
47,729,952 (2023 est.)
noun: Ugandan(s)
adjective: Ugandan
Baganda 16.5%, Banyankole 9.6%, Basoga 8.8%, Bakiga 7.1%, Iteso 7%, Langi 6.3%, Bagisu 4.9%, Acholi 4.4%, Lugbara 3.3%, other 32.1% (2014 est.)
English (official language, taught in schools, used in courts of law and by most newspapers and some radio broadcasts), Ganda or Luganda (most widely used of the Niger-Congo languages and the language used most often in the capital), other Niger-Congo languages, Nilo-Saharan languages, Swahili (official), Arabic
Protestant 45.1% (Anglican 32.0%, Pentecostal/Born Again/Evangelical 11.1%, Seventh Day Adventist 1.7%, Baptist .3%), Roman Catholic 39.3%, Muslim 13.7%, other 1.6%, none 0.2% (2014 est.)
Uganda has one of the youngest and most rapidly growing populations in the world; its total fertility rate is among the world’s highest at close to 5.5 children per woman in 2022. Except in urban areas, actual fertility exceeds women’s desired fertility by one or two children, which is indicative of the widespread unmet need for contraception, lack of government support for family planning, and a cultural preference for large families. High numbers of births, short birth intervals, and the early age of childbearing contribute to Uganda’s high maternal mortality rate. Gender inequities also make fertility reduction difficult; women on average are less-educated, participate less in paid employment, and often have little say in decisions over childbearing and their own reproductive health. However, even if the birth rate were significantly reduced, Uganda’s large pool of women entering reproductive age ensures rapid population growth for decades to come.
Unchecked, population increase will further strain the availability of arable land and natural resources and overwhelm the country’s limited means for providing food, employment, education, health care, housing, and basic services. The country’s north and northeast lag even further behind developmentally than the rest of the country as a result of long-term conflict (the Ugandan Bush War 1981-1986 and more than 20 years of fighting between the Lord’s Resistance Army (LRA) and Ugandan Government forces), ongoing inter-communal violence, and periodic natural disasters.
Uganda has been both a source of refugees and migrants and a host country for refugees. In 1972, then President Idi AMIN, in his drive to return Uganda to Ugandans, expelled the South Asian population that composed a large share of the country’s business people and bankers. Since the 1970s, thousands of Ugandans have emigrated, mainly to southern Africa or the West, for security reasons, to escape poverty, to search for jobs, and for access to natural resources. The emigration of Ugandan doctors and nurses due to low wages is a particular concern given the country’s shortage of skilled health care workers. Africans escaping conflicts in neighboring states have found refuge in Uganda since the 1950s; the country currently struggles to host tens of thousands from the Democratic Republic of the Congo, South Sudan, and other nearby countries.
0-14 years: 47.3% (male 11,439,303/female 11,136,111)
