Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Neulasta 6 mg solution for injection.
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each pre-filled syringe contains 6 mg of pegfilgrastim* in 0.6 ml solution for injection. The
concentration is 10 mg/ml based on protein only**.
*Produced in
Escherichia coli
cells by recombinant DNA technology followed by conjugation with
polyethylene glycol (PEG).
** The concentration is 20 mg/ml if the PEG moiety is included.
The potency of this product should not be compared to the potency of another pegylated or non-
pegylated protein of the same therapeutic class. For more information, see section 5.1.
Excipients known to have a recognised action: sorbitol E420, sodium acetate (see section 4.4).
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Clear, colourless solution for injection.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Reduction in the duration of neutropenia and the incidence of febrile neutropenia in patients treated
with cytotoxic chemotherapy for malignancy (with the exception of chronic myeloid leukaemia and
myelodysplastic syndromes).
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Neulasta therapy should be initiated and supervised by physicians experienced in oncology and/or
haematology.
One 6 mg dose (a single pre-filled syringe) of Neulasta is recommended for each chemotherapy cycle,
administered as a subcutaneous injection approximately 24 hours following cytotoxic chemotherapy.
The experience in children is limited (see section 4.8, 5.1 and 5.2).
No dose change is recommended in patients with renal impairment, including those with end stage
renal disease.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Limited clinical data suggest a comparable effect on time to recovery of severe neutropenia for
pegfilgrastim to filgrastim in patients with
de novo
acute myeloid leukaemia (see section 5.1).
However, the long-term effects of Neulasta have not been established in acute myeloid leukaemia;
therefore, it should be used with caution in this patient population.
Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor can promote growth of myeloid cells
in vitro
and similar effects
may be seen on some non-myeloid cells
in vitro
.
The safety and efficacy of Neulasta have not been investigated in patients with myelodysplastic
syndrome, chronic myelogenous leukaemia, and in patients with secondary Acute Myeloid Leukaemia
(AML); therefore, it should not be used in such patients. Particular care should be taken to distinguish
the diagnosis of blast transformation of chronic myeloid leukaemia from acute myeloid leukaemia.
The safety and efficacy of Neulasta administration in
de novo
AML patients aged < 55 years with
cytogenetics t(15;17) have not been established.
The safety and efficacy of Neulasta have not been investigated in patients receiving high dose
chemotherapy.
Rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000) pulmonary adverse effects, in particular interstitial pneumonia, have
been reported after G-CSF administration. Patients with a recent history of pulmonary infiltrates or
pneumonia may be at higher risk.
The onset of pulmonary signs such as cough, fever, and dyspnoea in association with radiological
signs of pulmonary infiltrates, and deterioration in pulmonary function along with increased neutrophil
count may be preliminary signs of Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). In such
circumstances Neulasta should be discontinued at the discretion of the physician and the appropriate
treatment given.
Common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10) but generally asymptomatic cases of splenomegaly and very rare
(< 1/10,000) cases of splenic rupture, including some fatal cases, have been reported following
administration of pegfilgrastim. Therefore, spleen size should be carefully monitored (e.g. clinical
examination, ultrasound). A diagnosis of splenic rupture should be considered in patients reporting left
upper abdominal pain or shoulder tip pain.
Treatment with Neulasta alone does not preclude thrombocytopenia and anaemia because full dose
myelosuppressive chemotherapy is maintained on the prescribed schedule. Regular monitoring of
platelet count and haematocrit is recommended.
Neulasta should not be used to increase the dose of cytotoxic chemotherapy beyond established dosage
regimens.
Sickle cell crises have been associated with the use of pegfilgrastim in patients with sickle cell disease.
Therefore, physicians should exercise caution when administering Neulasta in patients with sickle cell
disease, should monitor appropriate clinical parameters and laboratory status and be attentive to the
possible association of Neulasta with splenic enlargement and vaso-occlusive crisis.
White blood cell counts of 100 x 10
9
/l or greater have been observed in less than 1% of patients
receiving Neulasta. No adverse events directly attributable to this degree of leukocytosis have been
reported. Such elevation in white blood cells is transient, typically seen 24 to 48 hours after
administration and is consistent with the pharmacodynamic effects of Neulasta.

The safety and efficacy of Neulasta for the mobilisation of blood progenitor cells in patients or healthy
donors has not been adequately evaluated.
The needle cover of the pre-filled syringe contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex), which
may cause allergic reactions.
Increased haematopoietic activity of the bone marrow in response to growth factor therapy has been
associated with transient positive bone imaging findings. This should be considered when interpreting
bone-imaging results.
Neulasta contains sorbitol. Patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance should not
take this medicine.
Neulasta contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) sodium per 6 mg dose, i.e. essentially ‘sodium-
free’.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Due to the potential sensitivity of rapidly dividing myeloid cells to cytotoxic chemotherapy‚ Neulasta
should be administered approximately 24 hours after administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy. In
clinical studies, Neulasta has been safely administered 14 days before chemotherapy. Concomitant use
of Neulasta with any chemotherapy agent has not been evaluated in patients. In animal models
concomitant administration of Neulasta and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) or other antimetabolites has been
shown to potentiate myelosuppression.
Possible interactions with other haematopoietic growth factors and cytokines have not been
specifically investigated in clinical studies.
The potential for interaction with lithium, which also promotes the release of neutrophils, has not been
specifically investigated. There is no evidence that such an interaction would be harmful.
The safety and efficacy of Neulasta have not been evaluated in patients receiving chemotherapy
associated with delayed myelosuppression e.g., nitrosoureas.
Specific interaction or metabolism studies have not been performed, however, clinical studies have not
indicated an interaction of Neulasta with any other medicinal products.
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
There are no adequate data from the use of pegfilgrastim in pregnant women. Studies in animals have
shown reproductive toxicity (see section 5.3). The potential risk for humans is unknown.
