
32,513,805 (2023 est.)
noun: Mozambican(s)
adjective: Mozambican
African 99% (Makhuwa, Tsonga, Lomwe, Sena, and others), Mestizo 0.8%, other (includes European, Indian, Pakistani, Chinese) 0.2% (2017 est.)
Makhuwa 26.1%, Portuguese (official) 16.6%, Tsonga 8.6%, Nyanja 8.1, Sena 7.1%, Lomwe 7.1%, Chuwabo 4.7%, Ndau 3.8%, Tswa 3.8%, other Mozambican languages 11.8%, other 0.5%, unspecified 1.8% (2017 est.)
Roman Catholic 27.2%, Muslim 18.9%, Zionist Christian 15.6%, Evangelical/Pentecostal 15.3%, Anglican 1.7%, other 4.8%, none 13.9%, unspecified 2.5% (2017 est.)
Mozambique is a poor, sparsely populated country with high fertility and mortality rates and a rapidly growing youthful population – 45% of the population is younger than 15, as of 2020. Mozambique’s high poverty rate is sustained by natural disasters, disease, high population growth, low agricultural productivity, and the unequal distribution of wealth. The country’s birth rate is among the world’s highest, averaging around 5 children per woman (and higher in rural areas) for at least the last three decades. The sustained high level of fertility reflects gender inequality, low contraceptive use, early marriages and childbearing, and a lack of education, particularly among women. The high population growth rate is somewhat restrained by the country’s high HIV/AIDS and overall mortality rates. Mozambique ranks among the worst in the world for HIV/AIDS prevalence, HIV/AIDS deaths, and life expectancy at birth, as of 2022.
Mozambique is predominantly a country of emigration, but internal, rural-urban migration has begun to grow. Mozambicans, primarily from the country’s southern region, have been migrating to South Africa for work for more than a century. Additionally, approximately 1.7 million Mozambicans fled to Malawi, South Africa, and other neighboring countries between 1979 and 1992 to escape from civil war. Labor migrants have usually been men from rural areas whose crops have failed or who are unemployed and have headed to South Africa to work as miners; multiple generations of the same family often become miners. Since the abolition of apartheid in South Africa in 1991, other job opportunities have opened to Mozambicans, including in the informal and manufacturing sectors, but mining remains their main source of employment.
0-14 years: 45% (male 7,413,197/female 7,217,953)
15-64 years: 52.1% (male 8,153,175/female 8,787,792)
65 years and over: 2.9% (2023 est.) (male 461,904/female 479,784)
total dependency ratio: 86.1
youth dependency ratio: 81.3
elderly dependency ratio: 4.8
potential support ratio: 20.8 (2021 est.)
total: 17.2 years (2023 est.)
male: 16.6 years
female: 17.8 years
2.55% (2023 est.)
36.9 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
9.9 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
-1.5 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
three large populations clusters are found along the southern coast between Maputo and Inhambane, in the central area between Beira and Chimoio along the Zambezi River, and in and around the northern cities of Nampula, Cidade de Nacala, and Pemba; the northwest and southwest are the least populated areas as shown in this 
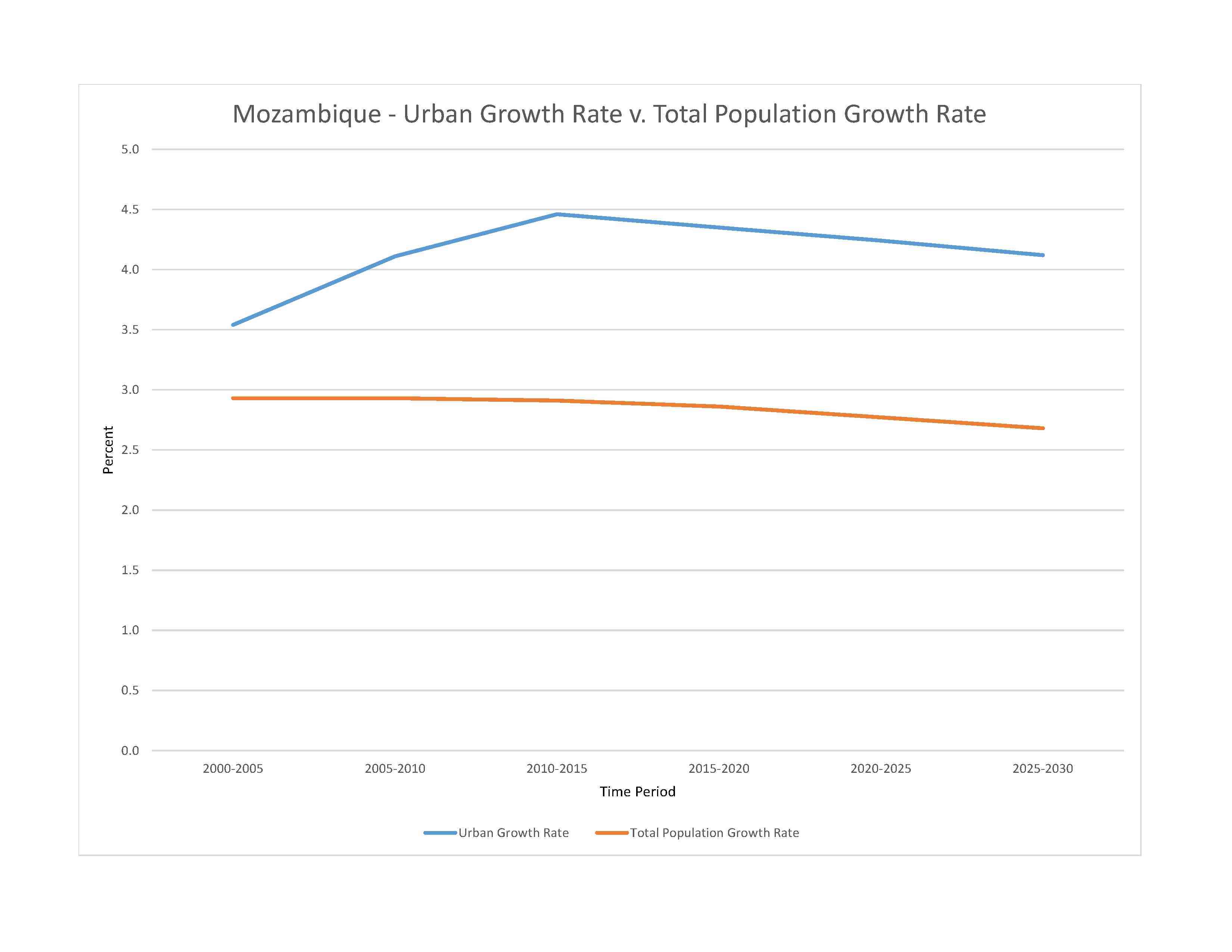
