
2,468,569 (2023 est.)
noun: Gambian(s)
adjective: Gambian
Mandinka/Jahanka 33.3%, Fulani/Tukulur/Lorobo 18.2%, Wolof 12.9%, Jola/Karoninka 11%, Serahuleh 7.2%, Serer 3.5%, other 4%, non-Gambian 9.9% (2019-20 est.)
English (official), Mandinka, Wolof, Fula, other indigenous vernaculars
Muslim 96.4%, Christian 3.5%, other or none 0.1% (2019-20 est.)
The Gambia’s youthful age structure – approximately 55% of the population is under the age of 25 as of 2021 – is likely to persist because the country’s total fertility rate remains strong at nearly 4 children per woman. The overall literacy rate is around 50%, and is significantly lower for women than for men. At least 70% of the populace are farmers who are reliant on rain-fed agriculture and cannot afford improved seeds and fertilizers. Crop failures caused by droughts between 2011 and 2013 increased poverty, food shortages, and malnutrition.
The Gambia is a source country for migrants and a transit and destination country for migrants and refugees. Since the 1980s, economic deterioration, drought, and high unemployment, especially among youths, have driven both domestic migration (largely urban) and migration abroad (legal and illegal). Emigrants are largely skilled workers, including doctors and nurses, and provide a significant amount of remittances. The top receiving countries for Gambian emigrants are Spain, the US, Nigeria, Senegal, and the UK. While the Gambia and Spain do not share historic, cultural, or trade ties, rural Gambians have migrated to Spain in large numbers because of its proximity and the availability of jobs in its underground economy (this flow slowed following the onset of Spain’s late 2007 economic crisis).
The Gambia’s role as a host country to refugees is a result of wars in several of its neighboring West African countries. Since 2006, refugees from the Casamance conflict in Senegal have replaced their pattern of flight and return with permanent settlement in The Gambia, often moving in with relatives along the Senegal-Gambia border. The strain of providing for about 7,400 Casamance refugees increased poverty among Gambian villagers. The number of refugees decreased to around 3,500 by 2022.
0-14 years: 38.86% (male 484,113/female 475,134)
15-64 years: 57.57% (male 700,049/female 721,057)
65 years and over: 3.57% (2023 est.) (male 38,954/female 49,262)
total dependency ratio: 85
youth dependency ratio: 80.5
elderly dependency ratio: 4.5
potential support ratio: 22.2 (2021 est.)
total: 19.9 years (2023 est.)
male: 19.5 years
female: 20.3 years
2.23% (2023 est.)
28 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