15-64 years: 50.31% (male 11,335,543/female 12,679,044)
65 years and over: 2.39% (2023 est.) (male 484,782/female 655,169)
total dependency ratio: 88.2
youth dependency ratio: 85.1
elderly dependency ratio: 3.2
potential support ratio: 31.7 (2021 est.)
total: 16.1 years (2023 est.)
male: 15.3 years
female: 16.9 years
3.22% (2023 est.)
40.3 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
4.9 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
-3.2 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
population density is relatively high in comparison to other African nations; most of the population is concentrated in the central and southern parts of the country, particularly along the shores of Lake Victoria and Lake Albert; the northeast is least populated as shown in this 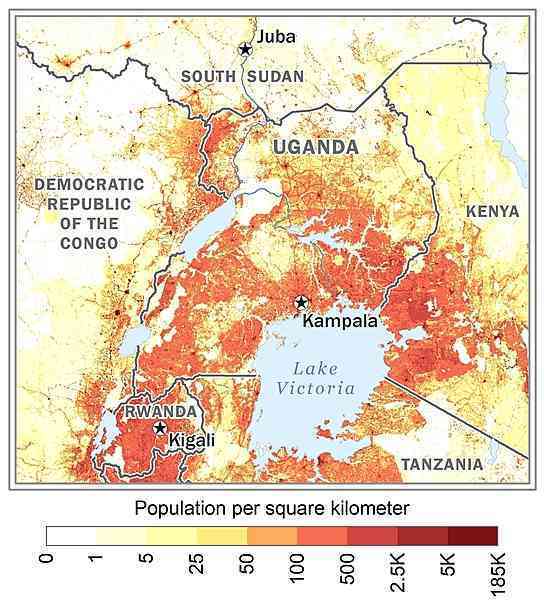
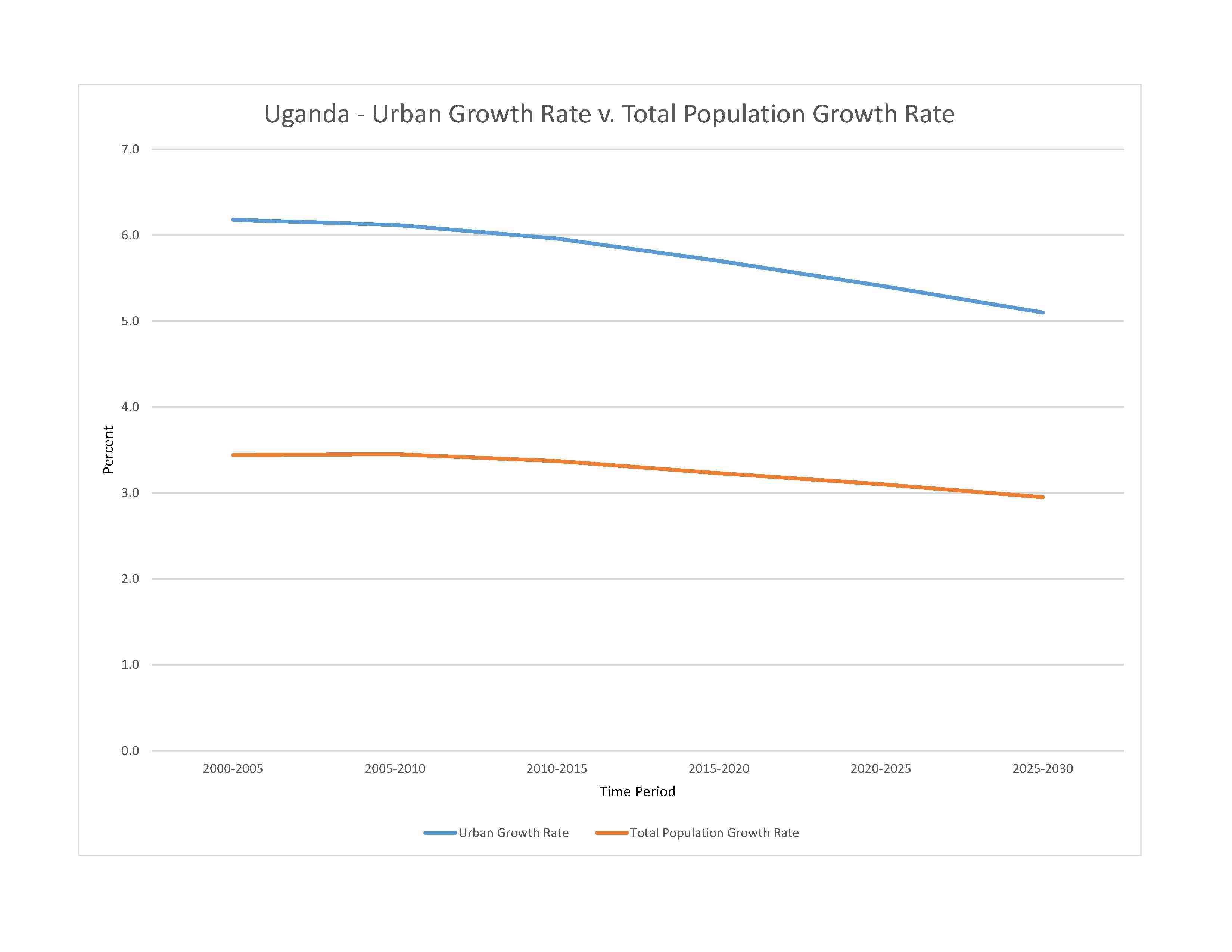
urban population: 26.8% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 5.41% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
3.846 million KAMPALA (capital) (2023)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.89 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.74 male(s)/female
total population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
19.4 years (2016 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 20-49
284 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 29.4 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 32.8 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 26 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 69.3 years (2023 est.)
male: 67.1 years
female: 71.6 years
5.26 children born/woman (2023 est.)
2.59 (2023 est.)
50.2% (2021)
improved: urban: 92.5% of population
rural: 80% of population
total: 83.1% of population
unimproved: urban: 7.5% of population
rural: 20% of population
total: 16.9% of population (2020 est.)
4% of GDP (2020)
0.15 physicians/1,000 population (2020)
0.5 beds/1,000 population
improved: urban: 67.3% of population
rural: 27.5% of population
total: 37.4% of population
unimproved: urban: 32.7% of population
rural: 72.5% of population
total: 62.6% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: very high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and Trypanosomiasis-Gambiense (African sleeping sickness), and sexually transmitted diseases: HIV/AIDS (2024)
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
5.3% (2016)
total: 6.82 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.85 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.5 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 5.46 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 8.4% (2020 est.)
male: 13% (2020 est.)
female: 3.7% (2020 est.)
7.6% (2019/20)
58.3% (2023 est.)
women married by age 15: 7.3%
women married by age 18: 34%
men married by age 18: 5.5% (2016 est.)
2.7% of GDP (2021 est.)
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 79%
male: 84%
female: 74.3% (2021)
NOTE: The information regarding Uganda on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Uganda 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Uganda 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.