Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Livensa 300 micrograms/24 hours transdermal patch
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each patch of 28 cm
2
contains 8.4 mg testosterone and provides 300 micrograms of testosterone per
24 hours.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Thin, clear, oval matrix-type transdermal patch consisting of three layers: a translucent backing film,
an adhesive matrix drug layer, and a protective release liner that is removed prior to application. Each
patch surface is stamped with T001.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Livensa is indicated for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in bilaterally
oophorectomised and hysterectomised (surgically induced menopause) women receiving concomitant
estrogen therapy.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The recommended daily dose of testosterone is 300 micrograms. This is achieved by applying the
patch twice weekly on a continuous basis. The patch should be replaced with a fresh patch every 3 to
4 days. A particular application site should be rotated with an interval of at least 7 days between
applications. Only one patch is to be worn at a time
.
The adhesive side of the patch should be applied to a clean, dry area of skin on the lower abdomen
below the waist. Patches should not be applied to the breasts or other body regions. A skin site with
minimal wrinkling and not covered by tight clothing is recommended. The site should not be oily,
damaged, or irritated. To prevent interference with the adhesive properties of Livensa, no creams,
lotions or powder should be applied to the skin where the patch is to be applied.
The patch should be applied immediately after opening the sachet and removing both parts of the
protective release liner. The patch should be pressed firmly in place for about 10 seconds, making
sure there is good contact with the skin, especially around the edges. If an area of the patch lifts,
pressure should be applied to that area. If the patch detaches prematurely, it may be reapplied. If the
same patch cannot be reapplied, a new patch should be applied to another location. In either case, the
original treatment regimen should be maintained. The patch is designed to remain in place during a
shower, bath, swimming or exercising.
Concomitant estrogen treatment
The appropriate use and restrictions associated with estrogen therapy should be considered before
Livensa therapy is initiated and during routine re-evaluation of treatment. Continued use of Livensa is
only recommended while concomitant use of estrogen is considered appropriate (i.e. the lowest
effective dose for the shortest possible duration).
Patients treated with conjugated equine estrogen (CEE) are not recommended to use Livensa, as
efficacy has not been demonstrated (see sections 4.4 and 5.1).
Duration of treatment
Livensa treatment response should be evaluated within 3-6 months of initiation, to determine if
continued therapy is appropriate. Patients who do not experience a meaningful benefit should be re-
evaluated and discontinuation of therapy be considered.
As the efficacy and safety of Livensa have not been evaluated in studies of longer duration than 1 year,
it is recommended that an appraisal of the treatment is undertaken every 6 months.
Children and adolescents:
There is no relevant indication for use of Livensa in children and adolescents.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
Known, suspected or past history of cancer of the breast or known or suspected estrogen-dependent
neoplasia, or any other condition consistent with the contraindications for the use of estrogen.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
At regular intervals during treatment, physicians should monitor patients for potential androgenic
undesirable effects (e.g. acne, changes in hair growth or hair loss). Patients should be advised to self
assess for androgenic undesirable effects. Signs of virilisation, such as voice deepening, hirsutism or
clitoromegaly, may be irreversible and discontinuation of treatment should be considered. In clinical
trials these reactions were reversible in the majority of patients (see section 4.8).
Severe skin erythema, local oedema and blistering may occur due to hypersensitivity to the patch at
the site of application. Use of the patch should be discontinued if this occurs.
The safety of Livensa has not been evaluated in double blind placebo controlled studies of longer than
1 year duration. There is little information on long-term safety, including effects on breast tissue, the
cardiovascular system and increase in insulin resistance.
Data in the literature regarding the influence of testosterone on the risk of breast cancer in women are
limited, inconclusive and conflicting. The long-term effect of testosterone treatment on the breast is
currently unknown, therefore patients should be carefully monitored with regard to breast cancer in
accordance with currently accepted screening practises and individual patient needs.
Patients with known cardiovascular disease have not been studied. Patients with cardiovascular risk
factors, in particular hypertension, and patients with known cardiovascular disease should be carefully
monitored, specifically regarding changes in blood pressure and weight.
