Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
OSSEOR 2 g granules for oral suspension
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each sachet contains 2 g of strontium ranelate.
Excipient: Each sachet also contains 20 mg of aspartame (E951).
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Granules for oral suspension
Yellow granules
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women to reduce the risk of vertebral and hip fractures
(see section 5.1).
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Posology
The recommended dose is one 2 g sachet once daily by oral administration.
Due to the nature of the treated disease, strontium ranelate is intended for long-term use.
The absorption of strontium ranelate is reduced by food, milk and derivative products and therefore,
OSSEOR should be administered in-between meals. Given the slow absorption, OSSEOR should be
taken at bedtime, preferably at least two hours after eating (see sections 4.5 and 5.2).
Patients treated with strontium ranelate should receive vitamin D and calcium supplements if dietary
intake is inadequate.
Elderly population
The efficacy and safety of strontium ranelate have been established in a broad age range (up to
100 years at inclusion) of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. No dose adjustment is required
in relation to age.
Renal impairment
Strontium ranelate is not recommended for patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance
below 30 ml/min) (see sections 4.4 and 5.2). No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild-to-
moderate renal impairment (30-70 ml/min creatinine clearance) (see section 5.2).
Hepatic impairment
As strontium ranelate is not metabolised, no dose adjustment is required in patients with hepatic
impairment.
Paediatric population
The safety and efficacy of OSSEOR in children aged below 18 years have not been established. No
data are available.
Method of administration
For oral use.
The granules in the sachets must be taken as a suspension in a glass containing a minimum of 30 ml
(approximately one third of a standard glass) of water.
Although in-use studies have demonstrated that strontium ranelate is stable in suspension for 24 hours
after preparation, the suspension should be drunk immediately after being prepared.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Use in patients with renal impairment
In the absence of bone safety data in patients with severe renal impairment treated with strontium
ranelate, OSSEOR is not recommended in patients with a creatinine clearance below 30 ml/min (see
section 5.2). In accordance with good medical practice, periodic assessment of renal function is
recommended in patients with chronic renal impairment. Continuation of treatment with OSSEOR in
patients developing severe renal impairment should be considered on an individual basis.
Venous thromboembolism
In phase III placebo-controlled studies, strontium ranelate treatment was associated with an increase in
the annual incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE), including pulmonary embolism (see section
4.8). The cause of this finding is unknown. OSSEOR should be used with caution in patients at
increased risk of VTE, including patients with a past history of VTE. When treating patients at risk, or
developing risk of VTE, particular attention should be given to possible signs and symptoms of VTE
and adequate preventive measures taken.
Skin reactions
Cases of severe hypersensitivity syndromes, including, in particular, drug rash with eosinophilia and
systemic symptoms (DRESS), sometimes fatal, have been reported with the use of OSSEOR (see
section 4.8). The DRESS syndrome is characterised by rash, fever, eosinophilia and systemic
involvement (e.g. adenopathy, hepatitis, interstitial nephropathy, interstitial lung disease). Time to
onset was usually around 3-6 weeks and the outcome in most cases favourable upon discontinuation of
OSSEOR and after initiation of corticosteroid therapy. Recovery could be slow and recurrences of the
syndrome have been reported in some cases after discontinuation of corticosteroid therapy.
Patients should be informed to stop OSSEOR immediately and permanently when a rash occurs and to
seek medical advice. Patients who have stopped treatment due to hypersensitivity reactions or other
serious allergic reactions should not re-start therapy with OSSEOR.
Interaction with laboratory test
Strontium interferes with colorimetric methods for the determination of blood and urinary calcium
concentrations. Therefore, in medical practice, inductively coupled plasma atomic emission
spectrometry or atomic absorption spectrometry methods should be used to ensure an accurate
assessment of blood and urinary calcium concentrations.
Excipient
OSSEOR contains a source of phenylalanine, which may be harmful for people with phenylketonuria.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Food, milk and derivative products, and medicinal products containing calcium may reduce the
bioavailability of strontium ranelate by approximately 60-70%. Therefore, administration of OSSEOR
and such products should be separated by at least two hours (see section 5.2).
