Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
NovoMix 30 Penfill 100 U/ml suspension for injection in cartridge
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
1 ml of the suspension contains 100 U soluble insulin aspart*/protamine-crystallised insulin aspart* in
the ratio 30/70 (equivalent to 3.5 mg). 1 cartridge contains 3 ml equivalent to 300 U.
*Insulin aspart is produced by recombinant DNA technology in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Suspension for injection in cartridge. Penfill.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults, adolescents and children aged 10 to 17 years.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The potency of insulin analogues, including insulin aspart, is expressed in units (U), whereas the
potency of human insulin is expressed in international units (IU).
NovoMix 30 dosing is individual and determined in accordance with the needs of the patient. Blood
glucose monitoring and insulin dose adjustments are recommended to achieve optimal glycaemic
control.
In patients with type 2 diabetes NovoMix 30 can be given as monotherapy. NovoMix 30 can also be
given in combination with oral antidiabetic medicinal products if the patient's blood glucose is
inadequately controlled with oral antidiabetic medicinal products alone. For patients with type 2
diabetes, the recommended starting dose of NovoMix 30 is 6 U at breakfast and 6 U at dinner (evening
meal). NovoMix 30 can also be initiated once daily with 12 U at dinner (evening meal). When using
NovoMix 30 once daily, it is generally recommended to move to twice-daily when reaching 30 units
by splitting the dose into equal breakfast and dinner doses. If twice daily dosing with NovoMix 30
results in recurrent daytime hypoglycaemic episodes, the morning dose can be split into morning and
lunchtime doses (thrice daily dose).
The following titration guideline is recommended for dose adjustments:
Pre-meal blood glucose level
NovoMix 30 dose
adjustment
6.2 – 7.8 mmol/l 111 – 140 mg/dl








The lowest of three previous days’ pre-meal levels should be used. The dose should not be increased if
hypoglycaemia occurred within these days. Dose adjustments can be made once a week until target
HbA
1c
is reached. Pre-meal blood glucose levels should be used to evaluate the adequacy of the
preceding dose.
The combination of NovoMix 30 with pioglitazone should only be considered following clinical
evaluation of the patient’s risk of developing signs or symptoms of fluid-related adverse reactions. The
initiation of NovoMix 30 should be undertaken cautiously titrating to the lowest dose required to
achieve glycaemic control (see section 4.4).
In patients with type 1 diabetes the individual insulin requirement is usually between 0.5 and
1.0 U/kg/day. NovoMix 30 may fully or partially meet this requirement. The daily insulin requirement
may be higher in patients with insulin resistance (e.g. due to obesity), and lower in patients with
residual endogenous insulin production.
Adjustment of dose may be necessary if patients undertake increased physical activity, change their
usual diet or during concomitant illness.
In patients with diabetes mellitus optimised metabolic control effectively delays the onset and slows
the progression of diabetic late complications. Optimised metabolic control, including glucose
monitoring, is therefore recommended.
Elderly (≥ 65 years old)
NovoMix 30 can be used in elderly patients; however there is limited experience with the use of
NovoMix 30 in combination with oral antidiabetic medicinal products in patients older than 75 years.
As with all insulin medicinal products, in elderly patients, glucose monitoring should be intensified
and insulin aspart dose adjusted on an individual basis.
Renal and hepatic impairment
Renal or hepatic impairment may reduce the patient’s insulin requirements.
As with all insulin medicinal products, in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, glucose
monitoring should be intensified and insulin aspart dose adjusted on an individual basis.
NovoMix 30 can be used in children and adolescents aged 10 years and above when premixed insulin
is preferred. For children from 6 to 9 years old limited clinical data exists (see section 5.1).
No clinical studies with NovoMix 30 have been carried out in children under the age of 6 years.
NovoMix 30 should only be used in this age group under careful medical supervision.
Transfer from other insulin medicinal products
When transferring a patient from biphasic human insulin to NovoMix 30, start with the same dose and
regimen. Then titrate according to individual needs (see titration guideline in table above).
As with all insulin medicinal products, close glucose monitoring is recommended during the transfer
and in the initial weeks thereafter (see section 4.4).
NovoMix 30 is for subcutaneous administration
only
. NovoMix 30 must not be administrated
intravenously, as it may result in severe hypoglycaemia. Intramuscular administration should be
avoided. NovoMix 30 is not to be used in insulin infusion pumps.