Neulasta should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary.
There is no clinical experience with breast-feeding women, therefore Neulasta should not be
administered to women who are breast-feeding.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
In randomised clinical studies in patients with malignancy receiving Neulasta after cytotoxic
chemotherapy, most adverse events were caused by the underlying malignancy or cytotoxic
chemotherapy.
The most frequently reported and very common study-drug related undesirable effect was bone pain
Bone pain was generally of mild-to-moderate severity, transient and could be controlled in most
patients with standard analgesics.
Allergic-type reactions, including anaphylaxis, skin rash, urticaria, angioedema, dyspnoea,
hypotension, injection site reactions, erythaema and flushing, occurring on initial or subsequent
treatment have been reported with Neulasta. In some cases, symptoms have recurred with rechallenge,
suggesting a causal relationship. If a serious allergic reaction occurs, appropriate therapy should be
administered, with close patient follow-up over several days. Pegfilgrastim should be permanently
discontinued in patients who experience a serious allergic reaction.
Reversible, mild to moderate elevations in uric acid and alkaline phosphatase, with no associated
clinical effects, were common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); reversible, mild to moderate elevations in lactate
dehydrogenase, with no associated clinical effects, were very common (≥ 1/10) in patients receiving
Neulasta following cytotoxic chemotherapy. Nausea was observed in healthy volunteers and patients
receiving chemotherapy.
Common (≥ 1/100 to <1/10) but generally asymptomatic cases of splenomegaly and very rare cases of
splenic rupture, including some fatal cases, have been reported following administration of
pegfilgrastim (see section 4.4). Other commonly reported undesirable effects include pain, injection
site pain; chest pain (non-cardiac); headache; arthralgia; myalgia; back, limb, musculo-skeletal and
neck pain.
Rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000) pulmonary adverse effects including interstitial pneumonia, pulmonary
oedema, pulmonary infiltrates and pulmonary fibrosis have been reported. Some of the reported cases
have resulted in respiratory failure or Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), which may be
fatal (see section 4.4)
Rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000) cases of thrombocytopenia and leukocytosis have been reported.
Rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000) cases of Sweet’s syndrome have been reported, although in some cases
underlying haematological malignancies may play a role.
Very rare (< 1/10,000) events of cutaneous vasculitis have been reported in patients treated with
Neulasta. The mechanism of vasculitis in patients receiving Neulasta is unknown.
Very rare (< 1/10,000) elevations in liver function tests (LFTs) for ALT (alanine aminotransferase) or
AST (aspartate aminotransferase), have been observed in patients after receiving pegfilgrastim
following cytotoxic chemotherapy. These elevations are transient and return to baseline.
Isolated cases of sickle cell crises have been reported in patients with sickle cell disease (see section
4.4).
A higher frequency of serious adverse events in younger children aged 0-5 years (92%) has been
observed compared to older children aged 6-11 and 12-21 years respectively (80% and 67%) and
adults. The most common adverse study medicinal product reaction was bone pain (see section 5.1 and
5.2).
There is no experience with overdose of Neulasta in humans.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Cytokines, ATC Code: L03AA13
Human granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) is a glycoprotein, which regulates the
production and release of neutrophils from the bone marrow. Pegfilgrastim is a covalent conjugate of
recombinant human G-CSF (r-metHuG-CSF) with a single 20 kd polyethylene glycol (PEG) molecule.
Pegfilgrastim is a sustained duration form of filgrastim due to decreased renal clearance.
Pegfilgrastim and filgrastim have been shown to have identical modes of action, causing a marked
increase in peripheral blood neutrophil counts within 24 hours, with minor increases in monocytes
and/or lymphocytes. Similarly to filgrastim, neutrophils produced in response to pegfilgrastim show
normal or enhanced function as demonstrated by tests of chemotactic and phagocytic function. As
with other haematopoietic growth factors, G-CSF has shown in vitro stimulating properties on human
endothelial cells. G-CSF can promote growth of myeloid cells, including malignant cells,
in vitro
and
similar effects may be seen on some non-myeloid cells
in vitro
.
In two randomised, double-blind, pivotal studies in patients with high risk stage II-IV breast cancer
undergoing myelosuppressive chemotherapy consisting of doxorubicin and docetaxel, use of
pegfilgrastim, as a single once per cycle dose, reduced the duration of neutropenia and the incidence of
febrile neutropenia similarly to that observed with daily administrations of filgrastim (a median of 11
daily administrations). In the absence of growth factor support, this regimen has been reported to result
in a mean duration of grade 4 neutropenia of 5 to7 days, and a 30-40% incidence of febrile
neutropenia. In one study (n = 157), which used a 6mg fixed dose of pegfilgrastim the mean duration
of grade 4 neutropenia for the pegfilgrastim group was 1.8 days compared with 1.6 days in the
filgrastim group (difference 0.23 days, 95% CI -0.15, 0.63). Over the entire study, the rate of febrile
neutropenia was 13% of pegfilgrastim-treated patients compared with 20% of filgrastim-treated
patients (difference 7%, 95% CI of -19%, 5%). In a second study (n = 310), which used a weight-
adjusted dose (100 micrograms/kg), the mean duration of grade 4 neutropenia for the pegfilgrastim
group was 1.7 days, compared with 1.8 days in the filgrastim group (difference 0.03 days, 95% CI -
0.36, 0.30). The overall rate of febrile neutropenia was 9% of patients treated with pegfilgrastim and
18% of patients treated with filgrastim (difference 9%, 95% CI of -16.8%,-1.1%).