urban population: 38.8% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 4.24% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
1.852 million Matola, 1.163 million MAPUTO (capital), 969,000 Nampula (2023)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.93 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.96 male(s)/female
total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
19.2 years (2011 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 20-49
127 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 59.8 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 61.7 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 57.8 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 57.7 years (2023 est.)
male: 56.4 years
female: 59 years
4.74 children born/woman (2023 est.)
2.33 (2023 est.)
27.1% (2015)
improved: urban: 93.4% of population
rural: 61.5% of population
total: 73.3% of population
unimproved: urban: 6.6% of population
rural: 38.5% of population
total: 26.7% of population (2020 est.)
7.6% of GDP (2020)
0.09 physicians/1,000 population (2020)
0.7 beds/1,000 population (2011)
improved: urban: 71.9% of population (2015 est.)
rural: 24.7% of population
total: 42.2% of population
unimproved: urban: 28.1% of population
rural: 75.3% of population
total: 57.8% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: very high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and sexually transmitted diseases: HIV/AIDS (2024)
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
note: on 31 August 2023, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued a Travel Alert for polio in Africa; Mozambique is currently considered a high risk to travelers for circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV); vaccine-derived poliovirus (VDPV) is a strain of the weakened poliovirus that was initially included in oral polio vaccine (OPV) and that has changed over time and behaves more like the wild or naturally occurring virus; this means it can be spread more easily to people who are unvaccinated against polio and who come in contact with the stool or respiratory secretions, such as from a sneeze, of an “infected” person who received oral polio vaccine; the CDC recommends that before any international travel, anyone unvaccinated, incompletely vaccinated, or with an unknown polio vaccination status should complete the routine polio vaccine series; before travel to any high-risk destination, the CDC recommends that adults who previously completed the full, routine polio vaccine series receive a single, lifetime booster dose of polio vaccine
7.2% (2016)
total: 1.46 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 1.03 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.22 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.21 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 14.3% (2020 est.)
male: 23% (2020 est.)
female: 5.6% (2020 est.)
14.6% (2019/20)
63.7% (2023 est.)
6.3% of GDP (2020 est.)
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 63.4%
male: 74.1%
female: 53.8% (2021)
total: 10 years
male: 10 years
female: 9 years (2017)
NOTE: The information regarding Mozambique on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Mozambique 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Mozambique 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.