As divalent cations can form complexes with oral tetracycline and quinolone antibiotics at the gastro-
intestinal level and thereby reduce their absorption, simultaneous administration of strontium ranelate
with these medicinal products is not recommended. As a precautionary measure, OSSEOR treatment
should be suspended during treatment with oral tetracycline or quinolone antibiotics.
An
in vivo
clinical interaction study showed that the administration of aluminium and magnesium
hydroxides either two hours before or together with strontium ranelate caused a slight decrease in the
absorption of strontium ranelate (20-25% AUC decrease), while absorption was almost unaffected
when the antacid was given two hours after strontium ranelate. It is therefore preferable to take
antacids at least two hours after OSSEOR. However, when this dosing regimen is impractical due to
the recommended administration of OSSEOR at bedtime, concomitant intake remains acceptable.
No interaction was observed with oral supplementation of vitamin D.
No evidence of clinical interactions or relevant increase of blood strontium levels with medicinal
products expected to be commonly prescribed concomitantly with OSSEOR in the target population
were found during clinical trials. These included: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents (including
acetylsalicylic acid), anilides (such as paracetamol), H
2
blockers and proton pump inhibitors, diuretics,
digoxin and cardiac glycosides, organic nitrates and other vasodilators for cardiac diseases, calcium
channel blockers, beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II antagonists, selective beta-2
adrenoceptor agonists, oral anticoagulants, platelet aggregation inhibitors, statins, fibrates and
benzodiazepine derivatives.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
OSSEOR is only intended for use in postmenopausal women.
There are no data from the use of strontium ranelate in pregnant women.
At high doses, animal studies have shown reversible bone effects in the offspring of rats and rabbits
treated during pregnancy (see section 5.3). If OSSEOR is used inadvertently during pregnancy,
treatment must be stopped.
Breast-feeding
Physico-chemical data suggest excretion of Strontium ranelate in human milk OSSEOR should not be
used during breast-feeding
Fertility
No effects were observed on males and females fertility in animal studies.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Strontium ranelate has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
OSSEOR has been studied in clinical trials involving nearly 8,000 participants. Long-term safety has
been evaluated in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis treated for up to 60 months with
strontium ranelate 2 g/day (n=3,352) or placebo (n=3,317) in phase III studies. Mean age was 75 years
at inclusion and 23% of the patients enrolled were 80 to 100 years of age.
There were no differences in the nature of adverse reactions between treatment groups regardless of
whether patients were aged below or above 80 at inclusion.
Overall incidence rates for adverse reactions with strontium ranelate did not differ from placebo and
adverse reactions were usually mild and transient. The most common adverse reactions consisted of
nausea and diarrhoea, which were generally reported at the beginning of treatment with no noticeable
difference between groups afterwards. Discontinuation of therapy was mainly due to nausea (1.3% and
2.2% in the placebo and strontium ranelate groups respectively).
In phase III studies, the annual incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) observed over 5 years
was approximately 0.7%, with a relative risk of 1.4 (95% CI = [1.0 ; 2.0]) in strontium ranelate treated
patients as compared to placebo (see section 4.4).
The following adverse reactions have been reported during clinical studies and/or post marketing use
with Strontium ranelate.Adverse reactions, defined as adverse events considered at least possibly
attributable to strontium ranelate treatment in phase III studies are listed below using the following
convention (frequencies
versus
placebo): very common (>1/10); common (>1/100, <1/10); uncommon
(>1/1,000, <1/100); rare (>1/10,000, <1/1,000); very rare (<1/10,000) ; not known (cannot be
estimated from the available data).
Percentage of Patients
Experiencing the adverse
reaction
Treatment
Frequency category
Adverse Reaction
Strontium
ranelate
(n=3352)
Disturbances in consciousness
Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Bronchial hyperreactivity
Gastrointestinal disorders
Oral mucosal irritation (stomatitis and/or mouth ulceration)
Serum transaminase increased (in association with
hypersensitivity skin reactions)















Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Hypersensitivity skin reactions (rash, pruritus, urticaria,
angioedema)
Severe hypersensitivity syndromes including Stevens-Johnson
syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis and DRESS (see Section
4.4)
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Musculoskeletal pain (muscle spasm, myalgia, bone pain,
arthralgia and pain in extremity)
General disorders and administration site conditions
Pyrexia (in association with hypersensitivity skin reactions)
Blood and Lymphatic disorders
Eosinophilia (in association with hypersensitivity skin reactions)
Lymphadenopathy (in association with hypersensitivity skin
reactions)
Blood Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) increased
b
a
Post-marketing experience
b
Musculo-skeletal fraction > 3 times the upper limit of the normal range. In most cases, these values
spontaneously reverted to normal without change in treatment.
