
5,946,984 (2023 est.)
noun: Dane(s)
adjective: Danish
Danish (includes Greenlandic (who are predominantly Inuit) and Faroese) 84.2%, Turkish 1.1%, other 14.7% (largest groups are Polish, Romanian, Syrian, Ukrainian, German, and Iraqi) (2023 est.)
note: data represent population by country of origin
Danish, Faroese, Greenlandic (an Inuit dialect), German (small minority); note - English is the predominant second language
major-language sample(s):
Verdens Faktabog, den uundværlig kilde til grundlæggende oplysninger. (Danish)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Danish audio sample:
Evangelical Lutheran (official) 74.7%, Muslim 5.5%, other/none/unspecified (denominations of less than 1% each in descending order of size include Roman Catholic, Jehovah's Witness, Serbian Orthodox Christian, Jewish, Baptist, Buddhist, Church of Jesus Christ, Pentecostal, and nondenominational Christian) 19.8% (2019 est.)
Modern immigration to Denmark began in the 1960s and 1970s, although immigration, primarily from the Nordic countries and Western Europe, has earlier roots. Dutch migrants came in the 16th century and Germans in the 18th, in both cases to work in agriculture. Between the late 19th century and World War I, Denmark absorbed unskilled Polish, German, and Swedish labor migrants in significant numbers, sometimes at the request of the Danish Government. Between the two World Wars, Denmark received many Eastern European, Jewish, and German migrants. It wasn’t until after World War II, that refugees began seeking sanctuary in Demark, including a large number of German refugees and later Hungarians, Czechs, and Polish Jews. Denmark also imported foreign labor during the 1960s, mainly from Turkey, the former Yugoslavia, and Pakistan. Although the “guest worker” program was halted in 1973, immigrants continued to arrive to be reunited with family members who were already in Denmark as refugees or as guest workers. Non-European refugees came from Chile, Uganda, and Vietnam. In the 1990s, Denmark began receiving migrants and refugees from new places, including Russia, Hungary, Bosnia, Iran, Iraq, and Lebanon. Despite raising more restrictions on immigration, in the 2000s, Denmark continued to receive asylum seekers, particularly from Afghanistan, Iraq, Somalia, and the former Yugoslavia, as well as labor migrants from new EU member states.
In more recent years, Denmark has severely limited its refugee intake, aiming to accept as few refugees outside of the UN resettlement program as possible. In the mid-2010s, Denmark passed legislation enabling it to withdraw temporary protective status as soon as conditions in the home country, as determined by Denmark, have improved. This policy has lead Denmark, to deem Damascus and other areas in Syria safe for return, making it the only country in Europe to do so. Consequently, some Syrian refugees have had their residency status revoked, and they are detained in deportation centers because Denmark does not have diplomatic relations with Syria and, therefore, cannot send them back. Copenhagen hopes its stricter policies will discourage asylum seekers, particularly those from non-Western countries.
0-14 years: 16.24% (male 495,887/female 469,976)
15-64 years: 63.13% (male 1,900,182/female 1,854,222)
65 years and over: 20.63% (2023 est.) (male 566,363/female 660,354)
total dependency ratio: 57.3
youth dependency ratio: 25.4
elderly dependency ratio: 31.9
potential support ratio: 3.1 (2021 est.)
total: 42.2 years (2023 est.)
male: 41 years
female: 43.3 years
0.44% (2023 est.)