In diabetic patients the metabolic effects of testosterone may decrease blood glucose and therefore
insulin requirements. Patients with diabetes mellitus have not been studied.
Little information is available on the effects of testosterone on the endometrium. The limited data
evaluating the effect of testosterone on the endometrium neither allow conclusions nor reassurances on
the incidence of endometrial cancer.
Oedema (with or without congestive heart failure) may be a serious complication from high doses of
testosterone or other anabolic steroids in patients with pre-existing cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease.
However, this is not expected from the low dose of testosterone delivered by the Livensa patch.
Livensa is recommended for use in surgically menopausal women up to the age of 60. Consistent with
the prevalence of HSDD, there are limited data above the age of 60.
Efficacy and safety of Livensa 300 micrograms in naturally menopausal women with HSDD on
concomitant estrogen, with or without progestogen, have not been evaluated. Livensa 300 micrograms
is not recommended in naturally menopausal women.
Whereas Livensa is indicated with concomitant estrogen therapy, the subgroup of patients receiving
oral conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) did not demonstrate a significant improvement in sexual
function. Therefore, Livensa should not be used in women on concomitant CEE (see sections 4.2 and
5.1).
Androgens may decrease levels of thyroxin-binding globulin, resulting in decreased total T4 serum
levels and increased resin uptake of T3 and T4. Free thyroid hormone levels remain unchanged,
however, and there is no clinical evidence of thyroid dysfunction.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No interaction studies have been performed. When testosterone is given concomitantly with
anticoagulants, the anticoagulant effect may increase. Patients receiving oral anticoagulants require
close monitoring, especially when testosterone therapy is started or stopped.
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
Livensa must not be used in women who are or may become pregnant or by breast-feeding women.
Testosterone may induce virilising effects on the female foetus when administered to a pregnant
woman. Studies in animals have shown reproductive toxicity (see section 5.3).
In case of inadvertent exposure during pregnancy, use of Livensa must be discontinued.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Livensa has no influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
The adverse reaction most often reported (30.4 %) was application site reactions. The majority of
these adverse reactions consisted of mild erythema and itching and did not result in patient
withdrawal.
Hirsutism was also very commonly reported. Most reports concerned the chin and upper lip, were
mild (≥ 90 %), and less than 1 % of all patients withdrew from the studies due to hirsutism. Hirsutism
was reversible in the majority of patients.
Other androgenic effects commonly reported were acne, voice deepening and alopecia. More than
90 % of these reports were considered mild. These reactions were reversible in the majority of
patients. Less than 1 % of patients withdrew from the studies because of any of these reactions. All
other common adverse events resolved in the majority of patients.
During 6-month double blind exposure the following adverse reactions occurred in the treatment group
(n=549) at a greater incidence than placebo (n=545) and were assessed by the investigators as possibly
or probably related to Livensa treatment. If an adverse reaction occurred at a higher frequency in the
integrated phase III studies (Livensa patients n=1,498, placebo patients n=1,297), this frequency is
reported in the table.
MedDRA
System organ class
Uncommon
≥ 1/1,000, < 1/100






MedDRA
System organ class
Uncommon
≥ 1/1,000, < 1/100
Infections and infestations
Blood and lymphatic system
disorders
Metabolism and nutrition
disorders
Disturbance in attention,
dysgeusia, impaired balance,
hyperaesthesia, oral
paraesthesia, transient
ischemic attack
Respiratory, thoracic and
mediastinal disorders
Nasal congestion, throat
tightness
Gastrointestinal disorders
Diarrhoea, dry mouth,
nausea
Skin and subcutaneous tissue
disorders
Eczema, increased sweating,
rosacea
Musculoskeletal and connective
tissue disorders
Reproductive system and breast
disorders
Breast cyst, clitoral
engorgement, enlarged
clitoris, genital pruritus,
vaginal burning sensation
General disorders and
administration site conditions
Application site
reaction
(erythema,
itching)
Anasarca, asthenia, chest
tightness, chest discomfort
Abnormal blood fibrinogen,
increased heart rate,
increased alanine
aminotransferase, increased
aspartate aminotransferase,
increased blood bilirubin,
abnormal liver function test,
increased blood triglycerides
No new or other adverse reactions have been identified from the post-marketing spontaneous reporting
system.
