
22,489,126 (2023 est.)
noun: Burkinabe (singular and plural)
adjective: Burkinabe
Mossi 52%, Fulani (Peuhl) 8.4%, Gurma 7%, Bobo 4.9%, Gurunsi 4.6%, Senufo 4.5%, Bissa 3.7%, Lobi 2.4%, Dagara 2.4%, Tuareg/Bella 1.9%, Dyula 0.8%, unspecified/no answer 0.3%, other 7.2% (2010 est.)
Mossi 52.9%, Fula 7.8%, Gourmantche 6.8%, Dyula 5.7%, Bissa 3.3%, Gurunsi 3.2%, French (official) 2.2%, Bwamu 2%, Dagara 2%, San 1.7%, Marka 1.6%, Bobo 1.5%, Senufo 1.5%, Lobi 1.2%, other 6.6% (2019 est.)
Muslim 63.8%, Roman Catholic 20.1%, Animiste 9%, Protestant 6.2%, other 0.2%, none 0.7% (2019 est.)
Burkina Faso has a young age structure – the result of declining mortality combined with steady high fertility – and continues to experience rapid population growth, which is putting increasing pressure on the country’s limited arable land. Almost 65% of the population is under the age of 25 as of 2020, and the population is growing at 2.5% annually. Mortality rates, especially those of infants and children, have decreased because of improved health care, hygiene, and sanitation, but women continue to have an average of more than 4 children. Even if fertility were substantially reduced, today’s large cohort entering their reproductive years would sustain high population growth for the foreseeable future. Only about a third of the population is literate and unemployment is widespread, dampening the economic prospects of Burkina Faso’s large working-age population.
Migration has traditionally been a way of life for Burkinabe, with seasonal migration being replaced by stints of up to two years abroad. Cote d’Ivoire remains the top destination, although it has experienced periods of internal conflict. Under French colonization, Burkina Faso became a main labor source for agricultural and factory work in Cote d’Ivoire. Burkinabe also migrated to Ghana, Mali, and Senegal for work between the world wars. Burkina Faso attracts migrants from Cote d’Ivoire, Ghana, and Mali, who often share common ethnic backgrounds with the Burkinabe. Despite its food shortages and high poverty rate, Burkina Faso has become a destination for refugees in recent years and hosts about 33,600 Malian refugees as of October 2022.
(2018)
0-14 years: 42.19% (male 4,813,760/female 4,674,649)
15-64 years: 54.62% (male 5,899,774/female 6,383,134)
65 years and over: 3.19% (2023 est.) (male 305,233/female 412,576)
total dependency ratio: 87.4
youth dependency ratio: 82.6
elderly dependency ratio: 4.8
potential support ratio: 20.9 (2021 est.)
total: 18.5 years (2023 est.)
male: 17.7 years
female: 19.3 years
2.46% (2023 est.)
32.7 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
7.5 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
-0.6 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
Most of the population is located in the center and south. Nearly one-third of the population lives in cities. The capital and largest city is Ouagadougou (Ouaga), with a population of 1.8 million as shown in this 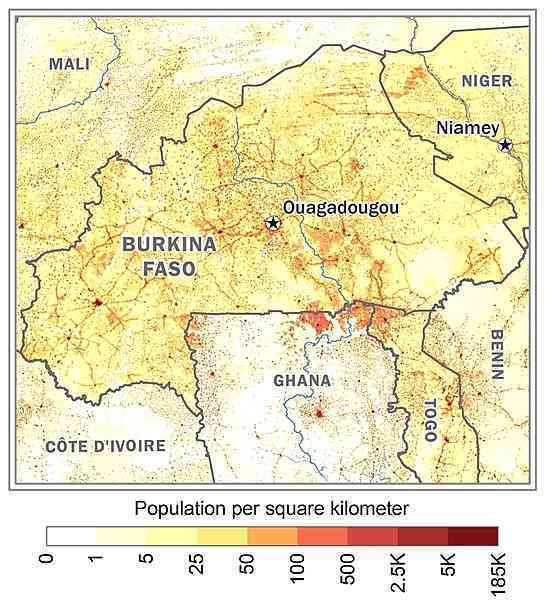
(2019)
urban population: 32.5% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 4.75% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)

3.204 million OUAGADOUGOU (capital), 1.129 million Bobo-Dioulasso (2023)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.92 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.74 male(s)/female
total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
20.1 years (2021 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
264 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 48.2 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 52.4 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 43.8 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 63.8 years (2023 est.)
male: 62 years
female: 65.7 years
4.14 children born/woman (2023 est.)
2.04 (2023 est.)
35.3% (2020/21)
improved: urban: 94.7% of population
rural: 71.3% of population
total: 78.5% of population
unimproved: urban: 5.3% of population
rural: 28.7% of population
total: 21.5% of population (2020 est.)
6.7% of GDP (2020)
0.09 physicians/1,000 population (2019)
0.4 beds/1,000 population
improved: urban: 90.8% of population
rural: 37.7% of population
total: 54% of population
unimproved: urban: 9.2% of population
rural: 62.3% of population
total: 46% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: very high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever, malaria, and sexually transmitted diseases: hepatitis B (2024)
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
note: on 31 August 2023, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued a Travel Alert for polio in Africa; Burkina Faso is currently considered a high risk to travelers for circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV); vaccine-derived poliovirus (VDPV) is a strain of the weakened poliovirus that was initially included in oral polio vaccine (OPV) and that has changed over time and behaves more like the wild or naturally occurring virus; this means it can be spread more easily to people who are unvaccinated against polio and who come in contact with the stool or respiratory secretions, such as from a sneeze, of an “infected” person who received oral polio vaccine; the CDC recommends that before any international travel, anyone unvaccinated, incompletely vaccinated, or with an unknown polio vaccination status should complete the routine polio vaccine series; before travel to any high-risk destination, the CDC recommends that adults who previously completed the full, routine polio vaccine series receive a single, lifetime booster dose of polio vaccine
5.6% (2016)
total: 7.28 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 1 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.08 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.31 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 5.88 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 14.3% (2020 est.)
male: 22.1% (2020 est.)
female: 6.4% (2020 est.)
17.5% (2021)
73.5% (2023)
5.5% of GDP (2020 est.)
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 46%
male: 54.5%
female: 37.8% (2021)
total: 9 years
male: 9 years
female: 9 years (2020)
NOTE: The information regarding Burkina Faso on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Burkina Faso 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Burkina Faso 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.