
13,400,541 (2023 est.)
noun: Rwandan(s)
adjective: Rwandan
Hutu, Tutsi, Twa
Kinyarwanda (official, universal Bantu vernacular) 93.2%, French (official)
major-language sample(s):
Inkoranya nzimbuzi y'isi, isoko fatizo y'amakuru y'ibanze. (Kinyarwanda)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Christian 95.9% (Protestant 57.7% [includes Adventist 12.6%], Roman Catholic 38.2%), Muslim 2.1%, other 1% (includes traditional, Jehovah's Witness), none 1.1% (2019-20 est.)
Rwanda’s fertility rate declined sharply during the last decade, as a result of the government’s commitment to family planning, the increased use of contraceptives, and a downward trend in ideal family size. Increases in educational attainment, particularly among girls, and exposure to social media also contributed to the reduction in the birth rate. The average number of births per woman decreased from a 5.6 in 2005 to 4.5 in 2016 and 3.3 in 2022. Despite these significant strides in reducing fertility, Rwanda’s birth rate remains very high and will continue to for an extended period of time because of its large population entering reproductive age. Because Rwanda is one of the most densely populated countries in Africa, its persistent high population growth and increasingly small agricultural landholdings will put additional strain on families’ ability to raise foodstuffs and access potable water. These conditions will also hinder the government’s efforts to reduce poverty and prevent environmental degradation.
The UNHCR recommended that effective 30 June 2013 countries invoke a cessation of refugee status for those Rwandans who fled their homeland between 1959 and 1998, including the 1994 genocide, on the grounds that the conditions that drove them to seek protection abroad no longer exist. The UNHCR’s decision is controversial because many Rwandan refugees still fear persecution if they return home, concerns that are supported by the number of Rwandans granted asylum since 1998 and by the number exempted from the cessation. Rwandan refugees can still seek an exemption or local integration, but host countries are anxious to send the refugees back to Rwanda and are likely to avoid options that enable them to stay. Conversely, Rwanda itself hosts approximately 125,000 refugees as of 2022; virtually all of them fleeing conflict in neighboring Burundi and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
0-14 years: 37.95% (male 2,569,106/female 2,515,849)
15-64 years: 59.1% (male 3,844,259/female 4,075,978)
65 years and over: 2.95% (2023 est.) (male 158,647/female 236,702)
total dependency ratio: 72.5
youth dependency ratio: 67.1
elderly dependency ratio: 5.4
potential support ratio: 18.4 (2021 est.)
