
33,846,114 (2023 est.)
noun: Ghanaian(s)
adjective: Ghanaian
Akan 45.7%, Mole-Dagbani 18.5%, Ewe 12.8%, Ga-Dangme 7.1%, Gurma 6.4%, Guan 3.2%, Grusi 2.7%, Mande 2%, other 1.6% (2021 est.)
Asante 16%, Ewe 14%, Fante 11.6%, Boron (Brong) 4.9%, Dagomba 4.4%, Dangme 4.2%, Dagarte (Dagaba) 3.9%, Kokomba 3.5%, Akyem 3.2%, Ga 3.1%, other 31.2% (2010 est.)
note: English is the official language
Christian 71.3% (Pentecostal/Charismatic 31.6%, Protestant 17.4%, Catholic 10%, other 12.3%), Muslim 19.9%, traditionalist 3.2%, other 4.5%, none 1.1% (2021 est.)
Ghana has a young age structure, with approximately 56% of the population under the age of 25 as of 2020. Its total fertility rate fell significantly during the 1980s and 1990s but has stalled at around four children per woman for the last few years. Fertility remains higher in the northern region than the Greater Accra region. On average, desired fertility has remained stable for several years; urban dwellers want fewer children than rural residents. Increased life expectancy, due to better health care, nutrition, and hygiene, and reduced fertility have increased Ghana’s share of elderly persons; Ghana’s proportion of persons aged 60+ is among the highest in Sub-Saharan Africa. Poverty has declined in Ghana, but it remains pervasive in the northern region, which is susceptible to droughts and floods and has less access to transportation infrastructure, markets, fertile farming land, and industrial centers. The northern region also has lower school enrollment, higher illiteracy, and fewer opportunities for women.
Ghana was a country of immigration in the early years after its 1957 independence, attracting labor migrants largely from Nigeria and other neighboring countries to mine minerals and harvest cocoa – immigrants composed about 12% of Ghana’s population in 1960. In the late 1960s, worsening economic and social conditions discouraged immigration, and hundreds of thousands of immigrants, mostly Nigerians, were expelled.
During the 1970s, severe drought and an economic downturn transformed Ghana into a country of emigration; neighboring Cote d’Ivoire was the initial destination. Later, hundreds of thousands of Ghanaians migrated to Nigeria to work in its booming oil industry, but most were deported in 1983 and 1985 as oil prices plummeted. Many Ghanaians then turned to more distant destinations, including other parts of Africa, Europe, and North America, but the majority continued to migrate within West Africa. Since the 1990s, increased emigration of skilled Ghanaians, especially to the US and the UK, drained the country of its health care and education professionals. Internally, poverty and other developmental disparities continue to drive Ghanaians from the north to the south, particularly to its urban centers.
0-14 years: 37.72% (male 6,445,288/female 6,321,989)
15-64 years: 57.92% (male 9,420,940/female 10,181,376)
65 years and over: 4.36% (2023 est.) (male 660,991/female 815,530)
total dependency ratio: 68.7
youth dependency ratio: 62.9
elderly dependency ratio: 5.9
potential support ratio: 17 (2021 est.)
total: 21.3 years (2023 est.)
male: 20.4 years
female: 22.2 years
2.19% (2023 est.)
28 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
6 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
-0.2 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
population is concentrated in the southern half of the country, with the highest concentrations being on or near the Atlantic coast as shown in this 