11.3 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
9.6 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
2.7 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
with excellent access to the North Sea, Skagerrak, Kattegat, and the Baltic Sea, population centers tend to be along coastal areas, particularly in Copenhagen and the eastern side of the country's mainland
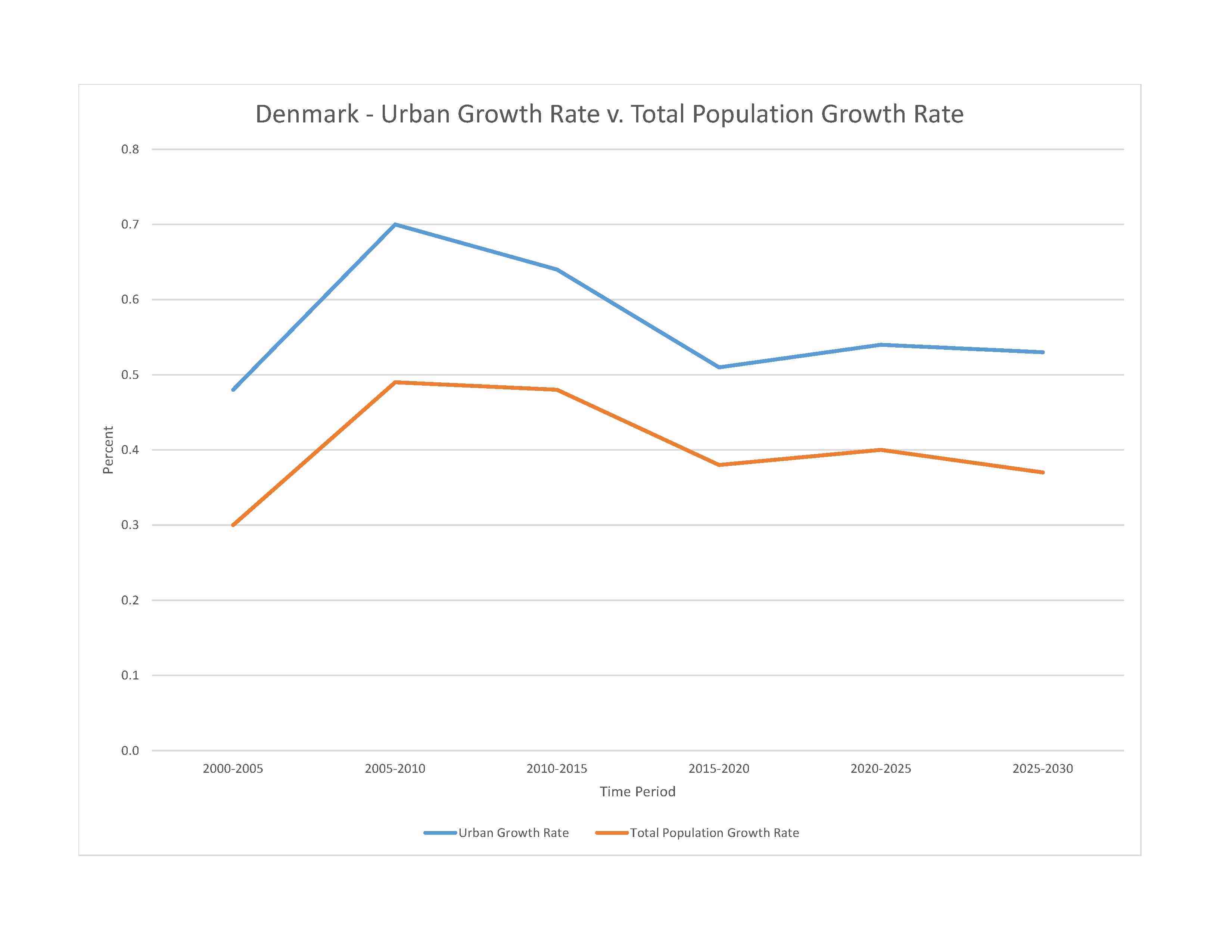
urban population: 88.5% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 0.54% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
1.381 million COPENHAGEN (capital) (2023)
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.86 male(s)/female
total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
29.8 years (2020 est.)
5 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 3 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 3.4 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 2.5 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 81.9 years (2023 est.)
male: 80 years
female: 83.9 years
1.77 children born/woman (2023 est.)
0.86 (2023 est.)
N/A
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
10.5% of GDP (2020)
4.23 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
2.6 beds/1,000 population (2019)
improved: urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved: urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
19.7% (2016)
total: 9.16 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 3.42 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 4.08 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 1.66 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 17.5% (2020 est.)
male: 17.8% (2020 est.)
female: 17.1% (2020 est.)
N/A
59.6% (2023 est.)
women married by age 18: 0.7% (2021 est.)
6.4% of GDP (2020 est.)
total population: NA
male: NA
female: NA
total: 19 years
male: 18 years
female: 19 years (2020)
NOTE: The information regarding Denmark on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Denmark 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Denmark 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.