
116,434,200 (2023 est.)
noun: Filipino(s)
adjective: Philippine
Tagalog 26%, Bisaya/Binisaya 14.3%, Ilocano 8%, Cebuano 8%, Illonggo 7.9%, Bikol/Bicol 6.5%, Waray 3.8%, Kapampangan 3%, Maguindanao 1.9%, Pangasinan 1.9%, other local ethnicities 18.5%, foreign ethnicities 0.2% (2020 est.)
Tagalog 39.9%, Bisaya/Binisaya 16%, Hiligaynon/Ilonggo 7.3%, Ilocano 7.1%, Cebuano 6.5%, Bikol/Bicol 3.9%, Waray 2.6%, Kapampangan 2.4%, Maguindanao 1.4%, Pangasinan/Panggalato 1.3%, other languages/dialects 11.2%, unspecified 0.4% (2020 est.)
major-language sample(s):
Ang World Factbook, ang mapagkukunan ng kailangang impormasyon. (Tagalog)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
note: data represent percentage of households; unspecified Filipino (based on Tagalog) and English are official languagesTaga; eight major dialects - Tagalog, Cebuano, Ilocano, Hiligaynon or Ilonggo, Bicol, Waray, Pampango, and Pangasinan
Tagalog audio sample:
Roman Catholic 78.8%, Muslim 6.4%, Iglesia ni Cristo 2.6%, other Christian 3.9%, other 8.2%, none/unspecified
The Philippines is an ethnically diverse country that is in the early stages of demographic transition. Its fertility rate has dropped steadily since the 1950s. The decline was more rapid after the introduction of a national population program in the 1970s in large part due to the increased use of modern contraceptive methods, but fertility has decreased more slowly in recent years. The country’s total fertility rate (TFR) – the average number of births per woman – dropped below 5 in the 1980s, below 4 in the 1990s, and below 3 in the 2010s. TFR continues to be above replacement level at 2.9 and even higher among the poor, rural residents, and the less-educated. Significant reasons for elevated TFR are the desire for more than two children, in part because children are a means of financial assistance and security for parents as they age, particularly among the poor.
The Philippines are the source of one of the world’s largest emigrant populations, much of which consists of legal temporary workers known as Overseas Foreign Workers or OFWs. As of 2019, there were 2.2 million OFWs. They work in a wide array of fields, most frequently in services (such as caregivers and domestic work), skilled trades, and construction but also in professional fields, including nursing and engineering. OFWs most often migrate to Middle Eastern countries, but other popular destinations include Hong Kong, China, and Singapore, as well as employment on ships. Filipino seafarers make up 35-40% of the world’s seafarers, as of 2014. Women OFWs, who work primarily in domestic services and entertainment, have outnumbered men since 1992.
Migration and remittances have been a feature of Philippine culture for decades. The government has encouraged and facilitated emigration, regulating recruitment agencies and adopting legislation to protect the rights of migrant workers. Filipinos began emigrating to the US and Hawaii early in the 20th century. In 1934, US legislation limited Filipinos to 50 visas per year except during labor shortages, causing emigration to plummet. It was not until the 1960s, when the US and other destination countries – Canada, Australia, and New Zealand – loosened their immigration policies, that Filipino emigration expanded and diversified. The government implemented an overseas employment program in the 1970s, promoting Filipino labor to Gulf countries needing more workers for their oil industries. Filipino emigration increased rapidly. The government had intended for international migration to be temporary, but a lack of jobs and poor wages domestically, the ongoing demand for workers in the Gulf countries, and new labor markets in Asia continue to spur Philippine emigration.
0-14 years: 30.49% (male 18,133,279/female 17,366,394)
15-64 years: 64.06% (male 37,667,819/female 36,923,236)
65 years and over: 5.45% (2023 est.) (male 2,516,561/female 3,826,911)
total dependency ratio: 56.2
youth dependency ratio: 47.8
elderly dependency ratio: 8.3
potential support ratio: 12 (2021 est.)
total: 25.4 years (2023 est.)
male: 24.9 years
female: 26 years
1.58% (2023 est.)
