
32,440,172 (2023 est.)
noun: Peruvian(s)
adjective: Peruvian
Mestizo (mixed Amerindian and White) 60.2%, Amerindian 25.8%, White 5.9%, African descent 3.6%, other (includes Chinese and Japanese descent) 1.2%, unspecified 3.3% (2017 est.)
Spanish (official) 82.9%, Quechua (official) 13.6%, Aymara (official) 1.6%, Ashaninka 0.3%, other native languages (includes a large number of minor Amazonian languages) 0.8%, other (includes foreign languages and sign language) 0.2%, none 0.1%, unspecified 0.7% (2017 est.)
major-language sample(s):
La Libreta Informativa del Mundo, la fuente indispensable de información básica. (Spanish)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Spanish audio sample:
Roman Catholic 60%, Christian 14.6% (includes Evangelical 11.1%, other 3.5%), other 0.3%, none 4%, unspecified 21.1% (2017 est.)
Peru's urban and coastal communities have benefited much more from recent economic growth than rural, Afro-Peruvian, indigenous, and poor populations of the Amazon and mountain regions. The poverty rate has dropped substantially during the last decade but remains stubbornly high at about 30% (more than 55% in rural areas). After remaining almost static for about a decade, Peru's malnutrition rate began falling in 2005, when the government introduced a coordinated strategy focusing on hygiene, sanitation, and clean water. School enrollment has improved, but achievement scores reflect ongoing problems with educational quality. Many poor children temporarily or permanently drop out of school to help support their families. About a quarter to a third of Peruvian children aged 6 to 14 work, often putting in long hours at hazardous mining or construction sites.
Peru was a country of immigration in the 19th and early 20th centuries, but has become a country of emigration in the last few decades. Beginning in the 19th century, Peru brought in Asian contract laborers mainly to work on coastal plantations. Populations of Chinese and Japanese descent - among the largest in Latin America - are economically and culturally influential in Peru today. Peruvian emigration began rising in the 1980s due to an economic crisis and a violent internal conflict, but outflows have stabilized in the last few years as economic conditions have improved. Nonetheless, more than 2 million Peruvians have emigrated in the last decade, principally to the US, Spain, and Argentina.
0-14 years: 26.04% (male 4,311,243/female 4,136,849)
15-64 years: 65.94% (male 10,452,598/female 10,937,233)
65 years and over: 8.02% (2023 est.) (male 1,134,587/female 1,467,662)
total dependency ratio: 53
youth dependency ratio: 37.1
elderly dependency ratio: 13.1
potential support ratio: 7.9 (2021 est.)
total: 30.1 years (2023 est.)
male: 29.1 years
female: 31.1 years
0.5% (2023 est.)