NovoMix 30 has a faster onset of action than biphasic human insulin and should generally be given
immediately before a meal. When necessary, NovoMix 30 can be given soon after a meal.
NovoMix 30 Penfill is designed to be used with Novo Nordisk insulin delivery systems and NovoFine
or NovoTwist needles. The patient should be advised not to use any counterfeit needles.
NovoMix 30 Penfill is accompanied by a package leaflet with detailed instructions for use to be
followed.
NovoMix 30 is administered subcutaneously by injection in the thigh or in the abdominal wall. If
convenient, the gluteal or deltoid region may be used. Injection sites should always be rotated within
the same region. The influence of different injection sites on the absorption of NovoMix 30 has not
been investigated. As with all insulin medicinal products, the duration of action will vary according to
the dose, injection site, blood flow, temperature and level of physical activity.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Inadequate dosing or discontinuation of treatment, especially in type 1 diabetes, may lead to
hyperglycaemia and diabetic ketoacidosis. Usually the first symptoms of hyperglycaemia develop
gradually over a period of hours or days. They include thirst, increased frequency of urination, nausea,
vomiting, drowsiness, flushed dry skin, dry mouth, loss of appetite as well as acetone odour of breath.
In type 1 diabetes, untreated hyperglycaemic events eventually lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, which is
potentially lethal.
Before travelling between different time zones the patient should seek the doctor’s advice since this
may mean that the patient has to take the insulin and meals at different times.
Omission of a meal or unplanned, strenuous physical exercise may lead to hypoglycaemia.
Hypoglycaemia may occur if the insulin dose is too high in relation to the insulin requirement (see
section 4.8 and 4.9).
Compared with biphasic human insulin, NovoMix 30 may have a more pronounced glucose lowering
effect up to 6 hours after injection. This may have to be compensated for in the individual patient,
through adjustment of insulin dose and/or food intake.
Patients, whose blood glucose control is greatly improved, e.g. by intensified insulin therapy, may
experience a change in their usual warning symptoms of hypoglycaemia, and should be advised
accordingly. Usual warning symptoms may disappear in patients with longstanding diabetes.
Tighter control of glucose levels can increase the potential for hypoglycaemic episodes and therefore
require special attention during dose intensification as outlined in section 4.2.
Since NovoMix 30 should be administered in immediate relation to a meal the rapid onset of action
should be considered in patients with concomitant diseases or treatment where a delayed absorption of
food might be expected.
Concomitant illness, especially infections and feverish conditions, usually increases the patient’s
insulin requirements. Concomitant diseases in the kidney, liver or affecting the adrenal, pituitary or
thyroid gland can require changes in insulin dose.
When patients are transferred between different types of insulin medicinal products, the early warning
symptoms of hypoglycaemia may change or become less pronounced than those experienced with
their previous insulin.
Transfer from other insulin medicinal products
Transferring a patient to another type or brand of insulin should be done under strict medical
supervision. Changes in strength, brand (manufacturer), type, origin (animal, human, human insulin
analogue) and/or method of manufacture (recombinant DNA versus animal source insulin) may result
in the need for a change in dose. Patients transferred to NovoMix 30 from another type of insulin may
require an increased number of daily injections or a change in dose from that used with their usual
insulins. If an adjustment is needed, it may occur with the first dose or during the first few weeks or
months.
As with any insulin therapy, injection site reactions may occur and include pain, redness, hives,
inflammation, swelling and itching. Continuous rotation of the injection site within a given area may
help to reduce or prevent these reactions. Reactions usually resolve in a few days to a few weeks. On
rare occasions, injection site reactions may require discontinuation of NovoMix 30.
Combination of NovoMix 30 with pioglitazone
There have been cases of cardiac failure reported from the market when pioglitazone was used in
combination with insulin, especially in patients with risk factors for development of cardiac heart
failure. Patients should be observed for signs and symptoms of heart failure, weight gain and oedema
when NovoMix 30 is used in combination with pioglitazone. As a consequence of increased insulin
sensitivity, patients receiving pioglitazone in dual therapy with insulin may be at risk for dose-related
hypoglycaemia, and a reduction in the dose of insulin may be necessary.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
A number of medicinal products are known to interact with the glucose metabolism.
The following substances may reduce the patient’s insulin requirements:
Oral antidiabetic medicinal products, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI), beta-blockers,
angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, salicylates, anabolic steroids and sulphonamides.
The following substances may increase the patient’s insulin requirements:
Oral contraceptives, thiazides, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, sympathomimetics, growth
hormone and danazol.
Beta-blockers may mask the symptoms of hypoglycaemia.
Octreotide/lanreotide may both increase or decrease insulin requirement.
Alcohol may intensify or reduce the hypoglycaemic effect of insulin.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
There is limited clinical experience with NovoMix 30 in pregnancy.
Animal reproduction studies have not revealed any differences between insulin aspart and human
insulin regarding embryotoxicity or teratogenicity.
In general, intensified blood glucose control and monitoring of pregnant women with diabetes are
recommended throughout pregnancy and when contemplating pregnancy. Insulin requirements usually
fall in the first trimester and increase subsequently during the second and third trimesters. After
delivery, insulin requirements return rapidly to pre-pregnancy levels.
There are no restrictions on treatment with NovoMix 30 during breast-feeding. Insulin treatment of the
nursing mother presents no risk to the baby. However, the NovoMix 30 dose may need to be adjusted.
Animal reproduction studies have not revealed any differences between insulin aspart and human
insulin regarding fertility.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The patient’s ability to concentrate and react may be impaired as a result of hypoglycaemia. This may
constitute a risk in situations where these abilities are of special importance (e.g. driving a car or using
machines).
Patients should be advised to take precautions to avoid hypoglycaemia while driving. This is
particularly important in those who have reduced or absent awareness of the warning signs of
hypoglycaemia or have frequent episodes of hypoglycaemia. The advisability of driving should be
considered in these circumstances.
a. Summary of the safety profile
Adverse reactions observed in patients using NovoMix are mainly dose-dependent and due to the
pharmacologic effect of insulin.
The most frequently reported adverse reaction during treatment is hypoglycaemia. The frequencies of
hypoglycaemia vary with patient population, dose regimens and level of glycaemic control, please see
section c below.
At the beginning of the insulin treatment, refraction anomalies, oedema and local hypersensitivity
reactions (pain, redness, hives, inflammation, swelling and itching at the injection site) may occur;
these reactions are usually of transitory nature. Fast improvement in blood glucose control may be
associated with acute painful neuropathy, which is usually reversible. Intensification of insulin therapy
with abrupt improvement in glycaemic control may be associated with temporary worsening of
diabetic retinopathy, while long-term improved glycaemic control decreases the risk of progression of
diabetic retinopathy.
b. Tabulated list of adverse reactions
Adverse reactions listed below are based on clinical trial data and classified according to MedDRA
frequency and System Organ Class. Frequency categories are defined according to the following
convention: Very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100);
rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000); very rare (< 1/10,000); not known (cannot be estimated from the
available data).
Uncommon - Urticaria, rash, eruptions
Very rare - Anaphylactic reactions*





Metabolism and nutrition
disorders
Very common – Hypoglycaemia*
Rare - Peripheral neuropathy
Uncommon - Refraction disorders
Skin and subcutaneous tissue
disorders
Uncommon - Diabetic retinopathy
Uncommon – Lipodystrophy*
Uncommon - Local hypersensitivity
General disorders and
administration site conditions
c. Description of selected adverse reactions
Hypoglycaemia:
The most frequently reported adverse reaction is hypoglycaemia. It may occur if the insulin dose is too
high in relation to the insulin requirement. Severe hypoglycaemia may lead to unconsciousness and/or
convulsions and may result in temporary or permanent impairment of brain function or even death.
The symptoms of hypoglycaemia usually occur suddenly. They may include cold sweats, cool pale
skin, fatigue, nervousness or tremor, anxiousness, unusual tiredness or weakness, confusion, difficulty
in concentration, drowsiness, excessive hunger, vision changes, headache, nausea and palpitation.
In clinical trials the frequency of hypoglycaemia varied with patient population, dose regimens and
level of glycaemic control. During clinical trials the overall rates of hypoglycaemia did not differ
between patients treated with insulin aspart compared to human insulin.
Anaphylactic reactions:
The occurrence of generalised hypersensitivity reactions (including generalised skin rash, itching,
sweating, gastrointestinal upset, angioneurotic oedema, difficulties in breathing, palpitation and
reduction in blood pressure ) is very rare but can potentially be life threatening.
Lipodystrophy:
Lipodystrophy is reported as uncommon. It may occur at the injection site; therefore it is
recommended to rotate injection sites within an area.
Based on post-marketing sources and clinical trials, the frequency, type and severity of adverse
reactions observed in the paediatric population do not indicate any differences to the broader
experience in the general population.
e. Other special populations
Based on post-marketing sources and clinical trials, the frequency, type and severity of adverse
reactions observed in the elderly patients and in patients with renal or hepatic impairment do not
indicate any differences to the broader experience in the general population.