22.2 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
6.3 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
population concentrated where good farmlands lie; highest concentrations are northwest and south-central Luzon, the southeastern extension of Luzon, and the islands of the Visayan Sea, particularly Cebu and Negros; Manila is home to one-eighth of the entire national population
urban population: 48.3% of total population (2023)
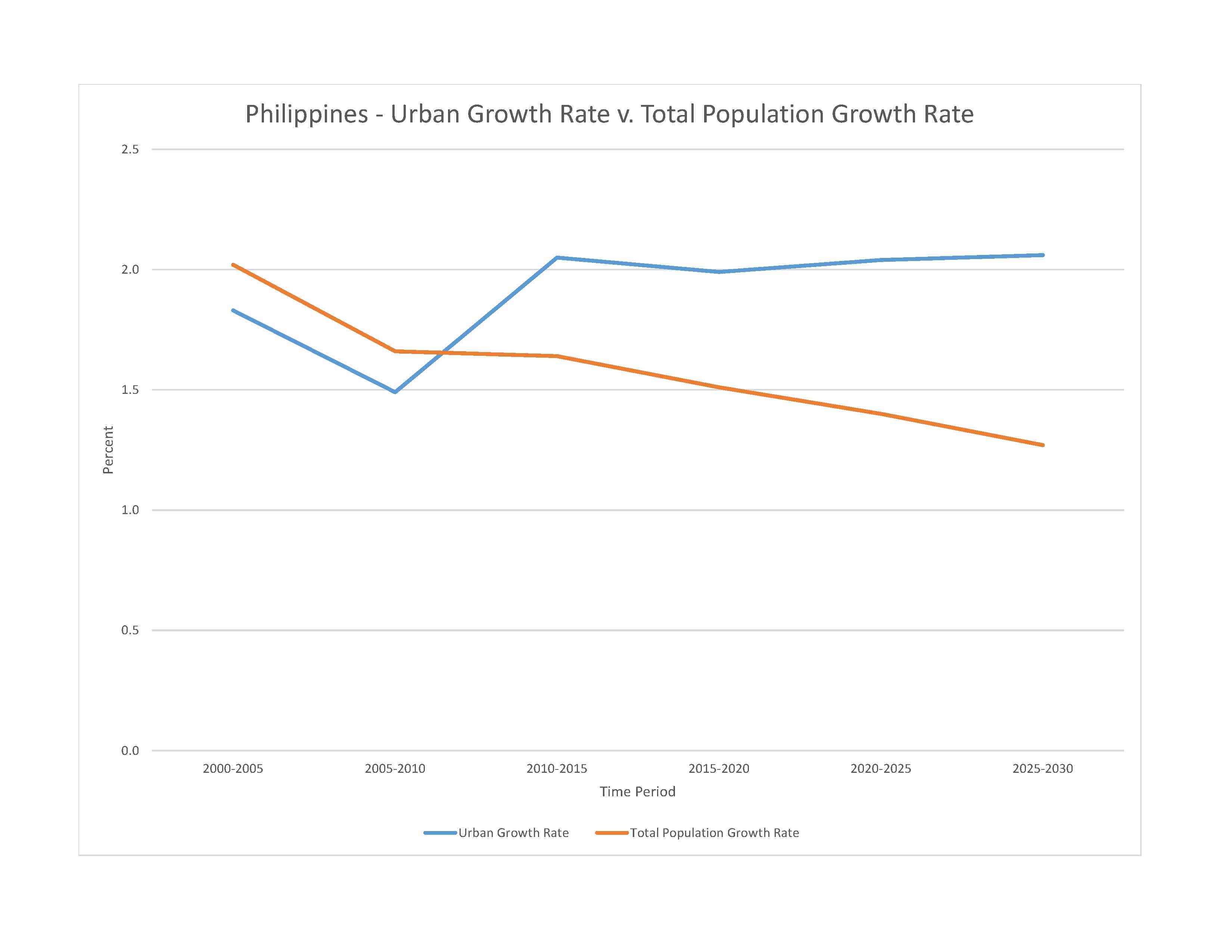
rate of urbanization: 2.04% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
14.667 million MANILA (capital), 1.949 million Davao, 1.025 million Cebu City, 931,000 Zamboanga, 960,000 Antipolo, 803,000 Cagayan de Oro City, 803,000 Dasmarinas (2023)
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.66 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
23.6 years (2022 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
78 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 22.1 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 24.4 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 19.7 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 70.5 years (2023 est.)
male: 67 years
female: 74.2 years
2.77 children born/woman (2023 est.)
1.35 (2023 est.)
54.1% (2017)
improved: urban: 99.1% of population
rural: 95% of population
total: 97% of population
unimproved: urban: 0.9% of population
rural: 5% of population
total: 3% of population (2020 est.)
5.1% of GDP (2020)
0.77 physicians/1,000 population (2020)
1 beds/1,000 population (2014)
improved: urban: 96% of population
rural: 91% of population
total: 93.4% of population
unimproved: urban: 4% of population
rural: 9% of population
total: 6.6% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria
water contact diseases: leptospirosis
6.4% (2016)
total: 4.85 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 1.47 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.03 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 3.34 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 22.9% (2020 est.)
male: 39.3% (2020 est.)
female: 6.5% (2020 est.)
19.1% (2018)
59.3% (2023 est.)
women married by age 15: 2.2%
women married by age 18: 16.5% (2017 est.)
3.7% of GDP (2020 est.)
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 96.3%
male: 95.7%
female: 96.9% (2019)
total: 13 years
male: 13 years
female: 13 years (2020)
one of only two predominantly Christian nations in Southeast Asia, the other being Timor-Leste
NOTE: The information regarding Philippines on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Philippines 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Philippines 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.