. .
|
I
-
Identical twin
- Twins produced by the division of a single zygote; both have identical genotypes.
See also:
fraternal twin
-
Immunotherapy
- Using the immune system to treat disease, for example, in the development of vaccines. May also refer to the therapy of diseases caused by the immune system.
See also:
cancer
-
Imprinting
- A phenomenon in which the disease phenotype depends on which parent passed on the disease gene. For instance, both Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes are inherited when the same part of chromosome 15 is missing. When the father's complement of 15 is missing, the child has Prader-Willi, but when the mother's complement of 15 is missing, the child has Angelman syndrome.
-
In situ hybridization
- Use of a DNA or RNA probe to detect the presence of the complementary DNA sequence in cloned bacterial or cultured eukaryotic cells.
-
In vitro
- Studies performed outside a living organism such as in a laboratory.
-
In vivo
- Studies carried out in living organisms.
-
Independent assortment
- During meiosis each of the two copies of a gene is distributed to the germ cells independently of the distribution of other genes.
See also:
linkage
-
Informatics
-
See:
bioinformatics
-
Informed consent
- An individual willingly agrees to participate in an activity after first being advised of the risks and benefits.
See also:
privacy
-
Inherit
- In genetics, to receive genetic material from parents through biological processes.
-
Inherited
-
See:
inherit
-
Insertion
- A chromosome abnormality in which a piece of DNA is incorporated into a gene and thereby disrupts the gene's normal function.
See also:
chromosome, DNA, gene, mutation
-
Insertional mutation
-
See:
insertion
-
Intellectual property rights
- Patents, copyrights, and trademarks.
See also:
patent
-
Interference
- One crossover event inhibits the chances of another crossover event. Also known as positive interference. Negative interference increases the chance of a second crossover.
See also:
crossing over
-
Interphase
- The period in the cell cycle when DNA is replicated in the nucleus; followed by mitosis.
-
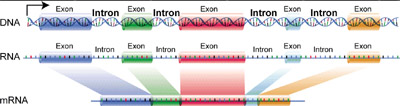
Intron
- DNA sequence that interrupts the protein-coding sequence of a gene; an intron is transcribed into RNA but is cut out of the message before it is translated into protein.
See also:
exon
-
Isoenzyme
- An enzyme performing the same function as another enzyme but having a different set of amino acids. The two enzymes may function at different speeds.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
|

|










 - Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).
- Please bookmark this page (add it to your favorites).