
10,536,338 (2023 est.)
noun: Swede(s)
adjective: Swedish
Swedish 79.6%, Syrian 1.9%, Iraqi 1.4%, Finnish 1.3%, other 15.8%
(2022 est.)
note: data represent the population by country of birth; the indigenous Sami people are estimated to number between 20,000 and 40,000
Swedish (official)
major-language sample(s):
The World Factbook, den obestridliga källan för grundläggande information. (Swedish)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
note: Finnish, Sami, Romani, Yiddish, and Meankieli are official minority languages
Swedish audio sample:
Church of Sweden (Lutheran) 53.9%, other (includes Roman Catholic, Orthodox, Baptist, Muslim, Jewish, and Buddhist) 8.9%, none or unspecified 37.2% (2021 est.)
note: estimates reflect registered members of faith communities eligible for state funding (not all religions are state-funded and not all people who identify with a particular religion are registered members) and the Church of Sweden
Sweden, the largest Nordic country in terms of size and population, is also Europe’s most sparsely populated. Most Swedish men and women agree that both partners should contribute to household income. Swedish society is very gender equal, which is reflected in the country’s public policies. A generous leave policy and high-quality subsidized childcare allows mothers and fathers to balance work and family life. Sweden’s income-replacement-based parental leave policy encourages women to establish themselves in the workforce before having children. In fact, Swedish women have one of the highest labor participation rates in Europe and one of its highest total fertility rates (TFR), the number of children women have in their lifetime. Postponement of parenthood has increased steadily. Since the late 1960s, marriage and divorce rates have declined, while non-marital cohabitation and births out of wedlock have increased rapidly. Sweden’s TFR has hovered for decades around 2, which is close to replacement level and among Europe’s highest.
Sweden experienced “the great emigration” between 1850 and the 1930s when, faced with famines, approximately 1.5 million Swedes sought a better life in the Americas and Australia. However, since World War II, Sweden has been a country of immigration. During World War II, thousands of refugees from neighboring countries worked in Swedish factories, agriculture, and forestry, replacing Swedish men who were called up for military service. During the 1950s and 1960s, Sweden joined the Geneva Convention and granted permanent residence to refugees from the USSR and the Warsaw Pact countries. During this period, Sweden also welcomed labor migrants, mainly from Finland and other Nordic countries, who bolstered the tax base needed to fund the country’s welfare programs.
Until 1971, labor migrants, particularly from Finland, southern Europe (including then Yugoslavia, Italy, and Greece) the Baltics, and Turkey, came to Sweden as its industries flourished. Companies recruited many of the workers, but others came on their own. Sweden’s labor demand eventually decreased, and the job market became saturated. The government restricted the flow of labor migrants, putting an end to labor migration from non-Nordic countries in 1972. From then until the 1990s, inflows consisted largely of asylum seekers from the Middle East, the Balkans, and South America, as well as persons looking to reunite with family members already in Sweden. The country began a new era of labor immigration in 2008, as companies were encouraged to hire non-EU workers. Among the largest source countries have been India, Thailand, and China. As of 2020, over a quarter of Sweden’s population had a migrant background.
0-14 years: 17.26% (male 936,274/female 882,347)
15-64 years: 62.05% (male 3,346,891/female 3,190,608)
65 years and over: 20.69% (2023 est.) (male 1,021,707/female 1,158,511)
total dependency ratio: 60.8
youth dependency ratio: 28.5
elderly dependency ratio: 32.3
potential support ratio: 3.1 (2021 est.)
total: 41 years (2023 est.)
male: 40 years
female: 42 years
0.51% (2023 est.)
