Product Characteristics
ANNEX I
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
1.
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
SOMAVERT 10 mg powder and solvent
for solution for injection.
2.
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each vial contains 10 mg of pegvisomant.
After reconstitution, 1 ml of solution contains 10 mg pegvisomant.
Pegvisomant is produced in
E.Coli
by recombinant DNA technology.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Powder and solvent for solution for injection.
The powder is white to slightly off-white.
4.1.
Therapeutic indications
Treatment of patients with acromegaly who have had an inadequate response to surgery and/or
radiation therapy and in whom an appropriate medical treatment with somatostatin analogues did not
normalize IGF-I concentrations or was not tolerated.
4.2.
Posology and method of administration
Treatment should be initiated under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of
acromegaly.
For the different dosage regimens the following strengths are available: SOMAVERT 10 mg,
SOMAVERT 15 mg and SOMAVERT 20 mg.
For instructions on preparation, see section 6.6.
A loading dose of 80 mg pegvisomant should be administered subcutaneously under medical
supervision. Following this, SOMAVERT 10 mg reconstituted in 1 ml of solvent should be
administered once daily as a subcutaneous injection.
The site of injection should be rotated daily to help prevent lipohypertrophy.
Dose adjustments should be based on serum IGF-I levels.
Serum IGF-I concentrations should be
measured every four to six weeks and appropriate dose adjustments made in increments of 5 mg/day in
order to maintain the serum IGF-I concentration within the age-adjusted normal range and to maintain
an optimal therapeutic response.
The maximum dose should not exceed 30 mg/day.
No dose adjustment is required.
There is no experience in children.
Patients with impaired hepatic or renal function
The safety and effectiveness of SOMAVERT in patients with renal or hepatic insufficiency has not
been established.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
4.4.
Special warnings and precautions for use
Growth hormone-secreting pituitary tumours may sometimes expand, causing serious complications
(for example, visual field defects). Treatment by SOMAVERT does not reduce tumour size. All
patients with these tumours should be carefully monitored in order to avoid any eventual progression
in tumour size under treatment.
SOMAVERT is a potent antagonist of growth hormone action. A growth hormone deficient state may
result from SOMAVERT administration, despite the presence of elevated serum growth hormone
levels. Serum IGF-I concentrations should be monitored and maintained within the age-adjusted
normal range by adjustment of SOMAVERT dosing.
Serum concentrations of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) should be
monitored at four to six week intervals for the first six months of treatment with SOMAVERT, or at
any time in patients exhibiting symptoms suggestive of hepatitis. Evidence of obstructive biliary tract
disease should be ruled out in patients with elevations of ALT and AST or in patients with a prior
history of treatment with any somatostatin analogue. Administration of SOMAVERT should be
discontinued if signs of liver disease persist.
The study conducted with SOMAVERT in diabetic patients treated either by insulin or by oral
hypoglycaemic medicinal products revealed the risk of hypoglycemia in this population. Therefore, in
acromegalic patients with diabetes mellitus, doses of insulin or hypoglycaemic medicinal products
may need to be decreased (see also section 4.5).
The therapeutic benefits of a reduction in IGF-I concentration which results in improvement of the
patient’s clinical condition could potentially increase fertility in female patients. Patients should be
advised to use adequate contraception if necessary. SOMAVERT is not recommended during
pregnancy (see also section 4.6).
4.5.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No interaction studies have been performed. It should be considered whether to continue treatment
with somatostatin analogues. The use of SOMAVERT in combination with other medicinal products
for the treatment of acromegaly has not been extensively investigated.
Patients receiving insulin or oral hypoglycaemic medicinal products may require dose reduction of
these active substances due to the effect of pegvisomant on insulin sensitivity
(see section 4.4).
SOMAVERT has significant structural similarity to growth hormone which causes it to cross-react in
commercially available growth hormone assays. Since serum concentrations of therapeutically-
effective doses of SOMAVERT are generally 100 to 1000 times higher than the actual serum growth
hormone concentrations seen in acromegalics, measurements of serum growth hormone concentrations
will be spuriously reported in commercially available growth hormone assays. SOMAVERT
treatment should therefore not be monitored or adjusted based on serum growth hormone
concentrations reported from these assays.
4.6.
Pregnancy and lactation
For pegvisomant no clinical data on exposed pregnancies are available.
Animal studies are insufficient with respect to effects on pregnancy, embryonal/foetal development,
parturition or postnatal development (see section 5.3).The potential risk for humans is unknown.
SOMAVERT should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary (see also section 4.4).
The excretion of pegvisomant in breast milk has not been studied in animals. Clinical data are too
limited (one reported case) to draw any conclusion on the excretion of pegvisomant in human breast
milk. Therefore, SOMAVERT should not be used in breast-feeding women. However, breast-feeding
may be continued if SOMAVERT is discontinued: this decision should take into account the benefit of
SOMAVERT therapy to the mother and the benefit of breastfeeding to the child.
4.7.
Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
The list below contains adverse reactions seen in clinical trials.
In clinical studies, for patients treated with pegvisomant (n=160), the majority of adverse reactions to
pegvisomant were of mild to moderate intensity, of limited duration and did not require
discontinuation of treatment.
The most commonly reported adverse reactions considered related to SOMAVERT occurring in ≥ 5%
of patients with acromegaly during the clinical trials were injection site reactions 11%, sweating 7%,
headache 6% and asthenia 6%.
Adverse reactions are listed according to the following categories:
Very common: ≥1/10
Common: ≥1/100 to <1/10
Uncommon: ≥1/1,000 to <1/100
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
Uncommon:
thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, leukocytosis, bleeding tendency
Nervous system disorders:
Common:
headache, dizziness, somnolence, tremor
hypoesthesia, dysgeusia, migraine, narcolepsy
Ear and labyrinth disorders:
Uncommon:
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:
Uncommon:
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common:
diarrhoea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension, dyspepsia,
flatulence
dry mouth, hemorrhoids, salivary hypersecretion, tooth disorder
Renal and urinary disorders:
Uncommon:
heamaturia, proteinuria, polyuria, renal impairment
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
Common:
face oedema, dry skin, contusion, tendency to bruise, night sweats
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders:
Common:
arthralgia, myalgia, peripheral swelling
Metabolism and nutrition disorders:
Common:
hypercholesterolemia, weight gain, hyperglycemia, hunger
hypertriglyceridemia, hypoglycemia
Vascular disorders:
Common:
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Common:
influenza-like illness, fatigue, injection site bruising or bleeding, injection site
reaction (including injection site hypersensitivity), injection site hypertrophy
(e.g. lipohypertrophy)*
oedema lower limb, pyrexia, weakness, asthenia, feeling abnormal, impaired
healing, peripheral oedema
Hepatobiliary disorders:
Common
abnormal liver function tests (e.g. transaminase elevation) (see section 4.4)
Psychiatric disorders:
Common:
abnormal dreams, sleep disorder
anger, apathy, confusion, increased libido, panic attack, short term memory loss
*see Additional Information below.
Most injection site reactions characterised as localised erythemas and soreness, spontaneously
resolved with local symptomatic treatment, while SOMAVERT therapy continued. Occurrence of
injection site hypertrophies has been observed, including lipohypertrophy.
The development of isolated low-titre anti-growth hormone antibodies was observed in 16.9% of
patients treated with SOMAVERT. The clinical significance of these antibodies is unknown.
There is limited experience of overdosage with SOMAVERT. In the one reported incident of acute
overdosage, where 80 mg/day was administered for 7 days, the patient experienced a slight increase in
fatigue and dry mouth.
In the week following discontinuation of treatment the adverse reactions noted
were: insomnia, increased fatigue, a trace of foot oedema, fine tremor, and weight gain. Two weeks
after stopping treatment, leukocytosis and moderate bleeding from injection and vein puncture sites
was observed which were considered possibly related to SOMAVERT.
In cases of overdose, administration of SOMAVERT should be discontinued and not resumed until
IGF-I levels return to within or above the normal range.
5.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1.
Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Other anterior pituitary lobe hormones and analogues, ATC code:
H01AX01.
Pegvisomant is an analogue of human growth hormone that has been genetically modified to be a
growth hormone receptor antagonist.
Pegvisomant binds to growth hormone receptors on cell surfaces, where it blocks growth hormone
binding, and thus interferes with intracellular growth hormone signal transduction. Pegvisomant is
highly selective for the GH receptor, and does not cross-react with other cytokine receptors, including
prolactin. Inhibition of growth hormone action with pegvisomant leads to decreased serum
concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), as well as other growth hormone-responsive
serum proteins such as free IGF-I, the acid-labile subunit of IGF-I (ALS), and insulin-like growth
factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3).
Acromegalic patients (n=112) have been treated in a 12-week, randomised, double-blind, multicentre
study comparing placebo and pegvisomant. Dose-dependent, statistically significant reductions in
mean IGF-I (p<0.0001), free IGF-I (p<0.05), IGFBP-3 (p<0.05) and ALS (p<0.05) were observed at
all post-baseline visits in the pegvisomant treatment groups. The serum IGF-1 was normalised at the
end of the study (week 12) in 9.7%, 38.5%, 75% and 82% of subjects treated with placebo, 10 mg/day,
15 mg/day or 20 mg/day SOMAVERT respectively.
Statistically significant differences from placebo (p<0.05) were observed for improvements in the total
signs and symptoms score for all dose groups compared to placebo.
A cohort of 38 acromegalic subjects has been followed in a long-term, open-label, dose-titration study
for at least 12 consecutive months of daily dosing with pegvisomant (mean = 55 weeks). The mean
IGF-I concentration in this cohort fell from 917 ng/ml to 299 ng/ml on pegvisomant, with 92%
achieving a normal (age-adjusted) IGF-I concentration.
5.2.
Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption of pegvisomant following subcutaneous administration is slow and prolonged, and peak
serum pegvisomant concentrations are not generally attained until 33-77 hours after administration.
The mean extent of absorption of a subcutaneous dose was 57% relative to an intravenous dose.
The apparent volume of distribution of pegvisomant is relatively small (7-12 l). The mean total body
systemic clearance of pegvisomant following multiple doses is estimated to be 28 ml/h for
subcutaneous doses ranging from 10 to 20 mg/day. Renal clearance of pegvisomant is negligible and
accounts for less than 1% of total body clearance. Pegvisomant is slowly eliminated from serum, with
mean estimates of half-life generally ranging from 74 to 172 hours following either single or multiple-
doses. The metabolism of pegvisomant is not studied.
After single subcutaneous pegvisomant administration no linearity is observed with rising doses of
10, 15 or 20 mg. Approximately linear pharmacokinetics is observed at steady state in the population
pharmacokinetic studies. The data from 145 patients in two long-term studies who received daily
doses of 10, 15, or 20 mg, demonstrate pegvisomant mean serum concentrations (± SD) of
approximately 8800 ± 6300, 13200 ± 8000 and 15600 ± 10300 ng/ml, respectively.
The pharmacokinetics of pegvisomant are similar in normal healthy volunteers and acromegaly
patients, although heavier individuals tend to have a higher total body clearance of pegvisomant than
lighter individuals, and may thus require greater doses of pegvisomant.
No pharmacokinetic data in special populations (children, populations with renal and hepatic
impairment) are available.
5.3.
Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data revealed no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of repeated
dose toxicity in rat and monkey. However, due to the marked pharmacological response in monkey,
systemic exposures higher than those achieved in patients at therapeutic doses have not been studied.
Except for one segment II test in the rabbit, no other reproductive toxicity studies were conducted.
No data on carcinogenic potential are available.
6.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Powder:
Glycine
Mannitol (E421)
Sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous
Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate
Solvent:
Water for Injections
This medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products except those mentioned in
section 6.6.
After reconstitution, the product should be used immediately.
6.4.
Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C). Do not freeze. Keep the container in the outer carton in order to
protect from light.
After reconstitution:
Use immediately.
6.5.
Nature and contents of container
Powder in a vial (type I glass) with a rubber stopper (butyl) and 8 ml solvent in a vial (type I glass),
with a stopper (rubber butyl). Pack size of 30.
6.6.
Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Reconstitute using 1 ml solvent.
Add solvent to vial with powder for injection. Gently dissolve the powder with a slow, swirling
motion. Do not shake vigorously, as this might cause denaturation of the active ingredient.
After reconstitution, if the solution is cloudy or contains particulate matter, the product must be
discarded.
For single use only. Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with
local requirements.
7.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Pfizer Limited
Sandwich
Kent CT13 9NJ
United Kingdom
8.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
9.
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorization: 13/11/2002
Date of last renewal: 20/09/2007
10.
DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
1.
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
SOMAVERT 15 mg powder and solvent
for solution for injection.
2.
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each vial contains 15 mg of pegvisomant.
After reconstitution, 1 ml of solution contains 15 mg pegvisomant.
Pegvisomant is produced in
E.Coli
by recombinant DNA technology.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Powder and solvent for solution for injection.
The powder is white to slightly off-white.
4.1.
Therapeutic indications
Treatment of patients with acromegaly who have had an inadequate response to surgery and/or
radiation therapy and in whom an appropriate medical treatment with somatostatin analogues did not
normalize IGF-I concentrations or was not tolerated.
4.2.
Posology and method of administration
Treatment should be initiated under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of
acromegaly.
For the different dosage regimens the following strengths are available: SOMAVERT 10 mg,
SOMAVERT 15 mg and SOMAVERT 20 mg.
For instructions on preparation, see section 6.6.
A loading dose of 80 mg pegvisomant should be administered subcutaneously under medical
supervision. Following this, SOMAVERT 10 mg reconstituted in 1 ml of solvent should be
administered once daily as a subcutaneous injection.
The site of injection should be rotated daily to help prevent lipohypertrophy.
Dose adjustments should be based on serum IGF-I levels.
Serum IGF-I concentrations should be
measured every four to six weeks and appropriate dose adjustments made in increments of 5 mg/day in
order to maintain the serum IGF-I concentration within the age-adjusted normal range and to maintain
an optimal therapeutic response.
The maximum dose should not exceed 30 mg/day.
No dose adjustment is required.
There is no experience in children.
Patients with impaired hepatic or renal function
The safety and effectiveness of SOMAVERT in patients with renal or hepatic insufficiency has not
been established.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
4.4.
Special warnings and precautions for use
Growth hormone-secreting pituitary tumours may sometimes expand, causing serious complications
(for example, visual field defects). Treatment by SOMAVERT does not reduce tumour size. All
patients with these tumours should be carefully monitored in order to avoid any eventual progression
in tumour size under treatment.
SOMAVERT is a potent antagonist of growth hormone action. A growth hormone deficient state may
result from SOMAVERT administration, despite the presence of elevated serum growth hormone
levels. Serum IGF-I concentrations should be monitored and maintained within the age-adjusted
normal range by adjustment of SOMAVERT dosing.
Serum concentrations of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) should be
monitored at four to six week intervals for the first six months of treatment with SOMAVERT, or at
any time in patients exhibiting symptoms suggestive of hepatitis. Evidence of obstructive biliary tract
disease should be ruled out in patients with elevations of ALT and AST or in patients with a prior
history of treatment with any somatostatin analogue.
Administration of SOMAVERT should be
discontinued if signs of liver disease persist.
The study conducted with SOMAVERT in diabetic patients treated either by insulin or by oral
hypoglycaemic medicinal products revealed the risk of hypoglycemia in this population. Therefore, in
acromegalic patients with diabetes mellitus, doses of insulin or hypoglycaemic medicinal products
may need to be decreased (see also section 4.5).
The therapeutic benefits of a reduction in IGF-I concentration which results in improvement of the
patient’s clinical condition could potentially increase fertility in female patients. Patients should be
advised to use adequate contraception if necessary. SOMAVERT is not recommended during
pregnancy (see also section 4.6).