Good tolerance was shown in a clinical study investigating the repeated administration of 4 g
strontium ranelate per day over 25 days in healthy postmenopausal women. Single administration of
doses up to 11 g in healthy young male volunteers did not cause any particular symptoms.
Following episodes of overdoses during clinical trials (up to 4 g/day for a maximal duration of
147 days), no clinically relevant events were observed.
Administration of milk or antacids may be helpful to reduce the absorption of the active substance. In
the event of substantial overdose, vomiting may be considered to remove unabsorbed active substance.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Drugs for the treatment of bone diseases - Other drugs affecting bone
structure and mineralisation, ATC code: M05BX03
Mechanism of action
In vitro
, strontium ranelate:
- increases bone formation in bone tissue culture as well as osteoblast precursor replication and
collagen synthesis in bone cell culture;
- reduces bone resorption by decreasing osteoclast differentiation and resorbing activity.
This results in a rebalance of bone turnover in favour of bone formation.









The activity of strontium ranelate was studied in various non-clinical models. In particular, in intact
rats, strontium ranelate increases trabecular bone mass, trabeculae number and thickness; this results in
an improvement of bone strength.
In bone tissue of treated animals and humans, strontium is mainly adsorbed onto the crystal surface
and only slightly substitutes for calcium in the apatite crystal of newly formed bone. Strontium
ranelate does not modify the bone crystal characteristics. In iliac crest bone biopsies obtained after up
to 60 months of treatment with strontium ranelate 2 g/day in phase III trials, no deleterious effects on
bone quality or mineralisation were observed.
The combined effects of strontium distribution in bone (see section 5.2) and increased X-ray
absorption of strontium as compared to calcium, leads to an amplification of bone mineral density
(BMD) measurement by dual-photon X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). Available data indicate that these
factors account for approximately 50% of the measured change in BMD over 3 years of treatment with
OSSEOR 2 g/day. This should be taken into account when interpreting BMD changes during
treatment with OSSEOR. In phase III studies, which demonstrated the anti-fracture efficacy of
OSSEOR treatment, measured mean BMD increased from baseline with OSSEOR by approximately
4% per year at the lumbar spine and 2% per year at the femoral neck, reaching 13% to 15% and 5% to
6% respectively after 3 years, depending on the study.
In phase III studies, as compared to placebo, biochemical markers of bone formation (bone-specific
alkaline phosphatase and C-terminal propeptide of type I procollagen) increased and those of bone
resorption (serum C-telopeptide and urinary N-telopeptide cross links) decreased from the third month
of treatment up to 3 years.
Secondary to the pharmacological effects of strontium ranelate, slight decreases in calcium and
parathyroid hormone (PTH) serum concentrations, increases in blood phosphorus concentrations and
in total alkaline phosphatase activity were observed, with no observed clinical consequences.
Clinical efficacy
Osteoporosis is defined as BMD of the spine or hip 2.5 SD or more below the mean value of a normal
young population. A number of risk factors are associated with postmenopausal osteoporosis including
low bone mass, low bone mineral density, early menopause, a history of smoking and a family history
of osteoporosis. The clinical consequence of osteoporosis is fractures. The risk of fractures is
increased with the number of risk factors.
Treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis:
The anti-fracture studies program of OSSEOR was made up of two placebo-controlled phase III
studies: SOTI study and TROPOS study. SOTI involved 1,649 postmenopausal women with
established osteoporosis (low lumbar BMD and prevalent vertebral fracture) and a mean age of
70 years. TROPOS involved 5,091 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis (low femoral neck BMD
and prevalent fracture in more than half of them) and a mean age of 77 years. Together, SOTI and
TROPOS enrolled 1,556 patients over 80 years at inclusion (23.1% of the study population). In
addition to their treatment (2 g/day strontium ranelate or placebo), the patients received adapted
calcium and vitamin D supplements throughout both studies.