total: 20.5 years (2023 est.)
male: 19.8 years
female: 21.2 years
1.68% (2023 est.)
25.7 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
5.8 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
-3.2 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
one of Africa's most densely populated countries; large concentrations tend to be in the central regions and along the shore of Lake Kivu in the west as shown in this 
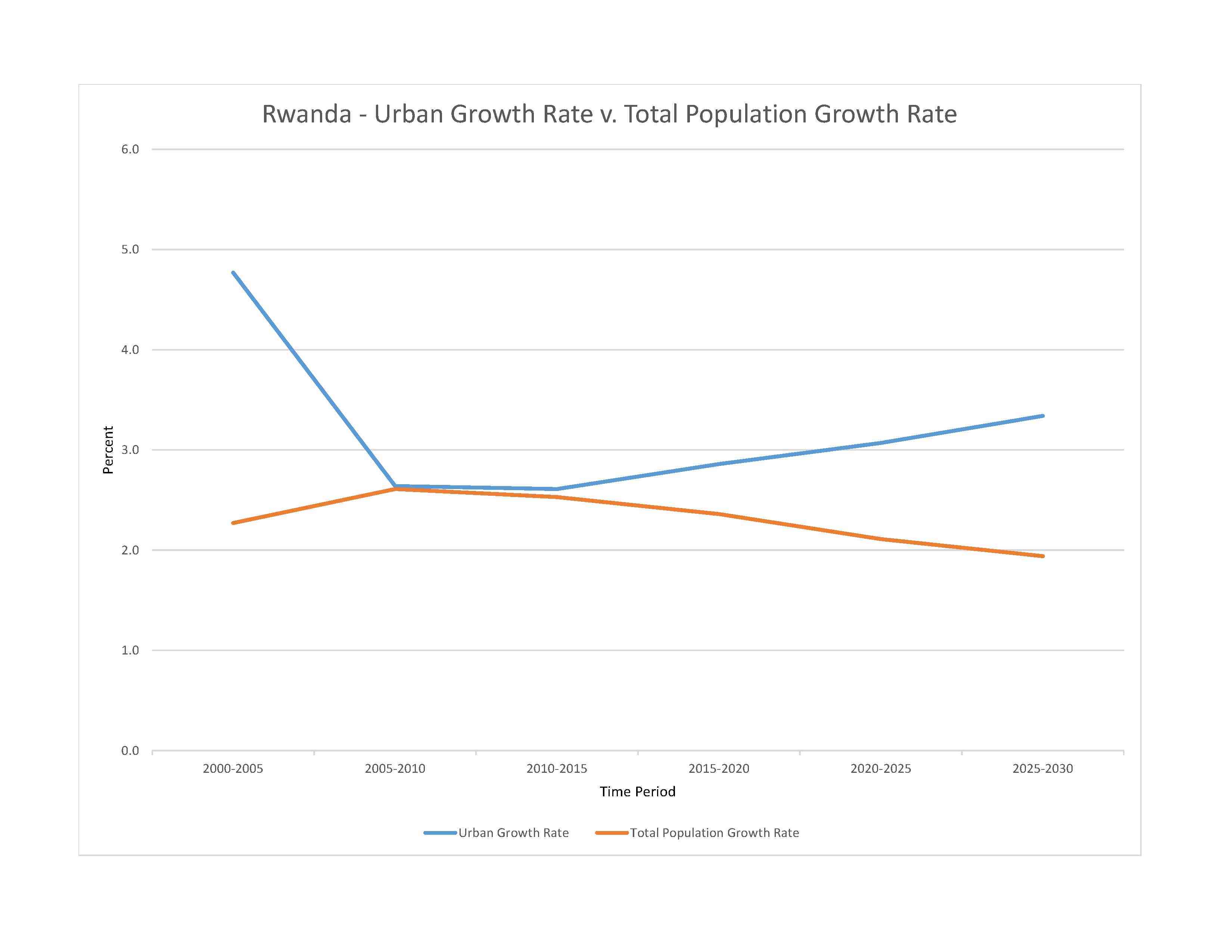
urban population: 17.9% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 3.07% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
1.248 million KIGALI (capital) (2023)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.94 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.67 male(s)/female
total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
23 years (2019/20 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
259 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 25.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 28.1 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 23.1 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 66.2 years (2023 est.)
male: 64.2 years
female: 68.2 years
3.23 children born/woman (2023 est.)
1.59 (2023 est.)
64.1% (2019/20)
improved: urban: 92.3% of population
rural: 80.7% of population
total: 82.7% of population
unimproved: urban: 7.7% of population
rural: 19.3% of population
total: 17.3% of population (2020 est.)
7.3% of GDP (2020)
0.12 physicians/1,000 population (2019)
improved: urban: 89.1% of population
rural: 83.2% of population
total: 84.2% of population
unimproved: urban: 10.9% of population
rural: 16.8% of population
total: 15.8% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: very high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and sexually transmitted diseases: HIV/AIDS (2024)
animal contact diseases: rabies
5.8% (2016)
total: 6.35 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.23 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.03 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.09 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 6 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 13.7% (2020 est.)
male: 20.1% (2020 est.)
female: 7.2% (2020 est.)
7.7% (2019/20)
50.4% (2023 est.)
women married by age 18: 0.4% (2020 est.)
3.8% of GDP (2021 est.)
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 75.9%
male: 78.7%
female: 73.3% (2021)
total: 11 years
male: 11 years
female: 11 years (2019)
NOTE: The information regarding Rwanda on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Rwanda 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Rwanda 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.