
218,689,757 (2023 est.)
noun: Brazilian(s)
adjective: Brazilian
mixed 45.3%, White 43.5%, Black 10.2%, Indigenous 0.6%, Asian 0.4% (2022 est.)
Portuguese (official and most widely spoken language); note - less common languages include Spanish (border areas and schools), German, Italian, Japanese, English, and a large number of minor Amerindian languages
major-language sample(s):
O Livro de Fatos Mundiais, a fonte indispensável para informação básica. (Brazilian Portuguese)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Roman Catholic 50%, Evangelical 31%, Spiritist 3%, Umbanda, Candomble, or other Afro-Brazilian religions 2%, Jewish 0.3%, atheist 1%, other 2%, none 10% (2020 est.)
Brazil's rapid fertility decline since the 1960s is the main factor behind the country's slowing population growth rate, aging population, and fast-paced demographic transition. Brasilia has not taken full advantage of its large working-age population to develop its human capital and strengthen its social and economic institutions but is funding a study abroad program to bring advanced skills back to the country. The current favorable age structure will begin to shift around 2025, with the labor force shrinking and the elderly starting to compose an increasing share of the total population. Well-funded public pensions have nearly wiped out poverty among the elderly, and Bolsa Familia and other social programs have lifted tens of millions out of poverty. More than half of Brazil's population is considered middle class, but poverty and income inequality levels remain high; the Northeast, North, and Center-West, women, and black, mixed race, and indigenous populations are disproportionately affected. Disparities in opportunities foster social exclusion and contribute to Brazil's high crime rate, particularly violent crime in cities and favelas (slums).
Brazil has traditionally been a net recipient of immigrants, with its southeast being the prime destination. After the importation of African slaves was outlawed in the mid-19th century, Brazil sought Europeans (Italians, Portuguese, Spaniards, and Germans) and later Asians (Japanese) to work in agriculture, especially coffee cultivation. Recent immigrants come mainly from Argentina, Chile, and Andean countries (many are unskilled illegal migrants) or are returning Brazilian nationals. Since Brazil's economic downturn in the 1980s, emigration to the United States, Europe, and Japan has been rising but is negligible relative to Brazil's total population. The majority of these emigrants are well-educated and middle-class. Fewer Brazilian peasants are emigrating to neighboring countries to take up agricultural work.
0-14 years: 19.77% (male 22,084,172/female 21,148,290)
15-64 years: 69.72% (male 75,612,047/female 76,853,504)
65 years and over: 10.51% (2023 est.) (male 9,848,975/female 13,142,769)
total dependency ratio: 43.1
youth dependency ratio: 29.4