OSSEOR reduced the relative risk of new vertebral fracture by 41% over 3 years in the SOTI study
(table 1). The effect was significant from the first year. Similar benefits were demonstrated in women
with multiple fractures at baseline. With respect to clinical vertebral fractures (defined as fractures
associated with back pain and/or a body height loss of at least 1 cm), the relative risk was reduced by
38%. OSSEOR also decreased the number of patients with a body height loss of at least 1 cm as
compared to placebo. Quality of life assessment on the QUALIOST specific scale as well as the
General Health perception score of the SF-36 general scale indicated benefit of OSSEOR, compared
with placebo.
Efficacy of OSSEOR to reduce the risk of new vertebral fracture was confirmed in the TROPOS
study, including for osteoporotic patients without fragility fracture at baseline.
Table 1
: Incidence of patients with vertebral fracture and relative risk reduction
Relative Risk Reduction vs.
placebo (95%CI), p value
New vertebral fracture
over 3 years
New vertebral fracture
over the 1
st
year
New clinical vertebral
fracture over 3 years
New vertebral fracture
over 3 years
In patients over 80 years of age at inclusion, a pooled analysis of SOTI and TROPOS studies showed
that OSSEOR reduced the relative risk of experiencing new vertebral fractures by 32% over 3 years
(incidence of 19.1% with strontium ranelate vs. 26.5% with placebo).
In an
a-posteriori
analysis of patients from the pooled SOTI and TROPOS studies with baseline
lumbar spine and / or femoral neck
BMD in the osteopenic range and without prevalent fracture but
with at least one additional risk factor for fracture (N=176), OSSEOR reduced the risk of a first
vertebral fracture by 72% over 3 years (incidence of vertebral fracture
3.6% with strontium ranelate
vs. 12.0% with placebo).
An
a-posteriori
analysis was performed on a subgroup of patients from the TROPOS study of
particular medical interest and at high-risk of fracture [defined by a femoral neck BMD T-score ≤ -
3 SD (manufacturer’s range corresponding to -2.4 SD using NHANES III) and an age ≥ 74 years
(n=1,977, i.e. 40% of the TROPOS study population)]. In this group, over 3 years of treatment,
OSSEOR reduced the risk of hip fracture by 36% relative to the placebo group (table 2).
Table 2
: Incidence of patients with hip fracture and relative risk reduction in patients with BMD ≤ -2.4 SD
(NHANES III) and age ≥ 74 years
Relative Risk Reduction vs.
placebo (95%CI), p value
Hip fracture over 3 years
Paediatric population
The European Medicines Agency has waived the obligation to submit the results of studies with
OSSEOR in all subsets of the paediatric population in osteoporosis (see section 4.2 for information on
paediatric use).
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Strontium ranelate is made up of 2 atoms of stable strontium and 1 molecule of ranelic acid, the
organic part permitting the best compromise in terms of molecular weight, pharmacokinetics and
acceptability of the medicinal product. The pharmacokinetics of strontium and ranelic acid have been
assessed in healthy young men and healthy postmenopausal women, as well as during long-term
exposure in postmenopausal osteoporotic women including elderly women.
Due to its high polarity, the absorption, distribution and binding to plasma proteins of ranelic acid are
low. There is no accumulation of ranelic acid and no evidence of metabolism in animals and humans.
Absorbed ranelic acid is rapidly eliminated unchanged via the kidneys.






Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of strontium is about 25% (range 19-27%) after an oral dose of 2 g
strontium ranelate. Maximum plasma concentrations are reached 3-5 hours after a single dose of 2 g.
Steady state is reached after 2 weeks of treatment. Intake of strontium ranelate with calcium or food
reduces the bioavailability of strontium by approximately 60-70%, compared with administration
3 hours after a meal. Due to the relatively slow absorption of strontium, food and calcium intake
should be avoided both before and after administration of OSSEOR. Oral supplementation with
vitamin D has no effect on strontium exposure.
Distribution
Strontium has a volume of distribution of about 1 l/kg. The binding of strontium to human plasma
proteins is low (25%) and strontium has a high affinity for bone tissue. Measurement of strontium
concentration in iliac crest bone biopsies from patients treated for up to 60 months with strontium
ranelate 2 g/day indicate that bone strontium concentrations may reach a plateau after about 3 years of
treatment. There are no data in patients to demonstrate elimination kinetics of strontium from bone
off-therapy.