The mode of administration of Livensa makes overdose unlikely. Removal of the patch results in a
rapid decrease in serum testosterone levels (see section 5.2).
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Androgens, testosterone, ATC code: G03BA03





















Testosterone, the primary circulating androgen in women, is a naturally occurring steroid, secreted by
the ovaries and adrenal glands. In premenopausal women, the rate of production of testosterone is 100
to 400 micrograms/24 hours, of which half is contributed by the ovary as either testosterone or a
precursor. Serum levels of androgens fall as women age. In women, who have undergone bilateral
oophorectomy, serum levels of testosterone decline by approximately 50 % within days after surgery.
Livensa is a transdermal therapy for HSDD, which improves sexual desire while achieving
testosterone concentrations compatible with premenopausal levels.
Two multi-centre, double-blind, placebo-controlled six month studies in 562 (INTIMATE SM1) and
533 (INTIMATE SM2) oophorectomised and hysterectomised women (surgically induced
menopause), aged 20 to 70 years, with HSDD on concomitant estrogen were used to evaluate the
efficacy and safety of Livensa. Total satisfying sexual activity (primary endpoint), sexual desire, and
distress associated with low sexual desire (secondary endpoints) were evaluated with validated
instruments.
In the combined study analysis at 24 weeks, the difference in the mean frequency of total satisfying
episodes between Livensa and placebo was 1.07 per 4 weeks.
A significantly higher percentage of women who received Livensa reported a benefit in the three
endpoints, that they considered clinically meaningful compared to women who received placebo. In
the combined phase III data, excluding patients taking oral CEE, in whom there was no significant
improvement in sexual function, 50.7 % of women (n=274) treated with Livensa and 29.4 % of those
treated with placebo (n=269) were responders with regard to total satisfying sexual activity (primary
endpoint), when a responder was predefined as having an increase in the 4-week frequency of
satisfying activities of > 1.
Effects of Livensa were observed at 4 weeks after initiation of therapy (the first measured time point)
and at all monthly efficacy time points thereafter.
Efficacy versus placebo was significant across a range of subgroups which included patients separated
by the following baseline characteristics: age (all subgroups up to age 65 years); body weight (up to
80 kg) and oophorectomy (up to 15 years ago).
Subgroup analyses suggested that the route and type of concomitant estrogen (transdermal oestradiol,
oral conjugated equine estrogen (CEE), oral non-CEE) can influence patient response. A responder
analysis of the pivotal phase II and III studies showed significant improvements in all three major
clinical endpoints versus placebo in patients on concomitant transdermal and oral non-CEE estrogens.
However, the subgroup of patients receiving oral CEE did not demonstrate a significant improvement
in sexual activity compared to placebo (see sections 4.2 and 4.4).
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption:
Testosterone from Livensa is transported across intact skin by a passive diffusion process that is
primarily controlled by permeation across the stratum corneum. Livensa is designed to systemically
deliver 300 micrograms/day. Following application of the patch on abdominal skin, maximum serum
concentrations of testosterone are reached within 24-36 hours, with a wide inter-individual variability.
Serum concentrations of testosterone attain steady-state by the application of the second patch when
applied in a twice-a-week regimen. Livensa did not influence serum concentrations of sex hormone
binding globulin (SHBG), estrogens or adrenal hormones.
