
230,842,743 (2023 est.)
noun: Nigerian(s)
adjective: Nigerian
Hausa 30%, Yoruba 15.5%, Igbo (Ibo) 15.2%, Fulani 6%, Tiv 2.4%, Kanuri/Beriberi 2.4%, Ibibio 1.8%, Ijaw/Izon 1.8%, other 24.9% (2018 est.)
note: Nigeria, Africa's most populous country, is composed of more than 250 ethnic groups
English (official), Hausa, Yoruba, Igbo (Ibo), Fulani, over 500 additional indigenous languages
Muslim 53.5%, Roman Catholic 10.6%, other Christian 35.3%, other 0.6% (2018 est.)
Nigeria’s population is projected to grow from more than 186 million people in 2016 to 392 million in 2050, becoming the world’s fourth most populous country. Nigeria’s sustained high population growth rate will continue for the foreseeable future because of population momentum and its high birth rate. Abuja has not successfully implemented family planning programs to reduce and space births because of a lack of political will, government financing, and the availability and affordability of services and products, as well as a cultural preference for large families. Increased educational attainment, especially among women, and improvements in health care are needed to encourage and to better enable parents to opt for smaller families.
Nigeria needs to harness the potential of its burgeoning youth population in order to boost economic development, reduce widespread poverty, and channel large numbers of unemployed youth into productive activities and away from ongoing religious and ethnic violence. While most movement of Nigerians is internal, significant emigration regionally and to the West provides an outlet for Nigerians looking for economic opportunities, seeking asylum, and increasingly pursuing higher education. Immigration largely of West Africans continues to be insufficient to offset emigration and the loss of highly skilled workers. Nigeria also is a major source, transit, and destination country for forced labor and sex trafficking.
0-14 years: 40.69% (male 47,978,838/female 45,940,446)
15-64 years: 55.95% (male 64,923,147/female 64,241,948)
65 years and over: 3.36% (2023 est.) (male 3,635,334/female 4,123,030)
total dependency ratio: 86
youth dependency ratio: 80.6
elderly dependency ratio: 5.5
potential support ratio: 18 (2021 est.)
total: 19.2 years (2023 est.)
male: 18.9 years
female: 19.4 years
2.53% (2023 est.)
34 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
8.5 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
-0.2 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
largest population of any African nation; significant population clusters are scattered throughout the country, with the highest density areas being in the south and southwest as shown in this 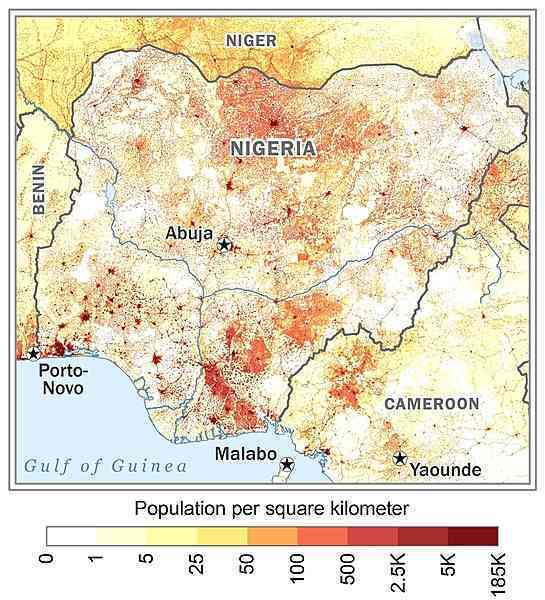
urban population: 54.3% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 3.92% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
15.946 million Lagos, 4.348 million Kano, 3.875 million Ibadan, 3.840 million ABUJA (capital), 3.480 million Port Harcourt, 1.905 million Benin City (2023)
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.88 male(s)/female
total population: 1.02 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
20.4 years (2018 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
1,047 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 55.2 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 60.4 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 49.6 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 61.8 years (2023 est.)
male: 59.9 years
female: 63.8 years
4.57 children born/woman (2023 est.)
2.22 (2023 est.)
16.6% (2018)
improved: urban: 95.3% of population
rural: 68.8% of population
total: 82.6% of population
unimproved: urban: 4.7% of population
rural: 31.2% of population
total: 17.4% of population (2020 est.)