In a placebo-controlled, double blind study in patients with breast cancer the effect of pegfilgrastim on
the incidence of febrile neutropenia was evaluated following administration of a chemotherapy
regimen associated with a febrile neutropenia rate of 10-20% (docetaxel 100 mg/m
2
every 3 weeks for
4 cycles). Nine hundred and twenty eight patients were randomised to receive either a single dose of
pegfilgrastim or placebo approximately 24 hours (Day 2) after chemotherapy in each cycle. The
incidence of febrile neutropenia was lower for patients randomised to receive pegfilgrastim compared
with placebo (1% versus 17%, p<0.001). The incidence of hospitalisations and IV anti-infective use
associated with a clinical diagnosis of febrile neutropenia was lower in the pegfilgrastim group
compared with placebo (1% versus 14%, p<0.001; and 2% versus 10%, p<0.001)
A small (n = 83), Phase II, randomised, double-blind study in patients receiving chemotherapy for
de
novo
acute myeloid leukaemia compared pegfilgrastim (single dose of 6 mg) with filgrastim,
administered during induction chemotherapy. Median time to recovery from severe neutropenia was
estimated as 22 days in both treatment groups. Long term outcome was not studied (see section 4.4).
In a phase II (n = 37) multicentre, randomised, open-label study of paediatric sarcoma patients
receiving 100 μg/kg pegfilgrastim following cycle 1 of vincristine, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide
(VAdriaC/IE) chemotherapy, a longer duration of severe neutropenia (neutrophils < 0.5 x 10
9
) was
observed in younger children aged 0-5 yrs (8.9 days) compared to older children aged 6-11 years and
12-21 years (6 days and 3.7 days,
respectively) and adults. Additionally a higher incidence of febrile
neutropenia was observed in younger children aged 0-5 yrs (75%) compared to older children aged
6-11 years and 12-21 years (70% and 33%, respectively) and adults (see sections 4.8 and 5.2).
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
After a single subcutaneous dose of pegfilgrastim, the peak serum concentration of pegfilgrastim
occurs at 16 to 120 hours after dosing and serum concentrations of pegfilgrastim are maintained during
the period of neutropenia after myelosuppressive chemotherapy. The elimination of pegfilgrastim is
non-linear with respect to dose; serum clearance of pegfilgrastim decreases with increasing dose.
Pegfilgrastim appears to be mainly eliminated by neutrophil mediated clearance, which becomes
saturated at higher doses. Consistent with a self-regulating clearance mechanism, the serum
concentration of pegfilgrastim declines rapidly at the onset of neutrophil recovery (see Figure 1).
Figure 1. Profile of Median Pegfilgrastim Serum Concentration and Absolute Neutrophil Count
(ANC) in Chemotherapy Treated Patients after a Single 6 mg Injection
Due to the neutrophil-mediated clearance mechanism, the pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim is not
expected to be affected by renal or hepatic impairment. In a open label, single dose study (n = 31)
various stages of renal impairment, including end-stage renal disease, had no impact on the
pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim.
Limited data indicate that the pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim in elderly subjects (> 65 years) is
similar to that in adults.
The pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim were studied in 37 paediatric patients with sarcoma, who
received 100 μg/kg pegfilgrastim after the completion of VAdriaC/IE chemotherapy. The youngest
age group (0-5 years) had a higher mean exposure to pegfilgrastim (AUC) (± Standard Deviation)
(47.9 ± 22.5 μg·hr/ml) than older children aged 6-11 years and 12-21 years (22.0 ± 13.1 μg·hr/ml and
29.3 ± 23.2 μg·hr/ml, respectively) (see section 5.1). With the exception of the youngest age group
(0-5 years), the mean AUC in paediatric subjects appeared similar to that for adult patients with
high-risk stage II-IV breast cancer and receiving 100 μg/kg pegfilgrastim after the completion of
doxorubicin/docetaxel (see sections 4.8 and 5.1).
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Preclinical data from conventional studies of repeated dose toxicity revealed the expected
pharmacological effects including increases in leukocyte count, myeloid hyperplasia in bone marrow,
extramedullary haematopoiesis and splenic enlargement.



















































































There were no adverse effects observed in offspring from pregnant rats given pegfilgrastim
subcutaneously, but in rabbits pegfilgrastim has been shown to cause embryo/foetal toxicity (embryo
loss) at low subcutaneous doses. In rat studies, it was shown that pegfilgrastim may cross the placenta.
The relevance of these findings for humans is not known.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Sodium acetate*
Sorbitol (E420)
Polysorbate 20
Water for injections
*Sodium acetate is formed by titrating glacial acetic acid with sodium hydroxide.
This medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products, particularly with sodium
chloride solutions.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
Neulasta may be exposed to room temperature (not above 30°C) for a maximum single period of up to
72 hours. Neulasta left at room temperature for more than 72 hours should be discarded.
Do not freeze. Accidental exposure to freezing temperatures for a single period of less than 24 hours
does not adversely affect the stability of Neulasta.
Keep the container in the outer carton, in order to protect from light.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
0.6 ml of solution for injection in a pre-filled syringe (Type I glass), with a rubber stopper, and with a
stainless steel needle. Pack size of one, in either blistered, with or without an automatic needle guard
or non-blistered packaging. Single use only.
The needle cover of the pre-filled syringe contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex) (see
section 4.4).
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for
disposal and other handling
Before administration, Neulasta solution should be inspected visually for particulate matter. Only a
solution that is clear and colourless should be injected.
Excessive shaking may aggregate pegfilgrastim, rendering it biologically inactive.
Allow the pre-filled syringe to reach room temperature before injecting.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Amgen Europe B.V.
Minervum 7061
4817 ZK Breda
The Netherlands
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/02/227/001 1 pack blistered syringe
EU/1/02/227/002 1 pack unblistered syringe
EU/1/02/227/004 1 pack blistered syringe with needle guard
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 22 August 2002
Date of last renewal: 16 July 2007
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines
MANUFACTURER OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE
SUBSTANCE AND MANUFACTURING
AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
MANUFACTURER OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE SUBSTANCE AND
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer of the biological active substance
Amgen Inc.
