
20,216,029 (2023 est.)
noun: Zambian(s)
adjective: Zambian
Bemba 21%, Tonga 13.6%, Chewa 7.4%, Lozi 5.7%, Nsenga 5.3%, Tumbuka 4.4%, Ngoni 4%, Lala 3.1%, Kaonde 2.9%, Namwanga 2.8%, Lunda (north Western) 2.6%, Mambwe 2.5%, Luvale 2.2%, Lamba 2.1%, Ushi 1.9%, Lenje 1.6%, Bisa 1.6%, Mbunda 1.2%, other 13.8%, unspecified 0.4% (2010 est.)
Bemba 33.4%, Nyanja 14.7%, Tonga 11.4%, Lozi 5.5%, Chewa 4.5%, Nsenga 2.9%, Tumbuka 2.5%, Lunda (North Western) 1.9%, Kaonde 1.8%, Lala 1.8%, Lamba 1.8%, English (official) 1.7%, Luvale 1.5%, Mambwe 1.3%, Namwanga 1.2%, Lenje 1.1%, Bisa 1%, other 9.7%, unspecified 0.2% (2010 est.)
note: Zambia is said to have over 70 languages, although many of these may be considered dialects; all of Zambia's major languages are members of the Bantu family; Chewa and Nyanja are mutually intelligible dialects
Protestant 75.3%, Roman Catholic 20.2%, other 2.7% (includes Muslim, Buddhist, Hindu, and Baha'i), none 1.8% (2010 est.)
Zambia’s poor, youthful population consists primarily of Bantu-speaking people representing nearly 70 different ethnicities. Zambia’s high fertility rate continues to drive rapid population growth, averaging almost 3% annually between 2000 and 2010, and reaching over 3.3% in 2022. The country’s total fertility rate has fallen by less than 1.5 children per woman during the last 30 years and still averages among the world’s highest, almost 6 children per woman, largely because of the country’s lack of access to family planning services, education for girls, and employment for women. Zambia also exhibits wide fertility disparities based on rural or urban location, education, and income. Poor, uneducated women from rural areas are more likely to marry young, to give birth early, and to have more children, viewing children as a sign of prestige and recognizing that not all of their children will live to adulthood. HIV/AIDS is prevalent in Zambia and contributes to its low life expectancy.
Zambian emigration is low compared to many other African countries and is comprised predominantly of the well-educated. The small amount of brain drain, however, has a major impact in Zambia because of its limited human capital and lack of educational infrastructure for developing skilled professionals in key fields. For example, Zambia has few schools for training doctors, nurses, and other health care workers. Its spending on education is low compared to other Sub-Saharan countries.
0-14 years: 42.49% (male 4,334,425/female 4,255,464)
15-64 years: 54.77% (male 5,529,526/female 5,541,857)
65 years and over: 2.74% (2023 est.) (male 250,984/female 303,773)
total dependency ratio: 81.8
youth dependency ratio: 78.7
elderly dependency ratio: 3.2
potential support ratio: 31.6 (2021 est.)
total: 18.2 years (2023 est.)
male: 18 years
female: 18.4 years
2.86% (2023 est.)
34.5 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
6 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
0.2 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
one of the highest levels of urbanization in Africa; high density in the central area, particularly around the cities of Lusaka, Ndola, Kitwe, and Mufulira as shown in this 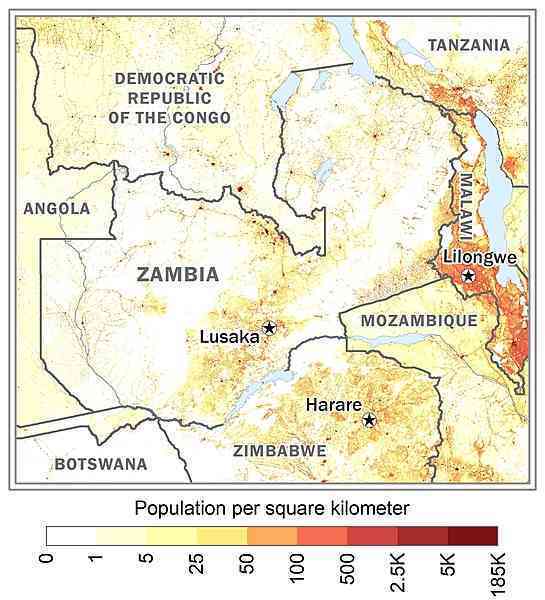
urban population: 46.3% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 4.15% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
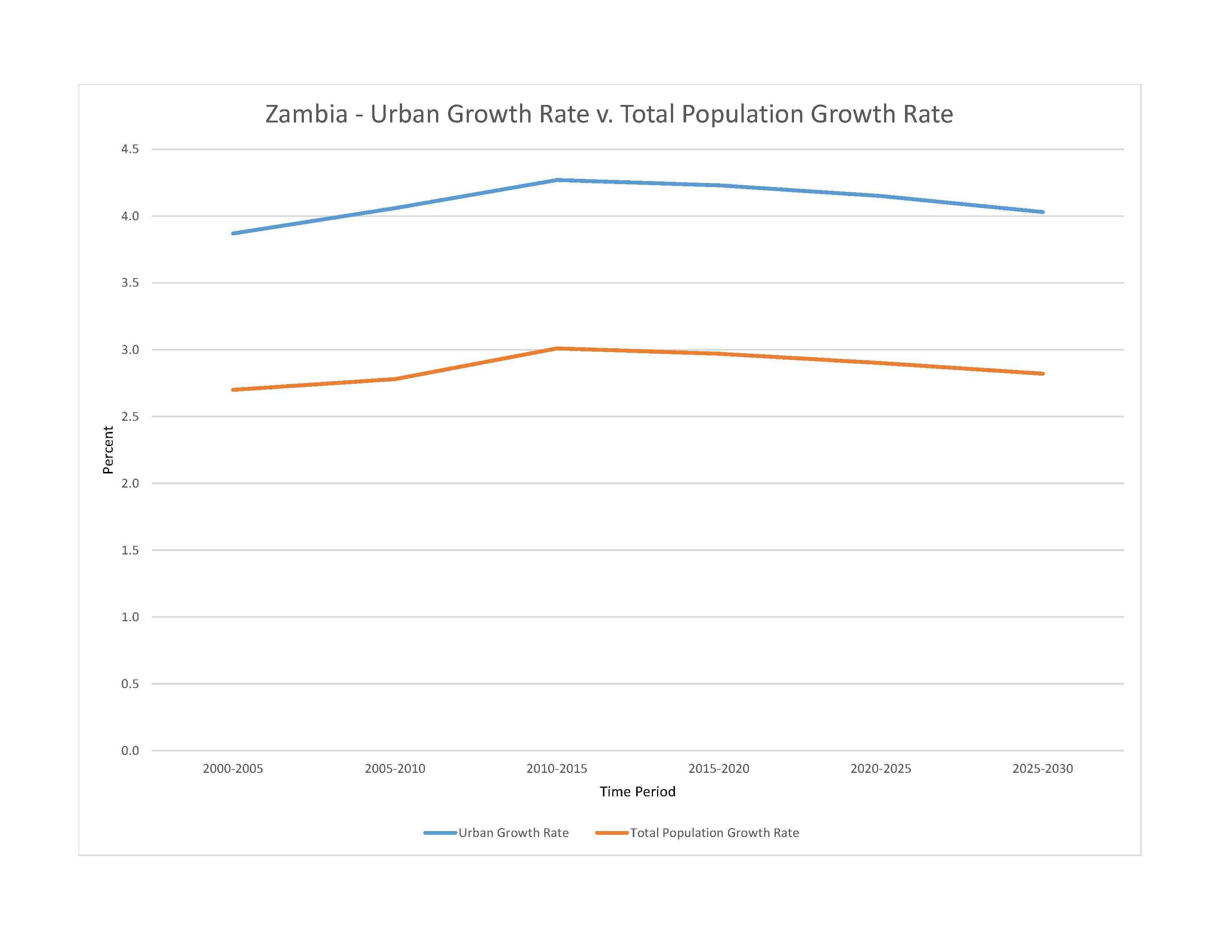
