
1,130,043 (2023 est.)
noun: liSwati (singular), emaSwati (plural); note - former term, Swazi(s), still used among English speakers
adjective: Swati; note - former term, Swazi, still used among English speakers
predominantly Swazi; smaller populations of other African ethnic groups, including the Zulu, as well as people of European ancestry
English (official, used for government business), siSwati (official)
Christian 90% (Zionist - a blend of Christianity and traditional African religions - 40%, Roman Catholic 20%, other Christian 30% - includes Anglican, Methodist, Church of Jesus Christ, Jehovah's Witness), Muslim 2%, other 8% (includes Baha'i, Buddhist, Hindu, indigenous, Jewish) (2015 est.)
Eswatini, a small, predominantly rural, landlocked country surrounded by South Africa and Mozambique, suffers from severe poverty and the world’s highest HIV/AIDS prevalence rate. A weak and deteriorating economy, high unemployment, rapid population growth, and an uneven distribution of resources all combine to worsen already persistent poverty and food insecurity, especially in rural areas. Erratic weather (frequent droughts and intermittent heavy rains and flooding), overuse of small plots, the overgrazing of cattle, and outdated agricultural practices reduce crop yields and further degrade the environment, exacerbating Eswatini's poverty and subsistence problems. Eswatini's extremely high HIV/AIDS prevalence rate – nearly 28% of adults have the disease – compounds these issues. Agricultural production has declined due to HIV/AIDS, as the illness causes households to lose manpower and to sell livestock and other assets to pay for medicine and funerals.
Swazis, mainly men from the country’s rural south, have been migrating to South Africa to work in coal, and later gold, mines since the late 19th century. Although the number of miners abroad has never been high in absolute terms because of Eswatini's small population, the outflow has had important social and economic repercussions. The peak of mining employment in South Africa occurred during the 1980s. Cross-border movement has accelerated since the 1990s, as increasing unemployment has pushed more Swazis to look for work in South Africa (creating a "brain drain" in the health and educational sectors); southern Swazi men have continued to pursue mining, although the industry has downsized. Women now make up an increasing share of migrants and dominate cross-border trading in handicrafts, using the proceeds to purchase goods back in Eswatini. Much of today’s migration, however, is not work-related but focuses on visits to family and friends, tourism, and shopping.
0-14 years: 32.16% (male 181,886/female 181,491)
15-64 years: 63.88% (male 336,243/female 385,599)
65 years and over: 3.97% (2023 est.) (male 16,654/female 28,170)
