected by turning the dial
either way. Do not turn the dial to correct the dose when the needle is inserted in the skin.
You cannot set a dose larger than the number of units remaining in the cartridge.
Keeping the needle upwards, press the push-button and the dose selector returns to 0.
Insert the needle into your skin. Use the injection technique advised by your doctor.
Deliver the dose by pressing the push-button fully down (picture
D
). You will hear clicks as the
dose selector returns to 0.
After the injection, the needle should remain under the skin for at least 6 seconds to ensure that
the full dose has been delivered.
Make sure not to block the dose selector while injecting, as the dose selector must be allowed to
return to 0 when you press the push-button.
Discard the needle after each injection.
Replace the big outer needle cap and unscrew the needle (picture
E
). Dispose of it carefully.
Use a new needle for each injection.
Be sure to remove and discard the needle after each injection and store your InnoLet without the
needle attached. Otherwise the liquid may leak out which can cause inaccurate dosing.
Healthcare professionals, relatives and other carers should follow general precautionary measures for
removal and disposal of needles to eliminate the risk of unintended needle penetration.
Dispose of your used InnoLet carefully without the needle attached.
Needles and Levemir InnoLet must not be shared.
Your InnoLet is designed to work accurately and safely. It should be handled with care. If it is
dropped, damaged or crushed, there is a risk of leakage of insulin.
Do not refill your
InnoLet.
You can clean your InnoLet by wiping it with a medicinal swab. Do not soak it in surgical spirit or
wash or lubricate it. This may damage the mechanism.
Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/levemir.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|



























































































































































































































































































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