4.5.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No interaction studies have been performed. It should be considered whether to continue treatment
with somatostatin analogues. The use of SOMAVERT in combination with other medicinal products
for the treatment of acromegaly has not been extensively investigated.
Patients receiving insulin or oral hypoglycaemic medicinal products may require dose reduction of
these active substances due to the effect of pegvisomant on insulin sensitivity
(see section 4.4).
SOMAVERT has significant structural similarity to growth hormone which causes it to cross-react in
commercially available growth hormone assays. Since serum concentrations of therapeutically-
effective doses of SOMAVERT are generally 100 to 1000 times higher than the actual serum growth
hormone concentrations seen in acromegalics, measurements of serum growth hormone concentrations
will be spuriously reported in commercially available growth hormone assays. SOMAVERT
treatment should therefore not be monitored or adjusted based on serum growth hormone
concentrations reported from these assays.
4.6.
Pregnancy and lactation
For pegvisomant no clinical data on exposed pregnancies are available.
Animal studies are insufficient with respect to effects on pregnancy, embryonal/foetal development,
parturition or postnatal development (see section 5.3). The potential risk for humans is unknown.
SOMAVERT should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary (see also section 4.4).
The excretion of pegvisomant in breast milk has not been studied in animals. Clinical data are too
limited (one reported case) to draw any conclusion on the excretion of pegvisomant in human breast
milk. Therefore, SOMAVERT should not be used in breast-feeding women. However, breast-feeding
may be continued if SOMAVERT is discontinued: this decision should take into account the benefit of
SOMAVERT therapy to the mother and the benefit of breastfeeding to the child.
4.7.
Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
The list below contains adverse reactions seen in clinical trials.
In clinical studies, for patients treated with pegvisomant (n=160), the majority of adverse reactions to
pegvisomant were of mild to moderate intensity, of limited duration and did not require
discontinuation of treatment.
The most commonly reported adverse reactions considered related to SOMAVERT occurring in ≥ 5%
of patients with acromegaly during the clinical trials were injection site reactions 11%, sweating 7%,
headache 6% and asthenia 6%.
Adverse reactions are listed according to the following categories:
Very common: ≥1/10
Common: ≥1/100 to <1/10
Uncommon: ≥1/1,000 to <1/100
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
Uncommon:
thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, leukocytosis, bleeding tendency
Nervous system disorders:
Common:
headache, dizziness, somnolence, tremor
hypoesthesia, dysgeusia, migraine, narcolepsy
Ear and labyrinth disorders:
Uncommon:
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:
Uncommon:
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common:
diarrhoea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension, dyspepsia,
flatulence
dry mouth, hemorrhoids, salivary hypersecretion, tooth disorder
Renal and urinary disorders:
Uncommon:
heamaturia, proteinuria, polyuria, renal impairment
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
Common:
face oedema, dry skin, contusion, tendency to bruise, night sweats
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders:
Common:
arthralgia, myalgia, peripheral swelling
Metabolism and nutrition disorders:
Common:
hypercholesterolemia, weight gain, hyperglycemia, hunger
hypertriglyceridemia, hypoglycemia
Vascular disorders:
Common:
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Common:
influenza-like illness, fatigue, injection site bruising or bleeding, injection site
reaction (including injection site hypersensitivity), injection site hypertrophy
(e.g. lipohypertrophy)*
oedema lower limb, pyrexia, weakness, asthenia, feeling abnormal, impaired
healing, peripheral oedema
Hepatobiliary disorders:
Common
abnormal liver function tests (e.g. transaminase elevation) (see section 4.4)
Psychiatric disorders:
Common:
abnormal dreams, sleep disorder
anger, apathy, confusion, increased libido, panic attack, short term memory loss
*see Additional Information below.
Most injection site reactions characterised as localised erythemas and soreness, spontaneously
resolved with local symptomatic treatment, while SOMAVERT therapy continued. Occurrence of
injection site hypertrophies has been observed, including lipohypertrophy.
The development of isolated low-titre anti-growth hormone antibodies was observed in 16.9% of
patients treated with SOMAVERT. The clinical significance of these antibodies is unknown.
There is limited experience of overdosage with SOMAVERT. In the one reported incident of acute
overdosage, where 80 mg/day was administered for 7 days, the patient experienced a slight increase in
fatigue and dry mouth.
In the week following discontinuation of treatment the adverse reactions noted
were: insomnia, increased fatigue, a trace of foot oedema, fine tremor, and weight gain. Two weeks
after stopping treatment, leukocytosis and moderate bleeding from injection and vein puncture sites
was observed which were considered possibly related to SOMAVERT.
In cases of overdose, administration of SOMAVERT should be discontinued and not resumed until
IGF-I levels return to within or above the normal range.
5.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1.
Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Other anterior pituitary lobe hormones and analogues, ATC code
H01AX01.
Pegvisomant is an analogue of human growth hormone that has been genetically modified to be a
growth hormone receptor antagonist.
Pegvisomant binds to growth hormone receptors on cell surfaces, where it blocks growth hormone
binding, and thus interferes with intracellular growth hormone signal transduction. Pegvisomant is
highly selective for the GH receptor, and does not cross-react with other cytokine receptors, including
prolactin. Inhibition of growth hormone action with pegvisomant leads to decreased serum
concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), as well as other growth hormone-responsive
serum proteins such as free IGF-I, the acid-labile subunit of IGF-I (ALS), and insulin-like growth
factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3).
Acromegalic patients (n=112) have been treated in a 12-week, randomised, double-blind, multicentre
study comparing placebo and pegvisomant. Dose-dependent, statistically significant reductions in
mean IGF-I (p<0.0001), free IGF-I (p<0.05), IGFBP-3 (p<0.05) and ALS (p<0.05) were observed at
all post-baseline visits in the pegvisomant treatment groups. The serum IGF-1 was normalised at the
end of the study (week 12) in 9.7%, 38.5%, 75% and 82% of subjects treated with placebo, 10 mg/day,
15 mg/day or 20 mg/day SOMAVERT respectively.
Statistically significant differences from placebo (p<0.05) were observed for improvements in the total
signs and symptoms score for all dose groups compared to placebo.
A cohort of 38 acromegalic subjects has been followed in a long-term, open-label, dose-titration study
for at least 12 consecutive months of daily dosing with pegvisomant (mean = 55 weeks). The mean
IGF-I concentration in this cohort fell from 917 ng/ml to 299 ng/ml on pegvisomant, with 92%
achieving a normal (age-adjusted) IGF-I concentration.
5.2.
Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption of pegvisomant following subcutaneous administration is slow and prolonged, and peak
serum pegvisomant concentrations are not generally attained until 33-77 hours after administration.
The mean extent of absorption of a subcutaneous dose was 57% relative to an intravenous dose.
The apparent volume of distribution of pegvisomant is relatively small (7-12 l). The mean total body
systemic clearance of pegvisomant following multiple doses is estimated to be 28 ml/h for
subcutaneous doses ranging from 10 to 20 mg/day. Renal clearance of pegvisomant is negligible and
accounts for less than 1% of total body clearance. Pegvisomant is slowly eliminated from serum, with
mean estimates of half-life generally ranging from 74 to 172 hours following either single or multiple-
doses. The metabolism of pegvisomant is not studied.
After single subcutaneous pegvisomant administration no linearity is observed with rising doses of
10, 15 or 20 mg. Approximately linear pharmacokinetics is observed at steady state in the population
pharmacokinetic studies. The data from 145 patients in two long-term studies who received daily
doses of 10, 15, or 20 mg, demonstrate pegvisomant mean serum concentrations (± SD) of
approximately 8800 ± 6300, 13200 ± 8000 and 15600 ± 10300 ng/ml, respectively.
The pharmacokinetics of pegvisomant are similar in normal healthy volunteers and acromegaly
patients, although heavier individuals tend to have a higher total body clearance of pegvisomant than
lighter individuals, and may thus require greater doses of pegvisomant.
No pharmacokinetic data in special populations (children, populations with renal and hepatic
impairment) are available.
5.3.
Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data revealed no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of repeated
dose toxicity in rat and monkey. However, due to the marked pharmacological response in monkey,
systemic exposures higher than those achieved in patients at therapeutic doses have not been studied.
Except for one segment II test in the rabbit, no other reproductive toxicity studies were conducted.