5.7 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
settlements are found scattered along the Gambia River; the largest communities, including the capital of Banjul, and the country's largest city, Serekunda, are found at the mouth of the Gambia River along the Atlantic coast as shown in this 
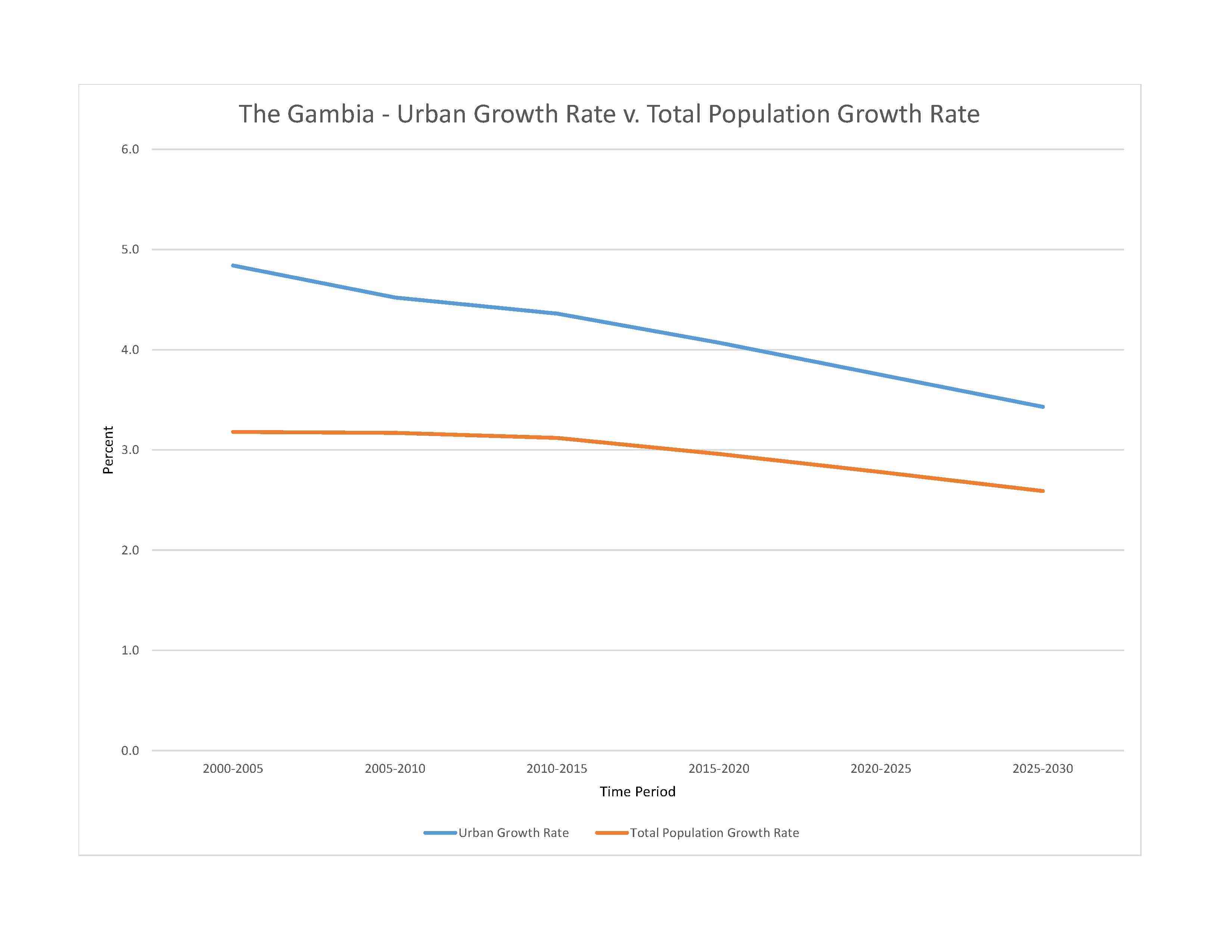
urban population: 64.5% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 3.75% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
481,000 BANJUL (capital) (2023)
note: includes the local government areas of Banjul and Kanifing
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.79 male(s)/female
total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
20.7 years (2019/20 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
458 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 36.4 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 39.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 32.9 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 68 years (2023 est.)
male: 66.3 years
female: 69.8 years
3.66 children born/woman (2023 est.)
1.8 (2023 est.)
18.9% (2019/20)
improved: urban: 91.8% of population
rural: 85.7% of population
total: 89.5% of population
unimproved: urban: 8.2% of population
rural: 14.3% of population
total: 10.5% of population (2020 est.)
2.6% of GDP (2020)
0.08 physicians/1,000 population (2020)
1.1 beds/1,000 population (2011)
improved: urban: 75.8% of population
rural: 33.6% of population
total: 60% of population
unimproved: urban: 24.2% of population
rural: 66.4% of population
total: 40% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: very high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and sexually transmitted diseases: hepatitis B (2024)
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
10.3% (2016)
total: 2.67 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.21 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.02 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 2.44 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 11.1% (2020 est.)
male: 21.4% (2020 est.)
female: 0.8% (2020 est.)
11.6% (2019/20)
60.9% (2023 est.)
women married by age 15: 5.6%
women married by age 18: 23.1%
men married by age 18: 0.2% (2020 est.)
2.8% of GDP (2020 est.)
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 58.1%
male: 65.2%
female: 51.2% (2021)
NOTE: The information regarding Gambia The on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Gambia The 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Gambia The 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.