Biotransformation
As a divalent cation, strontium is not metabolised. Strontium ranelate does not inhibit cytochrome
P450 enzymes.
Elimination
The elimination of strontium is time and dose independent. The effective half-life of strontium is about
60 hours. Strontium excretion occurs via the kidneys and the gastrointestinal tract. Its plasma
clearance is about 12 ml/min (CV 22%) and its renal clearance about 7 ml/min (CV 28%).
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
Elderly
Population pharmacokinetic data showed no relationship between age and apparent clearance of
strontium in the target population.
Patients with renal impairment
In patients with mild-to-moderate renal impairment (30-70 ml/min creatinine clearance), strontium
clearance decreases as creatinine clearance decreases (approximately 30% decrease over the creatinine
clearance range 30 to 70 ml/min) and thereby induces an increase in strontium plasma levels. In phase
III studies, 85% of the patients had a creatinine clearance between 30 and 70 ml/min and 6% below
30 ml/min at inclusion, and the mean creatinine clearance was about 50 ml/min. No dosage adjustment
is therefore required in patients with mild-to-moderate renal impairment.
There is no pharmacokinetic data in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance below
30 ml/min).
Patients with hepatic impairment
There is no pharmacokinetic data in patients with hepatic impairment. Due to the pharmacokinetic
properties of strontium, no effect is expected.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data revealed no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety
pharmacology, genotoxicity and carcinogenic potential.
Chronic oral administration of strontium ranelate at high doses in rodents induced bone and tooth
abnormalities, mainly consisting of spontaneous fractures and delayed mineralisation. These effects
were reported at bone strontium levels 2-3 times higher than long-term clinical bone strontium levels
and were reversible after cessation of treatment.
Developmental toxicity studies in rats and rabbits resulted in bone and tooth abnormalities (e.g. bent
long bones and wavy ribs) in the offspring. In rats, these effects were reversible 8 weeks after
cessation of treatment.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Aspartame (E951)
Maltodextrin
Mannitol (E421)
Once reconstituted in water, the suspension is stable for 24 hours. However, it is recommended
to drink the suspension immediately after preparation (see section 4.2)
6.4 Special precautions for storage
This medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
Paper/polyethylene/aluminium/polyethylene sachets.
Pack sizes
Boxes containing 7, 14, 28, 56, 84 or 100 sachets.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
LES LABORATOIRES SERVIER
22, rue Garnier
92200 Neuilly-sur-Seine
France
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/04/287/001
EU/1/04/287/002
EU/1/04/287/003
EU/1/04/287/004
EU/1/04/287/005
EU/1/04/287/006
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 21/09/2004
Date of renewal: 21/09/2009
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
MM/YYYY
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the European Medicines
A. MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH RELEASE
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
Les Laboratoires Servier Industrie
905, route de Saran
45520 Gidy
France
CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
•
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
•
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND
EFFECTIVE USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Pharmacovigilance system:
The MAH must ensure that the system of Pharmacovigilance, as described in the version n°2
presented in Module 1.8.1. of the Marketing Authorisation Application, is in place and functioning
before and whilst the product is on the market.
Risk Management Plan (RMP)
The MAH commits to performing the studies and additional pharmacovigilance activities detailed in
the Pharmacovigilance Plan, as agreed in version n°2 of the Risk Management Plan (RMP) presented
in Module 1.8.2. of the Marketing Authorisation Application and any subsequent updates of the RMP
agreed by the CHMP.
As per the CHMP Guideline on Risk Management Systems for medicinal products for human use, the
updated RMP should be submitted at the same time as the following Periodic Safety Update Report
(PSUR).
In addition, an updated RMP should be submitted :
- When new information is received that may impact on the current Safety Specification,
Pharmacovigilance Plan or risk minimisation activities,
- Within 60 days of an important (pharmacovigilance or risk minimisation) milestone being reached,
- At the request of the European Medicines Agency.
PSURs
The MAH will continue to submit 6-monthly PSURs, unless otherwise specified by the Committee for
Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP).
ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
1.
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
OSSEOR 2 g granules for oral suspension
Strontium ranelate
2.
