
976,143 (2023 est.)
noun: Djiboutian(s)
adjective: Djiboutian
Somali 60%, Afar 35%, other 5% (mostly Yemeni Arab, also French, Ethiopian, and Italian)
French (official), Arabic (official), Somali, Afar
Sunni Muslim 94% (nearly all Djiboutians), other 6% (mainly foreign-born residents - Shia Muslim, Christian, Hindu, Jewish, Baha'i, and atheist)
Djibouti is a poor, predominantly urban country, characterized by high rates of illiteracy, unemployment, and childhood malnutrition. Approximately 70% of the population lives in cities and towns (predominantly in the capital, Djibouti). The rural population subsists primarily on nomadic herding. Prone to droughts and floods, the country has few natural resources and must import more than 80% of its food from neighboring countries or Europe. Health care, particularly outside the capital, is limited by poor infrastructure, shortages of equipment and supplies, and a lack of qualified personnel. More than a third of health care recipients are migrants because the services are still better than those available in their neighboring home countries. The nearly universal practice of female genital cutting reflects Djibouti’s lack of gender equality and is a major contributor to obstetrical complications and its high rates of maternal and infant mortality. A 1995 law prohibiting the practice has never been enforced.
Because of its political stability and its strategic location at the confluence of East Africa and the Gulf States along the Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea, Djibouti is a key transit point for migrants and asylum seekers heading for the Gulf States and beyond. Each year some 100,000 people, mainly Ethiopians and some Somalis, journey through Djibouti, usually to the port of Obock, to attempt a dangerous sea crossing to Yemen. However, with the escalation of the ongoing Yemen conflict, Yemenis began fleeing to Djibouti in March 2015, with almost 20,000 arriving by August 2017. Most Yemenis remain unregistered and head for Djibouti City rather than seeking asylum at one of Djibouti’s three spartan refugee camps. Djibouti has been hosting refugees and asylum seekers, predominantly Somalis and lesser numbers of Ethiopians and Eritreans, at camps for 20 years, despite lacking potable water, food shortages, and unemployment.
0-14 years: 28.65% (male 140,365/female 139,299)
15-64 years: 67.21% (male 284,488/female 371,529)
65 years and over: 4.15% (2023 est.) (male 17,757/female 22,705)
total dependency ratio: 50.6
youth dependency ratio: 47.5