total dependency ratio: 64
youth dependency ratio: 57.4
elderly dependency ratio: 6.5
potential support ratio: 15.3 (2021 est.)
total: 24.4 years (2023 est.)
male: 23.1 years
female: 25.5 years
0.72% (2023 est.)
22.8 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
9.5 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
-6.1 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
because of its mountainous terrain, the population distribution is uneven throughout the country, concentrating primarily in valleys and plains as shown in this 
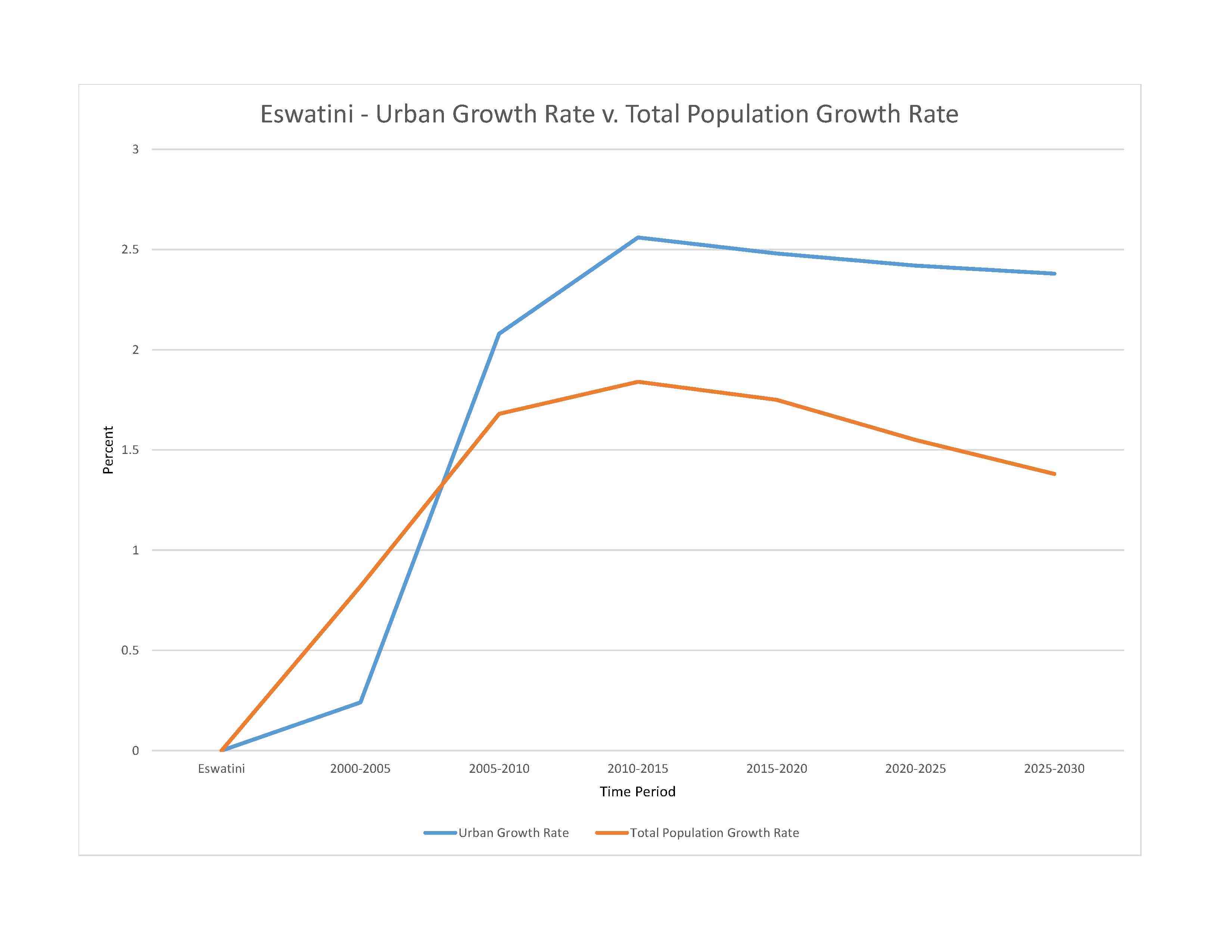
urban population: 24.8% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 2.42% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
68,000 MBABANE (capital) (2018)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.87 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.59 male(s)/female
total population: 0.9 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
437 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
total: 38.1 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 42.3 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 33.9 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 60.2 years (2023 est.)
male: 58.2 years
female: 62.3 years
2.41 children born/woman (2023 est.)
1.19 (2023 est.)
66.1% (2014)
improved: urban: 97.5% of population
rural: 74.8% of population
total: 80.3% of population
unimproved: urban: 2.5% of population
rural: 25.2% of population
total: 19.7% of population (2020 est.)
6.5% of GDP (2020)
0.14 physicians/1,000 population (2020)
2.1 beds/1,000 population (2011)
improved: urban: 92.3% of population
rural: 83.9% of population
total: 85.9% of population
unimproved: urban: 7.7% of population
rural: 16.1% of population
total: 14.1% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: intermediate (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: sexually transmitted diseases: HIV/ADIS, hepatitis B (2024)
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
16.5% (2016)
total: 7.68 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 2.45 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.06 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 5.17 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 9.2% (2020 est.)
male: 16.5% (2020 est.)
female: 1.8% (2020 est.)
5.8% (2014)
37.1% (2023 est.)
5% of GDP (2021 est.)
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 88.4%
male: 88.3%
female: 88.5% (2018)
total: 13 years
male: 13 years
female: 12 years (2013)
NOTE: The information regarding Eswatini on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Eswatini 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Eswatini 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.