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each sachet contains 2 g strontium ranelate.
Also contains aspartame (E 951).
4.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Granules for oral suspension.
7 sachets
5.
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
For oral use
Read the package leaflet before use

















6.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
7.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
9.
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
10.
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11.
NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Les Laboratoires Servier
22, rue Garnier
92200 Neuilly-sur-Seine
France
12.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14.
GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE

























PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
1.
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
OSSEOR 2 g granules for oral suspension
Strontium ranelate
2.
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each sachet contains 2 g strontium ranelate.
Also contains aspartame (E 951).
4.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Granules for oral suspension.
14 sachets
5.
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
For oral use
Read the package leaflet before use















6.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
7.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
9.
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
10.
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11.
NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Les Laboratoires Servier
22, rue Garnier
92200 Neuilly-sur-Seine
France
12.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14.
GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE

























PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
1.
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
OSSEOR 2 g granules for oral suspension
Strontium ranelate
2.
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each sachet contains 2 g strontium ranelate.
Also contains aspartame (E 951).
4.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Granules for oral suspension.
28 sachets
5.
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
For oral use
Read the package leaflet before use















6.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
7.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
9.
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
10.
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11.
NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Les Laboratoires Servier
22, rue Garnier
92200 Neuilly-sur-Seine
France
12.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14.
GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE

























PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING
1.
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
OSSEOR 2 g granules for oral suspension
Strontium ranelate
2.
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each sachet contains 2 g strontium ranelate.
Also contains aspartame (E 951).
4.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Granules for oral suspension.
56 sachets
84 sachets
100 sachets
5.
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
For oral use
Read the package leaflet before use
6.
SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
7.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY


























9.
SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
10.
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11.
NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Les Laboratoires Servier
22, rue Garnier
92200 Neuilly-sur-Seine
France
12.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/04/287/004 56 sachets
EU/1/04/287/005/ 84 sachets
EU/1/04/287/006 100 sachets
14.
GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE





















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
OSSEOR 2 g granules for oral suspension
Strontium ranelate
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine.
-
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or your pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or your pharmacist.
What OSSEOR is and what it is used for
WHAT OSSEOR IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
OSSEOR is a non-hormonal medicine used to treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. OSSEOR
reduces the risk of fracture at the spine and at the hip.
About osteoporosis
Your body is constantly breaking down old bone and making new bone tissue. If you have
osteoporosis, your body breaks down more bone than it forms so that gradually bone loss occurs and
your bones become thinner and fragile. This is especially common in women after the menopause.
Many people with osteoporosis have no symptoms and you may not even know that you have it.
However, osteoporosis makes you more likely to have fractures (break bones), especially in your
spine, hips and wrists.
How OSSEOR works
OSSEOR, which contains the substance strontium ranelate, belongs to a group of medicines used to
treat bone diseases.
OSSEOR works by reducing bone breakdown and stimulating rebuilding of bone and therefore
reduces the risk of fracture. The newly formed bone is of normal quality.
if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to strontium ranelate or any of the other ingredients of
OSSEOR.
Take special care with OSSEOR:
Before taking OSSEOR talk to your doctor :
-
if you are being treated or have been treated for blood clots.
if you are confined to bed or if you are to undergo an operation. The risk of vein thrombosis
(blood clots in the leg) may be increased in the event of lengthy immobilisation.
if you have severe kidney disease.
During treatment, if you experience an allergic reaction (such as swelling of the face, tongue or throat,
difficulty in breathing or swallowing, skin rash), you must immediately stop taking OSSEOR and seek
medical advice. If you have stopped treatment due to hypersensitivity reactions it should be permanent
and you should not re-start therapy with OSSEOR.
Use in children
OSSEOR is not intended for use in children and adolescents (below the age of 18).
Taking other medicines:
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines,
including medicines obtained without a prescription.