No data on carcinogenic potential are available.
6.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Powder:
Glycine
Mannitol (E421)
Sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous
Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate
Solvent:
Water for Injections
This medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products except those mentioned in
section 6.6.
After reconstitution, the product should be used immediately.
6.4.
Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C). Do not freeze. Keep the container in the outer carton in order to
protect from light.
After reconstitution:
Use immediately.
6.5.
Nature and contents of container
Powder in a vial (type I glass) with a rubber stopper (butyl) and 8 ml solvent in a vial (type I glass),
with a stopper (rubber butyl). Pack size of 30.
6.6.
Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Reconstitute using 1 ml solvent.
Add solvent to vial with powder for injection. Gently dissolve the powder with a slow, swirling
motion. Do not shake vigorously, as this might cause denaturation of the active ingredient.
After reconstitution, if the solution is cloudy or contains particulate matter, the product must be
discarded.
For single use only. Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with
local requirements.
7.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Pfizer Limited
Sandwich
Kent CT13 9NJ
United Kingdom
8.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
9.
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorization: 13/11/2002
Date of last renewal: 20/09/2007
10.
DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
1.
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
SOMAVERT 20 mg powder and solvent
for solution for injection.
2.
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each vial contains 20 mg of pegvisomant.
After reconstitution, 1 ml of solution contains 20 mg pegvisomant.
Pegvisomant is produced in
E.Coli
by recombinant DNA technology.
For a full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Powder and solvent for solution for injection.
The powder is white to slightly off-white.
4.1.
Therapeutic indications
Treatment of patients with acromegaly who have had an inadequate response to surgery and/or
radiation therapy and in whom an appropriate medical treatment with somatostatin analogues did not
normalize IGF-I concentrations or was not tolerated.
4.2.
Posology and method of administration
Treatment should be initiated under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of
acromegaly.
For the different dosage regimens the following strengths are available: SOMAVERT 10 mg,
SOMAVERT 15 mg and SOMAVERT 20 mg.
For instructions on preparation, see section 6.6.
A loading dose of 80 mg pegvisomant should be administered subcutaneously under medical
supervision. Following this, SOMAVERT 10 mg reconstituted in 1 ml of solvent should be
administered once daily as a subcutaneous injection.
The site of injection should be rotated daily to help prevent lipohypertrophy.
Dose adjustments should be based on serum IGF-I levels
.
Serum IGF-I concentrations should be
measured every four to six weeks and appropriate dose adjustments made in increments of 5 mg/day in
order to maintain the serum IGF-I concentration within the age-adjusted normal range and to maintain
an optimal therapeutic response.
The maximum dose should not exceed 30 mg/day.
No dose adjustment is required.
There is no experience in children.
Patients with impaired hepatic or renal function
The safety and effectiveness of SOMAVERT in patients with renal or hepatic insufficiency has not
been established.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
4.4.
Special warnings and precautions for use
Growth hormone-secreting pituitary tumours may sometimes expand, causing serious complications
(for example, visual field defects). Treatment by SOMAVERT does not reduce tumour size. All
patients with these tumours should be carefully monitored in order to avoid any eventual progression
in tumour size under treatment.
SOMAVERT is a potent antagonist of growth hormone action. A growth hormone deficient state may
result from SOMAVERT administration, despite the presence of elevated serum growth hormone
levels. Serum IGF-I concentrations should be monitored and maintained within the age-adjusted
normal range by adjustment of SOMAVERT dosing.
Serum concentrations of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) should be
monitored at four to six week intervals for the first six months of treatment with SOMAVERT, or at
any time in patients exhibiting symptoms suggestive of hepatitis. Evidence of obstructive biliary tract
disease should be ruled out in patients with elevations of ALT and AST or in patients with a prior
history of treatment with any somatostatin analogue.
Administration of SOMAVERT should be
discontinued if signs of liver disease persist.
The study conducted with SOMAVERT in diabetic patients treated either by insulin or by oral
hypoglycaemic medicinal products revealed the risk of hypoglycemia in this population. Therefore, in
acromegalic patients with diabetes mellitus, doses of insulin or hypoglycaemic medicinal products
may need to be decreased (see also section 4.5).
The therapeutic benefits of a reduction in IGF-I concentration which results in improvement of the
patient’s clinical condition could potentially increase fertility in female patients. Patients should be
advised to use adequate contraception if necessary. SOMAVERT is not recommended during
pregnancy (see also section 4.6).
4.5.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No interaction studies have been performed. It should be considered whether to continue treatment
with somatostatin analogues. The use of SOMAVERT in combination with other medicinal products
for the treatment of acromegaly has not been extensively investigated.
Patients receiving insulin or oral hypoglycaemic medicinal products may require dose reduction of
these active substances due to the effect of pegvisomant on insulin sensitivity
(see section 4.4).
SOMAVERT has significant structural similarity to growth hormone which causes it to cross-react in
commercially available growth hormone assays. Since serum concentrations of therapeutically-
effective doses of SOMAVERT are generally 100 to 1000 times higher than the actual serum growth
hormone concentrations seen in acromegalics, measurements of serum growth hormone concentrations
will be spuriously reported in commercially available growth hormone assays. SOMAVERT
treatment should therefore not be monitored or adjusted based on serum growth hormone
concentrations reported from these assays.
4.6.
Pregnancy and lactation
For pegvisomant no clinical data on exposed pregnancies are available.
Animal studies are insufficient with respect to effects on pregnancy, embryonal/foetal development,
parturition or postnatal development (see section 5.3).The potential risk for humans is unknown.
SOMAVERT should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary (see also section 4.4).
The excretion of pegvisomant in breast milk has not been studied in animals. Clinical data are too
limited (one reported case) to draw any conclusion on the excretion of pegvisomant in human breast
milk. Therefore, SOMAVERT should not be used in breast-feeding women. However, breast-feeding
may be continued if SOMAVERT is discontinued: this decision should take into account the benefit of
SOMAVERT therapy to the mother and the benefit of breastfeeding to the child.
4.7.
Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
The list below contains adverse reactions seen in clinical trials.
In clinical studies, for patients treated with pegvisomant (n=160), the majority of adverse reactions to
pegvisomant were of mild to moderate intensity, of limited duration and did not require
discontinuation of treatment.
The most commonly reported adverse reactions considered related to SOMAVERT occurring in ≥ 5%
of patients with acromegaly during the clinical trials were injection site reactions 11%, sweating 7%,
headache 6% and asthenia 6%.
Adverse reactions are listed according to the following categories:
Very common: ≥1/10
Common: ≥1/100 to <1/10
Uncommon: ≥1/1,000 to <1/100
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
Uncommon:
thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, leukocytosis, bleeding tendency
Nervous system disorders:
Common:
headache, dizziness, somnolence, tremor
hypoesthesia, dysgeusia, migraine, narcolepsy
Ear and labyrinth disorders:
Uncommon:
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:
Uncommon:
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common:
diarrhoea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension, dyspepsia,
flatulence
dry mouth, hemorrhoids, salivary hypersecretion, tooth disorder
Renal and urinary disorders:
Uncommon:
heamaturia, proteinuria, polyuria, renal impairment
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
Common:
face oedema, dry skin, contusion, tendency to bruise, night sweats
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders:
Common:
arthralgia, myalgia, peripheral swelling
Metabolism and nutrition disorders:
Common:
hypercholesterolemia, weight gain, hyperglycemia, hunger
hypertriglyceridemia, hypoglycemia
Vascular disorders:
Common:
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Common:
influenza-like illness, fatigue, injection site bruising or bleeding, injection site
reaction (including injection site hypersensitivity), injection site hypertrophy
(e.g. lipohypertrophy)*