3.181 million LUSAKA (capital), 763,000 Kitwe (2023)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.83 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
19.2 years (2018 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 20-49
135 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
total: 36.3 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
male: 39.7 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 32.8 deaths/1,000 live births
total population: 66.6 years (2023 est.)
male: 64.9 years
female: 68.4 years
4.49 children born/woman (2023 est.)
2.21 (2023 est.)
49.6% (2018)
improved: urban: 90.2% of population
rural: 56.6% of population
total: 71.6% of population
unimproved: urban: 9.8% of population
rural: 43.4% of population
total: 28.4% of population (2020 est.)
5.6% of GDP (2020)
1.17 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
2 beds/1,000 population
improved: urban: 76.3% of population
rural: 31.9% of population
total: 51.7% of population
unimproved: urban: 23.7% of population
rural: 68.1% of population
total: 48.3% of population (2020 est.)
degree of risk: very high (2023)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and sexually transmitted diseases: HIV/AIDS (2024)
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
note: on 31 August 2023, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued a Travel Alert for polio in Africa; Zambia is currently considered a high risk to travelers for circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV); vaccine-derived poliovirus (VDPV) is a strain of the weakened poliovirus that was initially included in oral polio vaccine (OPV) and that has changed over time and behaves more like the wild or naturally occurring virus; this means it can be spread more easily to people who are unvaccinated against polio and who come in contact with the stool or respiratory secretions, such as from a sneeze, of an “infected” person who received oral polio vaccine; the CDC recommends that before any international travel, anyone unvaccinated, incompletely vaccinated, or with an unknown polio vaccination status should complete the routine polio vaccine series; before travel to any high-risk destination, the CDC recommends that adults who previously completed the full, routine polio vaccine series receive a single, lifetime booster dose of polio vaccine
8.1% (2016)
total: 3.82 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 1.26 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.04 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.36 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 2.16 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
total: 14.4% (2020 est.)
male: 25.1% (2020 est.)
female: 3.7% (2020 est.)
11.8% (2018/19)
53.3% (2023 est.)
women married by age 15: 5.2%
women married by age 18: 29%
men married by age 18: 2.8% (2018 est.)
3.7% of GDP (2020)
definition: age 15 and over can read and write English
total population: 86.7%
male: 90.6%
female: 83.1% (2018)
NOTE: The information regarding Zambia on this page is re-published from the 2024 World Fact Book of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and other sources. No claims are made regarding the accuracy of Zambia 2024 information contained here. All suggestions for corrections of any errors about Zambia 2024 should be addressed to the CIA or the source cited on each page.
This page was last modified 04 May 24, Copyright © 2024 ITA all rights reserved.