
5,506,280 (2023 est.)
noun: Liberian(s)
adjective: Liberian
Kpelle 20.2%, Bassa 13.6%, Grebo 9.9%, Gio 7.9%, Mano 7.2%, Kru 5.5%, Lorma 4.8%, Krahn 4.5%, Kissi, 4.3%, Mandingo 4.2%, Vai 3.8%, Gola 3.8%, Gbandi 2.9%, Mende 1.7%, Sapo 1%, Belle 0.7%, Dey 0.3%, other Liberian ethnic group 0.4%, other African 3%, non-African 0.2% (2022 est.)
English 20% (official) and 27 indigenous languages, including Liberian English (encompassing several varieties of English spoken by Liberians)
Christian 84.9%, Muslim 12%, Traditional 0.5%, other 0.1%, none 2.6% (2022 est.)
Liberia’s high fertility rate of nearly 5 children per woman and large youth cohort – more than 60% of the population is under the age of 25 as of 2020 – will sustain a high dependency ratio for many years to come. Significant progress has been made in preventing child deaths, despite a lack of health care workers and infrastructure. Infant and child mortality have dropped nearly 70% since 1990; the annual reduction rate of about 5.4% is the highest in Africa.
Nevertheless, Liberia’s high maternal mortality rate remains among the world’s worst; it reflects a high unmet need for family planning services, frequency of early childbearing, lack of quality obstetric care, high adolescent fertility, and a low proportion of births attended by a medical professional. Female mortality is also increased by the prevalence of female genital cutting (FGC), which is practiced by 10 of Liberia’s 16 tribes and affects more than two-thirds of women and girls. FGC is an initiation ritual performed in rural bush schools, which teach traditional beliefs on marriage and motherhood and are an obstacle to formal classroom education for Liberian girls.
Liberia has been both a source and a destination for refugees. During Liberia’s 14-year civil war (1989-2003), more than 250,000 people became refugees and another half million were internally displaced. Between 2004 and the cessation of refugee status for Liberians in June 2012, the UNHCR helped more than 155,000 Liberians to voluntarily repatriate, while others returned home on their own. Some Liberian refugees spent more than two decades living in other West African countries. Between 2011 and 2022, more than 300,000 Ivoirian refugees in Liberia have been repatriated; as of year-end 2022, less than 2,300 Ivoirian refugees were still living in Liberia.
0-14 years: 42.69% (male 1,187,795/female 1,162,699)
15-64 years: 54.5% (male 1,486,582/female 1,514,163)
65 years and over: 2.82% (2023 est.) (male 75,258/female 79,783)
total dependency ratio: 79.7
youth dependency ratio: 73.7
elderly dependency ratio: 6
potential support ratio: 16.7 (2021 est.)
total: 19.7 years (2023 est.)
male: 19.6 years
female: 19.9 years
2.37% (2023 est.)
33 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
8.5 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
-0.8 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
more than half of the population lives in urban areas, with approximately one-third living within an 80-km radius of Monrovia as shown in this 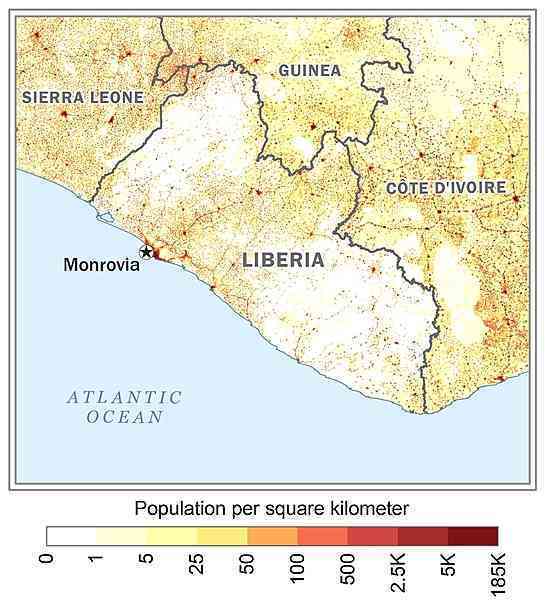
urban population: 53.6% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 3.41% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)

1.678 million MONROVIA (capital) (2023)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.94 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
19.1 years (2019/20 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
652 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 56.1 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 61.5 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 50.6 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 61.3 years (2023 est.)
male: 59.7 years
female: 63 years
4.03 children born/woman (2023 est.)
1.98 (2023 est.)
24.9% (2019/20)
improved: urban: 96.2% of population
rural: 70.6% of population
total: 84% of population
unimproved: urban: 3.8% of population
rural: 29.4% of population
total: 16% of population (2020 est.)
9.5% of GDP (2020)
0.05 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
improved: urban: 68% of population
rural: 25.2% of population
total: 47.5% of population
unimproved: urban: 32% of population
rural: 74.8% of population
total: 52.5% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: very high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and sexually transmitted diseases: hepatitis B (2024)
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
aerosolized dust or soil contact diseases: Lassa fever
9.9% (2016)
total: 3.12 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.38 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.44 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 2.28 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.02 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 8.2% (2020 est.)
male: 14.3% (2020 est.)
female: 2% (2020 est.)
10.9% (2019/20)
48.7% (2023 est.)
women married by age 15: 5.8% NA
women married by age 18: 24.9% NA
men married by age 18: 8.4% (2020 est.)
2.7% of GDP (2021 est.)
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 48.3%
male: 62.7%
female: 34.1% (2017)
NOTE: The information regarding Liberia on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Liberia 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Liberia 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.