elderly dependency ratio: 13.7
potential support ratio: 7.3 (2021 est.)
total: 34.7 years (2023 est.)
male: 33.6 years
female: 35.7 years
0.64% (2023 est.)
13.4 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
6.9 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
-0.2 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
the vast majority of people live along, or relatively near, the Atlantic coast in the east; the population core is in the southeast, anchored by the cities of São Paolo, Brasília, and Rio de Janeiro
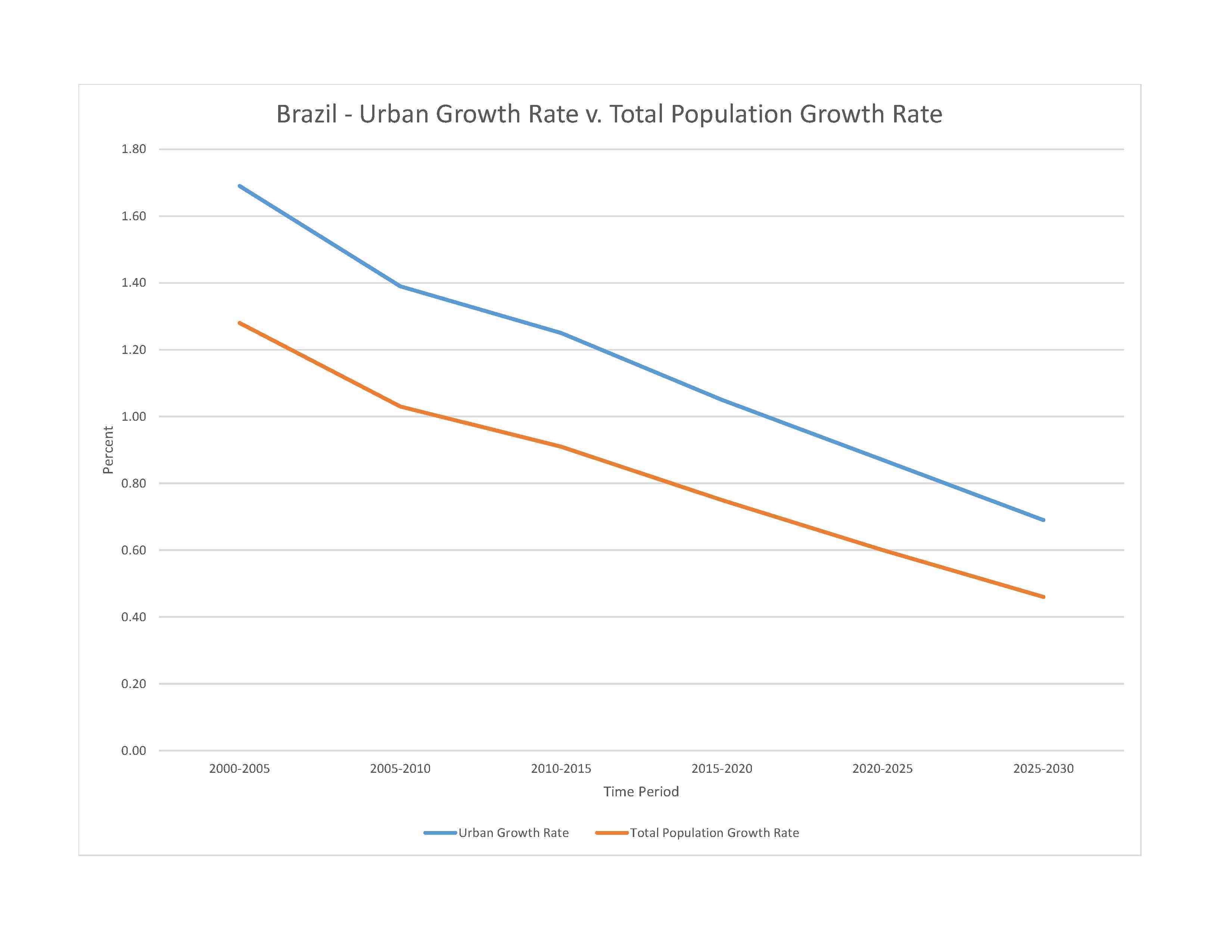
urban population: 87.8% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 0.87% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
22.620 million São Paulo, 13.728 million Rio de Janeiro, 6.248 million Belo Horizonte, 4.873 million BRASÍLIA (capital), 4.264 million Recife, 4.212 million Porto Alegre (2023)
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/female
total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
72 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 13.1 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 14.7 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 11.5 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 76.1 years (2023 est.)
male: 72.6 years
female: 79.8 years
1.75 children born/woman (2023 est.)
0.85 (2023 est.)
80.5% (2019)
improved: urban: 99.8% of population
rural: 96.9% of population
total: 99.4% of population
unimproved: urban: 0.2% of population
rural: 3.1% of population
total: 0.6% of population (2020 est.)
10.3% of GDP (2020)
2.31 physicians/1,000 population (2019)
2.1 beds/1,000 population (2017)
improved: urban: 94.1% of population
rural: 63.6% of population
total: 90.2% of population
unimproved: urban: 5.9% of population
rural: 36.4% of population
total: 9.8% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: very high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea and hepatitis A
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever, malaria, sexually transmitted diseases: hepatitis B (2024)
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
22.1% (2016)
total: 6.12 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 3.84 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.24 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 2 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.04 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 12.8% (2020 est.)
male: 16.2% (2020 est.)
female: 9.4% (2020 est.)
N/A
55.9% (2023 est.)
6% of GDP (2019 est.)
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 94.7%
male: 94.4%
female: 94.9% (2022)
total: 16 years
male: 15 years
female: 16 years (2020)
NOTE: The information regarding Brazil on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Brazil 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Brazil 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.