One Amgen Center Drive
Thousand Oaks
CA 91320
USA
Amgen Manufacturing Limited
P.O Box 4060
Road 31 km. 24.6
Juncos
Puerto Rico 00777-4060
USA
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
Amgen Europe BV
Minervum 7061
NL-4817 ZK Breda
The Netherlands
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to restricted medical prescription (See Annex I: Summary of Product
Characteristics, 4.2).
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
BLISTERED SYRINGE OUTER CARTON
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Neulasta 6 mg solution for injection
Pegfilgrastim
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each pre-filled syringe contains 6 mg of pegfilgrastim in 0.6 ml (10 mg/ml) solution for injection.
Excipients: sodium acetate, sorbitol (E420), polysorbate 20, water for injections.
Excipients known to have a recognised action: sorbitol (E420), sodium acetate.
See leaflet for further information.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Solution for injection in a single use pre-filled syringe (0.6 ml).
Solution for injection in a single use pre-filled syringe with automatic needle guard (0.6 ml).
Pack size of one.
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
For subcutaneous use.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator.
Do not freeze.
Keep the container in the outer carton, in order to protect from light.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Amgen Europe B.V.
Minervum 7061
4817 ZK Breda
The Netherlands
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/02/227/001 1 pack
EU/1/02/227/004 1 Pack with needle guard
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.




















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
UNBLISTERED SYRINGE OUTER CARTON
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Neulasta 6 mg solution for injection
Pegfilgrastim
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each pre-filled syringe contains 6 mg of pegfilgrastim in 0.6 ml (10 mg/ml) solution for injection.
Excipients: sodium acetate, sorbitol (E420), polysorbate 20, water for injections.
Excipients known to have a recognised action: sorbitol (E420), sodium acetate.
See leaflet for further information.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Solution for injection in a single use pre-filled syringe (0.6 ml).
Pack size of one.
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
For subcutaneous use.
Read the package leaflet before use.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY





















SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator.
Do not freeze.
Keep the container in the outer carton, in order to protect from light.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Amgen Europe B.V.
Minervum 7061
4817 ZK Breda
The Netherlands
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.



















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Neulasta 6 mg solution for injection in a pre-filled syringe
pegfilgrastim
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
1.
What Neulasta is and what it is used for
2.
Before you use Neulasta
3.
How to use Neulasta
4.
Possible side effects
5.
How to store Neulasta
6.
Further information
WHAT NEULASTA IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Neulasta is used to reduce the duration of neutropenia (low white blood cell count) and the occurrence
of febrile neutropenia (low white blood cell count with a fever) which can be caused by the use of
cytotoxic chemotherapy (medicines that destroy rapidly growing cells). White blood cells are
important as they help your body fight infection. These cells are very sensitive to the effects of
chemotherapy which can cause the number of these cells in your body to decrease. If white blood
cells fall to a low level there may not be enough left in the body to fight bacteria and you may have an
increased risk of infection.
Your doctor has given you Neulasta to encourage your bone marrow (part of the bone which makes
blood cells) to produce more white blood cells that help your body fight infection.
if you are hypersensitive (allergic) to pegfilgrastim, filgrastim,
E. coli
derived proteins, or any
of the other ingredients of Neulasta.
Take special care with Neulasta
if you experience a cough, fever and difficulty breathing;
if you have sickle cell anaemia;
if you get left upper abdominal pain or pain at the tip of your shoulder;
if you have an allergy to latex. The needle cover on the pre-filled syringe contains a derivative
of latex and may cause severe allergic reactions.
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines,
including medicines obtained without a prescription.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine. Neulasta has not been tested in
pregnant women. It is important to tell your doctor if you:
think you may be pregnant; or
You must stop breast feeding if you use Neulasta.
Driving
and
using
machines
The effect of Neulasta on the ability to drive or use machines is not known.
Important information about some of the ingredients of Neulasta
Neulasta contains sorbitol (a type of sugar). If you have been told by your doctor that you have an
intolerance to some sugars, contact your doctor before taking Neulasta. Neulasta is essentially
sodium-free.
Neulasta is for use in adults aged 18 and over.
Always take Neulasta exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor or
pharmacist if you are unsure. The usual dose is one 6 mg subcutaneous injection (injection under your
skin) using a pre-filled syringe and it should be given approximately 24 hours after your last dose of
chemotherapy at the end of each chemotherapy cycle.
Do not shake Neulasta vigorously as this may affect its activity
Injecting Neulasta yourself
Your doctor may decide that it would be more convenient for you to inject Neulasta yourself. Your
doctor or nurse will show you how to inject yourself. Do not try to inject yourself if you have not
been trained.
For further instructions on how to inject yourself with Neulasta, please read the section at the end of
this leaflet.
If you use more Neulasta than you should
If you use more Neulasta than you should contact your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
If you forget to inject Neulasta
If you have forgotten a dose of Neulasta, you should contact your doctor to discuss when you should
inject the next dose.
Like all medicines, Neulasta can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
A very common side effect (likely to occur in more than 1 in 10 patients) is bone pain. Your doctor
will tell you what you can take to ease the bone pain.
Common side effects (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 10 patients) include; pain and redness at the
site of the injection, headaches, and general aches and pains in the joints, muscles, chest, limbs, neck
or back. An uncommon side effect (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 100 patients) is nausea.
Allergic-type reactions to Neulasta, including redness and flushing, skin rash, raised areas of the skin
that itch and anaphylaxis (weakness, drop in blood pressure, difficulty breathing, swelling of the face),
have rarely (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 1,000 patients) been reported.