Serum Concentrations of Testosterone and SHBG in Patients Receiving Livensa in Clinical Safety and
Efficacy Studies
Hormone












Serum Concentrations of Testosterone and SHBG in Patients Receiving Livensa in Clinical Safety and
Efficacy Studies
Hormone
(pg/ml)
Total testosterone
(ng/dl)
DHT = dihydrotestosterone, SHBG = sex hormone binding globulin
SEM = Standard Error of the Mean
Distribution:
In women, circulating testosterone is primarily bound in the serum to SHBG (65-80 %) and to albumin
(20-30 %) leaving only about 0.5-2 % as the free fraction. The affinity of binding to serum SHBG is
relatively high and the SHBG bound fraction is regarded as not contributing to biological activity.
Binding to albumin is of relatively low affinity and is reversible. The albumin-bound fraction and the
unbound fraction are collectively termed ‘bioavailable’ testosterone. The amount of SHBG and
albumin in serum and the total testosterone concentration determine the distribution of free and
bioavailable testosterone. Serum concentration of SHBG is influenced by the route of administration
of concomitant estrogen therapy.
Metabolism:
Testosterone is metabolised primarily in the liver. Testosterone is metabolised to various
17-ketosteroids and further metabolism results in inactive glucuronides and other conjugates. The
active metabolites of testosterone are estradiol and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT has a greater
affinity to SHBG than does testosterone. DHT concentrations increased in parallel with testosterone
concentrations during Livensa treatment. There were no significant differences in serum estradiol and
estrone levels in patients treated with Livensa for up to 52 weeks compared to baseline.
On removal of an Livensa patch, testosterone serum concentrations return to near baseline values
within 12 hours due to its short terminal exponential half-life (approximately 2 hours). There was no
evidence of accumulation of testosterone over 52 weeks of treatment.
Elimination:
Testosterone is mainly excreted in the urine as glucuronic and sulphuric acid conjugates of
testosterone and its metabolites.
Toxicological studies of testosterone have only revealed effects which can be explained based on the
hormone profile.
Testosterone has been found to be nongenotoxic. Non-clinical studies on a relationship between
testosterone treatment and cancer suggest that high doses may promote tumour growth in sex organs,
mammary glands and liver in laboratory animals. The significance of these data for the use of Livensa
in patients is not known
.
Testosterone has a masculinising effect on female rat foetuses when dosed subcutaneously at 0.5 or
1 mg/day (as the propionate ester) to pregnant rats during organogenesis.
















PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Backing layer:
Translucent polyethylene backing film printed with proprietary ink containing sunset yellow FCF
(E110), latolrubine BK (E180) and copper phthalocyanine blue pigment.
Self adhesive matrix drug layer:
Sorbitan oleate,
Acrylic co-polymer adhesive containing 2-Ethylhexylacrylate – 1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone co-polymer.
Protective release liner:
Siliconised polyester film.
Special precautions for storage
Do not store above 30°C.
Do not refrigerate or freeze
.
Nature and contents of container
Each patch is packed in a sealed laminated sachet. The sachet material comprises of food grade
paper/polyethylene/aluminium foil/ethylene methacrylic acid copolymer (outer to inner layer). The
ethylene methacrylic acid copolymer (Surlyn
®
) is the heat seal layer which allows the two laminate
sachet stocks to be heat-sealed together to form the sachet.
Cartons of 2, 8 and 24 patches.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Warner Chilcott Deutschland GmbH
Dr.-Otto-Röhm-Strasse 2-4
64331 Weiterstadt
Germany
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
A. MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR
BATCH RELEASE
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
A. MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
Warner Chilcott Deutschland GmbH
Dr.-Otto-Röhm-Strasse 2-4
64331 Weiterstadt
Germany
Warner Chilcott France
Parc d’activité de la Grande Brèche
5 rue Désir Prévost
91070 Bondoufle
France
The printed package leaflet of the medicinal product must state the name and address of the
manufacturer responsible for the release of the concerned batch.
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
The MAH must ensure that the system of pharmacovigilance, presented in Module 1.8.1 of the
Marketing Authorisation, is in place and functioning before and whilst the product is on the market.