-You should stop taking OSSEOR if you have to take oral tetracyclines or quinolones (two types of
antibiotics). You can take OSSEOR again when you have finished taking these antibiotics. If you are
unsure about this ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- If you are taking medicines containing calcium, you should leave at least 2 hours before you take
OSSEOR.
- If you take antacids (medicines to relieve heartburn) you should take them at least 2 hours after
OSSEOR. If this is not possible, it is acceptable to take the two medicines at the same time.
Taking OSSEOR with food and drink:
Food, milk and milk products reduce the absorption of strontium ranelate. It is recommended that you
take OSSEOR in-between meals, preferably at bedtime at least two hours after food, milk or milk
products or calcium supplements.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding:
OSSEOR is meant for use only in postmenopausal women. Therefore, do not take OSSEOR during
pregnancy or when you are breastfeeding. If you take it by accident during pregnancy or
breastfeeding, stop taking it straight away and talk to your doctor.
Driving and using machines:
Osseor is unlikely to affect your ability to drive or use machines.
Important information about some of the ingredients of OSSEOR:
OSSEOR contains aspartame. If you suffer from phenylketonuria (a rare, hereditary disorder of the
metabolism) talk to your doctor before you start to take this medicine.
Always take OSSEOR exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor or
pharmacist if you are not sure.
OSSEOR is for oral use.
The recommended dose is one 2g sachet a day.
It is recommended that you take OSSEOR at bedtime, preferably at least 2 hours after dinner. You
may lie down immediately after taking OSSEOR if you wish.
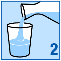
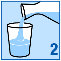
Take the granules contained in the sachets as a suspension in a glass of water (see instructions below).
OSSEOR can interact with milk and milk products, so it is important that you mix OSSEOR only with
water to be sure it works properly.
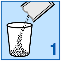
Empty the granules from the sachet into a glass;
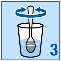
Stir until the granules are evenly dispersed in the water.
Drink straight away. You should not leave it more than 24 hours before you drink it. If for some
reason you cannot drink the medicine straight away, make sure you stir it again before drinking.
Your doctor may advise you to take calcium and vitamin D supplements in addition to OSSEOR. Do
not take calcium supplements at bedtime, at the same time as OSSEOR.
Your doctor will tell you how long you should continue to take OSSEOR. Osteoporosis-therapy is
usually required for a long period. It is important that you continue taking OSSEOR for as long as
your doctor prescribes the medicine.
If you take more OSSEOR than you should:
If you take too many sachets of OSSEOR, tell your doctor or pharmacist. They may advise you to
drink milk or take antacids to reduce the absorption of the active ingredient.
If you forget to take OSSEOR:
Do not take a double dose to make up for forgotten individual doses. Just carry on with the next dose
at the normal time.
Like all medicines, OSSEOR can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The frequency of possible side effects listed below is defined using the following convention:
very common (affects more than 1 user in 10)
common (affects 1 to 10 users in 100)
uncommon (affects 1 to 10 users in 1,000)
rare (affects 1 to 10 users in 10,000)
very rare (affects less than 1 user in 10,000)
not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
Common:
Nausea, diarrhoea, headache, skin irritation, memory troubles, fainting fit.
However, these effects were mild and short-lived and usually did not cause the patients to stop taking
their treatment. Talk to your doctor if any effects become troublesome or persist.
Uncommon:
Blood clots, seizures.


Not known:
Vomiting, abdominal pain, oral irritation (such as mouth ulcers and gum inflammation), bone, muscle
and/or joint pain, muscle cramps, hair loss, reduction in production of blood cells in the bone marrow,
hypersensitivity syndromes (allergic reactions including rash, a high temperature, increased levels of
liver enzymes seen in blood tests and increase in a type of white blood cell (eosinophilia), enlarged
lymph nodes), itching, hives, blistering, angioedema (such as swollen face, tongue or throat, difficulty
in breathing or swallowing), swelling in limbs, feeling confused, bronchial hyperreactivity (symptoms
include wheezing and shortness of breath).
In some cases very serious hypersensitivity reactions have been reported. Therefore you should
immediately stop taking OSSEOR and see your doctor if you experience symptoms of angioedema or
hypersensitivity syndrome.
If you have stopped treatment due to hypersensitivity syndrome, it should be permanent and you
should not re-start therapy with OSSEOR.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
This medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions.