Increased spleen size and very rare cases (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 10,000 patients) of spleen
rupture have been reported after the use of Neulasta. Some cases of splenic rupture were fatal.
It is important that you contact your doctor immediately if you experience pain in the upper left side of
the abdomen or left shoulder pain since this may relate to a problem with your spleen.
Rare (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 1,000 patients) cases of breathing problems have been reported
after taking G-CSFs. If you have a cough, fever and difficulty breathing please tell your doctor.
Some changes may occur in your blood, but these will be detected by routine blood tests. Your
platelet count may become low which might result in bruising. Your white blood cell count may
become high for a short period of time.
Sweet’s syndrome (plum-coloured, raised, painful lesions on the limbs and sometimes the face and
neck with fever) has occurred rarely (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 1,000 patients) but other factors
may play a role.
Very rarely (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 10,000 patients) cutaneous vasculitis (inflammation of
the blood vessels in the skin) has occurred in patients receiving Neulasta.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Neulasta after the expiry date which is stated on the box and on the syringe label (EXP).
The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
You may take Neulasta out of the refrigerator and keep it at room temperature (not above 30°C) for no
longer than 3 days. Once a syringe has been removed from the refrigerator and has reached room
temperature (not above 30°C) it must either be used within 3 days or disposed of.
Do not freeze. Neulasta may be used if it is accidentally frozen for a single period of less than
24 hours.
Keep the container in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
Do not use Neulasta if you notice it is cloudy or there are particles in it.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
Neulasta contains the active substance pegfilgrastim. Pegfilgrastim is a protein produced by
biotechnology in bacteria called
E. coli
. It belongs to a group of proteins called cytokines, and is very
similar to a natural protein (granulocyte-colony stimulating factor) produced by your own body.
The active substance is pegfilgrastim. Each pre-filled syringe contains 6 mg of pegfilgrastim in 0.6 ml
of solution.
The other ingredients are sodium acetate, sorbitol (E420), polysorbate 20 and water for injections.
What Neulasta looks like and contents of the pack
Neulasta is a solution for injection in a pre-filled syringe (6 mg/0.6 ml).
Each pack contains 1 pre-filled syringe. The syringes are provided either with or without a blister
wrapping. It is a clear, colourless liquid.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer:
Amgen Europe B.V.
Minervum 7061
4817 ZK Breda
The Netherlands
If you want more information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the
Marketing Authorisation Holder.
België/Belgique/Belgien
s.a. Amgen n.v.
Tel/Tél: +32 (0)2 7752711
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
s.a. Amgen
Belgique/Belgien
Tel/Tél: +32 (0)2 7752711
България
Амджен България ЕООД
Тел: +359 (0) 2 805 7020
Magyarország
Amgen Kft.
Tel: +36 1 35 44 700
Česká republika
Amgen s.r.o
Tel: +420 2 21 773 500
Malta
Amgen B.V.
The Netherlands
Tel: +31 (0) 76 5732500
Danmark
Amgen filial af Amgen AB, Sverige
Tlf: +45 39617500
Nederland
Amgen B.V.
Tel: +31 (0) 76 5732500
Deutschland
AMGEN GmbH
Tel: +49 (0)89 1490960
Norge
Amgen AB
Tel: +47 23308000
Eesti
Amgen Switzerland AG Eesti filiaal
Tel: +372 5125 501
Österreich
Amgen GmbH
Tel: +43 (0) 1 50 217
Ελλάδα
Genesis Pharma S.A.
Τηλ: +30 210 8771500
Polska
Amgen Sp. z o.o.
Tel: +48 22 581 3000
España
Amgen S.A.
Tel: +34 93 600 19 00
Portugal
AMGEN Biofarmacêutica, Lda.
Tel: +351 21 4220550
France
Amgen S.A.S
Tél: +33 (0)1 40 88 27 00
România
Amgen România SRL
Tel: +4021 527 3000
Ireland
Amgen Limited
United Kingdom
Tel: +44 (0)1223 420305
Suomi/Finland
Amgen AB, sivuliike Suomessa/Amgen AB, filial
i Finland
Puh/Tel: +358 (0)9 54900500
Ísland
Vistor hf.
Sími: +354 535 7000
Slovenská republika
Amgen Switzerland AG Slovakia
Tel: +421 33 321 13 22
Italia
Amgen Dompé S.p.A.
Tel: +39 02 6241121
Slovenija
AMGEN zdravila d.o.o.
Tel: +386 1 585 1767
Kύπρος
Genesis Pharma (Cyprus) Ltd
Τηλ: +357 22 76 99 46
Sverige
Amgen AB
Tel: +46 (0)8 6951100
Latvija
Amgen Switzerland AG Rīgas filiāle
Tel: +371 29284 807
United Kingdom
Amgen Limited
Tel: +44 (0)1223 420305
Lietuva
Amgen Switzerland AG Vilniaus filialas
Tel: +370 6983 6600
This leaflet was last approved in.
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) web
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Instructions for injecting with the Neulasta pre-filled syringe
This section contains information on how to give yourself an injection of Neulasta. It is important that
you do not try to give yourself the injection unless you have received training from your doctor, nurse,
or pharmacist. If you have questions about how to inject, please ask your doctor, nurse, pharmacist
for assistance.
How do you, or the person injecting you, use Neulasta pre-filled syringe?
You will need to give yourself the injection into the tissue just under the skin. This is known as a
subcutaneous injection.
To give yourself a subcutaneous injection you will need:
a pre-filled syringe of Neulasta; and
alcohol wipes or similar.
What should I do before I give myself a subcutaneous injection of Neulasta?
1.
Remove from the refrigerator.
2.
Do not shake the pre-filled syringe.
3.
Do not
remove the cover from the syringe until you are ready to inject.
4.