A specific overdose for insulin cannot be defined, however, hypoglycaemia may develop over
sequential stages if too high doses relative to the patient’s requirement are administered:
Mild hypoglycaemic episodes can be treated by oral administration of glucose or sugary
products. It is therefore recommended that the diabetic patient always carries sugar-containing
products
Severe hypoglycaemic episodes, where the patient has become unconscious, can be treated with
glucagon (0.5 to 1 mg) given intramuscularly or subcutaneously, by a trained person, or with
glucose given intravenously by a healthcare professional. Glucose must be given intravenously,
if the patient does not respond to glucagon within 10 to 15 minutes. Upon regaining
consciousness, administration of oral carbohydrates is recommended for the patient in order to
prevent a relapse.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Drugs used in diabetes. Insulins and analogues for injection,
intermediate-acting combined with fast-acting. ATC code: A10AD05.
NovoMix 30 is a biphasic suspension of 30% soluble insulin aspart (rapid-acting human insulin
analogue) and 70% protamine-crystallised insulin aspart (intermediate-acting human insulin
analogue).
The blood glucose lowering effect of insulin aspart is due to the facilitated uptake of glucose
following binding of insulin to receptors on muscle and fat cells and to the simultaneous inhibition of
glucose output from the liver.
NovoMix 30 is a biphasic insulin, which contains 30% soluble insulin aspart. This has a rapid onset of
action, thus allowing it to be given closer to a meal (within zero to 10 minutes of the meal) when
compared to soluble human insulin. The crystalline phase (70%) consists of protamine-crystallised
insulin aspart, which has an activity profile that is similar to that of human NPH insulin (Figure 1).
When NovoMix 30 is injected subcutaneously, the onset of action will occur within 10 to 20 minutes
of injection. The maximum effect is exerted between 1 and 4 hours after injection. The duration of
action is up to 24 hours.
Figure 1: Activity profile of NovoMix 30 (
___
) and biphasic human insulin 30 (---) in healthy subjects.
In a 3 month trial in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes NovoMix 30 showed equal control of
glycosylated haemoglobin compared to treatment with biphasic human insulin 30. Insulin aspart is
equipotent to human insulin on a molar basis. Compared to biphasic human insulin 30, administration
of NovoMix 30 before breakfast and dinner resulted in lower postprandial blood glucose after both
meals (breakfast and dinner).
A meta-analysis including nine trials in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes showed that fasting
blood glucose was higher in patients treated with NovoMix 30, than in
patients treated with biphasic
human insulin 30.
In one study, 341 patients with type 2 diabetes were randomised to treatment with NovoMix 30 either
alone or in combination with metformin, or to metformin together with sulfonylurea. The primary
efficacy variable - HbA
1c
after 16 weeks of treatment - did not differ between patients with NovoMix
30 combined with metformin and patients with metformin plus sulfonylurea. In this trial 57% of the
patients had baseline HbA
1c
above 9%; in these patients treatment with NovoMix 30 in combination
with metformin resulted in significantly lower HbA
1c
than metformin in combination with
sulfonylurea.
In one study, patients with type 2 diabetes, insufficiently controlled on oral hypoglycaemic agents
alone, were randomised to treatment with twice daily NovoMix 30 (117 patients) or once daily insulin
glargine (116 patients). After 28 weeks treatment following the dosing guideline outlined in section
4.2, the mean reduction in HbA
1c
was 2.8% with NovoMix 30 (mean at baseline = 9.7%). With
NovoMix 30, 66% and 42% of the patients reached HbA
1c
levels below 7% and 6.5%, respectively,
and mean FPG was reduced by about 7 mmol/L (from 14.0 mmol/L at baseline to 7.1 mmol/L).
In patients with type 2 diabetes a meta-analysis showed a reduced risk of overall nocturnal
hypoglycaemic episodes and major hypoglycaemia with NovoMix 30 compared to biphasic human
insulin 30. The risk of overall daytime hypoglycaemic episodes was increased in patients treated with
NovoMix 30.
A 16-week clinical trial comparing postprandial glycaemic control of meal-related NovoMix 30 with
meal-related human insulin/biphasic human insulin 30 and bedtime NPH insulin was performed in
167 subjects aged 10 to 18 years. Mean HbA
1c
remained similar to baseline throughout the trial in both
treatment groups, and there was no difference in hypoglycaemia rate with NovoMix 30 or biphasic
human insulin 30.