Do not use after the expiry date which is stated on the box and the sachet after EXP.
Once reconstituted in water, the suspension is stable for 24 hours. However, it is recommended to
drink the suspension immediately after preparation (see section 3)
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
The active substance is strontium ranelate. Each sachet contains 2 g of strontium ranelate.
The other ingredients are aspartame (E 951), maltodextrin, mannitol (E 421).
What OSSEOR looks like and contents of the pack
OSSEOR is available in sachets containing yellow granules for oral suspension.OSSEOR is supplied
in boxes of 7, 14, 28, 56, 84 or 100 sachets.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Les Laboratoires Servier
22, rue Garnier
92200 Neuilly-sur-Seine
France
Manufacturer
Les Laboratoires Servier Industrie
905, route de Saran
45520 Gidy
France
For any information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the Marketing
Authorisation Holder.
België/Belgique/Belgien
S.A. Servier Benelux N.V.
Tel: +32 (0)2 529 43 11
Luxembourg/Luxemburg
S.A. Servier Benelux N.V.
Tel: +32 (0)2 529 43 11
България
Сервие Медикал ЕООД
Тел.: +359 2 921 57 00
Magyarország
Servier Hungaria Kft.
Tel: +36 1 238 7799
Česká republika
Servier s.r.o.
Tel: +420 222 118 111
Malta
Galepharma Ltd
Tel: +(356) 21 247 082
Danmark
Servier Danmark A/S
Tlf: +45 36 44 22 60
Nederland
Servier Nederland Farma B.V.
Tel: +31 (0)71 5246700
Deutschland
Servier Deutschland GmbH
Tel: +49 (0)89 57095 01
Norge
Servier Danmark A/S
Tlf: +45 36 44 22 60
Eesti
CentralPharma Communications OÜ
Tel: +372 640 00 07
Österreich
Servier Austria GmbH
Tel: +43 (1) 524 39 99
Eλλάδα
ΣΕΡΒΙΕ ΕΛΛΑΣ ΦΑΡΜΑΚΕΥΤΙΚΗ ΕΠΕ
Τηλ: +30 210 939 1000
Polska
Servier Polska Sp. z o.o.
Tel: +48 (0) 22 594 90 00
España
Laboratorios Farmacéuticos Rovi, S.A.
Tel: +34 91 375 62 30
Portugal
BIAL - Portela & Cª, S.A
Tel.: +351 22 986 61 00
France
Les Laboratoires Servier
Tel: +33 (0)1 55 72 60 00
România
Servier Pharma SRL
Tel: +40 21 528 52 80
Ireland
Servier Laboratories (Ireland) Ltd.
Tel: +353 (0)1 6638110
Slovenija
Servier Pharma d.o.o.
Tel.: +386 (0)1 563 48 11
Ísland
Servier Laboratories
c/o Icepharma hf
Sími: +354 540 8000
Slovenská republika
Servier Slovensko spol. s r.o.
Tel.:+421 (0)2 5920 41 11
Italia
I.F.B. Stroder S.r.l.
Tel: +39 (055) 623271
Suomi/Finland
Servier Finland Oy
Puh/Tel: +358 (0)9 279 80 80
Κύπρος
Χ.Α.Παπαέλληνας & Σία Λτδ
Τηλ: +357 22741741
Sverige
Servier Sverige AB
Tel: +46 (8) 52 25 08 00
Latvija
SIA Servier Latvia
Tel. +371 67502039
United Kingdom
Servier Laboratories Ltd
Tel: +44 (0)1753 666409
Lietuva
UAB "SERVIER PHARMA"
Tel: +370 (5) 2 63 86 28
This leaflet was last approved in {date}
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency web site:
Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/osseor.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|



































































































































































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