Check the expiry date on the pre-filled syringe label (EXP). Do not use it if the date has passed
the last day of the month shown.
5.
Check the appearance of Neulasta. It must be a clear and colourless liquid. If there are particles
in it, you must not use it.
6.
For a more comfortable injection, let the pre-filled syringe stand for 30 minutes to reach room
temperature or hold the pre-filled syringe gently in your hand for a few minutes.
Do not
warm
Neulasta in any other way (for example, do not warm it in a microwave or in hot water).
Wash your hands thoroughly
U
.
Find a comfortable, well-lit, clean surface and put all the equipment you need within reach.
How do I prepare my Neulasta injection?
Before you inject Neulasta you must do the following:
1.
Hold the syringe barrel and gently take the cover from the needle
without twisting. Pull straight as shown in pictures 1 and 2. Do not
touch the needle or push the plunger.

2.
You may notice a small air bubble in the pre-filled syringe. You do not have to remove the air
bubble before injecting. Injecting the solution with the air bubble is harmless.
3.
You can now use the pre-filled syringe.
Where should I give my injection?
The most suitable places to inject yourself are:
the top of your thighs; and
the abdomen, except for the area around the navel.
If someone else is injecting you, they can also use the back of your arms.
How do I give my injection?
1.
Disinfect your skin by using an alcohol wipe and pinch the skin between your thumb and
forefinger, without squeezing it.
2.
Put the needle fully into the skin as shown by your nurse or doctor.
3.
Pull slightly on the plunger to check that a blood vessel has not been punctured. If you see
blood in the syringe, remove the needle and re-insert it in another place.
4.
Inject the liquid slowly and evenly, always keeping your skin pinched.
5.
After injecting the liquid, remove the needle and let go of your skin.
6.
If you notice a spot of blood at the injection site dab away with a cotton ball or tissues. Do not
rub the injection site.
If needed, you may cover the injection site with a bandage.
Only use each syringe for one injection. Do not use any Neulasta that is left in the syringe.
If you have any problems, please do not be afraid to ask your doctor or nurse for help and advice.
Disposing of used syringes
Do not put the cover back on used needles.
Keep used syringes out of the reach and sight of children.
The used syringe should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements. Ask your
pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect
the environment.

PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Neulasta 6 mg solution for injection in a pre-filled syringe
pegfilgrastim
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
1.
What Neulasta is and what it is used for
2.
Before you use Neulasta
3.
How to use Neulasta
4.
Possible side effects
5.
How to store Neulasta
6.
Further information
WHAT NEULASTA IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Neulasta is used to reduce the duration of neutropenia (low white blood cell count) and the occurrence
of febrile neutropenia (low white blood cell count with a fever) which can be caused by the use of
cytotoxic chemotherapy (medicines that destroy rapidly growing cells). White blood cells are
important as they help your body fight infection. These cells are very sensitive to the effects of
chemotherapy which can cause the number of these cells in your body to decrease. If white blood
cells fall to a low level there may not be enough left in the body to fight bacteria and you may have an
increased risk of infection.
Your doctor has given you Neulasta to encourage your bone marrow (part of the bone which makes
blood cells) to produce more white blood cells that help your body fight infection.
if you are hypersensitive (allergic) to pegfilgrastim, filgrastim,
E. coli
derived proteins, or any
of the other ingredients of Neulasta.
Take special care with Neulasta
if you experience a cough, fever and difficulty breathing;
if you have sickle cell anaemia;
if you get left upper abdominal pain or pain at the tip of your shoulder;
if you have an allergy to latex. The needle cover on the pre-filled syringe contains a derivative
of latex and may cause severe allergic reactions.
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines,
including medicines obtained without a prescription.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine. Neulasta has not been tested in
pregnant women. It is important to tell your doctor if you:
think you may be pregnant; or
You must stop breast feeding if you use Neulasta.
Driving
and
using
machines
The effect of Neulasta on the ability to drive or use machines is not known.
Important information about some of the ingredients of Neulasta
Neulasta contains sorbitol (a type of sugar). If you have been told by your doctor that you have an
intolerance to some sugars, contact your doctor before taking Neulasta. Neulasta is essentially
sodium-free.
Neulasta is for use in adults aged 18 and over.
Always take Neulasta exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor or
pharmacist if you are unsure. The usual dose is one 6 mg subcutaneous injection (injection under your
skin) using a pre-filled syringe and it should be given approximately 24 hours after your last dose of
chemotherapy at the end of each chemotherapy cycle.
Do not shake Neulasta vigorously as this may affect its activity
Injecting Neulasta yourself
Your doctor may decide that it would be more convenient for you to inject Neulasta yourself. Your
doctor or nurse will show you how to inject yourself. Do not try to inject yourself if you have not
been trained.
For further instructions on how to inject yourself with Neulasta, please read the section at the end of
this leaflet.
If you use more Neulasta than you should
If you use more Neulasta than you should contact your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
If you forget to inject Neulasta
If you have forgotten a dose of Neulasta, you should contact your doctor to discuss when you should
inject the next dose.
Like all medicines, Neulasta can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
A very common side effect (likely to occur in more than 1 in 10 patients) is bone pain. Your doctor
will tell you what you can take to ease the bone pain.
Common side effects (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 10 patients) include; pain and redness at the
site of the injection, headaches, and general aches and pains in the joints, muscles, chest, limbs, neck
or back. An uncommon side effect (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 100 patients) is nausea.
Allergic-type reactions to Neulasta, including redness and flushing, skin rash, raised areas of the skin
that itch and anaphylaxis (weakness, drop in blood pressure, difficulty breathing, swelling of the face),
have rarely (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 1,000 patients) been reported.
Increased spleen size and very rare cases (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 10,000 patients) of spleen
rupture have been reported after the use of Neulasta. Some cases of splenic rupture were fatal.