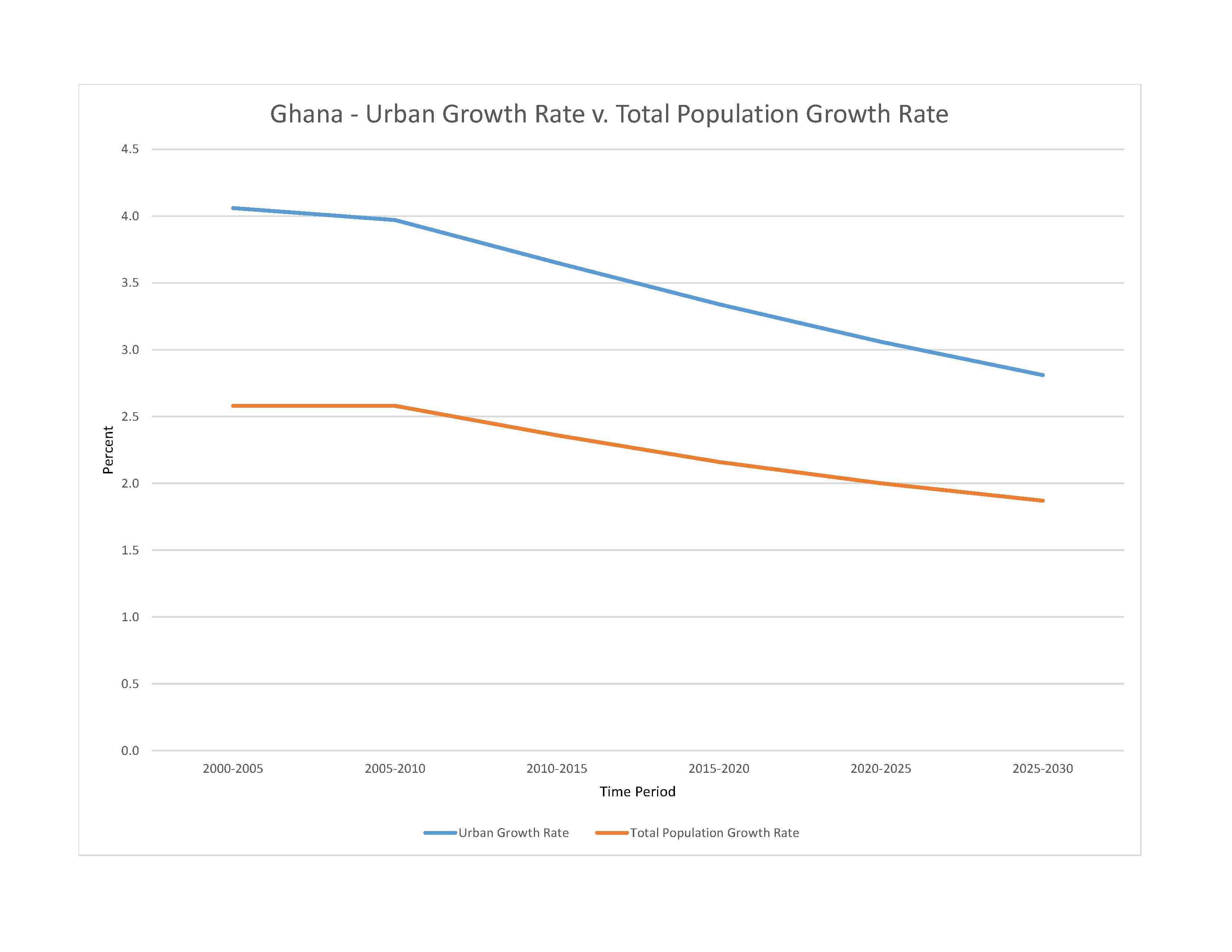
urban population: 59.2% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 3.06% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
3.768 million Kumasi, 2.660 million ACCRA (capital), 1.078 million Sekondi Takoradi (2023)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.93 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.81 male(s)/female
total population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
22.1 years (2022 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
263 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 31.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 35.3 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 28.4 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 69.7 years (2023 est.)
male: 68.1 years
female: 71.4 years
3.61 children born/woman (2023 est.)
1.78 (2023 est.)
27.2% (2017/18)
improved: urban: 98.7% of population
rural: 83.8% of population
total: 92.4% of population
unimproved: urban: 1.3% of population
rural: 16.2% of population
total: 7.6% of population (2020 est.)
4% of GDP (2020)
0.17 physicians/1,000 population (2020)
0.9 beds/1,000 population (2011)
improved: urban: 84.8% of population
rural: 52.8% of population
total: 71.1% of population
unimproved: urban: 15.2% of population
rural: 47.2% of population
total: 28.9% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: very high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and sexually transmitted diseases: hepatitis B (2024)
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
note: on 31 August 2023, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued a Travel Alert for polio in Africa; Ghana is currently considered a high risk to travelers for circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV); vaccine-derived poliovirus (VDPV) is a strain of the weakened poliovirus that was initially included in oral polio vaccine (OPV) and that has changed over time and behaves more like the wild or naturally occurring virus; this means it can be spread more easily to people who are unvaccinated against polio and who come in contact with the stool or respiratory secretions, such as from a sneeze, of an “infected” person who received oral polio vaccine; the CDC recommends that before any international travel, anyone unvaccinated, incompletely vaccinated, or with an unknown polio vaccination status should complete the routine polio vaccine series; before travel to any high-risk destination, the CDC recommends that adults who previously completed the full, routine polio vaccine series receive a single, lifetime booster dose of polio vaccine
10.9% (2016)
total: 1.59 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.53 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.05 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.39 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.61 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 3.5% (2020 est.)
male: 6.6% (2020 est.)
female: 0.3% (2020 est.)
12.6% (2017/18)
54.3% (2023 est.)
women married by age 15: 5%
women married by age 18: 19.3%
men married by age 18: 3.9% (2018 est.)
3.9% of GDP (2018 est.)
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 79%
male: 83.5%
female: 74.5% (2018)
total: 12 years
male: 12 years
female: 12 years (2020)
NOTE: The information regarding Ghana on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Ghana 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Ghana 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.