elderly dependency ratio: 6.9
potential support ratio: 14.4 (2021 est.)
total: 26 years (2023 est.)
male: 24.1 years
female: 27.6 years
1.93% (2023 est.)
22 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
7.1 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
4.4 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
most densely populated areas are in the east; the largest city is Djibouti, with a population over 600,000; no other city in the country has a total population over 50,000 as shown in this 
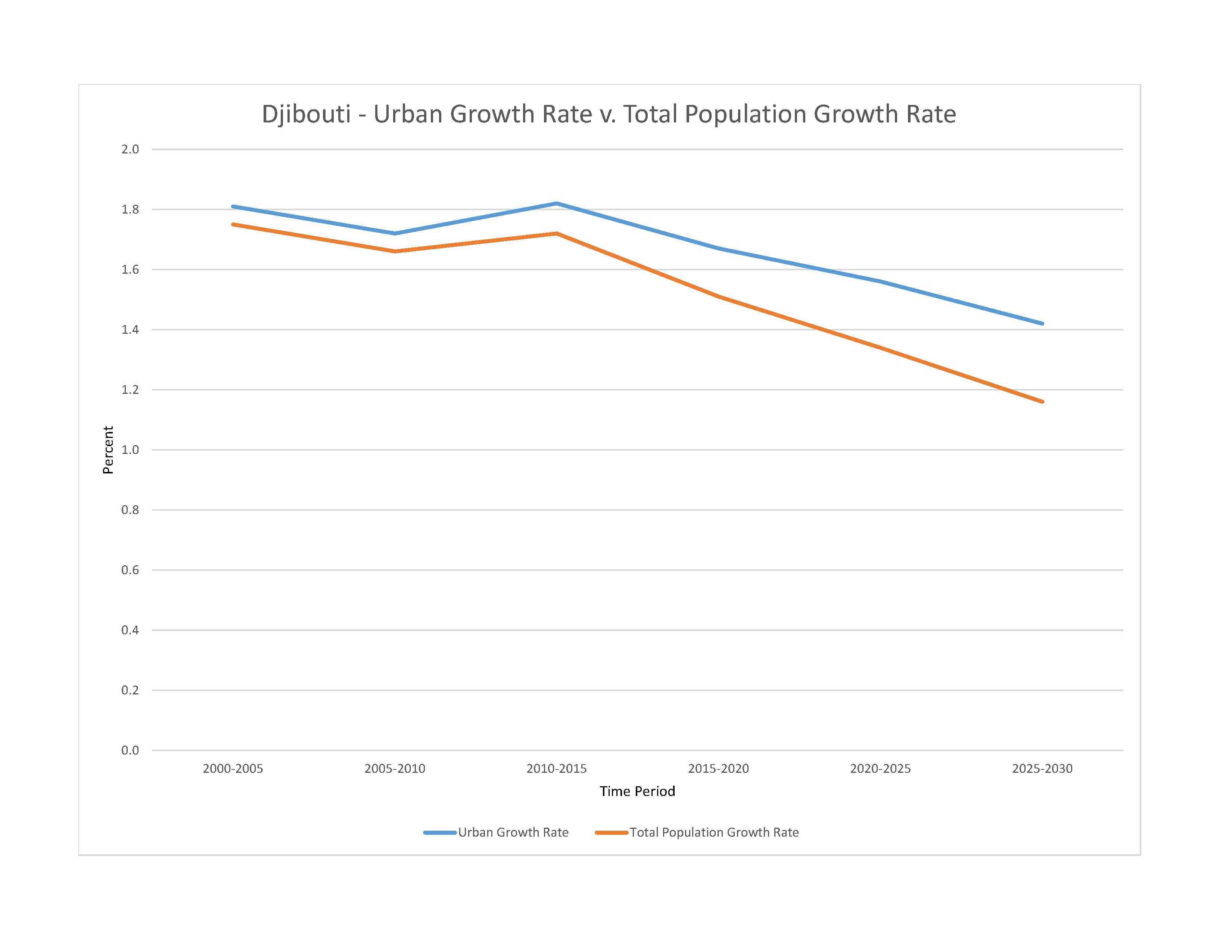
urban population: 78.6% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 1.56% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
600,000 DJIBOUTI (capital) (2023)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.77 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.78 male(s)/female
total population: 0.83 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
234 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 46 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 53.1 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 38.7 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 65.6 years (2023 est.)
male: 63 years
female: 68.3 years
2.13 children born/woman (2023 est.)
1.05 (2023 est.)
19% (2012)
improved: urban: 99.7% of population
rural: 59.3% of population
total: 90.8% of population
unimproved: urban: 0.3% of population
rural: 40.7% of population
total: 9.2% of population (2020 est.)
2% of GDP (2020)
0.22 physicians/1,000 population (2014)
1.4 beds/1,000 population (2017)
improved: urban: 87.7% of population
rural: 24.2% of population
total: 73.8% of population
unimproved: urban: 12.3% of population
rural: 75.8% of population
total: 26.2% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever, and sexually transmitted diseases: hepatitis B (2024)
13.5% (2016)
total: 0.21 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.05 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.02 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.14 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
16.2% (2019)
50.6% (2023 est.)
women married by age 15: 1.4%
women married by age 18: 6.5% (2019 est.)
3.6% of GDP (2018 est.)
total population: NA
male: NA
female: NA
total: 7 years
male: 7 years
female: 7 years (2011)
NOTE: The information regarding Djibouti on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Djibouti 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Djibouti 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.