It is important that you contact your doctor immediately if you experience pain in the upper left side of
the abdomen or left shoulder pain since this may relate to a problem with your spleen.
Rare (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 1,000 patients) cases of breathing problems have been reported
after taking G-CSFs. If you have a cough, fever and difficulty breathing please tell your doctor.
Some changes may occur in your blood, but these will be detected by routine blood tests. Your
platelet count may become low which might result in bruising. Your white blood cell count may
become high for a short period of time.
Sweet’s syndrome (plum-coloured, raised, painful lesions on the limbs and sometimes the face and
neck with fever) has occurred rarely (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 1,000 patients) but other factors
may play a role.
Very rarely (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 10,000 patients) cutaneous vasculitis (inflammation of
the blood vessels in the skin) has occurred in patients receiving Neulasta.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use Neulasta after the expiry date which is stated on the box and on the syringe label (EXP).
The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
You may take Neulasta out of the refrigerator and keep it at room temperature (not above 30°C) for no
longer than 3 days. Once a syringe has been removed from the refrigerator and has reached room
temperature (not above 30°C) it must either be used within 3 days or disposed of.
Do not freeze. Neulasta may be used if it is accidentally frozen for a single period of less than
24 hours.
Keep the container in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
Do not use Neulasta if you notice it is cloudy or there are particles in it.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
Neulasta contains the active substance pegfilgrastim. Pegfilgrastim is a protein produced by
biotechnology in bacteria called
E. coli
. It belongs to a group of proteins called cytokines, and is very
similar to a natural protein (granulocyte-colony stimulating factor) produced by your own body.
The active substance is pegfilgrastim. Each pre-filled syringe contains 6 mg of pegfilgrastim in 0.6 ml
of solution.
The other ingredients are sodium acetate, sorbitol (E420), polysorbate 20 and water for injections.
What Neulasta looks like and contents of the pack
Neulasta is a solution for injection in a pre-filled syringe (6 mg/0.6 ml).
Each pack contains 1 pre-filled syringe. The syringes are provided either with or without an automatic
needle guard or blister wrapping. It is a clear, colourless liquid.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer:
Amgen Europe B.V.
Minervum 7061
4817 ZK Breda
The Netherlands
If you want more information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the
Marketing Authorisation Holder.
België/Belgique/Belgien
s.a. Amgen n.v.
Tel/Tél: +32 (0)2 7752711
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
s.a. Amgen
Belgique/Belgien
Tel/Tél: +32 (0)2 7752711
България
Амджен България ЕООД
Тел: +359 (0) 2 805 7020
Magyarország
Amgen Kft.
Tel: +36 1 35 44 700
Česká republika
Amgen s.r.o
Tel: +420 2 21 773 500
Malta
Amgen B.V.
The Netherlands
Tel: +31 (0) 76 5732500
Danmark
Amgen filial af Amgen AB, Sverige
Tlf: +45 39617500
Nederland
Amgen B.V.
Tel: +31 (0) 76 5732500
Deutschland
AMGEN GmbH
Tel: +49 (0)89 1490960
Norge
Amgen AB
Tel: +47 23308000
Eesti
Amgen Switzerland AG Eesti filiaal
Tel: +372 5125 501
Österreich
Amgen GmbH
Tel: +43 (0) 1 50 217
Ελλάδα
Genesis Pharma S.A.
Τηλ: +30 210 8771500
Polska
Amgen Sp. z o.o.
Tel: +48 22 581 3000
España
Amgen S.A.
Tel: +34 93 600 19 00
Portugal
AMGEN Biofarmacêutica, Lda.
Tel: +351 21 4220550
France
Amgen S.A.S
Tél: +33 (0)1 40 88 27 00
România
Amgen România SRL
Tel: +4021 527 3000
Ireland
Amgen Limited
United Kingdom
Tel: +44 (0)1223 420305
Suomi/Finland
Amgen AB, sivuliike Suomessa/Amgen AB, filial
i Finland
Puh/Tel: +358 (0)9 54900500
Ísland
Vistor hf.
Sími: +354 535 7000
Slovenská republika
Amgen Switzerland AG Slovakia
Tel: +421 33 321 13 22
Italia
Amgen Dompé S.p.A.
Tel: +39 02 6241121
Slovenija
AMGEN zdravila d.o.o.
Tel: +386 1 585 1767
Kύπρος
Genesis Pharma (Cyprus) Ltd
Τηλ: +357 22 76 99 46
Sverige
Amgen AB
Tel: +46 (0)8 6951100
Latvija
Amgen Switzerland AG Rīgas filiāle
Tel: +371 29284 807
United Kingdom
Amgen Limited
Tel: +44 (0)1223 420305
Lietuva
Amgen Switzerland AG Vilniaus filialas
Tel: +370 6983 6600
This leaflet was last approved in.
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) web
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
INSTRUCTIONS FOR INJECTING WITH THE NEULASTA PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
This section contains information on how you, or the person injecting you, use the Neulasta pre-filled
syringe. It is important that you do not try to give yourself the injection unless you have received
training from your doctor, nurse or pharmacist. If you have questions about how to inject, please ask
your doctor, nurse or pharmacist for assistance.
Read all instructions thoroughly before using the pre-filled syringe.
To reduce the risk of accidental needle sticks to users, each pre-filled syringe is equipped with a
needle guard that is automatically activated to cover the needle after complete delivery of the pre-filled
syringe content.
DO NOT
attempt to unlock the pre-filled syringe prior to injection.
DO NOT
use the pre-filled syringe if the needle cover has been removed, or the needle guard has been
activated (covering the needle).
DO NOT
try to remove the detachable label on the pre-filled syringe barrel before administering the
injection.
How do I use the Neulasta pre-filled syringe?
Your doctor has prescribed a Neulasta pre-filled syringe for injection into the tissue just under the
skin. Your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist will tell you how much Neulasta you need and how frequently
it should be injected.