The MAH commits to performing the studies and additional pharmacovigilance activities detailed in
the Pharmacovigilance Plan.
An updated Risk Management Plan, as per the CHMP Guideline on Risk Management Systems for
medicinal products for human use, should be submitted at the same time as the PSURs, within 60 days
of an important (Pharmacovigilance or Risk minimisation) milestone being reached or when the results
of a study become available or at the request of the Competent authority.
ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
OUTER CARTON (Box of 2, 8 or 24 patches)
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Livensa 300 micrograms/24 hours transdermal patch
Testosterone
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
1 patch of 28 cm
2
contains 8.4 mg of testosterone and provides 300 micrograms per 24 hours.
Also contains: Sorbitan oleate, 2-Ethylhexylacrylate – 1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone copolymer, E110, E180,
copper phthalocyanine blue pigment, polyethylene, siliconised polyester.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
2 transdermal patches
8 transdermal patches
24 transdermal patches
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Apply immediately upon removal from the sachet.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Do not store above 30°C.
Do not refrigerate or freeze.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Warner Chilcott Deutschland GmbH
Dr.-Otto-Röhm-Strasse 2-4
64331 Weiterstadt
Germany
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE



















---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information to appear on the inside of the flap
When to apply the patch:
The patch needs to be changed twice weekly. Choose your two days and tick the box. Change the
patch only on these two days.
o
Sunday + Wednesday
o
Monday + Thursday
o
Tuesday + Friday
o
Wednesday + Saturday
o
Thursday + Sunday
o
Friday + Monday
o
Saturday + Tuesday
Continue to use for as long as your doctor prescribes.



PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE IMMEDIATE PACKAGING
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Livensa 300 micrograms/24 hours transdermal patch
Testosterone
Transdermal use
Read the package leaflet before use.
CONTENTS BY WEIGHT, BY VOLUME OR BY UNIT
1 patch of 28 cm
2
contains 8.4 mg of testosterone and provides 300 micrograms per 24 hours.















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Livensa 300 micrograms/24 hours transdermal patch
Testosterone
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
•
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms appear to be the same as yours.
If any of the side effects become serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this
leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
What you should consider before you use Livensa
WHAT LIVENSA IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Livensa is a transdermal patch which constantly releases small amounts of testosterone that is
absorbed through your skin into the bloodstream. The testosterone in Livensa is the same hormone as
that produced naturally in men and women.
After removal of the ovaries, testosterone drops to half of the levels compared to before the operation.
Decrease in testosterone has been associated with low sexual desire, reduced sexual thoughts and
reduced sexual arousal. All or any of these problems can cause personal distress or relationship
difficulties. The medical term for this condition is Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder, also known as
HSDD.
Livensa is used to treat HSDD.
Livensa is intended for use by women up to the age of 60 years who:
•
have a low sexual desire which is causing distress or concern, and
have had both of their ovaries removed, and
have had their womb removed (hysterectomy), and
are receiving estrogen therapy.
It may take longer than one month for you to notice an improvement. If you have not experienced a
positive effect of Livensa within 3-6 months, you should inform your doctor, who will suggest that
treatment be discontinued.
WHAT YOU SHOULD CONSIDER BEFORE YOU USE LIVENSA
if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to testosterone or any of the other ingredients of Livensa.
if you know that you have had in the past, currently have, or think that you might have, breast
cancer or any other cancer which your doctor has described as being caused or stimulated by the
female hormone estrogen, also called ‘estrogen-dependent’ cancers.
if you have other conditions that your doctor may consider not appropriate for the use of
estrogen and/or testosterone.
What Livensa is and what it is used for
Take special care with Livensa
•
if you have a history of heart, liver or kidney disease.
if you are diabetic, as testosterone may lower blood glucose levels.
if you have a history of excessive adult acne, body or facial hair, hair loss, enlargement of the
clitoris or voice deepening or hoarseness.