oedema lower limb, pyrexia, weakness, asthenia, feeling abnormal, impaired
healing, peripheral oedema
Hepatobiliary disorders:
Common
abnormal liver function tests (e.g. transaminase elevation) (see section 4.4)
Psychiatric disorders:
Common:
abnormal dreams, sleep disorder
anger, apathy, confusion, increased libido, panic attack, short term memory loss
*see Additional Information below.
Most injection site reactions characterised as localised erythemas and soreness, spontaneously
resolved with local symptomatic treatment, while SOMAVERT therapy continued. Occurrence of
injection site hypertrophies has been observed, including lipohypertrophy.
The development of isolated low-titre anti-growth hormone antibodies was observed in 16.9% of
patients treated with SOMAVERT. The clinical significance of these antibodies is unknown.
There is limited experience of overdosage with SOMAVERT. In the one reported incident of acute
overdosage, where 80 mg/day was administered for 7 days, the patient experienced a slight increase in
fatigue and dry mouth.
In the week following discontinuation of treatment the adverse reactions noted
were: insomnia, increased fatigue, a trace of foot oedema, fine tremor, and weight gain. Two weeks
after stopping treatment, leukocytosis and moderate bleeding from injection and vein puncture sites
was observed which were considered possibly related to SOMAVERT.
In cases of overdose, administration of SOMAVERT should be discontinued and not resumed until
IGF-I levels return to within or above the normal range.
5.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1.
Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Other anterior pituitary lobe hormones and analogues, ATC code
H01AX01.
Pegvisomant is an analogue of human growth hormone that has been genetically modified to be a
growth hormone receptor antagonist.
Pegvisomant binds to growth hormone receptors on cell surfaces, where it blocks growth hormone
binding, and thus interferes with intracellular growth hormone signal transduction. Pegvisomant is
highly selective for the GH receptor, and does not cross-react with other cytokine receptors, including
prolactin. Inhibition of growth hormone action with pegvisomant leads to decreased serum
concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), as well as other growth hormone-responsive
serum proteins such as free IGF-I, the acid-labile subunit of IGF-I (ALS), and insulin-like growth
factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3).
Acromegalic patients (n=112) have been treated in a 12-week, randomised, double-blind, multicentre
study comparing placebo and pegvisomant. Dose-dependent, statistically significant reductions in
mean IGF-I (p<0.0001), free IGF-I (p<0.05), IGFBP-3 (p<0.05) and ALS (p<0.05) were observed at
all post-baseline visits in the pegvisomant treatment groups. The serum IGF-1 was normalised at the
end of the study (week 12) in 9.7%, 38.5%, 75% and 82% of subjects treated with placebo, 20 mg/day,
15 mg/day or 20 mg/day SOMAVERT respectively.
Statistically significant differences from placebo (p<0.05) were observed for improvements in the total
signs and symptoms score for all dose groups compared to placebo.
A cohort of 38 acromegalic subjects has been followed in a long-term, open-label, dose-titration study
for at least 12 consecutive months of daily dosing with pegvisomant (mean = 55 weeks). The mean
IGF-I concentration in this cohort fell from 917 ng/ml to 299 ng/ml on pegvisomant, with 92%
achieving a normal (age-adjusted) IGF-I concentration.
5.2.
Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption of pegvisomant following subcutaneous administration is slow and prolonged, and peak
serum pegvisomant concentrations are not generally attained until 33-77 hours after administration.
The mean extent of absorption of a subcutaneous dose was 57% relative to an intravenous dose.
The apparent volume of distribution of pegvisomant is relatively small (7-12 l). The mean total body
systemic clearance of pegvisomant following multiple doses is estimated to be 28 ml/h for
subcutaneous doses ranging from 10 to 20 mg/day. Renal clearance of pegvisomant is negligible and
accounts for less than 1% of total body clearance. Pegvisomant is slowly eliminated from serum, with
mean estimates of half-life generally ranging from 74 to 172 hours following either single or multiple-
doses. The metabolism of pegvisomant is not studied.
After single subcutaneous pegvisomant administration no linearity is observed with rising doses of
10, 15 or 20 mg. Approximately linear pharmacokinetics is observed at steady state in the population
pharmacokinetic studies. The data from 145 patients in two long-term studies who received daily
doses of 10, 15, or 20 mg, demonstrate pegvisomant mean serum concentrations (± SD) of
approximately 8800 ± 6300, 13200 ± 8000 and 15600 ± 10300 ng/ml, respectively.
The pharmacokinetics of pegvisomant are similar in normal healthy volunteers and acromegaly
patients, although heavier individuals tend to have a higher total body clearance of pegvisomant than
lighter individuals, and may thus require greater doses of pegvisomant.
No pharmacokinetic data in special populations (children, populations with renal and hepatic
impairment) are available.
5.3.
Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data revealed no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of repeated
dose toxicity in rat and monkey. However, due to the marked pharmacological response in monkey,
systemic exposures higher than those achieved in patients at therapeutic doses have not been studied.
Except for one segment II test in the rabbit, no other reproductive toxicity studies were conducted.
No data on carcinogenic potential are available.
6.
PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
Powder:
Glycine
Mannitol (E421)
Sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous
Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate
Solvent:
Water for Injections
This medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products except those mentioned in
section 6.6.
After reconstitution, the product should be used immediately.
6.4.
Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C). Do not freeze. Keep the container in the outer carton in order to
protect from light.
After reconstitution:
Use immediately.
6.5.
Nature and contents of container
Powder in a vial (type I glass) with a rubber stopper (butyl) and 8 ml solvent in a vial (type I glass),
with a stopper (rubber butyl). Pack sizes of 1 or 30. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6.
Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Reconstitute using 1 ml solvent.
Add solvent to vial with powder for injection. Gently dissolve the powder with a slow, swirling
motion. Do not shake vigorously, as this might cause denaturation of the active ingredient.
After reconstitution, if the solution is cloudy or contains particulate matter, the product must be
discarded.
For single use only. Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with
local requirements.
7.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Pfizer Limited
Sandwich
Kent CT13 9NJ
United Kingdom
8.
MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
9.
DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION/RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorization: 13/11/2002
Date of last renewal: 20/09/2007
10.
DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
ANNEX II
A. MANUFACTURER(S) OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE
SUBSTANCE(S) AND MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION
HOLDER(S) RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH RELEASE
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
A. MANUFACTURER(S) OF THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S) AND
MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER(S) RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
RELEASE
Name and address of the manufacturer(s) of the biological active substance(s)
Diosynth RTP Inc.
6051 George Watts Hill Drive,
P.O. Box 13865, Research Triangle Park,
North Carolina 27709-3865,
USA
Name and address of the manufacturer(s) responsible for batch release
Pfizer Manufacturing Belgium NV
Rijksweg 12,
B-2870 Puurs,
Belgium
B. CONDITIONS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS REGARDING SUPPLY AND USE IMPOSED ON
THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Medicinal product subject to restricted medical prescription (See Annex I: Summary of Product
Characteristics, section 4.2).
CONDITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS WITH REGARD TO THE SAFE AND EFFECTIVE
USE OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
The MAH will continue to submit yearly PSURs for the following three years, unless otherwise
specified by the CHMP.
ANNEX III
LABELLING AND PACKAGE LEAFLET
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING AND THE IMMEDIATE
PACKAGING
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
SOMAVERT 10 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
Pegvisomant
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains 10 mg pegvisomant
Excipients:
Glycine
Mannitol (E421)
Sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous
Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder and solvent for solution for injection
30 vials of powder for solution for injection
30 vials of water for injections
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous use. Read the package leaflet before use
6. SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
Use immediately after reconstitution. For single use only.

