To give yourself an injection you will need:
a new Neulasta pre-filled syringe; and
alcohol wipes or similar.
What should I do before I give myself a subcutaneous injection of Neulasta?
Remove the pre-filled syringe from the refrigerator.
Do not
pick up the pre-filled syringe by the
plunger or needle cover. This could damage the device.
Leave the pre-filled syringe at room temperature for approximately 30 minutes. This will make
the injection more comfortable.
Do not
warm Neulasta in any other way (for example, in a
microwave or in hot water).
Do not
leave the syringe exposed to direct sunlight.
Do not
shake the pre-filled syringe.
Do not
remove the cover from the pre-filled syringe until you are ready to inject.
Check the expiry date on the pre-filled syringe label (EXP).
Do not
use it if the date has passed
the last day of the month shown.
Check the appearance of Neulasta. It must be a clear and colourless liquid. If it is cloudy or
there are particles in it, you must not use it.
Wash your hands thoroughly
.
Find a comfortable, well-lit, clean surface and put all the equipment you need within reach.
Where should I give my injection?
The best places to inject yourself are the top of your thighs and the abdomen. If
someone else is injecting for you, they can also use the back of your arms.
Change the injection site if you notice the area is red or sore.
How do I give my injection?
Disinfect your skin by using an alcohol wipe.
To avoid bending the needle, gently pull the cover from
the needle
straight off
without twisting as shown.
Do
not
touch the needle or push the plunger.
You may notice a small air bubble in the pre-filled
syringe. You do not have to remove the air bubble before
injecting. Injecting the solution with the air bubble is
harmless.
Pinch (without squeezing) the skin between your thumb and forefinger. Put the needle fully into
the skin as shown by your nurse or doctor.
Pull slightly on the plunger to check that a blood vessel has not been punctured. If you see
blood in the syringe, pull the needle out and re-insert it in another
place after disinfecting the skin.
Push the plunger with a slow
constant pressure, always
keeping your skin pinched.
Push the plunger all the way
down as far as it will go to inject
all the liquid.
The needle guard will not activate unless you empty the pre-filled syringe.

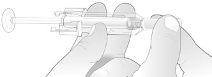



While the plunger is still pressed all the way down, remove the needle from the skin, then
release the plunger and allow the syringe to move up until the entire needle is covered by the
needle guard. If the needle guard is not activated, an incomplete injection may have occurred.
Call your health care provider if you think you have not received the full dose.
DO NOT
put the needle cover back on the needle.
If you notice a spot of blood you may gently dab it away with a cotton ball or tissue. Do not rub
the injection site.
If needed, you may cover the injection site with a plaster.
Only use each pre-filled syringe for one injection.
Do not
use any Neulasta that is left in the
syringe.
Remember:
If you have any problems, please ask your doctor or nurse for help and advice.
Disposing of used syringes
You do not need to put the needle cover back on used syringes.
Keep used syringes out of the reach and sight of children.
The used syringe should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements. Ask your
pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect
the environment.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following information is intended for medical or healthcare professionals only:
How to r emove the detachable label
The Neulasta pre-filled syringe comes with a detachable label that can be removed and placed on a
patient’s chart.
NOTE:
Only perform this step
U
after
U
you have given the injection and the safety guard is covering the
needle.


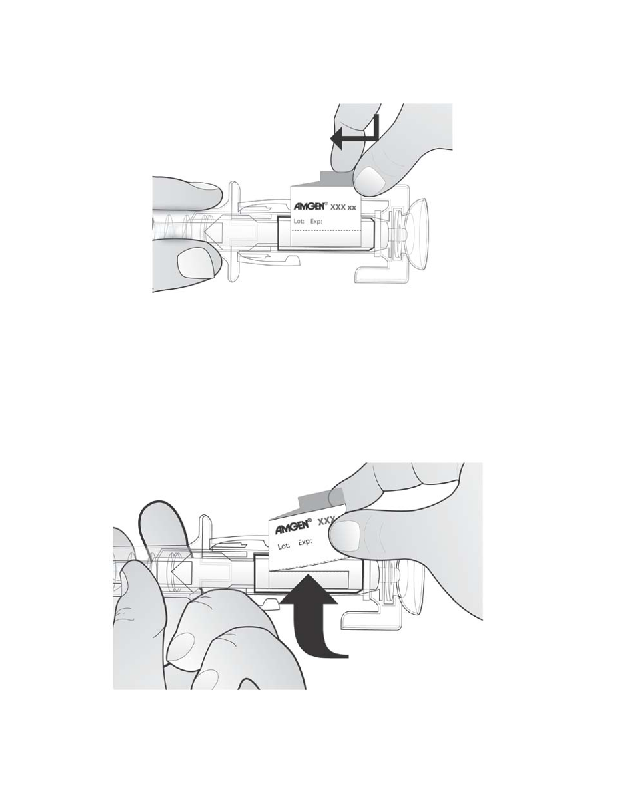
1.
Hold the syringe as shown and rotate the plunger
U
towards you
U
until you can see the tab of
the label
within the opening of the window as shown below.
2.
Slightly rotate the plunger
U
away from you
U
until the tab sticks up through the window as
shown below.

3.
Pull the tab up through the window, and then tear across the perforation
, as shown below.
Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/neulasta.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|


































































































































































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