3.4% of GDP (2020)
0.38 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
improved: urban: 81.6% of population
rural: 41.4% of population
total: 62.3% of population
unimproved: urban: 18.4% of population
rural: 58.6% of population
total: 37.7% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: very high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and sexually transmitted diseases: hepatitis B (2024)
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
respiratory diseases: meningococcal meningitis
aerosolized dust or soil contact diseases: Lassa fever
note 1: on 4 May 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued a Travel Health Notice for a Yellow Fever outbreak in Nigeria; a large, ongoing outbreak of yellow fever in Nigeria began in September 2017; the outbreak is now spread throughout the country with the Nigerian Ministry of Health reporting cases of the disease in multiple states (Bauchi, Benue, Delta, Ebonyi, and Enugu); the CDC recommends travelers going to Nigeria should receive vaccination against yellow fever at least 10 days before travel and should take steps to prevent mosquito bites while there; those never vaccinated against yellow fever should avoid travel to Nigeria during the outbreak (see attached map)
note 2: on 31 August 2023, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued a Travel Alert for polio in Africa; Nigeria is currently considered a high risk to travelers for circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV); vaccine-derived poliovirus (VDPV) is a strain of the weakened poliovirus that was initially included in oral polio vaccine (OPV) and that has changed over time and behaves more like the wild or naturally occurring virus; this means it can be spread more easily to people who are unvaccinated against polio and who come in contact with the stool or respiratory secretions, such as from a sneeze, of an “infected” person who received oral polio vaccine; the CDC recommends that before any international travel, anyone unvaccinated, incompletely vaccinated, or with an unknown polio vaccination status should complete the routine polio vaccine series; before travel to any high-risk destination, the CDC recommends that adults who previously completed the full, routine polio vaccine series receive a single, lifetime booster dose of polio vaccine
note 3: on 20 September 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention updated a Travel Health Alert for a diphtheria outbreak in several states in Nigeria; vaccination against diphtheria is essential to protect against disease; if you are traveling to an affected area, you should be up to date with your diphtheria vaccines; before travel, discuss the need for a booster dose with your healthcare professional; diphtheria is a serious infection caused by strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae bacteria that make a toxin from which people get very sick; diphtheria bacteria spread from person to person through respiratory droplets like from coughing or sneezing; people can also get sick from touching open sores or ulcers of people sick with diphtheria (see attached map)
note 1: The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) is reporting yellow fever outbreaks in multiple states (Bauchi, Benue, Delta, Ebonyi, and Enugu). Unless vaccinated, travelers should not visit these areas. Yellow fever is caused by a virus transmitted through bites of infected mosquitoes. Travelers to Nigeria should take steps to prevent yellow fever by getting vaccinated at least 10 days before travel and taking steps to prevent mosquito bites. Map courtesy of CDC.: 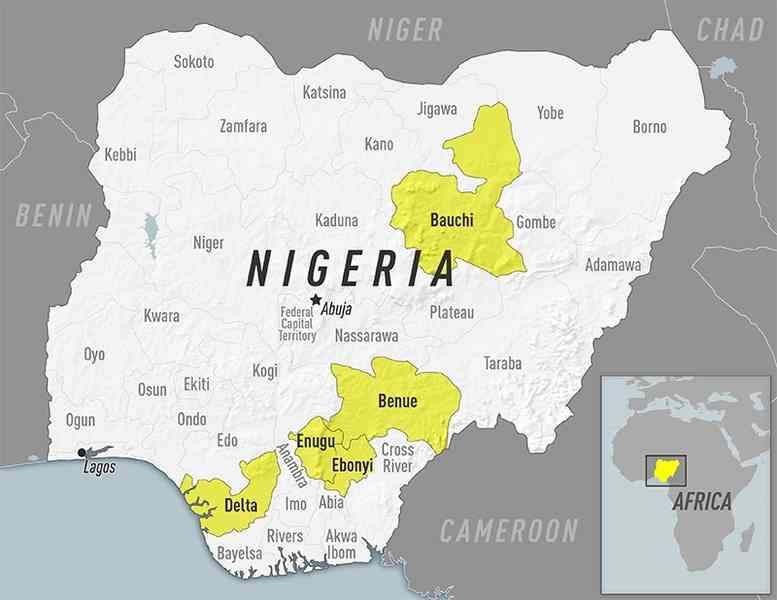 note 3: There is an outbreak of diphtheria in several states in Nigeria. Vaccination against diphtheria is essential to protect against disease. If you are traveling to an affected area, you should be up to date with your diphtheria vaccines. Map courtesy of CDC.:
note 3: There is an outbreak of diphtheria in several states in Nigeria. Vaccination against diphtheria is essential to protect against disease. If you are traveling to an affected area, you should be up to date with your diphtheria vaccines. Map courtesy of CDC.: 
8.9% (2016)
total: 4.49 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.73 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.09 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.4 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 3.27 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 3.7% (2020 est.)
male: 6.9% (2020 est.)
female: 0.5% (2020 est.)
18.4% (2019/20)
66.2% (2023 est.)
women married by age 15: 12.3%
women married by age 18: 30.3%
men married by age 18: 1.6% (2021 est.)
note: due to prolonged insecurity concerns, some parts of states, including Borno state, were not sampled
0.5% of GDP (2013)
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 62%
male: 71.3%
female: 52.7% (2018)
NOTE: The information regarding Nigeria on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Nigeria 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Nigeria 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.