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator. Do not freeze.
Keep the container in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Pfizer Limited
Sandwich
Kent CT13 9NJ
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE



















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING AND THE IMMEDIATE
PACKAGING
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
SOMAVERT 15 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
Pegvisomant
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains 15 mg pegvisomant
Excipients:
Glycine
Mannitol (E421)
Sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous
Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder and solvent for solution for injection
30 vials of powder for solution for injection
30 vials of water for injections
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous use. Read the package leaflet before use
6. SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
Use immediately after reconstitution. For single use only.

























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator. Do not freeze.
Keep the container in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Pfizer Limited
Sandwich
Kent CT13 9NJ
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE



















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING AND THE IMMEDIATE
PACKAGING
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
SOMAVERT 20 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
Pegvisomant
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains 20 mg pegvisomant
Excipients:
Glycine
Mannitol (E421)
Sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous
Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder and solvent for solution for injection
30 vials of powder for solution for injection
30 vials of water for injections
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous use. Read the package leaflet before use
6. SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
Use immediately after reconstitution. For single use only.

























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator. Do not freeze.
Keep the container in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Pfizer Limited
Sandwich
Kent CT13 9NJ
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE



















PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING AND THE IMMEDIATE
PACKAGING
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
SOMAVERT 20 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
Pegvisomant
STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each vial contains 20 mg pegvisomant
Excipients:
Glycine
Mannitol (E421)
Sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous
Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate
PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Powder and solvent for solution for injection
1 vial of powder for solution for injection
1 vial of water for injections
METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous use. Read the package leaflet before use
6. SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT
OF THE REACH AND SIGHT OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
Use immediately after reconstitution. For single use only.

























SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator. Do not freeze.
Keep the container in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF
APPROPRIATE
11. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Pfizer Limited
Sandwich
Kent CT13 9NJ
United Kingdom
12. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
13. MANUFACTURER’S BATCH NUMBER
14. GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription
16. INFORMATION IN BRAILLE



















PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
SOMAVERT 10 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
SOMAVERT 15 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
SOMAVERT 20 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
Pegvisomant
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
-
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet,
please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
What SOMAVERT is and what it is used for
1. WHAT SOMAVERT IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
SOMAVERT is used for the treatment of acromegaly, a hormonal disorder resulting from the
increased secretion of growth hormone (GH) and IGF-I (Insulin-like growth factors), which is
characterised by overgrowth of bone, soft tissue swelling, heart disease and related disorders.
SOMAVERT is a product of biotechnology. The active substance in SOMAVERT, pegvisomant is
known as a growth hormone receptor antagonist. These substances decrease the action of GH and
levels of IGF-I circulating in the blood.
2. BEFORE YOU USE SOMAVERT
If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to pegvisomant or any of the other ingredients of
SOMAVERT.
Take special care with SOMAVERT
If you experience disturbed vision or headaches while using SOMAVERT you must contact
your doctor immediately.
Your doctor or nurse will monitor the levels of IGF-I (Insulin-like growth factors) circulating in
the blood and adjust the dose of SOMAVERT if necessary.
Your doctor should also monitor your adenoma (benign tumour).
Your doctor or nurse will monitor the level of liver enzymes in the blood every 4-6 weeks for
the first six months of treatment with SOMAVERT. Administration of SOMAVERT should be
discontinued if signs of liver disease persist.
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again
If you are diabetic, your doctor may need to adjust the amount of insulin or other medicines you
are using.
Female patients should use adequate contraception as fertility may be increased. See also the
section about Pregnancy below.
You must tell your doctor if you have previously used other medicines for the treatment of acromegaly
or medicines for the treatment of diabetes.
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using or have recently used any other medicines,
including medicines obtained without a prescription.
As part of your treatment you may be given other medicines. It is important to keep using all your
medicines as well as SOMAVERT unless you are told otherwise by your doctor or pharmacist.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
The effects of SOMAVERT in pregnant women are not known, and so the use of SOMAVERT in
pregnant women is not recommended. You are advised to not become pregnant while taking
SOMAVERT therapy. In case you become pregnant, you must consult your doctor. Ask your doctor or
pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
It is not known if SOMAVERT passes into breast milk. You should not breast-feed while taking
SOMAVERT unless your doctor has discussed this with you.
Driving and using machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
Important information about some of the ingredients of SOMAVERT
This medicinal product contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per 10 mg dose, less than 1 mmol
sodium (23 mg) per 15 mg dose, or less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per 20 mg dose i.e. essentially
‘sodium-free’.
Always inject SOMAVERT exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor
or pharmacist if you are not sure.
A starting dose of 80 mg of SOMAVERT will be given subcutaneously (just under the skin) by your
doctor. Following this, the usual daily dose of SOMAVERT is 10 mg, which is given by
subcutaneous injection (just under the skin).
Every four to six weeks your doctor will make appropriate dose adjustments, made in increments of
5 mg pegvisomant/day, based on your so-called serum IGF-I levels to maintain an optimal therapeutic
response.
Method and route of administration
SOMAVERT is injected under the skin. The injection can be self-administered or given by another
person, for example your doctor or his/her assistant. The detailed instructions on injection procedure
provided at the end of this leaflet must be followed. You should continue to inject SOMAVERT for as
long as instructed by your doctor.
SOMAVERT must be dissolved before use. The injection must not be mixed in the same syringe or
vial as any other medicine.
Fatty tissue of the skin can build-up at the site of injection. To avoid this, use a slightly different place
for your injection each time, as described in Step 2 of the ‘Instructions for Preparing and Giving an
Injection of Somavert’ section of this leaflet. This gives your skin and the area under your skin time to
recover from one injection before it receives another one in the same place.
If you have the impression that the effect of SOMAVERT is too strong or too weak, talk to your
doctor or pharmacist.
If you inject more SOMAVERT than you should
If you accidentally inject more SOMAVERT than told to by your doctor it is unlikely to be serious,
but you should contact your doctor or pharmacist immediately.
If you forget to use SOMAVERT
If you forget to give yourself an injection you should inject the next dose as soon as you remember
and then continue to inject SOMAVERT as prescribed by your doctor. Do not inject a double dose to
make up for forgotten individual doses.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Like all medicines, SOMAVERT can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Common side effects (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 10 patients) include:
•
Headache, dizziness, sleepiness, uncontrolled trembling.
•
Diarrhoea, constipation, feeling sick, being sick, feeling bloated, indigestion, gas.
•
Sweating, itching, rash.
•
Joint pain, muscle pain, swelling of the extremities.
•
Increased blood cholesterol, weight gain, increased blood glucose, increased appetite.
•
Increased blood pressure.
•
Bruising or bleeding at injection site, soreness or swelling at injection site, build up of fat
below the surface of the skin at injection site.
•
Flu-like illness, fatigue.
•
Increased levels of substances that measure the function of the liver. These can be seen in the
results of blood tests.
•
Abnormal dreams, problems sleeping.
Uncommon side effects (likely to occur in fewer than 1 in 100 patients) include:
•
Decreased platelets in the blood, increased or decreased white cells in the blood, tendency to
bleed.
•
Decreased sense of touch, abnormal sense of taste, migraine.
•
Eyestrain, eye pain, inner ear problems.
•
Shortness of breath.
•
Dry mouth, increased saliva, tooth problems, hemorrhoids.
•
Blood in the urine, protein in the urine, increased urine, kidney problems.
•
Facial swelling, dry skin, tendency to bruise, night sweats.
•
Arthritis.
•
Increased fatty substances in the blood, decreased blood glucose.
•
Fever, weakness, feeling abnormal, impaired healing.
•
Anger, lack of interest, feeling confused, increased sex drive, panic attack, loss of memory.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please
tell your doctor or pharmacist.
About 17% of patients will develop antibodies to growth hormone during treatment. The antibodies do
not seem to stop SOMAVERT from working.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children
Do not use SOMAVERT after the expiry date which is stated on the vial and the carton after EXP. The
expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C). Do not freeze. Keep the vials in the outer carton in order to
protect from light.
After preparing the SOMAVERT solution it must be used immediately. Carefully dispose of any
SOMAVERT solution that has not been injected.
Do not use SOMAVERT if you notice that the solution is cloudy or contains particulate matter.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to
dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
-
The active substance is pegvisomant.
-
One vial of powder contains either 10 mg, 15 mg, or 20 mg. After reconstitution with 1 ml of
solvent, 1 ml of the clear solution contains either 10 mg, 15 mg or 20 mg pegvisomant.
-
The other ingredients are glycine, mannitol (E421), sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous and
sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate.
-
The solvent is water for injections. One vial of solvent contains 8 ml water for injections.
What SOMAVERT looks like and contents of the pack
SOMAVERT is presented as a powder and a solvent for injection, in a vial. Powder in a vial (either
10 mg, 15 mg, or 20 mg pegvisomant) and solvent in a vial (8 ml). Pack sizes of 1 and 30. Not all
pack sizes are marketed. The powder is white and the solvent is clear and colourless.
Marketing Authorisation holder:
Pfizer Limited
Sandwich
Kent CT13 9NJ
United Kingdom
Pfizer Manufacturing Belgium NV
Rijksweg 12
2870 Puurs
Belgium
For any information about this medicine, please contact the local representative of the Marketing
Authorisation Holder.
België/Belgique/Belgien Luxembourg/Luxemburg
Pfizer S.A./N.V. Pfizer S.A.
Tél/Tel: +32 (0)2 554 62 11 Tél/Tel: +32 (0)2 554 62 11
България Magyarország
Пфайзер Люксембург САРЛ, Клон България Pfizer Kft.
Тел.: +359 2 970 4333
V.J. Salomone Pharma Ltd.
Tel: +49 (0)30 550055 51000
Pfizer Luxembourg SARL Eesti filiaal
Pfizer Corporation Austria Ges.m.b.H.
Laboratórios Pfizer, Lda.
Tél: +33 (0)1 58 07 34 40
Pfizer Healthcare Ireland
Pfizer Luxembourg SARL, Pfizer, podružnica za
svetovanje s področja farmacevtske dejavnosti,
Ljubljana
Tel: 1800 633 363 (toll free)
+44 (0)1304 616161
Tel: + 386 (0)1 52 11 400
Pfizer Luxembourg SARL, organizačná zložka
Puh/Tel: +358 (0)9 43 00 40
Geo. Pavlides & Araouzos Ltd,
Pfizer Luxembourg SARL filiāle Latvijā
Pfizer Luxembourg SARL filialas Lietuvoje
This leaflet was last approved in {MM/YYYY}.
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) web site:
http://www.emea.europa.eu. There are also links to other websites about rare diseases and treatments.
<------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARING AND GIVING AN INJECTION OF SOMAVERT
The following instructions explain
how to prepare and inject SOMAVERT. Please read the
instructions carefully and follow them step by step. You will be instructed by your doctor or his/her
assistant on the technique of self-injection. Do not attempt to self-inject until you are sure that you
understand how to prepare and give an injection.
The powder must be dissolved with the solvent before use.
This injection should not be mixed in the same syringe or vial with any other medicine.
STEP 1. CHOOSING THE METHOD FOR PREPARING THE SOMAVERT SOLUTION
There are 2 methods for preparing the SOMAVERT solution. Please discuss with your healthcare
professional which method is best for you:
a) The Vial Adapter Method (MIXJECT™),
b) The Non-Vial Adapter Method.
a) VIAL ADAPTER METHOD (MIXJECT™)
•
Wash your hands thoroughly.
•
Collect:
1 vial of powder (SOMAVERT),
1 vial of solvent (Water for Injections),
1 luer-lock syringe of 1ml (for both reconstituting the SOMAVERT solution and giving the
injection) is recommended. However, other sizes and types of syringes can be used for the
preparation and injection of SOMAVERT. Please consult your healthcare professional for further
information.
2 MIXJECT™ vial adapters,
1 detachable needle (25 to 30 gauge),
Alcohol or antiseptic swabs and a proper disposal container for used needles and syringes.
•
Inspect the expiry dates on both the vial label and the syringe label. They should not be used after
the month and year shown.
After reconstitution with 1 ml of solvent, 1 ml of the clear solution contains either 10 mg, 15 mg, or
20 mg pegvisomant.
PREPARING THE SOMAVERT DOSE FOR INJECTION
1. Remove the protective plastic caps from the tops of both vial of solvent and vial of
SOMAVERT (Fig. 1). Take care not to touch the rubber vial stoppers. At this point, the stoppers
are clean. If the stoppers are touched or otherwise contaminated, you must clean them with an
antiseptic or alcohol swab before inserting a vial adapter through the stopper.
2. Open only one of the vial adapters by peeling back the protective cover. Leave the adapter in the
plastic packaging and do not touch the spike of the adapter.

























