
serious overpopulation and rapid urbanization have led to numerous environmental problems; urban air and water pollution; rapid deforestation; soil degradation; loss of arable land; oil pollution - water, air, and soil have suffered serious damage from oil spills
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Tropical Timber 2006
varies; equatorial in south, tropical in center, arid in north
agricultural land: 78% (2018 est.)
arable land: 37.3% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 7.4% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 33.3% (2018 est.)
forest: 9.5% (2018 est.)
other: 12.5% (2018 est.)
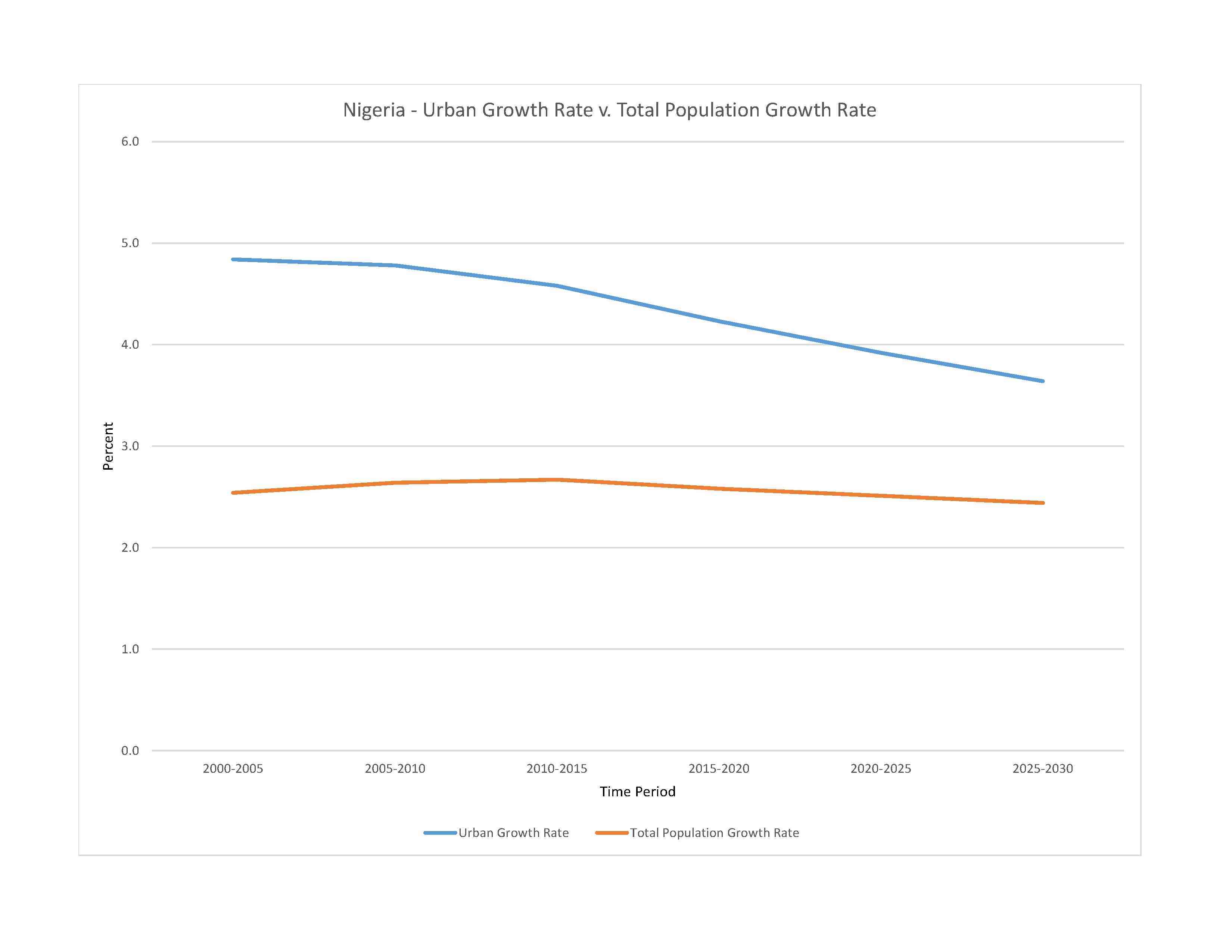
urban population: 54.3% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 3.92% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
widespread lack of access:due to persistent civil conflict in the northern areas, floods, high food prices, and an economic slowdown - about 25.3 million people are projected to face acute food insecurity during the June to August 2023 lean season; this would be a significant deterioration compared to last year, when 19.45 million people were estimated to be acutely food insecure; acute food insecurity is mostly driven by the deterioration of security conditions and conflicts in northern states, which have led to the displacement of about 3.17 million people as of March 2022 (the latest data available) and are constraining farmers’ access to their lands; widespread flooding in 2022, affecting about 4.5 million people across the country, has further compounded conditions, particularly in areas already facing high levels of insecurity; high food prices and the expected slowdown in economic growth in 2023 are additional drivers of acute food insecurity (2023)
1.02% of GDP (2018 est.)
0% of GDP (2018 est.)
particulate matter emissions: 55.64 micrograms per cubic meter (2019 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 120.37 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 143.99 megatons (2020 est.)
municipal solid waste generated annually: 27,614,830 tons (2009 est.)
fresh water lake(s): Lake Chad (endorheic lake shared with Niger, Chad, and Cameroon) - 10,360-25,900 sq km
note - area varies by season and year to year
Niger river mouth (shared with Guinea [s], Mali, Benin, and Niger) - 4,200 km
note – [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Niger (2,261,741 sq km)
Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Lake Chad (2,497,738 sq km)
Lake Chad Basin, Lullemeden-Irhazer Aquifer System
municipal: 5 billion cubic meters (2020 est.)
industrial: 1.97 billion cubic meters (2020 est.)
agricultural: 5.51 billion cubic meters (2020 est.)
286.2 billion cubic meters (2020 est.)
NOTE: The information regarding Nigeria on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Nigeria 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Nigeria 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.