10.8 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
9.5 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
3.8 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
most Swedes live in the south where the climate is milder and there is better connectivity to mainland Europe; population clusters are found all along the Baltic coast in the east; the interior areas of the north remain sparsely populated
urban population: 88.7% of total population (2023)
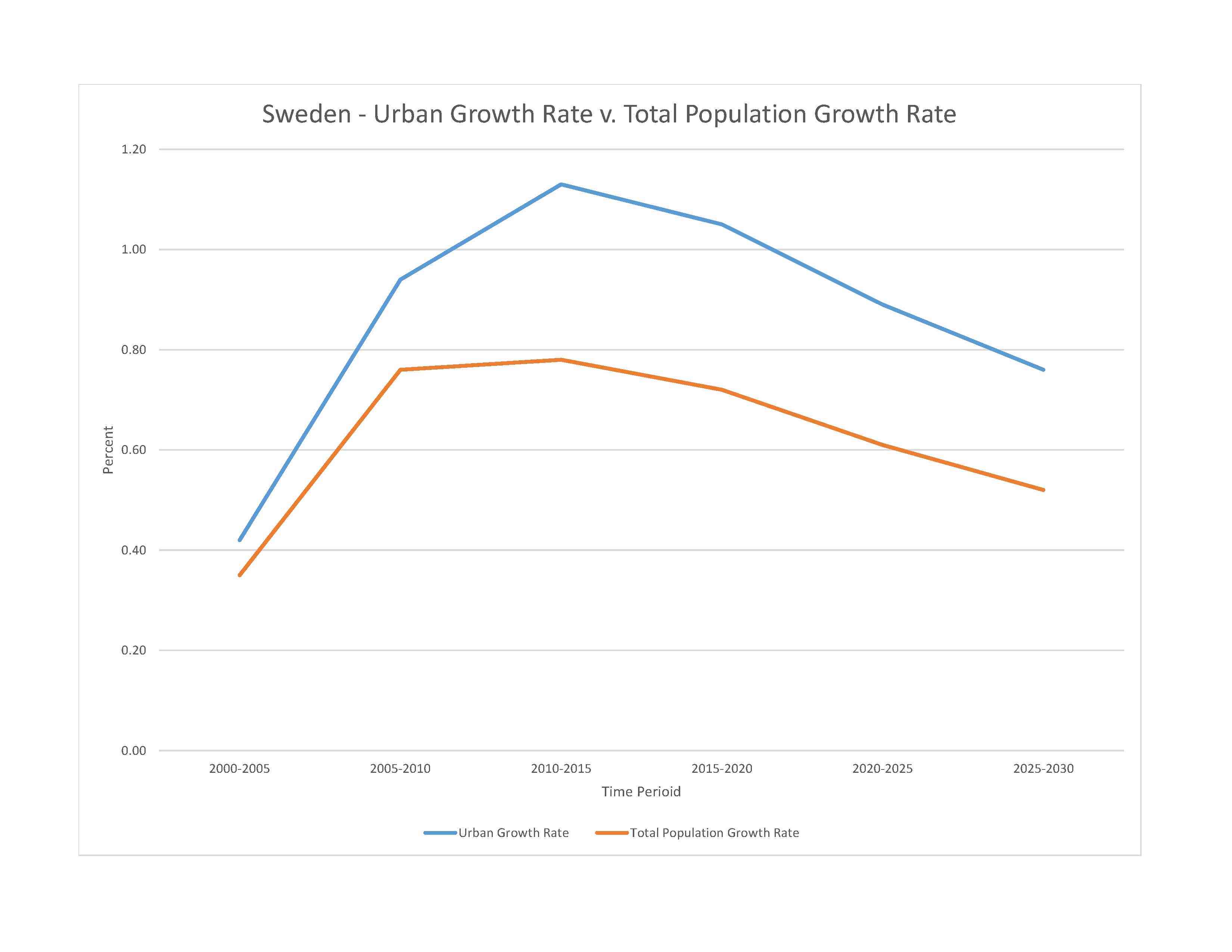
rate of urbanization: 0.89% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
1.700 million STOCKHOLM (capital) (2023)
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.88 male(s)/female
total population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
29.7 years (2020 est.)
5 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 2.3 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 2.5 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 2.1 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 82.8 years (2023 est.)
male: 81.1 years
female: 84.7 years
1.67 children born/woman (2023 est.)
0.8 (2023 est.)
70.3% (2017)
note: percent of women aged 16-49
improved: urban: 99.8% of population
rural: 99.7% of population
total: 99.8% of population
unimproved: urban: 0.2% of population
rural: 0.3% of population
total: 0.2% of population (2020 est.)
11.4% of GDP (2020)
7.09 physicians/1,000 population (2019)
2.1 beds/1,000 population (2018)
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
20.6% (2016)
total: 7.1 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 2.6 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 3.4 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 1 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.1 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 24% (2020 est.)
male: 29.8% (2020 est.)
female: 18.2% (2020 est.)
N/A
53.4% (2023 est.)
7.2% of GDP (2020 est.)
total population: NA
male: NA
female: NA
total: 20 years
male: 18 years
female: 21 years (2020)
NOTE: The information regarding Sweden on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Sweden 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Sweden 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.