3. While holding the plastic adapter packaging, place the adapter over the solvent vial and insert
the piercing spike of the vial adapter all the way in through the rubber stopper of the solvent
vial, using a pushing motion. (Fig. 2). Remove the plastic packaging from the vial adapter and
discard.
4. Remove the syringe from the protective packaging. Pull the plunger of the syringe out to the 1
ml mark. Hold the solvent vial, placed on a flat surface, with one hand and connect the tip of the
syringe to the vial adapter by twisting the syringe on the vial adapter clockwise (Fig. 3). Gently
push the plunger until the air is injected into the vial.
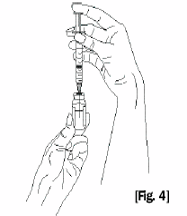
5. Securely grasp the solvent vial, adapter and syringe assembly. Carefully turn the vial, adapter
and syringe assembly upside down. Bring to eye level (Fig. 4).
6. Slide one hand carefully down the solvent vial so that with your thumb and forefinger you can
securely grasp the neck of the vial, and with your other fingers, the upper part of the syringe.
With the other hand, slowly pull the syringe plunger down to slightly past the 1 ml mark.
Examine the solution in the syringe for air bubbles. If bubbles are present, tap the syringe barrel
until the bubbles rise to the top of the syringe. Carefully push the plunger up to eject only the air
bubbles back into the vial. Recheck that 1 ml of solvent remains in the syringe.
Carefully turn the solvent vial, adapter and syringe assembly and place them upright on a clean
surface. Do not remove the syringe from the adapter at this point.