17 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
11 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
-0.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
approximately one-third of the population resides along the desert coastal belt in the west, with a strong focus on the capital city of Lima; the Andean highlands, or sierra, which is strongly identified with the country's Amerindian population, contains roughly half of the overall population; the eastern slopes of the Andes, and adjoining rainforest, are sparsely populated
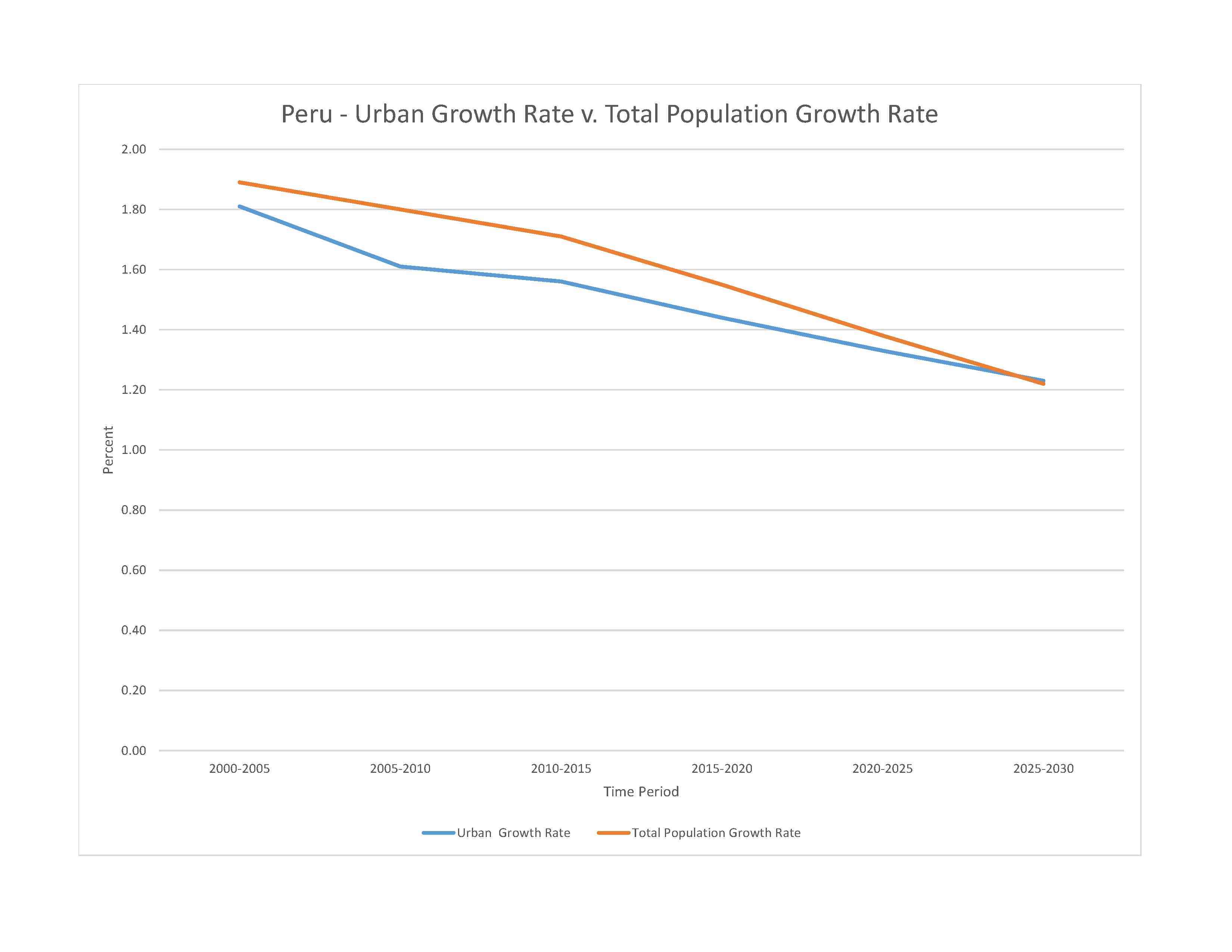
urban population: 78.9% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 1.33% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
11.204 million LIMA (capital), 959,000 Arequipa, 904,000 Trujillo (2023)
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.77 male(s)/female
total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
21.9 years (2013 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
69 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 10.8 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 11.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 9.7 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 68.9 years (2023 est.)
male: 65.4 years
female: 72.7 years
2.18 children born/woman (2023 est.)
1.06 (2023 est.)
77.4% (2020)
improved: urban: 97.2% of population
rural: 82.4% of population
total: 94% of population
unimproved: urban: 2.8% of population
rural: 17.6% of population
total: 6% of population (2020 est.)
6.3% of GDP (2020)
1.37 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
1.6 beds/1,000 population (2017)
improved: urban: 93.6% of population
rural: 65.3% of population
total: 87.4% of population
unimproved: urban: 6.4% of population
rural: 34.7% of population
total: 12.6% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: very high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever, malaria, Bartonellosis (Oroya fever), and sexually transmitted diseases: hepatitis B (2024)
19.7% (2016)
total: 5.74 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 3.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.46 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 2.26 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 8.1% (2020 est.)
male: 13.2% (2020 est.)
female: 3% (2020 est.)
2.1% (2021)
51.2% (2023 est.)
women married by age 15: 2%
women married by age 18: 14.1% (2020 est.)
4% of GDP (2021 est.)
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 94.5%
male: 97%
female: 92% (2020)
total: 15 years
male: 15 years
female: 15 years (2017)
NOTE: The information regarding Peru on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Peru 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Peru 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.