In a smaller (54 subjects) and younger (age range 6 to 12 years) population, treated in a double-blind,
cross-over trial (12 weeks on each treatment) the rate of hypoglycaemic episodes and the postprandial
glucose increase was significantly lower with NovoMix 30 compared to biphasic human insulin 30.
Final HbA
1c
was significantly lower in the biphasic human insulin 30 treated group compared with
NovoMix 30.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption, distribution and elimination
In insulin aspart substitution of amino acid proline with aspartic acid at position B28 reduces the
tendency to form hexamers as observed with soluble human insulin. The insulin aspart in the soluble
phase of NovoMix 30 comprises 30% of the total insulin; this is absorbed more rapidly from the
subcutaneous layer than the soluble insulin component of biphasic human insulin. The remaining 70%
is in crystalline form as protamine-crystallised insulin aspart; this has a prolonged absorption profile
similar to human NPH insulin.
The maximum serum insulin concentration is, on average, 50% higher with NovoMix 30 than with
biphasic human insulin 30. The time to maximum concentration is, on average, half of that for
biphasic human insulin 30. In healthy volunteers a mean maximum serum concentration of 140
±
32 pmol/l was reached about 60 minutes after a subcutaneous dose of 0.20 U/kg body weight. The
mean half life (t
½
) of NovoMix 30, reflecting the absorption rate of the protamine bound fraction, was
about 8-9 hours. Serum insulin levels returned to baseline 15-18 hours after a subcutaneous dose. In
type 2 diabetic patients, the maximum concentration was reached about 95 minutes after dosing, and
concentrations well above zero for not less than 14 hours post-dosing were measured.
The pharmacokinetics of NovoMix 30 has not been investigated in elderly patients, or patients with
renal or hepatic impairment.
The
pharmacokinetics
of NovoMix 30 has not
been investigated in
children
or
adolescents
.
However,
the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of soluble insulin aspart have been investigated
in children (6–12 years) and adolescents (13–17 years) with type 1 diabetes. Insulin aspart was rapidly
absorbed in both age groups, with similar t
max
as in adults. However, C
max
differed between the age
groups, stressing the importance of the individual titration of insulin aspart.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety
pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity and toxicity to reproduction and development.
In
in vitro
tests, including binding to insulin and IGF-1 receptor sites and effects on cell growth,
insulin aspart behaved in a manner that closely resembled human insulin. Studies also demonstrate that
the dissociation of binding to the insulin receptor of insulin aspart is equivalent to human insulin.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Glycerol
Phenol
Metacresol
Zinc chloride
Disodium phosphate dihydrate
Sodium chloride
Protamine sulphate
Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment)
Sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment)
Water for injections
In absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal
products.
After first opening: A maximum of 4 weeks when stored below 30°C.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C). Keep away from the cooling element. Do not freeze.
Keep the cartridge in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
After first opening or carried as a spare: Do not refrigerate. Store below 30°C.
NovoMix 30 must be protected from excessive heat and light.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
3 ml suspension in cartridge (type 1 glass) with a plunger (bromobutyl) and a stopper
(bromobutyl/polyisoprene) in a carton. The cartridge contains a glass ball to facilitate resuspension.
Pack sizes of 5 and 10 cartridges. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Needles and NovoMix 30 Penfill must not be shared. The cartridge must not be refilled.
After removing NovoMix 30 Penfill from the refrigerator, it is recommended to allow NovoMix 30
Penfill to reach room temperature before resuspending the insulin as instructed for first time use.
NovoMix 30 must not be used if the resuspended liquid does not appear uniformly white and cloudy.
The necessity of resuspending the NovoMix 30 suspension immediately before use is to be stressed to
the patient.
NovoMix 30 which has been frozen must not be used.
The patient should be advised to discard the needle after each injection.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd
Denmark
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/00/142/004
EU/1/00/142/005
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 1 August 2000
Date of last renewal: 2 July 2010
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
NovoMix 50 Penfill
100 U/ml suspension for injection in cartridge
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
1 ml of the suspension contains 100 U soluble insulin aspart*/protamine-crystallised insulin aspart* in
the ratio 50/50 (equivalent to 3.5 mg). 1 cartridge contains 3 ml equivalent to 300 U.
*Insulin aspart is produced by recombinant DNA technology in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Suspension for injection in cartridge. Penfill.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The potency of insulin analogues, including insulin aspart, is expressed in units (U), whereas the
potency of human insulin is expressed in international units (IU).
NovoMix 50 dosing is individual and determined in accordance with the needs of the patient. Blood
glucose monitoring and insulin dose adjustments are recommended to archive optimal glycaemic
control.
The individual insulin requirement is usually between 0.5 and 1.0 U/kg/day
in adult patients and this
may be fully or partially supplied with NovoMix 50. The daily insulin requirement may be higher in
patients with insulin resistance (e.g. due to obesity), and lower in patients with residual endogenous
insulin production.
In patients with type 2 diabetes,
NovoMix 50 can be given as monotherapy or in combination with
metformin, when the blood glucose is inadequately controlled with metformin alone.
Adjustment of dose may be necessary if patients undertake increased physical activity, change their
usual diet or during concomitant illness.
In patients with diabetes mellitus optimised metabolic control effectively delays the onset and slows
the progression of diabetic late complications. Optimised metabolic control, including glucose
monitoring, is therefore recommended.
As with all insulin medicinal products, in elderly patients (≥ 65 years old) and patients with hepatic or
renal impairment, glucose monitoring should be intensified and insulin aspart dose adjusted on an
individual basis.
Renal or hepatic impairment may reduce the patient’s insulin requirements.
No clinical studies with NovoMix 50 have been carried out in children or adolescents under the age of
18 years.
NovoMix 50 should only be used in this age group under careful medical supervision.
Transfer from other insulin medicinal products
Transfer to NovoMix 50 from other insulin preparations may require adjustment of dose and timing of
administration. As with all insulin medicinal products, close glucose monitoring is recommended
during the transfer and in the initial weeks thereafter (see section 4.4).
NovoMix 50 is for subcutaneous administration
only
. NovoMix 50 must not be administrated
intravenously, as it may result in severe hypoglycaemia. Intramuscular administration should be
avoided. NovoMix 50 is not to be used in insulin infusion pumps.
The rapid onset of action and early peak of activity of insulin aspart allows NovoMix 50 to be given
immediately before a meal. When necessary, NovoMix 50 can be given soon after a meal.
NovoMix 50 Penfill is designed to be used with Novo Nordisk insulin delivery systems and NovoFine
or NovoTwist needles. The patient should be advised not to use any counterfeit needles.
NovoMix 50 Penfill is accompanied by a package leaflet with detailed instructions for use to be
followed.
NovoMix 50 is administered subcutaneously by injection in the thigh or in the abdominal wall. If
convenient, the gluteal or deltoid region may be used. Injection sites should always be rotated within
the same region. The influence of different injection sites on the absorption of NovoMix 50 has not
been investigated. As with all insulin medicinal products, the duration of action will vary according to
the dose, injection site, blood flow, temperature and level of physical activity.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Inadequate dosing or discontinuation of treatment, especially in type 1 diabetes, may lead to
hyperglycaemia and diabetic ketoacidosis. Usually the first symptoms of hyperglycaemia develop
gradually over a period of hours or days. They include thirst, increased frequency of urination, nausea,
vomiting, drowsiness, flushed dry skin, dry mouth, loss of appetite as well as acetone odour of breath.
In type 1 diabetes, untreated hyperglycaemic events eventually lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, which is
potentially lethal.
Before travelling between different time zones the patient should seek the doctor’s advice since this
may mean that the patient has to take the insulin and meals at different times.
Omission of a meal or unplanned, strenuous physical exercise may lead to hypoglycaemia.
Hypoglycaemia may occur if the insulin dose is too high in relation to the insulin requirement (see
section 4.8 and 4.9).
Patients, whose blood glucose control is greatly improved, e.g. by intensified insulin therapy, may
experience a change in their usual warning symptoms of hypoglycaemia, and should be advised
accordingly. Usual warning symptoms may disappear in patients with longstanding diabetes.
Since NovoMix 50 should be administered in immediate relation to a meal the rapid onset of action
should be considered in patients with concomitant diseases or treatment where a delayed absorption of
food might be expected.
Concomitant illness, especially infections and feverish conditions, usually increases the patient’s
insulin requirements. Concomitant diseases in the kidney, liver or affecting the adrenal, pituitary or
thyroid gland can require changes in insulin dose.
When patients are transferred between different types of insulin medicinal products, the early warning
symptoms of hypoglycaemia may change or become less pronounced than those experienced with
their previous insulin.
Transfer from other insulin medicinal products
Transferring a patient to another type or brand of insulin should be done under strict medical
supervision. Changes in strength, brand (manufacturer), type, origin (animal, human, human insulin
analogue) and/or method of manufacture (recombinant DNA versus animal source insulin)
may result
in the need for a change in dose. Patients transferred to NovoMix 50 from another type of insulin may
require an increased number of daily injections or a change in dose from that used with their usual
insulins. If an adjustment is needed, it may occur with the first dose or during the first few weeks or
months.
As with any insulin therapy, injection site reactions may occur and include pain, redness, hives,
inflammation, swelling and itching. Continuous rotation of the injection site within a given area may
help to reduce or prevent these reactions. Reactions usually resolve in a few days to a few weeks. On
rare occasions, injection site reactions may require discontinuation of NovoMix 50.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
A number of medicinal products are known to interact with the glucose metabolism.
The following substances may reduce the patient’s insulin requirements:
Oral antidiabetic medicinal products, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI), beta-blockers,
angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, salicylates, anabolic steroids and sulphonamides.
The following substances may increase the patient’s insulin requirements:
Oral contraceptives, thiazides, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, sympathomimetics, growth
hormone and danazol.
Beta-blockers may mask the symptoms of hypoglycaemia.
Octreotide/lanreotide may both increase or decrease insulin requirement.
Alcohol may intensify or reduce the hypoglycaemic effect of insulin.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
There is limited clinical experience with NovoMix 50 in pregnancy.
Animal reproduction studies have not revealed any differences between insulin aspart and human
insulin regarding embryotoxicity or teratogenicity.
In general, intensified blood glucose control and monitoring of pregnant women with diabetes are
recommended throughout pregnancy and when contemplating pregnancy. Insulin requirements usually
fall in the first trimester and increase subsequently during the second and third trimesters. After
delivery, insulin requirements return rapidly to pre-pregnancy levels.
There are no restrictions on treatment with NovoMix 50 during breast-feeding. Insulin treatment of the
nursing mother presents no risk to the baby. However, the NovoMix 50 dose may need to be adjusted.
Animal reproduction studies have not revealed any differences between insulin aspart and human
insulin regarding fertility.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The patient’s ability to concentrate and react may be impaired as a result of hypoglycaemia. This may
constitute a risk in situations where these abilities are of special importance (e.g. driving a car or using
machines).
Patients should be advised to take precautions to avoid hypoglycaemia while driving. This is
particularly important in those who have reduced or absent awareness of the warning signs of
hypoglycaemia or have frequent episodes of hypoglycaemia. The advisability of driving should be
considered in these circumstances.
a. Summary of the safety profile
Adverse reactions observed in patients using NovoMix are mainly dose-dependent and due to the
pharmacologic effect of insulin.
The most frequently reported adverse reaction during treatment is hypoglycaemia. The frequencies of
hypoglycaemia vary with patient population, dose regimens and level of glycaemic control, please see
section c below.
At the beginning of the insulin treatment, refraction anomalies, oedema and local hypersensitivity
reactions (pain, redness, hives, inflammation, swelling and itching at the injection site) may occur;
these reactions are usually of transitory nature. Fast improvement in blood glucose control may be
associated with acute painful neuropathy, which is usually reversible. Intensification of insulin therapy
with abrupt improvement in glycaemic control may be associated with temporary worsening of
diabetic retinopathy, while long-term improved glycaemic control decreases the risk of progression of
diabetic retinopathy.
b. Tabulated list of adverse reactions
Adverse reactions listed below are based on clinical trial data and classified according to MedDRA
frequency and System Organ Class. Frequency categories are defined according to the following
convention: Very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100);
rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000); very rare (< 1/10,000); not known (cannot be estimated from the
Uncommon - Urticaria, rash, eruptions
Very rare - Anaphylactic reactions*
Metabolism and nutrition
disorders
Very common – Hypoglycaemia*
Rare - Peripheral neuropathy
Uncommon - Refraction disorders
Skin and subcutaneous tissue
disorders
Uncommon - Diabetic retinopathy
Uncommon – Lipodystrophy*
Uncommon - Local hypersensitivity
General disorders and
administration site conditions
c. Description of selected adverse reactions
Hypoglycaemia:
The most frequently reported adverse reaction is hypoglycaemia. It may occur if the insulin dose is too
high in relation to the insulin requirement. Severe hypoglycaemia may lead to unconsciousness and/or
convulsions and may result in temporary or permanent impairment of brain function or even death.
The symptoms of hypoglycaemia usually occur suddenly. They may include cold sweats, cool pale
skin, fatigue, nervousness or tremor, anxiousness, unusual tiredness or weakness, confusion, difficulty
in concentration, drowsiness, excessive hunger, vision changes, headache, nausea and palpitation.
In clinical trials the frequency of hypoglycaemia varied with patient population, dose regimens and
level of glycaemic control. During clinical trials the overall rates of hypoglycaemia did not differ
between patients treated with insulin aspart compared to human insulin.
Anaphylactic reactions:
The occurrence of generalised hypersensitivity reactions (including generalised skin rash, itching,
sweating, gastrointestinal upset, angioneurotic oedema, difficulties in breathing, palpitation and
reduction in blood pressure ) is very rare but can potentially be life threatening.
Lipodystrophy:
Lipodystrophy is reported as uncommon. It may occur at the injection site; therefore it is
recommended to rotate injection sites within an area.
No clinical studies with NovoMix 50 have been carried out in children or adolescents under the age of
18 years. NovoMix 50 should only be used in this age group under careful medical supervision. See
section 4.2.