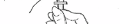

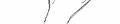























7. As explained for the first vial adapter, open now the second vial adapter by peeling back the
protective cover. Do not touch the vial adapter. Do not remove the adapter from the plastic
packaging. While holding the plastic adapter packaging, place the adapter over the SOMAVERT
vial and insert the piercing spike of the vial adapter all the way in through the rubber stopper of
the SOMAVERT vial, using a pushing motion (Fig. 5). Remove the plastic packaging from the
vial adapter and discard.
8. Disconnect the syringe from the solvent vial adapter and attach it to the vial adapter on the vial
of SOMAVERT. Tilt the vial of SOMAVERT, adapter and syringe assembly to the side and
gently inject the solvent down the inner side of the vial of SOMAVERT (Fig 6). Discard the
solvent vial as directed by your healthcare provider.
9. Hold the vial of SOMAVERT with the adapter and syringe still attached upright between your
hands and gently roll it to dissolve the powder (Fig. 7). DO NOT SHAKE THE VIAL. The
solution should be clear after the powder is dissolved. If the solution is cloudy or hazy, do not
inject it. Notify your pharmacy and request a replacement vial. Do not throw the vial away
because the pharmacy may request that you return it.
PREPARING THE INJECTION
10. Securely grasp the vial containing the SOMAVERT reconstituted solution, vial adapter and
syringe assembly. Carefully turn the vial, adapter and syringe assembly upside down. Bring to
eye level.
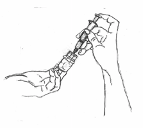
















11. As before, slide one hand carefully down the vial so that with your thumb and forefinger you
can securely grasp the neck of the vial, and with your other fingers, the upper portion of the
syringe. With the other hand, slowly pull the syringe plunger down to withdraw the full contents
of the vial (1 ml). (Fig.8).
Visually inspect the syringe for air bubbles. If bubbles are present, tap the syringe barrel until
the bubbles rise to the top of the syringe. Carefully push the plunger up to eject only the air
bubbles back into the vial. Recheck that 1 ml of the solution remains in the syringe. Carefully
turn the vial containing the SOMAVERT reconstituted solution, adapter and syringe assembly
and place them upright on a clean surface. Do not remove the syringe from the adapter at this
point.
12. Open the needle packaging so that only the end of the needle to be connected to the syringe is
exposed. The needle should be partially left in its protective packaging. Lay the needle with its
protective packaging on the tabletop. Disconnect the syringe from the vial. Discard the
protective packaging and attach the needle to the syringe. Keep the plastic cap on the needle
while preparing the site for injection (Fig. 9). Once reconstituted, SOMAVERT should be used
immediately. Please proceed to “STEP 2. GIVING THE INJECTION”.
b) NON VIAL ADAPTER METHOD
•
Wash your hands thoroughly.
•
Collect one vial of powder (SOMAVERT) and one vial of solvent (Water for Injections), one 3-ml
syringe with a 21-gauge, 1-inch detachable needle, one standard 1 ml insulin syringe, alcohol or
antiseptic swabs and a proper disposal container for used needles.
•
Inspect the expiry dates on both the vial label and the syringe label. They should not be used after
the month and year shown.
After reconstitution with 1 ml of solvent, 1 ml of the clear solution contains either 10 mg, 15 mg, or
20 mg pegvisomant.
PREPARING THE SOMAVERT DOSE FOR INJECTION
Remove the protective plastic caps from the tops of both vials. Take care not to touch the rubber vial
stoppers. At this point, the stoppers are clean. If the stoppers are touched or otherwise contaminated,













you must clean them with an antiseptic or alcohol swab before inserting a needle through the stopper.
Carefully remove the cap from the needle of the larger syringe (3 ml) and set the cap aside. This is the
solvent syringe.
1. Pull the plunger of the solvent syringe down to the1 ml mark. With one hand, securely hold the
vial of solvent and, with the other hand, insert the needle of the solvent syringe straight through
the center of the rubber stopper and deep into the vial. Gently push the plunger until the air is
injected into the vial. (Fig. 1)
2. Securely grasp the solvent vial and syringe assembly, with the needle still deeply inserted into
the vial. Carefully turn the vial and syringe assembly upside down. Bring to eye level. (Fig. 2)
3. Slide one hand carefully down the solvent vial so that with your thumb and forefinger you can
securely grasp the neck of the vial, and with your other fingers, the upper part of the syringe.













With the other hand, slowly pull the syringe plunger down to slightly past the 1 ml mark.
Examine the solution in the syringe for air bubbles. If bubbles are present, tap the syringe barrel
until the bubbles rise to the top of the syringe. Carefully push the plunger up to eject only the air
bubbles back into the vial. Recheck that 1 ml of solvent remains in the syringe, then withdraw
the needle from the vial. (Fig 3)
4. Insert the needle of the solvent syringe straight through the stopper of the vial with the powder
(SOMAVERT). Tilt the syringe to the side and gently inject the solvent down the inner side of
the vial of SOMAVERT. When the solvent syringe is empty, withdraw it from the vial. Discard
the solvent vial, syringe, and needle as directed by your healthcare provider. To minimise
accidental injury, recap the needle only if instructed to do so by your healthcare provider, and in
the manner demonstrated to you by your healthcare provider. (Fig 4)
5. Hold the vial of SOMAVERT upright between your hands and gently roll it to dissolve the
powder.
DO NOT SHAKE THE VIAL
. The solution should be clear after the powder is
dissolved. If the solution is cloudy or hazy, do not inject it. Notify your pharmacy and request a
replacement vial. Do not throw the vial away because the pharmacy may request that you return
it.
Inject SOMAVERT immediately.
(Fig. 5)
PREPARING THE INJECTION













6. Clean the rubber stopper of the vial of SOMAVERT with an antiseptic or alcohol swab. Remove
the cap from the syringe (1 ml). Pull the syringe plunger down to the 1-ml mark. With one hand,
securely hold the vial. With the other hand, insert the needle straight through the center of the
rubber stopper and deep into the vial. Gently push the plunger until the air is injected into the
vial. Securely grasp the vial and syringe assembly, with the needle still deeply inserted into the
vial. Carefully turn the vial and syringe assembly upside down. Bring to eye level. (Fig. 6)
7. As before, slide one hand carefully down the vial so that with your thumb and forefinger you
can securely grasp the neck of the vial, and with your other fingers, the upper portion of the
syringe. With the other hand, slowly pull the syringe plunger down to withdraw the full contents
of the vial (1 ml). To keep the needle tip within the liquid, you may have to slowly back it out of
the stopper as you draw out the liquid.
Visually inspect the syringe for air bubbles. If bubbles are present, tap the syringe barrel until
the bubbles rise to the top of the syringe. Carefully push the plunger up to eject only the air
bubbles back into the vial. Recheck that 1 ml of the solution remains in the syringe, then
withdraw the needle from the vial.
Recap the needle as directed by your health care provider to minimise accidental injury while
preparing the site for injection. (Fig. 7)
STEP 2. GIVING THE INJECTION
Choose an injection site on the upper arm, upper thigh, abdomen or buttocks. Always move on to a
different area with each day’s injection. It may be helpful to keep a record of each day’s injection site
as you take your daily dose of SOMAVERT. Do not use an area that has a rash or broken skin, or is
bruised or lumpy.
Clean the site with an antiseptic or alcohol swab, let the skin dry before injecting the product. Uncap
the needle if previously recapped.





With one hand, gently pinch up the skin at the site of injection. Hold the syringe with the other
hand, and in a single, smooth motion, push the needle completely into the skin straight down (at
a 90-degree angle). (Fig. A)
b. Be sure to keep the needle all the way into the skin while you slowly push the syringe plunger
down until the barrel is empty.
Release the pinched skin and pull the needle straight out. (Fig. B)
Do not rub the injection area. A small amount of bleeding may occur. If necessary, apply a
clean, dry cotton swab over the area and press gently for 1 or 2 minutes, or until the bleeding has
stopped. (Fig. C)
The syringe and needle should
NEVER
be reused. Dispose of the needle and syringe as instructed by
your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
All questions should be handled by a doctor, nurse or pharmacist familiar with SOMAVERT.
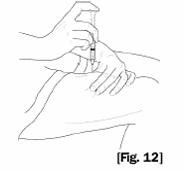

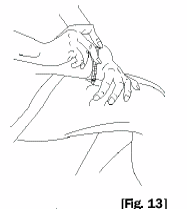










Source: European Medicines Agency
 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- If you wish to link to this page, you can do so by referring to the URL address below this line.
https://theodora.com/drugs/eu/somavert.html
Copyright © 1995-2021 ITA all rights reserved.
|




















































































































































































































































































































































































 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).










