If you have any of the above, tell your doctor before you start to use Livensa. Your doctor will advise
you on what you should do.
The efficacy of Livensa is reduced if your estrogen therapy is of a certain type (‘conjugated equine
estrogens’). Therefore, you need to discuss your type of estrogen with your doctor, who could advise
you which type of estrogen is suitable together with Livensa. If you stop estrogen therapy you must
also stop using Livensa. Keep in mind that estrogens should be administered for the shortest possible
duration.
Use Livensa only as long as you experience a positive effect of the treatment. There is no information
on the safety of Livensa beyond 12 months. There are limited data about the use in women above the
age of 60.
It is not known whether Livensa increases the risk of breast cancer. Your doctor will carefully monitor
you with regard to breast cancer.
Taking other medicines
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines,
including medicines obtained without prescription.
Take particular care if you are taking medicines containing any of the following active substances:
•
blood-thinning (anticoagulant) treatment
Children and adolescents
Livensa is not for use in children and adolescents.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Livensa is only indicated for women in their menopause after the ovaries and uterus have been
removed. Do not use Livensa if you are, or suspect that you may be pregnant or are able to become
pregnant, because it may cause harm to the unborn child.
Do not use Livensa in case of breast-feeding because it may cause harm to the child.
Driving and using machines
You can drive and use machines while using Livensa.
Livensa should be replaced twice weekly (each 3 to 4 days). The active substance is released from the
patch constantly over 3 to 4 days and is absorbed through your skin. Always use Livensa exactly as
your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure of the
instructions or if you want any more information.
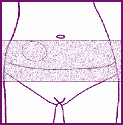
Where to stick the patch
•
Stick the patch onto your
lower abdomen,
below your waist.
Do not
stick the patch on the
breasts or bottom.
Make sure that your skin at the application site is:
9
clean and dry (free of lotions, moisturisers, and powders)
9
as smooth as possible (no major creases or skin folds)
9
not cut or irritated (free of rashes or other skin problems)
9
unlikely to be rubbed by clothing excessively
9
preferably free from hair.
When changing your patch, stick the new patch on to a
different area
of the skin
of your
abdomen
, otherwise you are more likely to cause skin irritation.
Only
one
patch is to be worn at a time.
If you are also using estrogen patches, make sure that the patch and the estrogen patch do not
overlap.
For at least one week after removing a patch, do not place a new patch in the same area.
How to stick on the patch
Step 1
Tear open the sachet. Do not use scissors as you may accidentally damage the patch. Remove
the patch. Apply the patch immediately after removing it from the sachet.
Step 2
While holding the patch, remove half of the protective liner that covers the sticky part of the
patch. Avoid touching the sticky side of the patch with your fingers.
Step 3
Apply the sticky side of the patch to the selected area onto your skin. Press the sticky side of
the patch firmly into place for about 10 seconds.
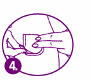
Step 4
Fold back the patch and carefully remove the other half of the liner. Press the entire patch
firmly against your skin with the palm of your hand for about 10 seconds. Use your fingers to



make sure the edges of the patch stick to the skin. If an area of the patch lifts, apply pressure
to that area.
How to change your patch
•
You will need to change your patch every 3 to 4 days, which means using
two patches each
week
. This will mean that you wear one patch for 3 days and the other for 4 days. Decide
which two days each week you are going to change your patch, and change the patch on the
same two days each week.
For example:
If you decide to start treatment on a Monday, then you have to change your patch
always on a Thursday and a Monday.
o
Sunday + Wednesday
9
Monday + Thursday
o
Tuesday + Friday
o
Wednesday + Saturday
o
Thursday + Sunday
o
Friday + Monday
o
Saturday + Tuesday
As a reminder, mark on the outer carton your chosen patch-change days.
On the patch-change day, remove the used patch and immediately stick the new patch on to a
different area
of skin
of your abdomen
. Continue your treatment for as long as your doctor
advises.