e. Other special populations
Based on post-marketing sources and clinical trials, the frequency, type and severity of adverse
reactions observed in the elderly patients and in patients with renal or hepatic impairment do not
indicate any differences to the broader experience in the general population.
A specific overdose for insulin cannot be defined, however, hypoglycaemia may develop over
sequential stages if too high doses relative to the patient’s requirement are administered:
Mild hypoglycaemic episodes can be treated by oral administration of glucose or sugary
products. It is therefore recommended that the diabetic patient always carries sugar-containing
products
Severe hypoglycaemic episodes, where the patient has become unconscious, can be treated with
glucagon (0.5 to 1 mg) given intramuscularly or subcutaneously, by a trained person, or with
glucose given intravenously by a healthcare professional. Glucose must be given intravenously,
if the patient does not respond to glucagon within 10 to 15 minutes. Upon regaining
consciousness, administration of oral carbohydrates is recommended for the patient in order to
prevent a relapse.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Drugs used in diabetes. Insulins and analogues for injection,
intermediate-acting combined with fast-acting. ATC code: A10AD05.
NovoMix 50 is a biphasic suspension of 50% soluble insulin aspart (rapid-acting human insulin
analogue) and 50% protamine-crystallised insulin aspart (intermediate-acting human insulin
analogue).
The blood glucose lowering effect of insulin aspart is due to the facilitated uptake of glucose
following binding of insulin to receptors on muscle and fat cells and to the simultaneous inhibition of
glucose output from the liver.
NovoMix 50 is a biphasic insulin, which contains 50% soluble insulin aspart. This has a rapid onset of
action, thus allowing it to be given closer to a meal (within zero to 10 minutes of the meal) when
compared to soluble human insulin. The crystalline phase (50%) consists of protamine-crystallised
insulin aspart, which has an activity profile that is similar to that of human NPH insulin.
When NovoMix 50 is injected subcutaneously, the onset of action will occur within 10 to 20 minutes
of injection. The maximum effect is exerted between 1 and 4 hours after injection. The duration of
action is 14 to 24 hours (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Activity Profile for NovoMix 50 in Healthy Caucasian Subjects.
Insulin aspart is equipotent to human insulin on a molar basis.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption, distribution and elimination
In insulin aspart substitution of amino acid proline with aspartic acid at position B28 reduces the
tendency to form hexamers as observed with soluble human insulin. The insulin aspart in the soluble
phase of NovoMix 50 comprises 50% of the total insulin; this is absorbed more rapidly from the
subcutaneous layer than the soluble insulin component of biphasic human insulin. The remaining 50%
is in crystalline form as protamine-crystallised insulin aspart; this has a prolonged absorption profile
similar to human NPH insulin.
In healthy volunteers a mean maximum serum concentration of 445 ± 135 pmol/l was reached about
60 minutes after a subcutaneous dose of 0.30 U/kg body weight. In type 2 patients with diabetes, the
maximum concentration was reached about 95 minutes after dosing.
The pharmacokinetics of NovoMix 50 has not been investigated in paediatrics, elderly patients or
patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety
pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity and toxicity to reproduction and development.
In
in vitro
tests, including binding to insulin and IGF-1 receptor sites and effects on cell growth,
insulin aspart behaved in a manner that closely resembled human insulin. Studies also demonstrate that
the dissociation of binding to the insulin receptor of insulin aspart is equivalent to human insulin.

PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Glycerol
Phenol
Metacresol
Zinc chloride
Disodium phosphate dihydrate
Sodium chloride
Protamine sulphate
Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment)
Sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment)
Water for injections
In absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal
products.
After first opening: A maximum of 4 weeks when stored below 30°C.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C). Keep away from the cooling element. Do not freeze.
Keep the cartridge in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
After first opening or carried as a spare: Do not refrigerate. Store below 30°C.
NovoMix 50 must be protected from excessive heat and light.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
3 ml suspension in cartridge (type 1 glass) with a plunger (bromobutyl) and a stopper
(bromobutyl/polyisoprene) in a carton. The cartridge contains a glass ball to facilitate resuspension.
Pack sizes of 1, 5 and 10 cartridges. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Needles and NovoMix 50 Penfill must not be shared. The cartridge must not be refilled.
After removing NovoMix 50 Penfill from the refrigerator, it is recommended to allow NovoMix 50
Penfill to reach room temperature before resuspending the insulin as instructed for first time use.
NovoMix 50 must not be used if the resuspended liquid does not appear uniformly white and cloudy.
The necessity of resuspending the NovoMix 50 suspension immediately before use is to be stressed to
the patient.
NovoMix 50 which has been frozen must not be used.
The patient should be advised to discard the needle after each injection.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd
Denmark
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/00/142/011
EU/1/00/142/012
EU/1/00/142/013
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 1 August 2000
Date of last renewal: 2 July 2010
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
NovoMix 70 Penfill 100 U/ml suspension for injection in cartridge
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
1 ml of the suspension contains 100 U soluble insulin aspart*/protamine-crystallised insulin aspart* in
the ratio 70/30 (equivalent to 3.5 mg). 1 cartridge contains 3 ml equivalent to 300 U.
*Insulin aspart is produced by recombinant DNA technology in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Suspension for injection in cartridge. Penfill.
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The potency of insulin analogues, including insulin aspart, is expressed in units (U), whereas the
potency of human insulin is expressed in international units (IU).
NovoMix 70 dosing is individual and determined in accordance with the needs of the patient. Blood
glucose monitoring and insulin dose adjustments are recommended to archive optimal glycaemic
control.
The individual insulin requirement is usually between 0.5 and 1.0 U/kg/day in adult patients and this
may be fully or partially supplied with NovoMix 70. The daily insulin requirement may be higher in
patients with insulin resistance (e.g. due to obesity), and lower in patients with residual endogenous
insulin production.
In patients with type 2 diabetes, NovoMix 70 can be given as monotherapy or in combination with
metformin, when the blood glucose is inadequately controlled with metformin alone.
Adjustment of dose may be necessary if patients undertake increased physical activity, change their
usual diet or during concomitant illness.
In patients with diabetes mellitus optimised metabolic control effectively delays the onset and slows
the progression of diabetic late complications. Optimised metabolic control, including glucose
monitoring, is therefore recommended.
As with all insulin medicinal products, in elderly patients (≥ 65 years old) and patients with hepatic or
renal impairment, glucose monitoring should be intensified and insulin aspart dose adjusted on an
individual basis.
Renal or hepatic impairment may reduce the patient’s insulin requirements.
No clinical studies with NovoMix 70 have been carried out in children or adolescents under the age of
18 years.
NovoMix 70 should only be used in this age group under careful medical supervision.
Transfer from other insulin medicinal products
Transfer to NovoMix 70 from other insulin preparations may require adjustment of dose and timing of
administration. As with all insulin medicinal products, close glucose monitoring is recommended
during the transfer and in the initial weeks thereafter (see section 4.4).
NovoMix 70 is for subcutaneous administration
only
. NovoMix 70 must not be administrated
intravenously, as it may result in severe hypoglycaemia. Intramuscular administration should be
avoided. NovoMix 70 is not to be used in insulin infusion pumps.
The rapid onset of action and early peak of activity of insulin aspart allows NovoMix 70 to be given
immediately before a meal. When necessary, NovoMix 70 can be given soon after a meal.
NovoMix 70 Penfill is designed to be used with Novo Nordisk insulin delivery systems and NovoFine
or NovoTwist needles. The patient should be advised not to use any counterfeit needles.
NovoMix 70 Penfill is accompanied by a package leaflet with detailed instructions for use to be
followed.
NovoMix 70 is administered subcutaneously by injection in the thigh or in the abdominal wall. If
convenient, the gluteal or deltoid region may be used. Injection sites should always be rotated within
the same region. The influence of different injection sites on the absorption of NovoMix 70 has not
been investigated. As with all insulin medicinal products, the duration of action will vary according to
the dose, injection site, blood flow, temperature and level of physical activity.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Inadequate dosing or discontinuation of treatment, especially in type 1 diabetes, may lead to
hyperglycaemia and diabetic ketoacidosis. Usually the first symptoms of hyperglycaemia develop
gradually over a period of hours or days. They include thirst, increased frequency of urination, nausea,
vomiting, drowsiness, flushed dry skin, dry mouth, loss of appetite as well as acetone odour of breath.
In type 1 diabetes, untreated hyperglycaemic events eventually lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, which is
potentially lethal.
Before travelling between different time zones the patient should seek the doctor’s advice since this
may mean that the patient has to take the insulin and meals at different times.
Omission of a meal or unplanned, strenuous physical exercise may lead to hypoglycaemia.
Hypoglycaemia may occur if the insulin dose is too high in relation to the insulin requirement (see
section 4.8 and 4.9).
Patients, whose blood glucose control is greatly improved, e.g. by intensified insulin therapy, may
experience a change in their usual warning symptoms of hypoglycaemia, and should be advised
accordingly. Usual warning symptoms may disappear in patients with longstanding diabetes.
Since NovoMix 70 should be administered in immediate relation to a meal the rapid onset of action
should be considered in patients with concomitant diseases or treatment where a delayed absorption of
food might be expected.
Concomitant illness, especially infections and feverish conditions, usually increases the patient’s
insulin requirements. Concomitant diseases in the kidney, liver or affecting the adrenal, pituitary or
thyroid gland can require changes in insulin dose.
When patients are transferred between different types of insulin medicinal products, the early warning
symptoms of hypoglycaemia may change or become less pronounced than those experienced with
their previous insulin.
Transfer from other insulin medicinal products
Transferring a patient to another type or brand of insulin should be done under strict medical
supervision. Changes in strength, brand (manufacturer), type, origin (animal, human, human insulin
analogue) and/or method of manufacture (recombinant DNA versus animal source insulin)
may result
in the need for a change in dose. Patients transferred to NovoMix 70 from another type of insulin may
require an increased number of daily injections or a change in dose from that used with their usual
insulins. If an adjustment is needed, it may occur with the first dose or during the first few weeks or
months.
As with any insulin therapy, injection site reactions may occur and include pain, redness, hives,
inflammation, swelling and itching. Continuous rotation of the injection site within a given area may
help to reduce or prevent these reactions. Reactions usually resolve in a few days to a few weeks. On
rare occasions, injection site reactions may require discontinuation of NovoMix 70.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
A number of medicinal products are known to interact with the glucose metabolism.
The following substances may reduce the patient’s insulin requirements:
Oral antidiabetic medicinal products, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI), beta-blockers,
angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, salicylates, anabolic steroids and sulphonamides.
The following substances may increase the patient’s insulin requirements:
Oral contraceptives, thiazides, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, sympathomimetics, growth
hormone and danazol.
Beta-blockers may mask the symptoms of hypoglycaemia.
Octreotide/lanreotide may both increase or decrease insulin requirement.
Alcohol may intensify or reduce the hypoglycaemic effect of insulin.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
There is limited clinical experience with NovoMix 70 in pregnancy.
Animal reproduction studies have not revealed any differences between insulin aspart and human
insulin regarding embryotoxicity or teratogenicity.
In general, intensified blood glucose control and monitoring of pregnant women with diabetes are
recommended throughout pregnancy and when contemplating pregnancy. Insulin requirements usually
fall in the first trimester and increase subsequently during the second and third trimesters. After
delivery, insulin requirements return rapidly to pre-pregnancy levels.
There are no restrictions on treatment with NovoMix 70 during breast-feeding. Insulin treatment of the
nursing mother presents no risk to the baby. However, the NovoMix 70 dose may need to be adjusted.
Animal reproduction studies have not revealed any differences between insulin aspart and human
insulin regarding fertility.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The patient’s ability to concentrate and react may be impaired as a result of hypoglycaemia. This may
constitute a risk in situations where these abilities are of special importance (e.g. driving a car or using
machines).
Patients should be advised to take precautions to avoid hypoglycaemia while driving. This is
particularly important in those who have reduced or absent awareness of the warning signs of
hypoglycaemia or have frequent episodes of hypoglycaemia. The advisability of driving should be
considered in these circumstances.
a. Summary of the safety profile
Adverse reactions observed in patients using NovoMix are mainly dose-dependent and due to the
pharmacologic effect of insulin.
The most frequently reported adverse reaction during treatment is hypoglycaemia. The frequencies of
hypoglycaemia vary with patient population, dose regimens and level of glycaemic control, please see
section c below.
At the beginning of the insulin treatment, refraction anomalies, oedema and local hypersensitivity
reactions (pain, redness, hives, inflammation, swelling and itching at the injection site) may occur;
these reactions are usually of transitory nature. Fast improvement in blood glucose control may be
associated with acute painful neuropathy, which is usually reversible. Intensification of insulin therapy
with abrupt improvement in glycaemic control may be associated with temporary worsening of
diabetic retinopathy, while long-term improved glycaemic control decreases the risk of progression of
diabetic retinopathy.
b. Tabulated list of adverse reactions
Adverse reactions listed below are based on clinical trial data and classified according to MedDRA
frequency and System Organ Class. Frequency categories are defined according to the following
convention: Very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100);
rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000); very rare (< 1/10,000); not known (cannot be estimated from the
available data).
Uncommon - Urticaria, rash, eruptions
Very rare - Anaphylactic reactions*
Metabolism and nutrition
disorders
Very common – Hypoglycaemia*
Rare - Peripheral neuropathy
Uncommon - Refraction disorders
Skin and subcutaneous tissue
disorders
Uncommon - Diabetic retinopathy
Uncommon – Lipodystrophy*
Uncommon - Local hypersensitivity
General disorders and
administration site conditions
c. Description of selected adverse reactions
Hypoglycaemia:
The most frequently reported adverse reaction is hypoglycaemia. It may occur if the insulin dose is too
high in relation to the insulin requirement. Severe hypoglycaemia may lead to unconsciousness and/or
convulsions and may result in temporary or permanent impairment of brain function or even death.
The symptoms of hypoglycaemia usually occur suddenly. They may include cold sweats, cool pale
skin, fatigue, nervousness or tremor, anxiousness, unusual tiredness or weakness, confusion, difficulty
in concentration, drowsiness, excessive hunger, vision changes, headache, nausea and palpitation.
In clinical trials the frequency of hypoglycaemia varied with patient population, dose regimens and
level of glycaemic control. During clinical trials the overall rates of hypoglycaemia did not differ
between patients treated with insulin aspart compared to human insulin.
Anaphylactic reactions:
The occurrence of generalised hypersensitivity reactions (including generalised skin rash, itching,
sweating, gastrointestinal upset, angioneurotic oedema, difficulties in breathing, palpitation and
reduction in blood pressure ) is very rare but can potentially be life threatening.
Lipodystrophy:
Lipodystrophy is reported as uncommon. It may occur at the injection site; therefore it is
recommended to rotate injection sites within an area.
No clinical studies with NovoMix 70 have been carried out in children or adolescents under the age of
18 years. NovoMix 70 should only be used in this age group under careful medical supervision. See
section 4.2.
e. Other special populations