Fold the used patch in half, sticking the patch to itself, and discard it in a safe way in order to
keep it away from children (e.g. in a rubbish bin). Medicines should not be disposed of via
wastewater (do not flush it down the toilet). Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines
no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
What about showering, bathing and exercising?
You may shower, bath, swim and exercise as normal while wearing the patch. The patch is designed
to remain in place during these times. However, do not scrub the area where the patch has been placed
too hard.
What about sunbathing?
Always make sure your patch is covered by clothing.
What if your patch becomes loose, lifts at the edges or falls off?
If a patch does begin to come off, you may be able to make it stick again by pressing on it firmly. If
you cannot get the patch to stick successfully, remove the loose patch and use a new patch. Then
continue with your regular schedule of patch-change days, even if this means discarding a patch after
you have worn it for less than 3-4 days.
If you use more patches than you should
If you have applied more than one patch at a time
Remove
all the patches
sticking on to your skin
and consult your doctor or pharmacist for further
information on how to continue treatment with Livensa. Overdosing with Livensa is unlikely when
used as directed, because once the patch is taken off testosterone is quickly removed by the body.

If you forget to use a patch
If you forget to change your patch
Change your patch as soon as you remember, and then continue with your regular schedule of patch-
change days, even if this means discarding a patch after you have worn it for less than 3-4 days.
Returning to your regular schedule will help you remember when to change your patch.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Like all medicines, Livensa can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Tell your doctor
immediately:
•
if you experience hair loss, enlargement of the clitoris, an increase in the amount of hair on the
chin or upper lip, voice deepening or hoarseness, although these side effects may be mild. They
are usually reversible if Livensa treatment is discontinued.
You should self assess for increased acne, increased hair growth on your face, loss of hair,
deepening of your voice or enlargement of your clitoris, which all could be signs of adverse
effects of testosterone, which is the active substance in Livensa.
if you notice any skin reactions at the site of application such as redness, oedema, or blistering.
In case of severe application site reaction, the treatment should be discontinued.
Very common side effects
The following side effects may occur very commonly (in more than 1 out of 10 patients).
o
rash/irritation/itching/redness at the site of the skin where the patch is applied
increase in the amount of hair on the chin or upper lip (likely to be mild and reversible)
Common side effects
The following side effects may occur commonly (in more than 1 out of 100, but less than 1 out of
10 patients), but most of them are mild in nature and reversible.
o
insomnia/inability to sleep properly
voice deepening or hoarseness
If any of the side effects become serious, or if you notice any side effects mentioned above or side
effects not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor.
•
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
•
Do not store above 30°C.
•
Do not refrigerate or freeze.
Do not use Livensa after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and sachet. The expiry date
refers to the last day of that month.
What Livensa contains
The active substance is testosterone. Each patch contains 8.4 mg of testosterone, releasing
300 micrograms of testosterone over 24 hours.
The other ingredients are: Sorbitan oleate, 2-Ethylhexylacrylate – 1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone co-polymer.
Backing layer: Translucent polyethylene backing film printed with proprietary ink containing sunset
yellow FCF (E110), latolrubine BK (E180) and copper phthalocyanine blue pigment.
Protective release liner: Siliconised polyester film.
What Livensa looks like and contents of the pack
Livensa is a thin, clear, oval patch with T001 stamped on the back.
The following pack sizes are available: 2, 8 and 24 patches. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Warner Chilcott Deutschland GmbH
Dr.-Otto-Röhm-Strasse 2-4
64331 Weiterstadt
Germany
Warner Chilcott France
Parc d’activité de la Grande Brèche
5 rue Désir Prévost
91070 Bondoufle
France
This leaflet was last approved in {MM/YYYY}
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) web
site: http://www.emea.eu.int/
Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/livensa.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|

























































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