Based on post-marketing sources and clinical trials, the frequency, type and severity of adverse
reactions observed in the elderly patients and in patients with renal or hepatic impairment do not
indicate any differences to the broader experience in the general population.
A specific overdose for insulin cannot be defined, however, hypoglycaemia may develop over
sequential stages if too high doses relative to the patient’s requirement are administered:
Mild hypoglycaemic episodes can be treated by oral administration of glucose or sugary
products. It is therefore recommended that the diabetic patient always carries sugar-containing
products
Severe hypoglycaemic episodes, where the patient has become unconscious, can be treated with
glucagon (0.5 to 1 mg) given intramuscularly or subcutaneously, by a trained person, or with
glucose given intravenously by a healthcare professional. Glucose must be given intravenously,
if the patient does not respond to glucagon within 10 to 15 minutes. Upon regaining
consciousness, administration of oral carbohydrates is recommended for the patient in order to
prevent a relapse.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Drugs used in diabetes. Insulins and analogues for injection,
intermediate-acting combined with fast-acting. ATC code: A10AD05.
NovoMix 70 is a biphasic suspension of 70% soluble insulin aspart (rapid-acting human insulin
analogue) and 30% protamine-crystallised insulin aspart (intermediate-acting human insulin
analogue).
The blood glucose lowering effect of insulin aspart is due to the facilitated uptake of glucose
following binding of insulin to receptors on muscle and fat cells and to the simultaneous inhibition of
glucose output from the liver.
NovoMix 70 is a biphasic insulin, which contains 70% soluble insulin aspart. This has a rapid onset of
action, thus allowing it to be given closer to a meal (within zero to 10 minutes of the meal) when
compared to soluble human insulin. The crystalline phase (30%) consists of protamine-crystallised
insulin aspart, which has an activity profile that is similar to that of human NPH insulin.
When NovoMix 70 is injected subcutaneously, the onset of action will occur within 10 to 20 minutes
of injection. The maximum effect is exerted between 1 and 4 hours after injection. The duration of
action is 14 to 24 hours (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Activity Profile for NovoMix 70 in Healthy Caucasian Subjects.
Insulin aspart is equipotent to human insulin on a molar basis.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption, distribution and elimination
In insulin aspart substitution of amino acid proline with aspartic acid at position B28 reduces the
tendency to form hexamers as observed with soluble human insulin. The insulin aspart in the soluble
phase of NovoMix 70 comprises 70% of the total insulin; this is absorbed more rapidly from the
subcutaneous layer than the soluble insulin component of biphasic human insulin. The remaining 30%
is in crystalline form as protamine-crystallised insulin aspart; this has a prolonged absorption profile
similar to human NPH insulin.
In healthy volunteers a mean maximum serum concentration of 645 ± 185 pmol/l was reached about
60 minutes after a subcutaneous dose of 0.30 U/kg body weight. In type 2 patients with diabetes, the
maximum concentration was reached about 75 minutes after dosing. In type 1 patients with diabetes a
mean maximum serum concentration of 721 ± 184 pmol/l was reached about 60 minutes after a
subcutaneous dose of 0.30 U/kg body weight.
The pharmacokinetics of NovoMix 70 has not been investigated in paediatrics, elderly patients or
patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety
pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity and toxicity to reproduction and development.
In
in vitro
tests, including binding to insulin and IGF-1 receptor sites and effects on cell growth,
insulin aspart behaved in a manner that closely resembled human insulin. Studies also demonstrate that
the dissociation of binding to the insulin receptor of insulin aspart is equivalent to human insulin.

PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Glycerol
Phenol
Metacresol
Zinc chloride
Disodium phosphate dihydrate
Sodium chloride
Protamine sulphate
Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment)
Sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment)
Water for injections
In absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal
products.
After first opening: A maximum of 4 weeks when stored below 30°C.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C). Keep away from the cooling element. Do not freeze.
Keep the cartridge in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
After first opening or carried as a spare: Do not refrigerate. Store below 30°C.
NovoMix 70 must be protected from excessive heat and light.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
3 ml suspension in cartridge (type 1 glass) with a plunger (bromobutyl) and a stopper
(bromobutyl/polyisoprene) in a carton. The cartridge contains a glass ball to facilitate resuspension.
Pack sizes of 1, 5 and 10 cartridges. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Needles and NovoMix 70 Penfill must not be shared. The cartridge must not be refilled.
After removing NovoMix 70 Penfill from the refrigerator, it is recommended to allow NovoMix 70
Penfill to reach room temperature before resuspending the insulin as instructed for first time use.
NovoMix 70 must not be used if the resuspended liquid does not appear uniformly white and cloudy.
The necessity of resuspending the NovoMix 70 suspension immediately before use is to be stressed to
the patient.
NovoMix 70 which has been frozen must not be used.
The patient should be advised to discard the needle after each injection.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd
Denmark
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/00/142/017
EU/1/00/142/018
EU/1/00/142/019
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 1 August 2000
Date of last renewal: 2 July 2010
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines
The active substance is insulin aspart. NovoMix 70 is a mixture consisting of 70% soluble
insulin aspart and 30% insulin aspart crystallised with protamine. 1 ml contains 100 U of insulin
aspart. Each pre-filled pen contains 300 U of insulin aspart in 3 ml suspension for injection
The other ingredients
are: glycerol, phenol, metacresol, zinc chloride, disodium phosphate
dihydrate, sodium chloride, protamine sulphate, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide and water
for injections.
What NovoMix 70 looks like and contents of the pack
NovoMix 70 comes as a white suspension in a pre-filled pen. The cartridge contains a glass ball to
facilitate resuspension. After resuspension the liquid shall appear uniformly white and cloudy.
Pack sizes of 1, 5 and 10 pre-filled pens of 3 ml. Not all packs may be marketed.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Novo Nordisk A/S
Novo Allé
DK-2880 Bagsværd, Denmark
Now turn over for information on how to use your FlexPen.
This leaflet was last approved in
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines
NOVOMIX 70 suspension for injection in a pre-filled pen. FlexPen. INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Please read the following instructions carefully before using your NovoMix 70 FlexPen.
Your FlexPen is a unique dial-a-dose insulin pen. You can select doses from 1 to 60 units in
increments of 1 unit. FlexPen is designed to be used with NovoFine or NovoTwist disposable needles
up to a length of 8 mm. Be sure you are not using any counterfeit needles. Ask your pharmacist. As a
precautionary measure, always carry a spare insulin delivery device in case your FlexPen is lost or
damaged.
The colour of the pen in the illustrations differs from your FlexPen.
Your FlexPen is designed to work accurately and safely. It must be handled with care. If it is dropped
or crushed, there is a risk of damage and leakage of insulin.
You can clean the exterior of your FlexPen by wiping it with a medicinal swab. Do not soak it, wash
or lubricate it as it may damage the pen.
Do not refill your FlexPen.
Preparing your NovoMix 70 FlexPen
Check the label to make sure that your FlexPen contains the correct type of insulin. Before your
first injection with a new FlexPen you must resuspend the insulin:
A
Let the insulin reach room temperature before you use it.

This makes it easier to resuspend.
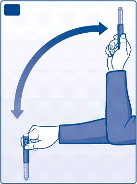
B
Roll the pen between your palms ten times – it is important that the pen is kept horizontal.
C
Then move the pen up and down ten times between the two positions as shown, so the glass ball
moves from one end of the cartridge to the other.
Repeat rolling and moving the pen until the liquid appears uniformly white and cloudy.
For every following injection move the pen up and down between the two positions at least ten times
until the liquid appears uniformly white and cloudy. If the moving procedure alone is not enough to
give a uniformly white and cloudy liquid, repeat the rolling and moving procedures (see B and C) until
the liquid does appear uniformly white and cloudy
After you have resuspended the insulin, complete all the following steps of injection without delay.
Always check there are at least 12 units of insulin left in the cartridge to allow resuspension. If
there are less than 12 units left, use a new FlexPen.
D
Remove the protective tab from a new disposable needle.
Screw the needle straight and tightly onto your FlexPen.
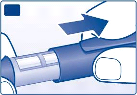

E
Pull off the big outer needle cap and keep it for later.
F
Pull off the inner needle cap and dispose of it.
Always use a new needle for each injection to prevent contamination.
Be careful not to bend or damage the needle before use.
To reduce the risk of unexpected needle sticks, never put the inner needle cap back on when you
have removed it from the needle.
Checking the insulin flow
Prior to each injection small amounts of air may collect in the cartridge during normal use. To
avoid injection of air and ensure proper dosing:
G
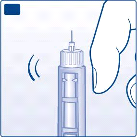
Turn the dose selector to select 2 units.
H
Hold your FlexPen with the needle pointing upwards and tap the cartridge gently with your finger a
few times to make any air bubbles collect at the top of the cartridge.




I
Keeping the needle upwards, press the push-button all the way in. The dose selector returns to 0.
A drop of insulin should appear at the needle tip. If not, change the needle and repeat the procedure no
more than six times.
If a drop of insulin still does not appear, the pen is defective, and you must use a new one.
Check that the dose selector is set at 0.
J
Turn the dose selector to select the number of units you need to inject.
The dose can be corrected either up or down by turning the dose selector in either direction until the
correct dose lines up with the pointer. When turning the dose selector be careful not to push the push-
button as insulin will come out.
You cannot select a dose larger than the number of units left in the cartridge.


Do not use the residual scale to measure your dose of insulin.
Insert the needle into your skin. Use the injection technique shown by your doctor or nurse.
K
Inject the dose by pressing the push-button all the way in until 0 lines up with the pointer. Be careful
only to push the push-button when injecting.
Turning the dose selector will not inject insulin.
L
Keep the push-button fully depressed after the injection until the needle has been withdrawn from the
skin.
The needle must remain under the skin for at least six seconds. This will ensure that the full dose has
been injected.
M
Lead the needle into the big outer needle cap without touching the big outer needle cap. When the
needle is covered, carefully push the big outer needle cap completely on and then unscrew the needle.
Dispose of it carefully and put the cap back on.
Always remove the needle after each injection and store your FlexPen without the needle
attached. Otherwise, the liquid may leak out which can cause inaccurate dosing.
Caregivers should be most careful when handling used needles to avoid needle sticks.
Dispose of the used FlexPen carefully without the needle attached.
Needles and NovoMix 70 FlexPen must not be shared.



Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/novomix.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|






































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































